Original title: "Golden Observation | Accelerating the construction of multi-country cryptocurrency legal frameworks while supervision is in progress"
image description
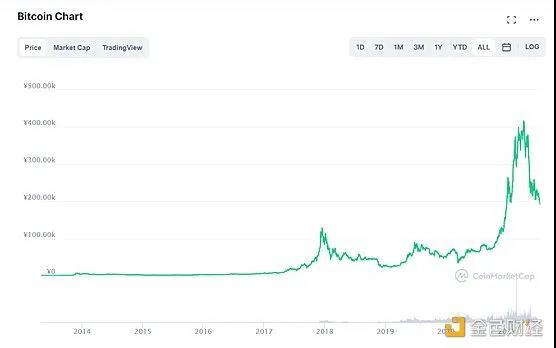
image description
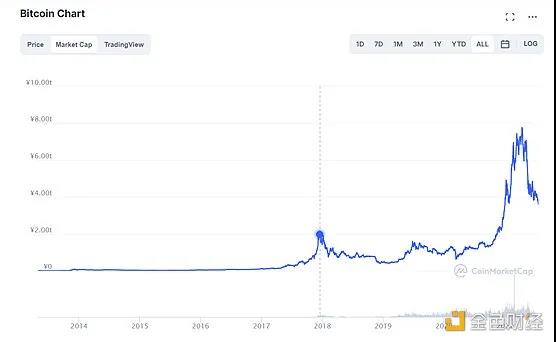
(Bitcoin market value change)
What is Bitcoin? Several principles of Bitcoin are mentioned in this paper.
A purely peer-to-peer electronic cash system that enables online payments to be initiated and paid directly by one party to another without passing through any financial institution;
Double payment can be prevented without the support of a trusted third party, and the peer-to-peer network environment is a solution to double payment;
Timestamp all transactions and incorporate them into an ever-extending hash-based proof-of-work chain as a transaction record. Unless the full proof-of-work is completed again, the formed transaction records will not be modifiable;
