Author: Xiang|W3.Hitchhiker
Related Reading
Besides data storage, what else do you know about Filecoin?

Related Reading
Besides data storage, what else do you know about Filecoin?
What else is worth paying attention to in Filecoin?
What is IPFS
HTTP
"IPFS"Powering the Decentralized Internet (web3.0)"HTTP"A peer-to-peer hypermedia protocol that preserves and develops human knowledge by making the network scalable, resilient and more open.
IPFS is a distributed system for storing and accessing files, websites, applications and data.
first level title
The target is a
The application layer protocol of the web is the hypertext transfer protocol (HTTP), which is the core of the traditional web. HTTP is implemented by two programs: a client program and a server program. The client program and the server program run on different end systems and exchange HTTP sessions. HTTP defines the structure of this data and the way the client and server interact.
A web page is made up of objects, and an object is just a file, such as an HTML file, a JPEG graphic, or a small video clip, and they can be addressed by URL addresses. Most web pages contain an html base file, and several referenced objects.
HTTP defines the way web clients request web pages from web servers, and the way servers deliver web pages to clients.
The job of the browser is to execute and parse the HTTP protocol and front-end code and then display the content. When submitting a query, the web side usually queries its database and returns the result to the requester, that is, the browser, and then the browser displays come out.
first level title"Disadvantages of the HTTP protocol"。
The Internet we use now runs under the http or https protocol. The http protocol is also the hypertext transfer protocol. It is a transmission protocol used to transmit hypertext from the World Wide Web server to the local browser. It has been 32 years since it was proposed in 1990. , he has made great contributions to the current explosive growth of the Internet and has achieved the prosperity of the Internet.
However, the HTTP protocol is an Internet communication protocol based on the C/S architecture, and based on the centralized operation mechanism of the backbone network, there are also many disadvantages.
Data on the Internet is often permanently erased because files are deleted or servers are shut down. Some people have calculated that the average lifespan of web pages on the Internet is only about 100 days. We often see that some websites appear
404 error
The concurrent mechanism of the backbone network restricts the speed of Internet access. This centralized backbone network model also leads to congestion during network access under high concurrency.
Under the existing http protocol, all data is stored on these centralized servers. Internet giants not only have absolute control and interpretation of our data, but also various supervision, blockade, and monitoring to a certain extent It also greatly limits innovation and development.
The cost is high and it is easy to be attacked. In order to support the HTTP protocol, companies with large traffic volumes, such as Baidu, Tencent, and Ali, have invested a lot of resources in maintaining servers and security risks to prevent DDoS and other attacks. The backbone network is subject to factors such as wars, natural disasters, and central server downtime, which may cause the entire Internet to interrupt services.
ipfs solution
Solutions for IPFS
IPFS provides the function of backtracking the historical version of the file, which makes it easy to view the historical version of the file, and the data cannot be deleted and can be stored permanently.
IPFS is a storage mode based on content addressing. The same files will not be stored repeatedly. It will squeeze excess resources, including storage space, and reduce data storage costs. If you switch to P2P downloading, the cost of bandwidth usage can be saved by nearly 60%.
IPFS is based on a P2P network, where data can be saved from multiple sources, and data can be downloaded from multiple nodes concurrently.
IPFS built on a decentralized distributed network is difficult to be centrally managed and restricted, and the Internet will be more open.
IPFS distributed storage can greatly reduce the dependence on the central backbone network.
To put it succinctly:
HTTP relies on a centralized server, which is vulnerable to attacks, and the traffic surges, the server is prone to downtime, the download speed is slow, and the storage cost is high;
IPFS is a distributed node, which is more secure and less prone to DDoS attacks. It does not rely on the backbone network, reduces storage costs and has a large storage space. The download speed is fast, and the historical version records of files can be searched, and theoretically, it can be permanently stored.

New technology replaces old technology, nothing more than two points:
First, it can improve system efficiency;
Second, system cost can be reduced.
IPFS does both.
