Original author:Xangle
Original compilation: Felix, PANews
The Cosmos ecosystem is developing rapidly in 2023, attracting many developers and projects with its unique interoperability and modular architecture. These features have opened up new horizons for blockchain technology.
This article will explore the major changes, major technology updates, and prominent new projects taking place within the Cosmos ecosystem in 2023. In addition, it also studies the technological progress and market changes of the Cosmos ecosystem, and how Cosmos redefines the existing blockchain paradigm.
1. Infrastructure
1.1 Major updates to Cosmos SDK
The modules managed by the Cosmos SDK are mainly used to develop chains in the Cosmos ecosystem. Here are the major updates to the SDK scheduled for release in 2023.
Version 0.47 Update
Upgrade to CometBFT: The rebranded CometBFT is a fork of the previously used consensus engine Tendermint and is now officially available in the Cosmos SDK. There are no breaking changes in version 0.47, this update is intended to help chains previously using Tendermint migrate to CometBFT.
Version 0.50 Update
ABCI 2.0: ABCI is the interface responsible for data exchange between the consensus engine and the application layer responsible for different functions on the chain. The consensus engine CometBFT (Tendermint) is responsible for block generation and transaction broadcasting, which is the process of determining the order of transactions. Due to the design of ABCI, there are limitations in processing transactions in the required order in the mempool. To overcome this problem, ABCI 2.0 added a new process called PrepareProposal to determine the order of transactions in the mempool and pass it to CometBFT.
Optimistic Execution: In the previous Cosmos SDK, all validators needed to agree in order to execute transactions and submit the results to the chain. This move slowed down the execution of transactions, and to overcome this issue, a feature called “Optimistic Execution” was introduced. This feature allows transactions to be executed and submitted without the consent of all validators, thereby increasing transaction throughput.
SDK Modules: The Cosmos SDK contains various modules for application development. Previously each modules update followed an updated version of the SDK, making it difficult to track the update history of each module. In version 0.50, each module is versioned independently, making it easier to track updates. Additionally, the data storage models Store and IAVL have been decoupled so that they can be updated independently.
1.2 Cosmos on Metamask
Since there are multiple chains in the Cosmos ecosystem, each chain has an independent address even if the mnemonic is the same. While currently integrated and managed using the Keplr wallet, this requires the use of a new wallet application, providing a poor user experience and raising the barrier to entry.
Cosmos is working on projects to solve this problem. In this context, Metamask implements full support for Snap, allowing custom functionality to be added on Metamask. Transactions can now be created on Cosmos-based chains, including Leap wallets. In other words, the technical foundation has been laid, and users who are familiar with EVM-based chains can be more easily attracted to the Cosmos ecosystem.
Leap wallet (https://cosmos.leapwallet.io/portfolio/overview)
1.3 MultiVM
Unfortunately, the Cosmos SDK does not support virtual machines for smart contracts. As a result, several projects have emerged to develop virtual machines that have been verified and used in other blockchains, or there are projects to develop virtual machines unique to the Cosmos ecosystem. There have been attempts to integrate various virtual machines (such as EVM, WasmVM, SolanaVM, MoveVM, etc.) with the Cosmos SDK, and some of them have been highly praised. If more commonly used virtual machines are supported, it will be easier for dApp developers to enter the Cosmos ecosystem.
2. Project
Here are some interesting and compelling projects emerging in the Cosmos ecosystem in 2023.
2.1 Celestia
The most popular project in the Cosmos ecosystem in 2023 is undoubtedly Celestia. Celestia is a representative modular blockchain project that roughly divides the functions of the blockchain into four parts:
Execution: The ability to process transactions and change chain state.
Settlement: Validates transactions processed by the computing layer.
Data availability: Store information from transactions and blocks and ensure it is always available.
Consensus: The ability to determine the validity of transactions or the order in which they are included in a block
Among these features, Celestia focuses on data availability. The combination of Celestia and the word L2 triggered the Rollup craze in the Cosmos ecosystem. For this purpose, a framework called Rollkit has been created and supported, which supports ABCI between Celestia and the Cosmos SDK.
