distributed storageAs an important part of Web3.0, the importance of IPFS is self-evident.
secondary title
Category 1: What is Filecoin?
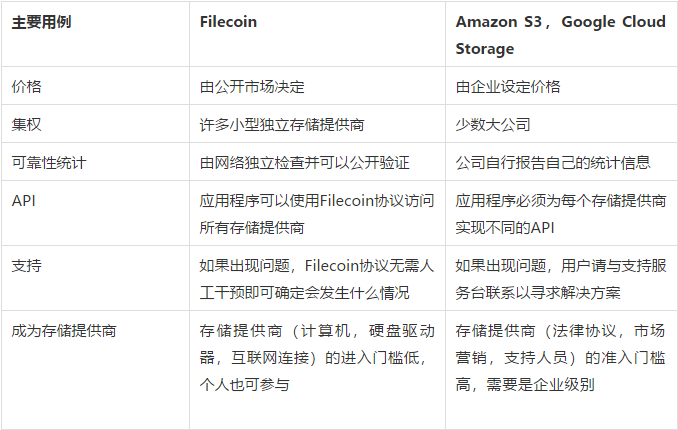
Users can choose their preferred compromise between cost, redundancy, and speed by choosing the miner that best suits their storage needs, and applications implementing Filecoin can negotiate storage with any miner on the network. Unlike centralized storage systems, Filecoin distributed storage does not require implementing different APIs for each provider. Users can at any time verify that their files were stored correctly by looking at proofs on the Filecoin blockchain.
for storage providers
Once storage providers implement the Filecoin protocol, they will have access to the entire marketplace of Filecoin users. Providers do not need to design their own storage APIs or promote their products themselves, because this is handled by Filecoin's protocol and network. Filecoin effectively eliminates barriers to entry and breaks the pain points of centralized storage.
What's new in Web3
Category 2: How Filecoin works
Filecoin node
In addition, nodes can also participate in the search contract and provide users with specified documents to obtain FIL. Currently, the Filecoin team is developing more node roles, such as nodes that promote network self-healing.
Filecoin miners
Customers need to send the file information that needs to be stored and a small amount of tokens to the storage market for quotation. Storage miners submit inquiries, and competition among miners can provide low-cost storage. A consensus on storage is reached between clients and miners to complete the pairing process.
After the supply and demand parties reach a deal, the customer sends the file to the storage miner, the miner adds the file to the disk partition, the partition is encapsulated by encryption, and the verification information is sent to the blockchain.
After the miners store the files in their own storage space of the miner node, the miners continue to prove that they are honestly storing the client's files through space-time proof and replication proof. The fee paid by the client to the miner is paid in installments. As time goes by, the miner will not only receive the FIL income paid by the client, but also receive block rewards from the network.
miner type
Storage miners are responsible for storing files and data on the network.
Retrieval miners, responsible for providing fast lanes to retrieve files.
Repair miners, to be implemented.
Storage Miners are the heart of the network. They earn Filecoin by storing data for clients and calculating cryptographic proofs to verify storage across time. The probability of earning block rewards and transaction fees is proportional to the amount of storage miners contribute to the Filecoin network.
trade
trade
Filecoin has two main types of transactions: storage transactions and retrieval transactions.
Category 3: Why choose Filecoin
open market
In Filecoin, file storage and retrieval transactions need to be negotiated on the open market, and anyone can join the Filecoin network without permission. Running miners only requires an Internet connection and spare disk space to participate in the Filecoin network. By lowering the barriers to entry, Filecoin can create a truly decentralized Internet.
competitive price
The price of storage and retrieval is determined by supply and demand, not by enterprise pricing departments. Filecoin offers reliable storage at very competitive prices, and miners compete based on their storage, reliability, and speed, not through marketing or locking in users.
reliable storage
self-healing
self-healing
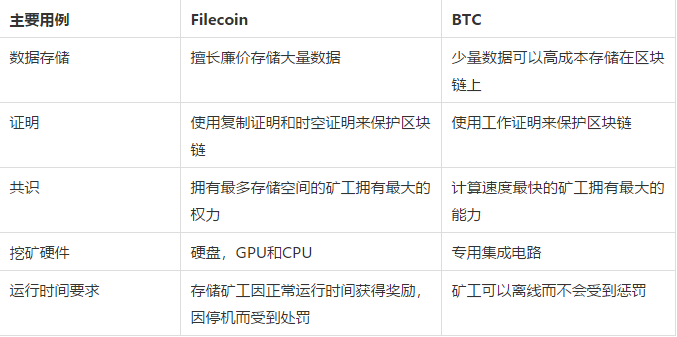
Category 4: Comparing Filecoin
Filecoin vs. Amazon S3, Google Cloud Storage
secondary title
Category Five: Filecoin Frequently Asked Questions
Will storing data on Filecoin be cheaper than other centralized cloud services?
Filecoin has created a highly competitive market for data storage. There will be many miners on the network offering many prices instead of one fixed price. Officials expect that Filecoin's permissionless model and low barriers to entry will lead to some very effective operating mechanisms and low-cost storage solutions.
What can I do if I accidentally lost a sector?
If the user loses the data itself, there will be no way to recover it and the user's reward will be cut. However, if the data itself is recoverable (for example, the user just missed the WindowPoSt), then the recovery process will be able to regain the sector.
Why Filecoin mining works best on AMD?
Currently, Filecoin's Proof of Replication (PoRep) tends to run on AMD processors. See the description of the Filecoin seal for more information. More precisely, it runs much slower on Intel CPUs. It's extremely competitive with some ARM processors (like the ones in newer Samsung phones), but they lack RAM to seal larger sectors. The main reason we see this advantage on AMD processors is due to their implementation of the SHA hardware instruction.
Which is better for miners, Lotus or Venus?
Lotus is the main reference implementation of the Filecoin protocol. At this stage, we recommend that most miners use Lotus to participate in the Filecoin network.
How fast is retrieval from the Filecoin network?
If you are retrieving data from IPFS or a remote fixed layer such as FPS, the retrieval should take on the order of milliseconds in the worst case. Recent tests retrieved from the Filecoin network directly show that sealed sectors holding data take about 1 hour to unseal. From department unsealing to data delivery, the best implementation estimate is 1-5 hours. If you need to retrieve data faster for your application, it is recommended that users build storage on Powergate or FPS.
In the process of data storage, what kind of punishment mechanism will be imposed if data is lost or cannot be accessed? What impact will it have on server cluster operators?
After learning the knowledge points, hurry up and click to read and bookmark it!
With the continuous evolution of blockchain technology, the ever-improving ecology of IPFS&Filecoin has attracted many developers in the encryption field, and distributed storage will also play an increasingly important role in the upcoming Web3.0 era.