Multiformats is a collection of a series of hash encryption algorithms and self-describing methods (you can know how the value is generated from the value). It has 6 mainstream encryption methods such as SHA1 \SHA256 \SHA512 \Blake3B to encrypt and describe nodeID and Generation of fingerprint data.
LibP2P is the core of the IPFS core. In the face of various transport layer protocols and complex network devices, it can help developers quickly build an available P2P network layer, which is fast and cost-effective. This is why IPFS technology is widely used in many areas. The reason why blockchain projects are favored.IPLD is actually a conversion middleware that unifies the existing heterogeneous data structures into one format to facilitate data exchange and interoperability between different systems. The data structures currently supported by IPLD, such as the block data of Bitcoin and Ethereum, also support IPFS and IPLD. This is also the second reason why IPFS is welcomed by the blockchain system. Its IPLD middleware can unify different block structures into one standard for delivery, providing developers with a relatively high standard of success without worrying about performance, Stability and bugs.
ipfs benefitsBenefits of IPFS
One that combines the concepts of Kademlia, BitTorrent, Git, etc.Hypermedia Distribution ProtocolAvoid central node failure, completely decentralized without review and controlpoint-to-point network
Sail into the Internet of Tomorrow——New browsers already support the IPFS protocol (brave, opera) by default. Traditional browsers can visit public IPFS gateways with addresses such as https://ipfs.io, or install
IPFS CompanionExtensions to access files stored on the IPFS networkNext Generation Content Distribution Network CDN——Only need to add files to the local node, so that the world can obtain files through cache-friendly content hash addresses and BitTorrent-like network bandwidth distribution
Complete Distributed Applications and Services
one of
Developer Toolset
IPFS defines how files are stored, indexed, and transmitted in the system, that is, the uploaded files are converted into a special data format for storage, and IPFS will hash the same file to determine its unique address. So no matter on any device, any place, the same file will point to the same address (different from URL, this address is native and guaranteed by encryption algorithm, you can't change it, and you don't need to change it). Then connect all the devices in the network through a file system, and then let the files stored on the IPFS system be quickly obtained anywhere in the world without being affected by firewalls (no network proxy required). So fundamentally speaking, IPFS can change the distribution mechanism of WEB content and make it complete decentralization.
first level title
How IPFS Works
IPFS is a peer-to-peer (p2p) storage network. Content can be accessed through nodes located anywhere in the world, which may deliver information, store information, or both. IPFS knows how to use its content address, not its location, to find the content you ask for.
Understand the three fundamental principles of IPFS:Unique identifier via content addressingContent Linking via Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)Content Discovery via Distributed Hash Table (DHT)These three principles rely on each other to create an IPFS ecosystem. let's start with
and content of
Uniquely identifies
start
Content addressing and unique identification of content"Content addressing and unique identification of content"
IPFS uses content addressing to identify content based on content rather than location. Finding items by content is something everyone does all the time.
For example, if you are looking for a book in the library, you are often looking for it by the title; that is content addressing, because you are asking what it is.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Aardvark
/Users/Alice/Documents/term_paper.doc
C:\Users\Joe\My Documents\project_sprint_presentation.ppt
If you used location addressing to find the book, you'd find it by its location:I want the books on the second floor, the third shelf, and the fourth floor, four books from the left.If someone moves that book, you're out of luck!