The longest chain will not only serve as proof of the observed sequence of events, but also be seen as coming from the largest pool of computing power from the CPU. As long as the computing power of the majority of CPUs is not controlled by cooperatively attacking nodes, the longest chain will be generated that is longer than the attacker.
The system itself requires very little technical facilities. Nodes do their best to disseminate information throughout the network. Nodes can leave and rejoin the network at any time, and use the longest proof of work as proof of transactions that occurred during the node's offline period.
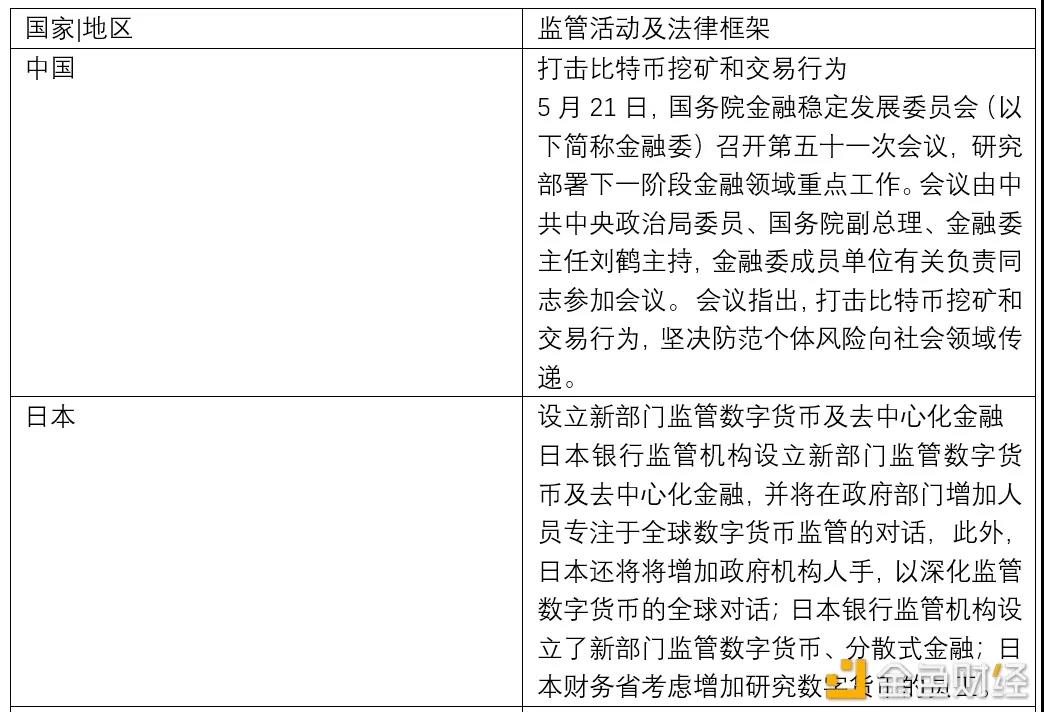
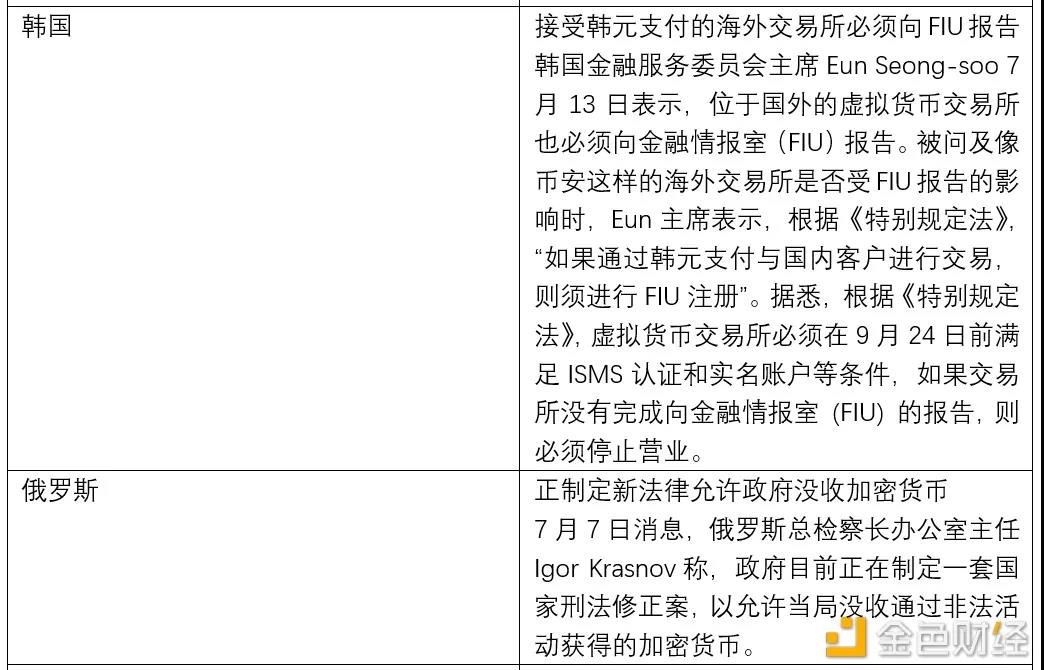
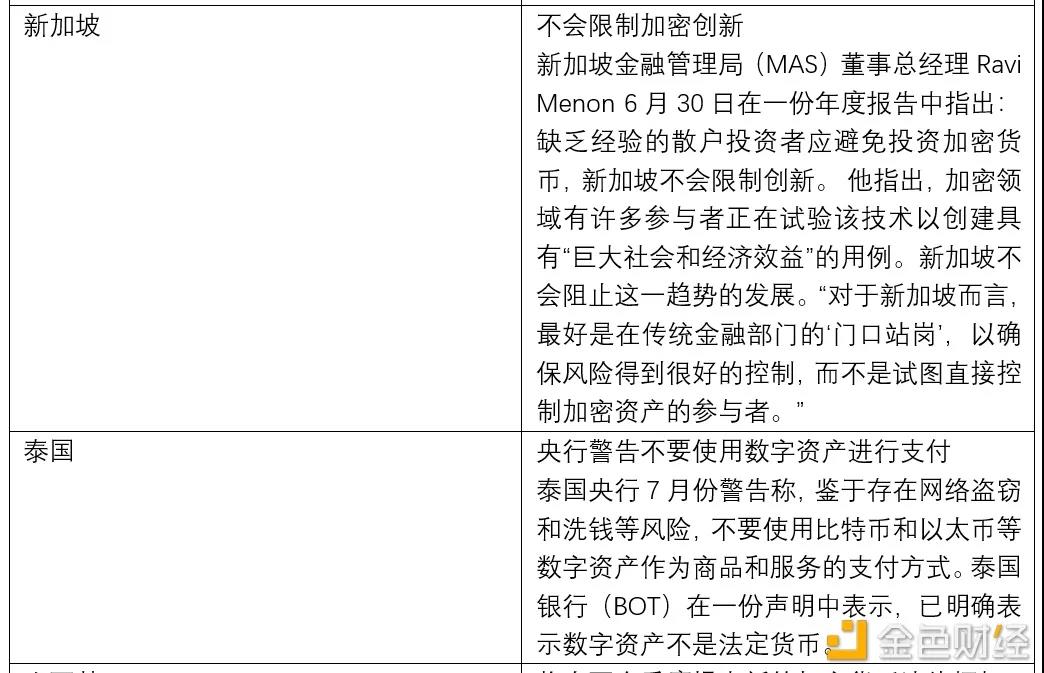
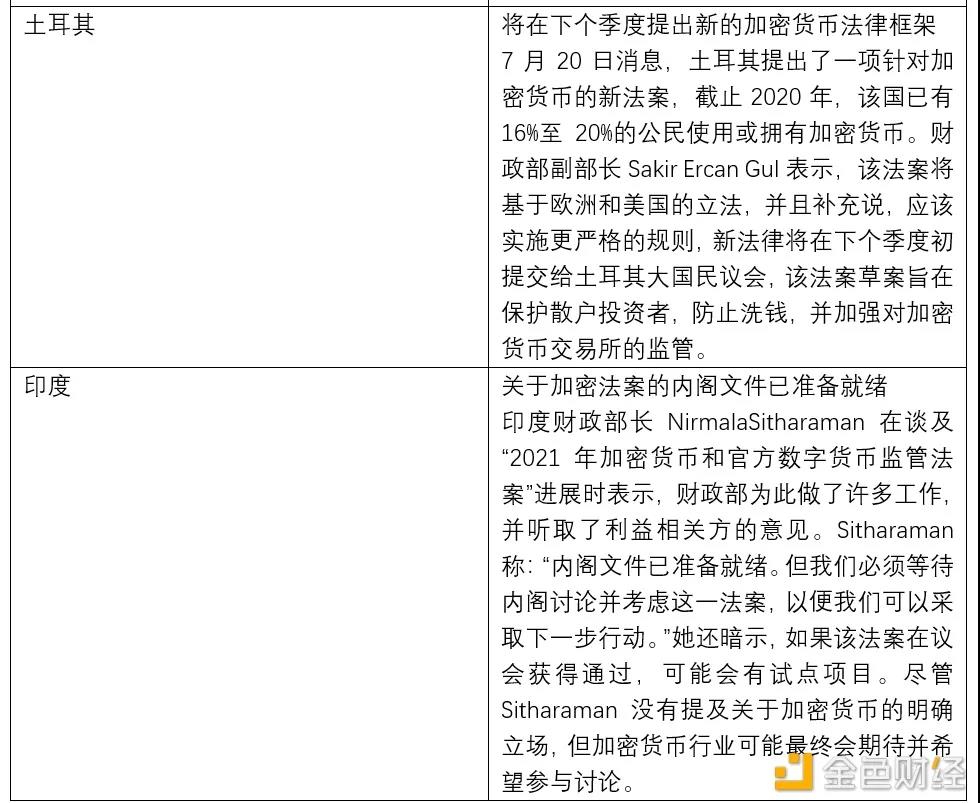
Based on the above characteristics, the operation of the Bitcoin network is feasible, and peer-to-peer transactions can be realized without centralized participation. Since the birth of Bitcoin, cryptocurrencies have developed rapidly, but the use and transaction of cryptocurrencies