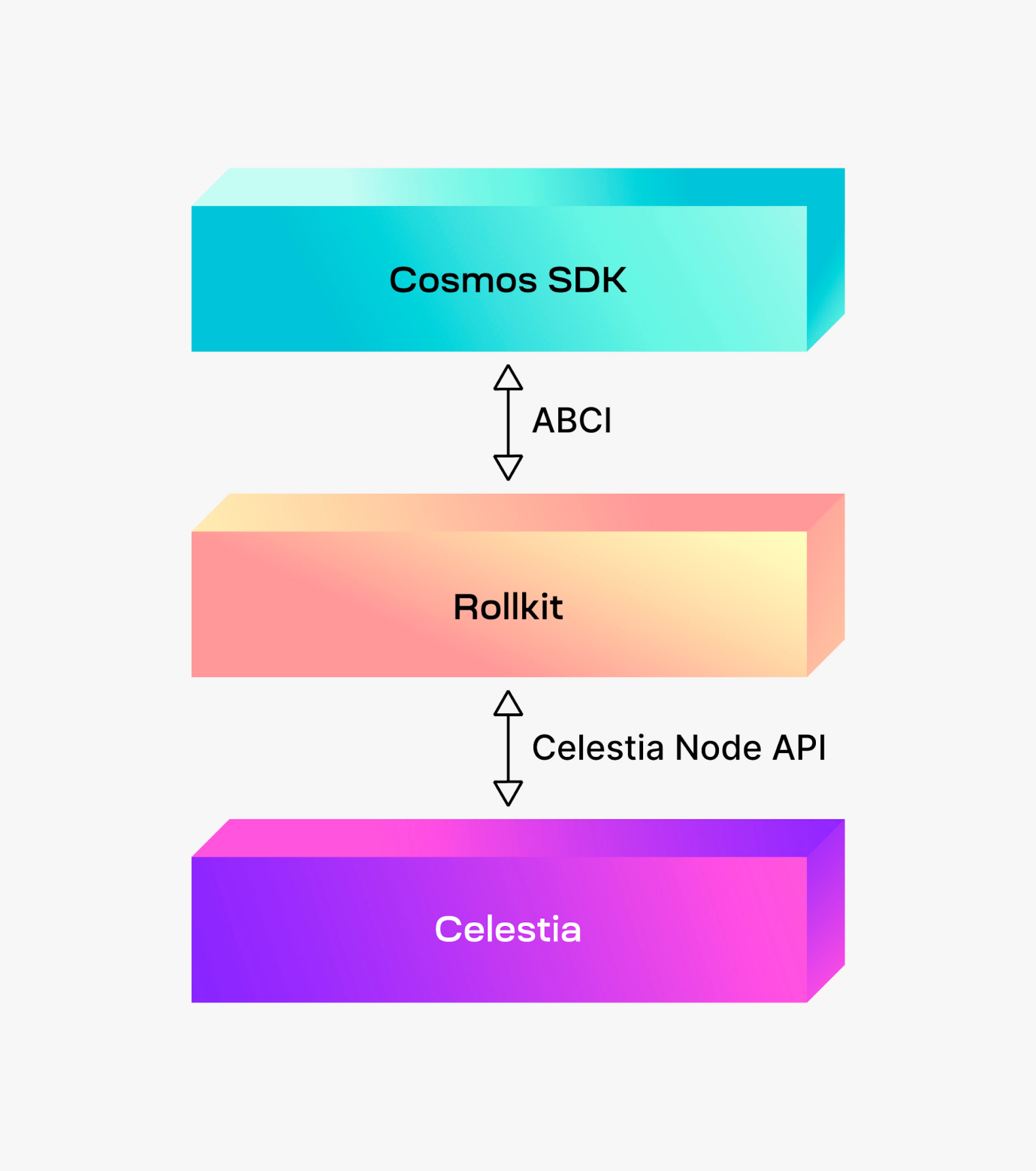
Celestia Rollkit ( https://docs.celestia.org/developers/rollkit )
Rollkit replaces Cosmos’ consensus engine Tendermint (more precisely CometBFT) and allows Celestia and the Cosmos SDK to communicate directly. Rollkit allows Sovereign Rollup by aggregating transactions in a block and leveraging Celestia’s consensus engine and data availability.