The problem exists both on the Internet and on your computer! Content is now looked up by location, for example:
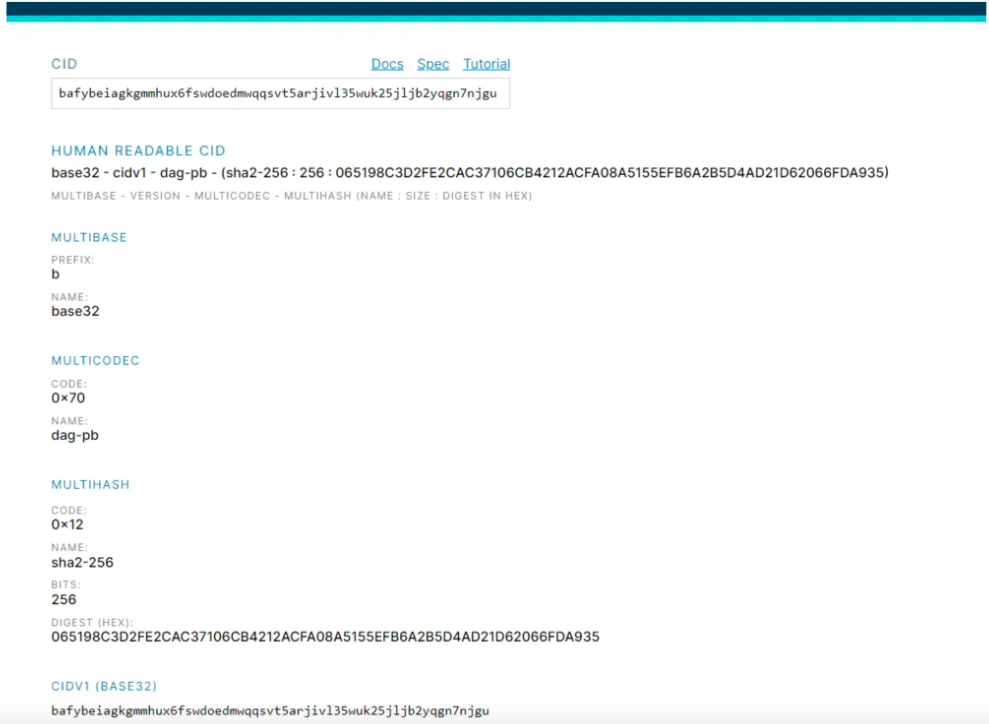
CID (Content Identifiers )
In contrast, every piece of content using the IPFS protocol has a *content identifier
*, that is, CID. A hash is unique to the content it came from, even though it may appear short compared to the original content.
Many distributed systems use content addressing through hashing to not only identify content but link it together—everything from the commits that support code to the blockchains that run cryptocurrencies take advantage of this strategy. However, the underlying data structures in these systems are not necessarily interoperable.
Originated in IPFS, it now exists in multiple formats and supports a wide range of projects including IPFS, IPLD, libp2p, and Filecoin. Although we'll share some IPFS examples throughout the course, this tutorial is about the anatomy of the CID itself, which every distributed information system uses as a core identifier for referencing content.
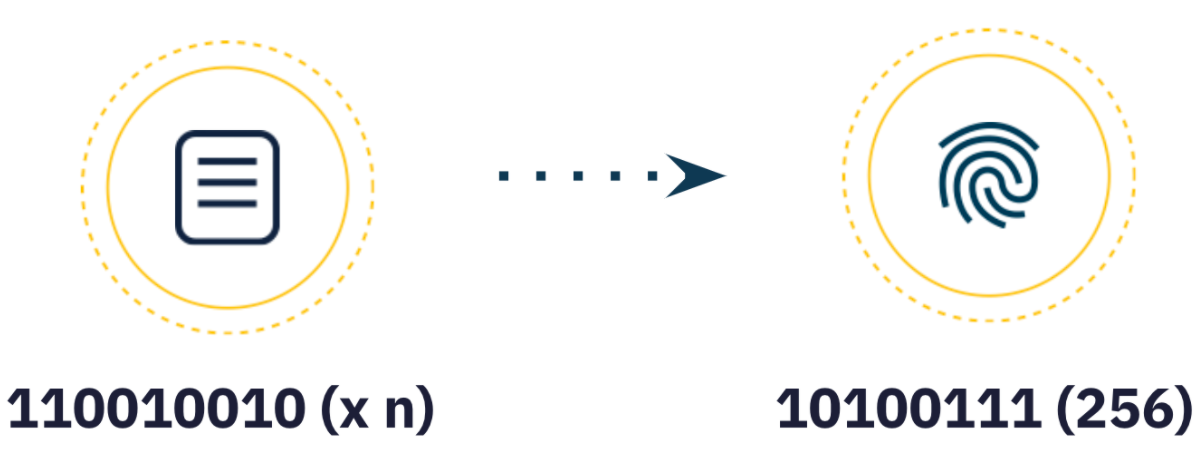
A content identifier or CID is a self-describing content addressable identifier. It does not indicate _where_ the content is stored, but forms a kind of address based on the content itself. The number of characters in a CID depends on the cryptographic hash of the underlying content, not the size of the content itself. Since most content in IPFS uses the hash sha2-256, most CIDs you encounter will be of the same size (256 bits, which equates to 32 bytes). This makes them easier to manage, especially when dealing with multiple pieces of content.For example, if we stored an image of an aardvark on the IPFS network, its CID would look like this: QmcRD4wkPPi6dig81r5sLj9Zm1gDCL4zgpEj9CfuRrGbzFIPFS link of uniswap demonstrated before
The first step in creating a CID is to transform the input data, using a cryptographic algorithm to map an arbitrary-sized input (data or file) to a fixed-sized output. This transformation is called a hash digital fingerprint or simply a hash (by default using sha2-256).in use
Encryption AlgorithmA hash must be generated with the following characteristics:
Certainty:The same input should always produce the same hash.