such as Bitcoin are accompanied by specific risks. For countries, they need to face the following two problems: First, the crimes involved in cryptocurrencies, including money laundering , black market payments, theft, fraud, tax evasion, etc. Another is that cryptocurrencies may affect monetary policy and financial stability. Therefore, regulatory authorities in various countries generally pay attention to the compliance and legality of Bitcoin transactions.
At present, the financial regulatory authorities of major countries have divided into four attitudes towards Bitcoin. One is to recognize or partially recognize the currency status of Bitcoin, represented by European countries such as El Salvador and Germany; the other is to only recognize the commodity attribute of Bitcoin, such as China. The third is to completely ban Bitcoin, represented by Thailand; the fourth is to wait and see cautiously, represented by India.
America
Europe



America
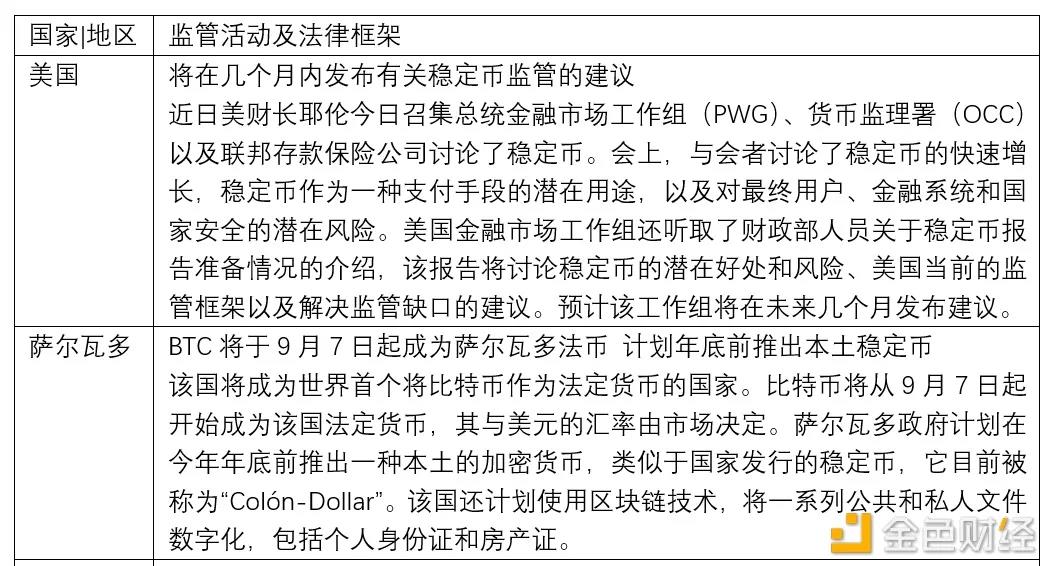


Asia