Original author:@yelsanwong
tutor:@CryptoScott_ETH , @Zou_Block
TL;DR
As one of the established Defi protocols, MakerDAOs design embodies the core values of blockchain technology - transparency, decentralization and censorship resistance. Although Defi suffered a series of major blows in 2022, MakerDAO continues to be a key player in the stablecoin and decentralized lending markets, introducing real-world assets to significantly increase protocol revenue, demonstrating strong market adaptability and innovation capabilities
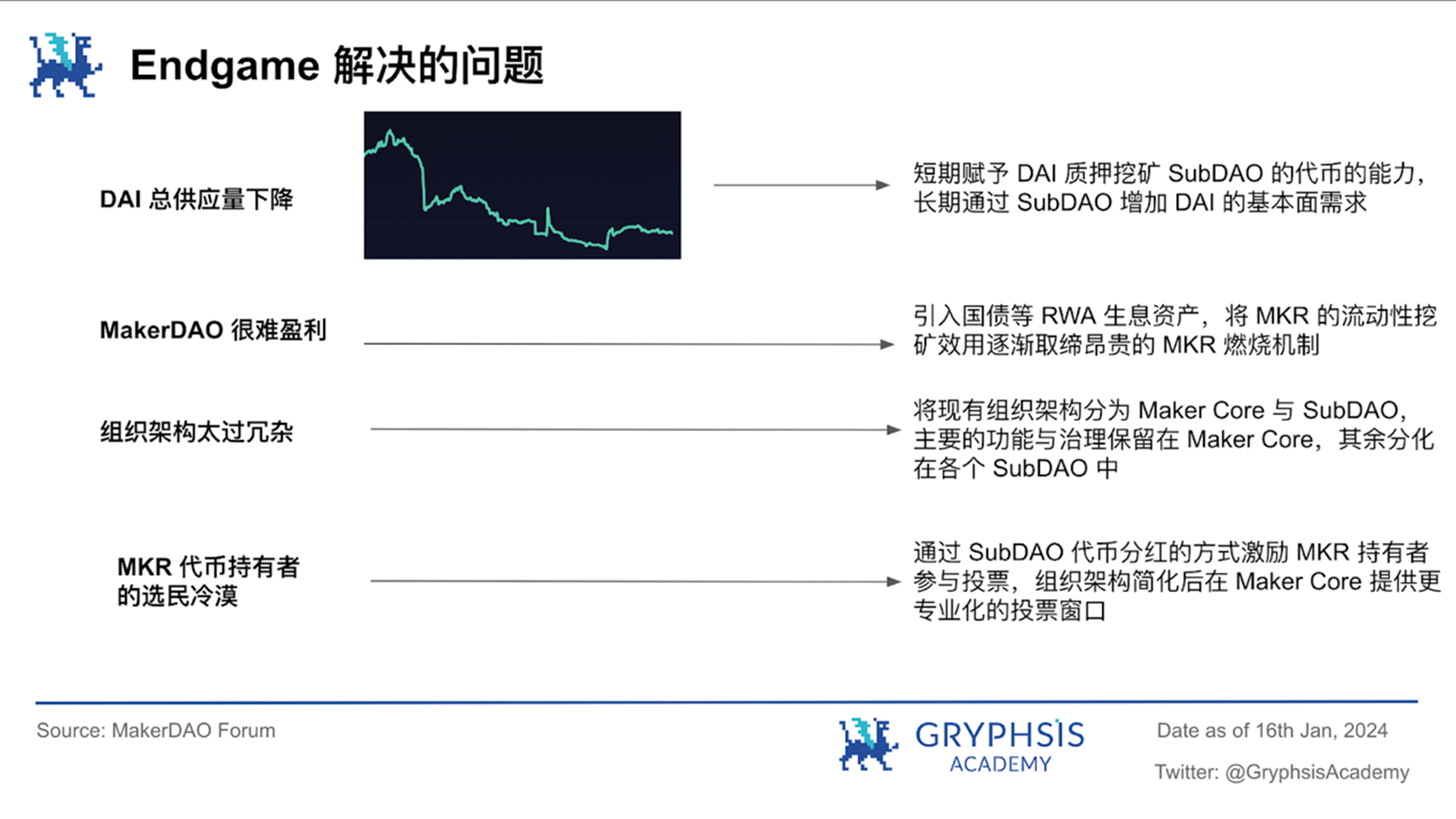
In order to realize the business potential of all existing but currently mostly hidden and low-priority processes, MakerDAO will officially begin implementing the Endgame plan in 2023. Split business segments into SubDAOs that are more professional, more suitable for their own business and dynamic governance, thereby greatly improving risk management capabilities and capital efficiency, allowing the increasingly bloated MakerDAO to establish a more efficient decentralized and transparent system ecosystem
The Endgame plan will step by step enhance its ability to withstand real-world risks through four stages: Pregame, Early Game, Midgame and Endgame through experimentation and practice, including running 6 initial SubDAOs in the early stage and issuing corresponding ERC 20 tokens. Achieve distribution through liquidity mining of tokens such as $DAI, $MKR and $ETHD
In the Early Game stage, or the first quarter of 2024, it is planned to further lay the foundation for the overall plan through the rebranding of $DAI and $MKR. During this period, the token economic models of $MKR and $DAI will be significantly different from the current ones. difference. MakerDAO and SubDAO will also lower the governance threshold with the launch of new tokens, further increasing the willingness of token holders to participate in governance
Regarding the current risk management and control of real-world assets, MakerDAO divides it into three stages: dove, eagle and phoenix according to the severe situation. We predict that MakerDAO will still maximize the income of the underlying assets through its RWA assets in the next two to three years.
In mid-2023, MakerDAO changed the repurchase and destruction mechanism of $MKR, and instead introduced a smart combustion engine to use part of the protocol’s surplus to repurchase $MKR and place it in Uniswap V2 to form the MKR/DAI trading pair to provide liquidity. It can be regarded as a kind of active market making. At the same time, the engine aims to create a dynamic balance in the future so that the number of new $MKR tokens issued each year is equal to the number burned, supporting the healthy circulation of $MKR