irrelevant:A small change in the input data should produce a completely different hash.
unidirectional:
It is not feasible to push back the input data from the hash.
uniqueness:
Multiformats
Only one file can produce a particular hash.
Note that if we change a single pixel in the aardvark image, the encryption algorithm will generate a completely different hash for the image.
MultiformatsWhen we fetch data using a content address, we are guaranteed to see the expected version of that data. This is quite different from location addressing on the traditional Web, where the content at a given address (URL) changes over time.
The structure of CID
Multiformats is mainly responsible for identity encryption and data self-description in the IPFS system.
Multiformats is a collection of protocols for future security systems. The self-describing format allows systems to cooperate and upgrade with each other.
The agreement includes the following agreements:
multihash - self-describing hash
multibase - self-describing base encoding
multicodec - self-describing serialization
first level title
Verifiability
Content Links Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG)
Verifiability
Verifiability
Ever backed up a file, then found those two files or directories months later and wondered if their contents were the same? You can compute a Merkle DAG for each backup without laboriously comparing files: if the CIDs of the root directories match, you know which ones can be safely deleted, and free up some space on your hard drive!
Assignability
Assignability
For example, the distribution of a large data. On traditional web networks:
The developer of the shared file is responsible for maintaining the server and its associated costs
The same server is likely to be used to respond to requests from all over the world
The data itself can be distributed monolithically as a single file archive
Difficulty finding alternative providers of the same data