2.2 Skip Protocol
Skip Protocol is a project with the vision of “sovereign transaction infrastructure for sovereign blockchains”. This protocol can improve the user experience of sovereign blockchains, make the order of transaction processing transparent, prevent malicious MEV, and improve the quality of the network.
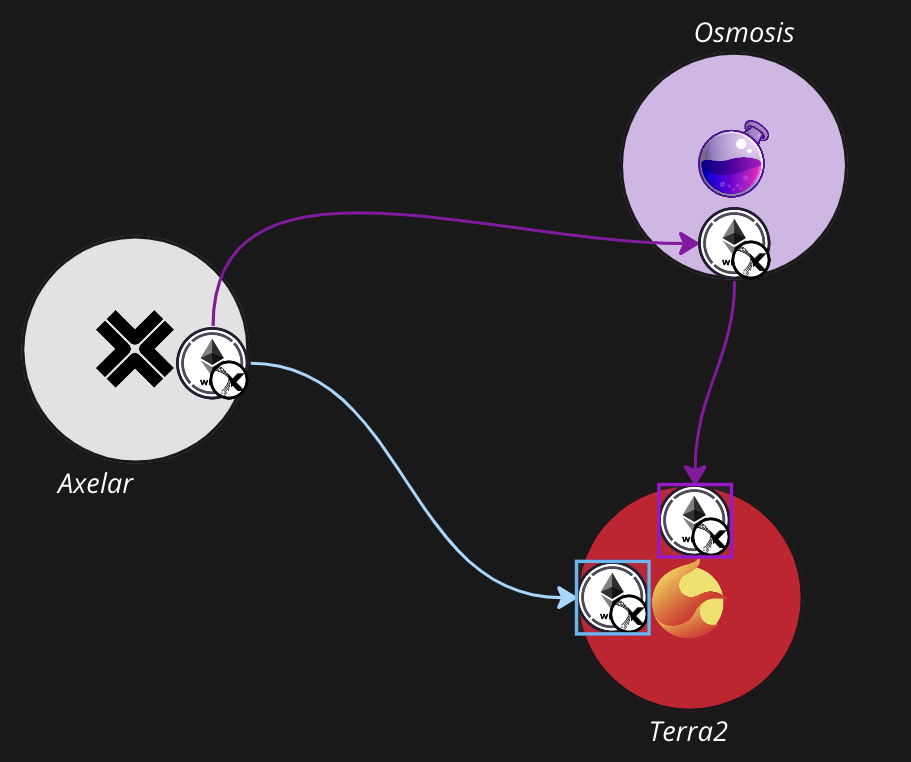
Among user experience improvements, the project aims to address issues with the Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol. IBC is a protocol for trading assets between different chains within Cosmos. In order to transfer assets via IBC, a communication channel must be created, and each channel needs to be given a unique ID for each connected chain. The picture below shows an example of ETH being sent from Axelar to Terra 2.

Skip API ( https://api-docs.skip.money/docs/ibc-routing-algorithm )
In addition, Skip proposes an optimal routing algorithm for delivering assets in the Cosmos ecosystem and provides a better user experience by determining the Denomination of assets.
Skip Protocol also provides various APIs that are useful for developing blockchains based on the Cosmos SDK, such as multi-chain transaction tracking. Skip also reported to the communityproposalIncorporate Skip functionality into the Cosmos SDK to contribute to ecological development.
SKIP API ( https://api-docs.skip.money/docs/ibc-routing-algorithm )
2.3 Other projects
Sei
Sei is positioned as a chain that specializes in transactions, and its goal is to become a fast Layer 1 instead of Rollup, which is also a major trend in blockchain development in 2023. Sei focuses on improving the performance of the chain by leveraging various technologies.
Injective
Injective is committed to building a blockchain ecosystem specifically for financial applications. Injective has established partnerships with Figment and Binance, and supports various dapps such as Helix and Hydro to join the Injective ecosystem.
dYdX
dYdX is considered the most successful DEX and has successfully migrated to Layer 1 using the Cosmos SDK.
dYdX strengthens governance through its own token.