We valued the $MKR token through the DCF valuation model and the comparable valuation model respectively. After a series of assumptions and modeling, we finally believe that the price of the $MKR token will reach $3396.72 at the end of the first quarter of 2024. - $4374.21, MakerDAOs fully diluted valuation (FDV) ranges from $3.321 billion to $4.277 billion. Compared with the data on January 16, 2024, $MKR still has some upside potential. This valuation is not intended as investment advice. Actual future market dynamics and MakerDAO’s operating performance will ultimately determine its true market value.
MakerDAO still needs to pay attention to its regulatory risks that cannot be ignored while innovating. Given that it has introduced a large number of US Treasury bonds as underlying assets, it is still very likely that it will receive continued attention and even regulatory measures from US government agencies. At the same time, because its own Endgame plan currently has fundamental changes to its governance token $MKR and stablecoin $DAI, these may affect the protocols risk tolerance and future development methods.
1. MakerDAO Overview
MakerDAO is a protocol based on the Ethereum blockchain that aims to provide a decentralized stablecoin DAI. The value of the stablecoin is pegged to the U.S. dollar, regulated through mechanisms such as over-collateralization and surplus buffers, without relying on issuance or guarantees from a central authority. The stability and value of DAI are ensured by smart contracts through automated regulation mechanisms involving the collateralization of crypto-assets such as Ethereum and other ERC-20 tokens locked and managed on the MakerDAO platform. This design aims to achieve the robustness and reliability of the protocol and provide users with a more trustworthy digital currency trading and asset management environment.
$MKR, the governance token in the MakerDAO ecosystem, plays a key role in protocol governance and system stability. $MKR token holders participate in key decisions by voting, such as the selection of collateral types, setting debt ceilings, adjustments to the stabilization fee, and other key system parameters. Additionally, the $MKR token serves as a debt offset mechanism in the event of a system loss, enhancing the financial soundness of the protocol.