Data may be in large chunks and must be downloaded serially from a single provider
It is difficult for others to share data
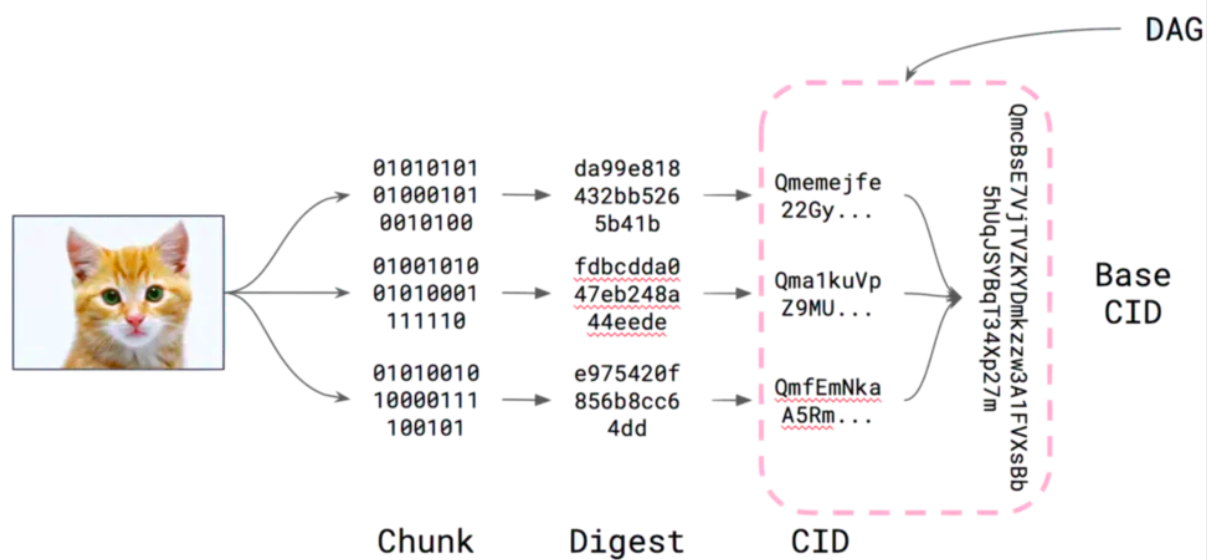
Merkle DAGs help us alleviate all of these problems. By converting the data into a content-addressed DAG:
Anyone who wants can help send and receive files
Nodes from all over the world can participate in serving data
It is easy to find alternative suppliers of the same data
The nodes that make up the DAG are small and can be downloaded in parallel from many different providers
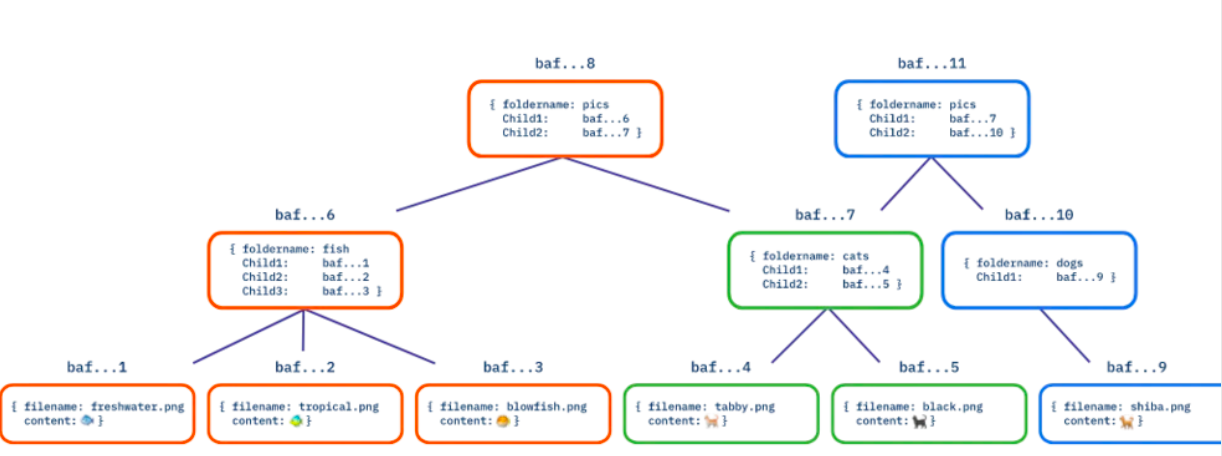
deduplication
deduplication
When the browser is optimized enough, it can avoid downloading this component multiple times. Whenever a user visits a new website, the browser only needs to download the nodes corresponding to different parts in its DAG, and the other parts that have been downloaded before do not need to be downloaded again! (think WordPress themes, Bootstrap CSS libraries, or common JavaScript libraries)
Libp2p
libp2pfirst level titleIPFSDistributed Hash Table (DHT)
is a modular network stack that starts from
network
Evolved into an independent project. Polkadot is also used, and eth2.0 is also partially used.
To explain why libp2p is such an important part of the decentralized web, we need to take a step back and understand where it came from. The initial implementation of libp2p started with IPFS, a peer-to-peer file sharing system. Let's start by exploring the network problems that IPFS aims to solve.first level title
NAT:network
Networks are very complex systems with their own rules and constraints, so we need to consider many situations and use cases when designing these systems:Your laptop may have a firewall installed that is blocking or restricting certain connections.
reliability:Your home WiFi router with NAT (Network Address Translation) that translates your laptop's local IP address to a single IP address that your network outside your home can connect to.