Stride
Stride is a liquidity staking protocol similar to Ethereum Lido. In the Cosmos ecosystem, liquidity staking is inherently difficult because assets are scattered across multiple chains. Stride aims to enable multi-chain liquidity staking in the Cosmos ecosystem by leveraging ICA (Inter-Chain Account), ICQ (Inter-Chain Query) and ICS (Inter-Chain Security).
Coreum
Coreum is a Layer 1 blockchain for enterprises that supports Wasm-based smart contracts, RWA tokenization, NeoBanking applications, and more.
3. On-chain performance
3.1 Development activities
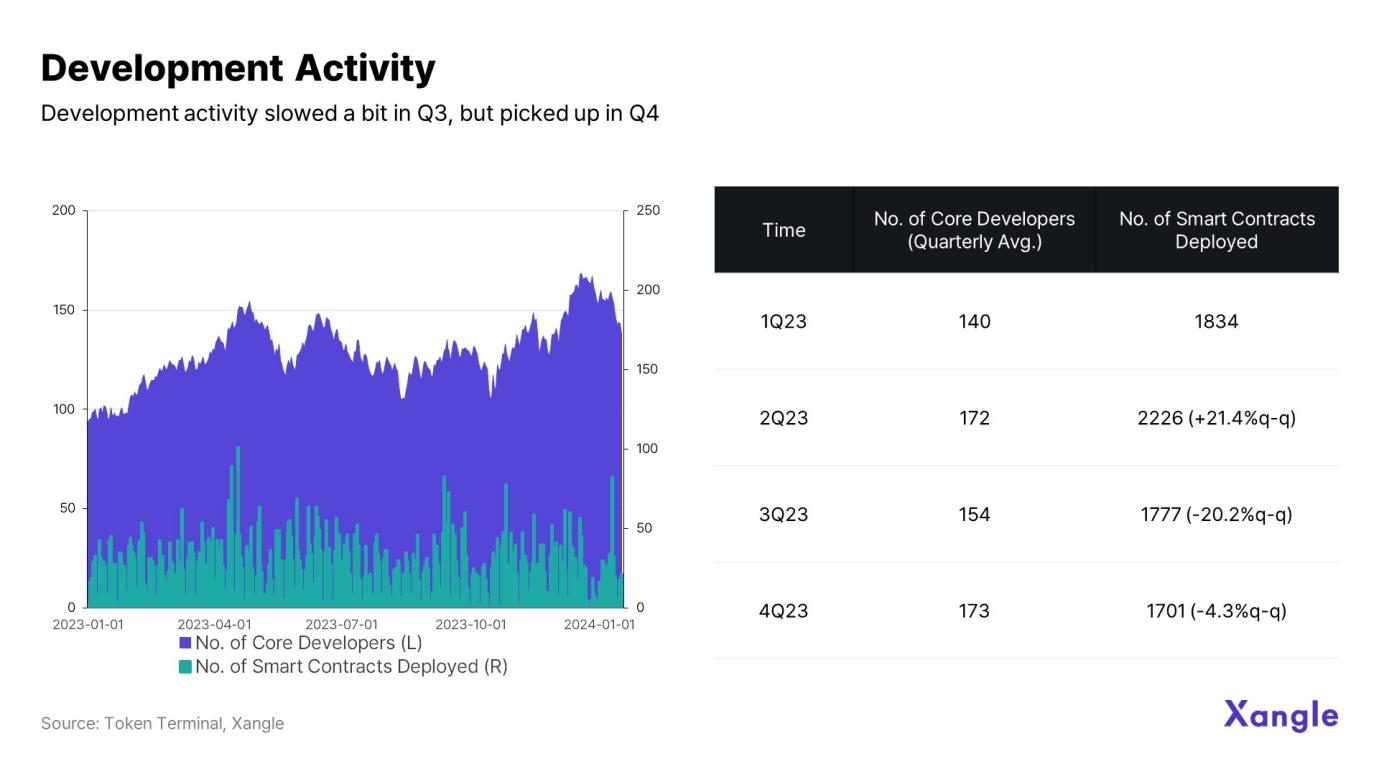
While development activity on the Cosmos network remains healthy overall, Q2 2023 had the highest number of smart contract deployments (2226) and the highest growth rate (21.4%). The number of core developers is gradually increasing, which is also a sign of active ecological infrastructure construction.