MakerDAO is designed to embody the core values of blockchain technology, namely transparency, decentralization and censorship resistance. Automated processes through smart contracts reduce middlemen and provide users with a more reliable and seamless financial services experience. With the rapid development of the DeFi field, MakerDAO continues to be a key player in the stable currency and decentralized lending market, demonstrating strong market adaptability and innovation capabilities. For example, the introduction of RWA assets such as U.S. Treasury bonds since the end of 2022 has not only brought DAI It brings more stability to real-world assets and creates considerable returns for itself.
In order to enhance the protocols continuous innovation capabilities, improve the organizational structure to make the governance decision-making process more efficient, and enhance the use of the protocols intangible value, MakerDAO has gradually proposed its long-term and thorough Endgame plan since 2022, and will officially begin implementation in 2023. This article will partially consider Endgame’s plans to value the $MKR token.
2. Endgame
2.1 Endgame underlying logic
Like the organizational structure of Googles parent company, Alphabet, the holding company achieves stable growth and maximizes profit returns through Google, while operating a variety of autonomous start-ups that have been isolated from risks, with technical and resource support provided by Google and Alphabet. Through diversification and diversification of investment ideas, we can strike a balance between a stable core business and riskier attempts to innovate, so that Alphabet can not only respond to the challenges of the current market, but also prepare for future changes and opportunities.
Apply the idea to MakerDAO, and divest valuable and potential businesses such as lending protocols, decentralized oracle networks, and real-world assets RWA from todays MakerDAO into different SubDAOs, and build around these values and potentials in SubDAO Issue tokens and then nurture the community by distributing the tokens, unlocking all the business potential that exists but is currently mostly hidden and low-priority.