High latency network:These networks have very slow connections, leaving users waiting a long time to see their content.
reliability:There are many networks scattered around the world, and many users often experience slow networks that do not have robust systems to provide users with a good connection. The connection is frequently disconnected, and the quality of the user's network system is not good, so it cannot provide the user with the due service.
roaming:Mobile addressing is another case where we need to guarantee that a user's device remains uniquely discoverable while navigating through different networks around the world. Currently, they work in distributed systems that require a large number of coordination points and connections, but the best solutions are decentralized.
Censorship:In the current state of the web, if you're a government entity, it's relatively easy to block websites on specific website domains. This is useful for stopping illegal activity, but becomes a problem when an authoritarian regime wants to deprive its population of access to resources.
have different propertiesRuntimes: There are many types of runtimes around, such as IoT (Internet of Things) devices (Raspberry Pi, Arduino, etc.), and they are gaining mass adoption. Because they're built with limited resources, their runtimes often use different protocols that make a lot of assumptions about their runtimes.
Even the most successful companies with vast resources can take decades to develop and deploy new protocols.
Data Privacy:
Consumers have recently grown concerned about the growing number of companies that do not respect user privacy.
Current issues with the p2p protocol
Peer Current Issues with P2P Protocols
Peer-to-Peer (P2P) Peer-to-peer (P2P) networks were conceived from the concept of the Internet as a way to create a resilient network that would function even if peer nodes were disconnected from the network due to a major natural or man-made disaster, allowing people to continue communicating .
P2P networks can be used for a variety of use cases, from video calling (such as Skype) to file sharing (such as IPFS, Gnutella, KaZaA, eMule, and BitTorrent).
basic concept
- Participants of the decentralized network. A peer node is an equally privileged, equally capable participant in an application. In IPFS, when you load the IPFS desktop application on your laptop, your device becomes a Peer node in the decentralized network IPFS.
- A decentralized network where workloads are shared among peer nodes. Therefore, in IPFS, each Peer node may host all or some files to be shared with other peer nodes. When a node requests files, any node that owns chunks of those files can participate in sending the requested files. The peer party requesting the data can then later share the data with other peer parties.
IPFS seeks inspiration from current and past web applications and research to try to improve its P2P system. There is a wealth of scientific papers in academia that provide ideas on how to solve some of these problems, but while the research has yielded preliminary results, it lacks code implementations that can be used and tweaked.
Code implementations of existing P2P systems are really hard to find, and where they do exist, they are often difficult to reuse or repurpose for the following reasons:
Bad or non-existent file
Restricted license or no license found
Very old code last updated more than ten years ago
No point of contact (no maintainer to contact)
Closed source (proprietary) code
deprecated product
no specification provided
No friendly API exposed
The implementation is too tightly coupled to a specific use case
Unable to use future protocol upgrades
There must be a better way. Seeing that the main problem was interoperability, the IPFS team imagined a better way to integrate all current solutions and provide a platform that fosters innovation. A new modular system that enables future solutions to be seamlessly integrated into the network stack.
This way, each project can focus only on its own goals:
the answer is:Modular。

IPFS is more focused on content addressing, i.e. finding, fetching and authenticating any content on the network.

libp2p focuses more on process addressing, i.e. finding, connecting and authenticating any data transfer process in the network. So how does libp2p do it?

the answer is:

IPLD
Modular
Ilibp2p has identified specific parts that make up the network stack:
Multi-language implementation, supporting 7 development languages, libp2p's JavaScript implementation is also suitable for browsers and mobile browsers! This is very important as it enables applications to run libp2p on desktop and mobile as well.