Meanwhile, the number of smart contracts deployed in Q2 and Q3 last year was 2,226 and 1,777 respectively, up from 1,701 in the fourth quarter. While development activity did slow down compared to the previous two quarters, activity levels continue to hold up given the decline at the end of Q4.
3.2 Network activities
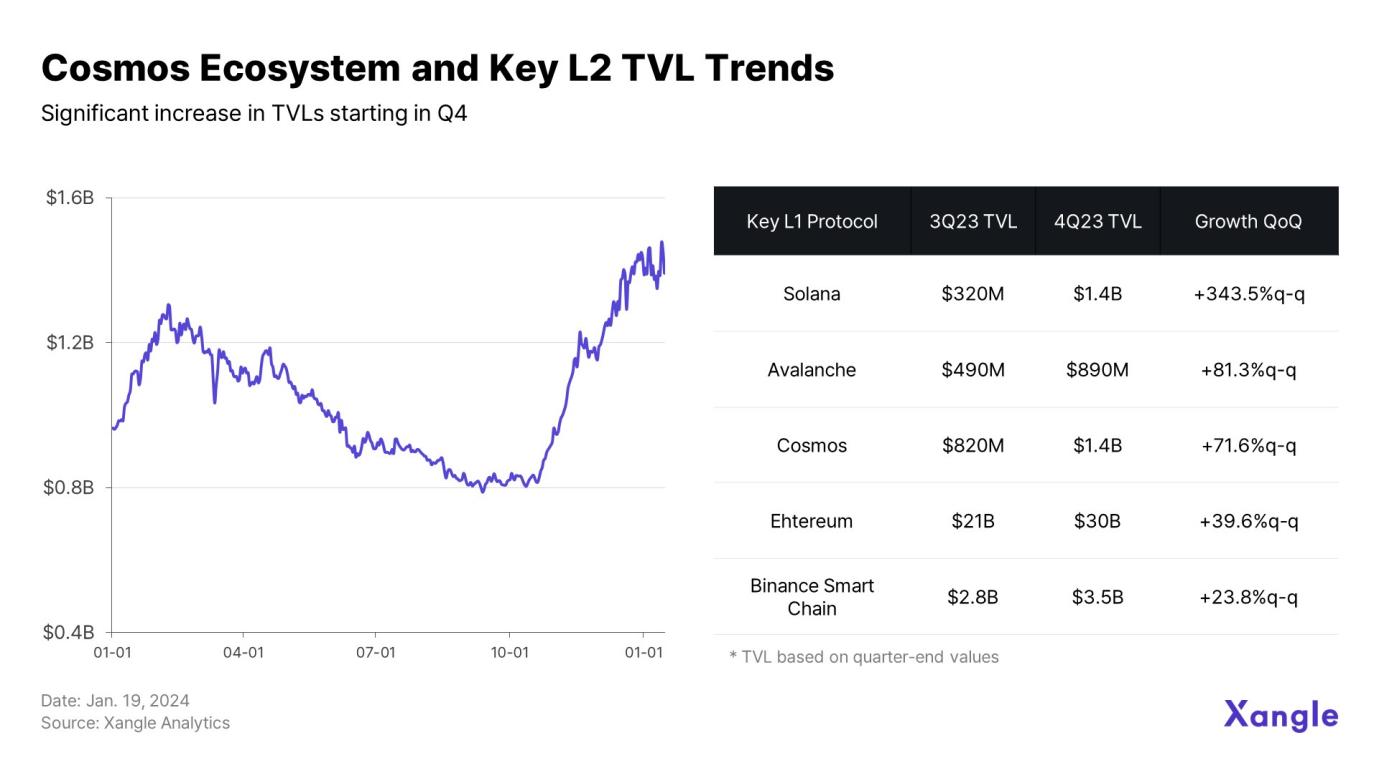
The most noteworthy aspect of Cosmos network activity is that development activity in Q2 and Q3 translated into growth in the entire ecosystem in Q4. As shown in the figure, TVL in the Cosmos ecosystem continued to decline in Q3, but then increased significantly in Q4.