Applications include file storage, video streaming, crypto wallets, development tools, and blockchain. The top projects in the blockchain already have the libp2p module using IPFS.IPLD is used to understand and process data.。
PLD is a conversion middleware, which unifies the existing heterogeneous data structure into one format, facilitates data exchange and interoperability between different systems, data model and decoding, and uses CID as a link.First, we define a "data model", which describes the domain and scope of the data. This is important as it is the foundation of everything we will build. (Broadly speaking, we can say that the data model is "like JSON", like map, string, list, etc.) After this, we define "codecs", which say how to parse it from the message and use it as the message we want form issued. IPLD has many codecs. You can choose to use a different codec depending on what other applications you wish to interact with, or simply on how well your own application likes performance versus human readability.
IPLD implements the top three layers of protocols:object, file, name
object layer
- Data in IPFS is organized in the structure of Merkle Directed Acyclic Graph (Merkle DAG). Nodes are called objects, which can contain data or links to other objects. Links are encrypted hashes of target data embedded in the source. These data structures provide many useful properties, such as content addressing, data tamper resistance, deduplication, etc.;
file layer
- In order to model a Git-like version control system on top of Merkle DAG, IPFS defines the following objects:
blob data block: a blob is a variable-sized data block (without links), representing a data block;list: used to organize blobs or other lists in an orderly manner, usually representing a file;
tree: represents a directory and contains blobs, lists and other trees;
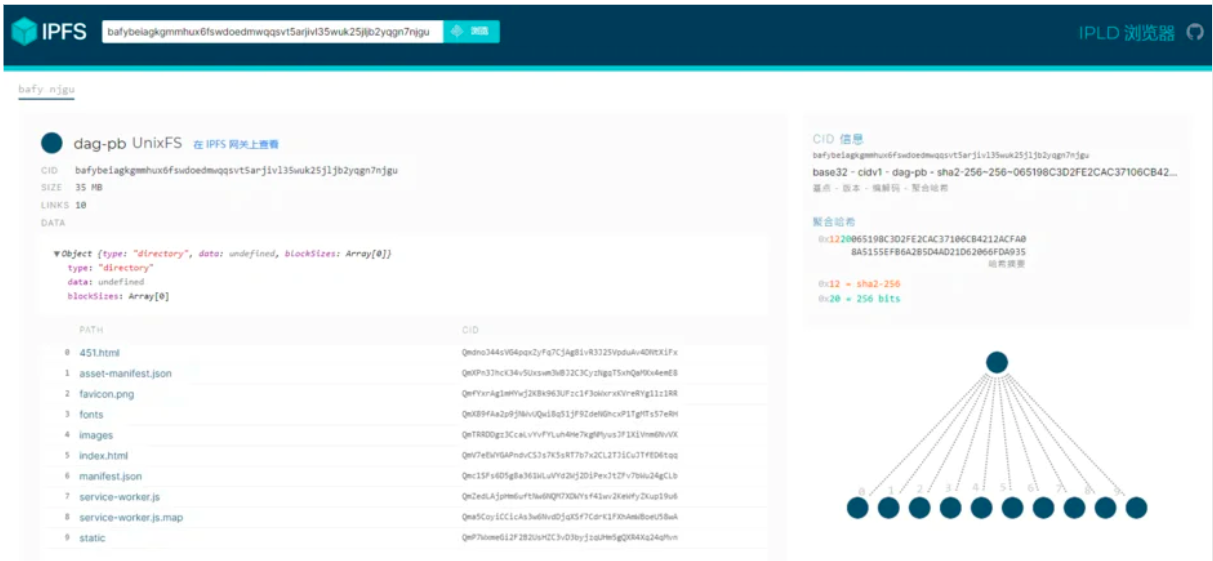
commit: similar to Git's commit, representing a snapshot in the object's version history;- Since each change of the object will change its hash value, a mapping is required for the hash value. IPNS (Inter Planetary Namespace System) assigns each user a mutable namespace, and objects can be published to paths signed by the user's private key to verify the authenticity of the object. Similar to URLs.
Filecoin
Corresponding to the display of IPLD:IPFS applies the functions of the above modules and integrates them into a containerized application program, which runs on independent nodes and is available for everyone to use and access in the form of Web services.
. IPFS allows participants in the network to store, request and transfer verifiable data to each other. But because IPFS is open source, it can be downloaded and used for free, and has been used by a large number of teams.