The explosive growth of TVL in the Cosmos ecosystem in the fourth quarter can be attributed to two factors. The first was the influx of liquidity into Layer 1 narratives in mid-October. In the second half of the year, a large amount of funds flowed into the Layer 1 ecosystem, and the explosive performance of Solana, Cosmos, and Avalanche drove the overall TVL increase.
In addition, the developer-friendly infrastructure environment, including the Cosmos SDK, and the vast blockchain connection network built on the IBC ecosystem have brought practical utility to users. A look at the TVL trend shows that this is not just a temporary rise, but an ongoing trend. Market satisfaction with the protocol’s maturity will likely drive Layer 1 liquidity, boosting Cosmos’ growth and reducing user churn.
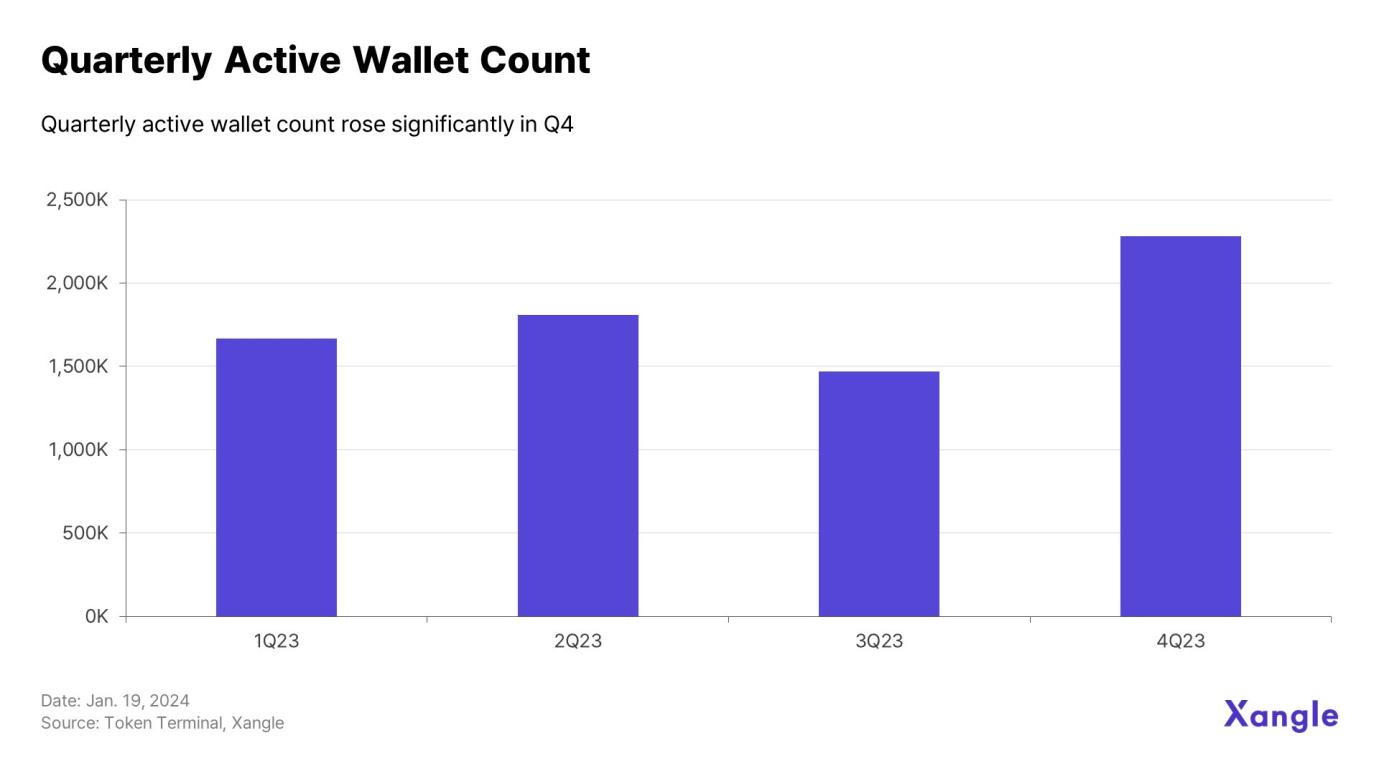
Compared with the worst-performing Q3 (1,470,050), the number of active wallets in Q4 also increased by nearly 55% to 2,280,335, reflecting the vitality of the ecosystem. The interoperability of the Cosmos IBC ecosystem drives increased on-chain activity.
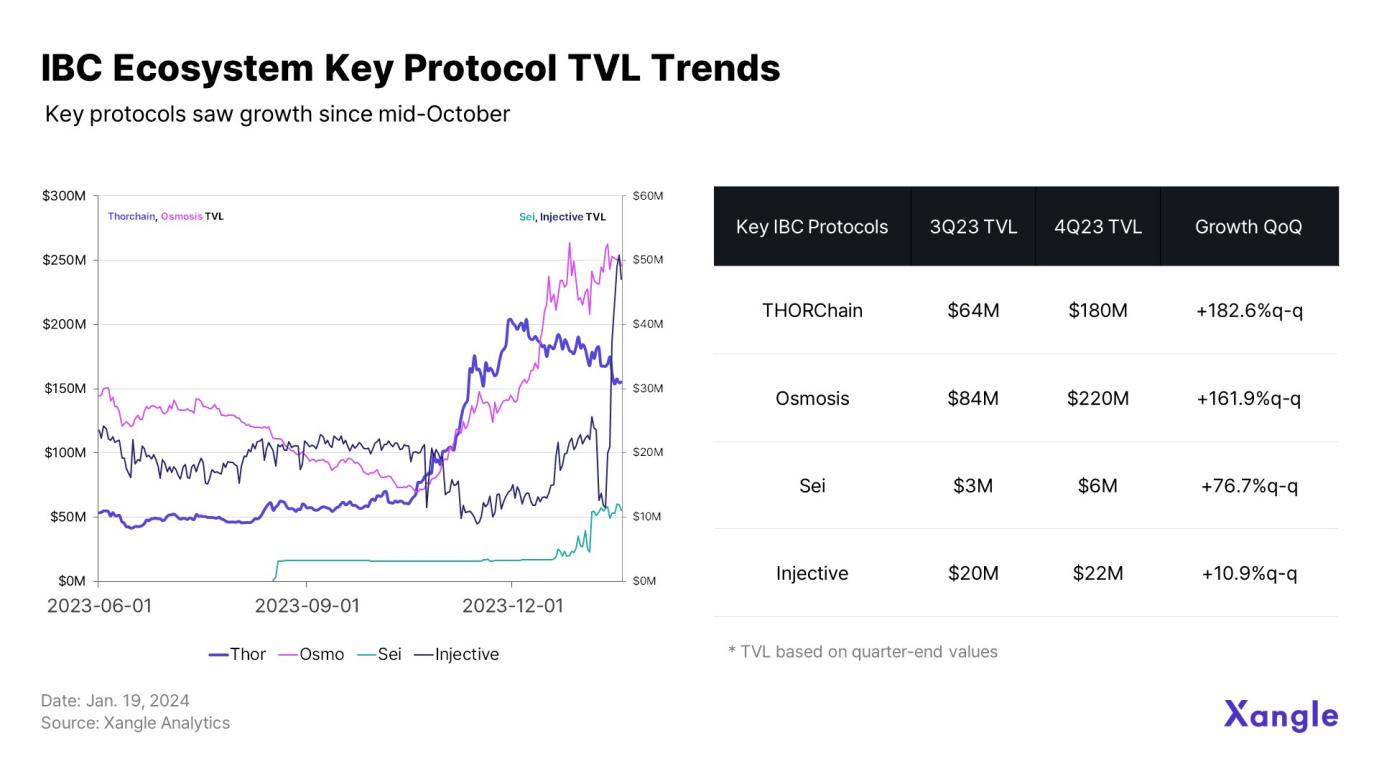
In addition, judging from the TVL trends of key protocols in the IBC ecosystem, the continued hype of protocols based on the Cosmos SDK in the second half of the year also played a role in revitalizing the ecosystem.
3.3 Network security
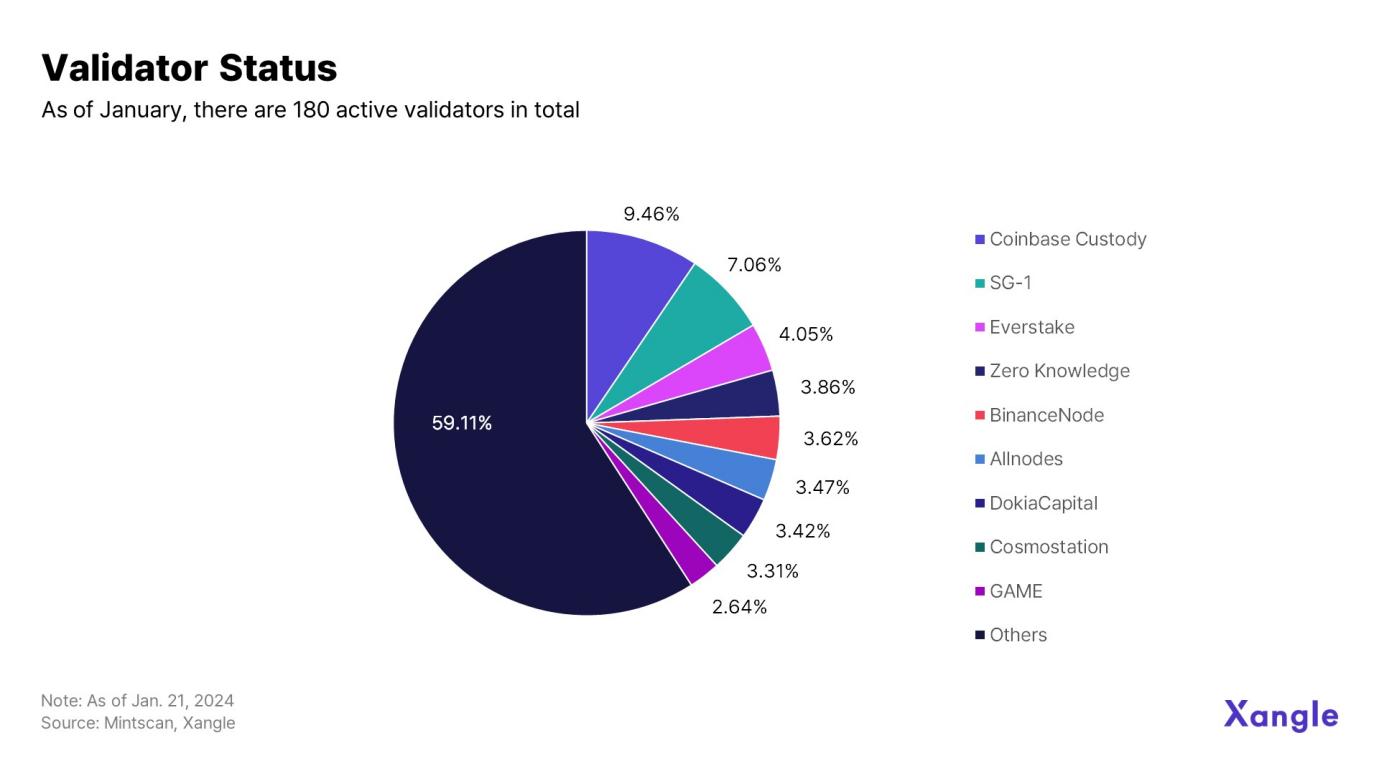
Cosmos currently has a total of 180 active validators. The top 9 validators hold 40.89% of the ATOM supply. There are currently 2.44 billion ATOMs pledged on Cosmos, accounting for approximately 65% of the total supply.
4 Conclusion
2023 is a landmark year for the Cosmos ecosystem, witnessing the development and major changes of several projects. These changes demonstrate that Cosmos is not just an area of blockchain technology, but is driving innovation across the entire blockchain ecosystem.
Celestia, Skip Protocol, and other well-known projects demonstrate the diversity and flexibility of the Cosmos ecosystem and how it continues to evolve. These projects pioneer new use cases for blockchain technology and help create more efficient, user-friendly blockchain environments.
The growth and development of the Cosmos ecosystem has heightened excitement about the future of blockchain technology. Opening the door to new opportunities for developers, users and investors, and paving the way for continued innovation for years to come. The Cosmos ecosystem is expected to continue this positive trend in the coming years, and new technical challenges and opportunities will continue to emerge along the way.