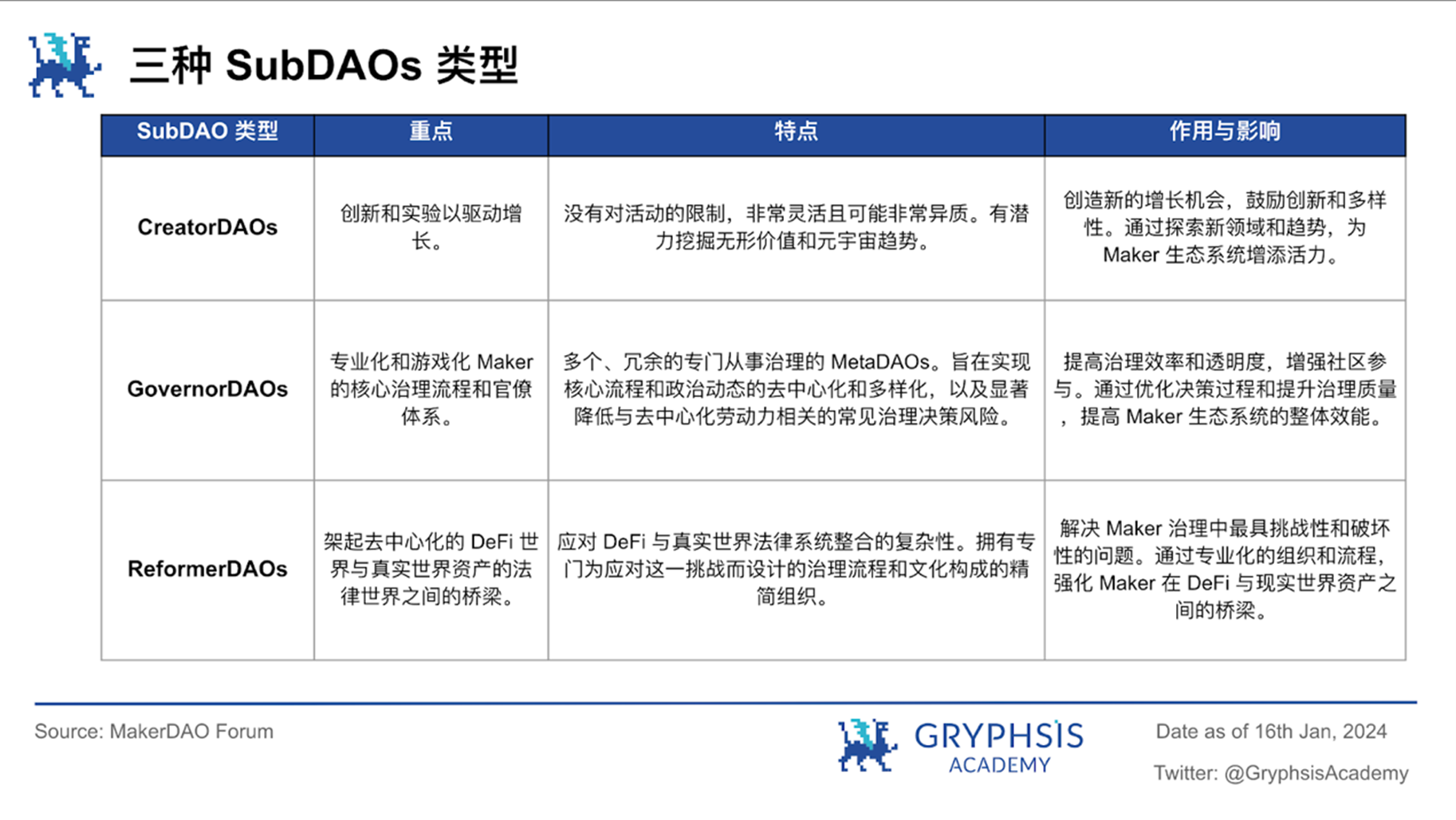 Taking RWA as an example, the current governance process and efficiency of MakerDAO cannot compete with traditional financial institutions when processing complex real-world financial transactions, but SubDAO allows MakerDAO to liberate MakerDAO from the complexity of direct management and focus on real-world asset transactions. Rather, simply incubating can develop more professional, adaptable, and dynamically governed SubDAOs that can overcome the obstacles MakerDAO has fallen into. MakerDAO can then use the already tested and understood D3M construct (Decentralized Direct Deposit Module, which leverages automation and smart contracts to optimize MakerDAO’s interaction with other DeFi protocols while managing risk and improving capital efficiency) to let these SubDAOs represent MakerDAO Work on RWA to reduce the overhead and complexity of MakerDAO. The main question becomes to compare the performance of different SubDAOs and decide who should be given more power. In other words, decentralize power, conduct innovative exploration in multiple threads, and allow the increasingly bloated MakerDAO to establish a more efficient decentralization and transparency ecosystem. In the cryptocurrency industry where the regulatory environment and uncertain risks are even less ideal, this is an effective way for MakerDAO to survive in the market for the long term.
Taking RWA as an example, the current governance process and efficiency of MakerDAO cannot compete with traditional financial institutions when processing complex real-world financial transactions, but SubDAO allows MakerDAO to liberate MakerDAO from the complexity of direct management and focus on real-world asset transactions. Rather, simply incubating can develop more professional, adaptable, and dynamically governed SubDAOs that can overcome the obstacles MakerDAO has fallen into. MakerDAO can then use the already tested and understood D3M construct (Decentralized Direct Deposit Module, which leverages automation and smart contracts to optimize MakerDAO’s interaction with other DeFi protocols while managing risk and improving capital efficiency) to let these SubDAOs represent MakerDAO Work on RWA to reduce the overhead and complexity of MakerDAO. The main question becomes to compare the performance of different SubDAOs and decide who should be given more power. In other words, decentralize power, conduct innovative exploration in multiple threads, and allow the increasingly bloated MakerDAO to establish a more efficient decentralization and transparency ecosystem. In the cryptocurrency industry where the regulatory environment and uncertain risks are even less ideal, this is an effective way for MakerDAO to survive in the market for the long term.
For a decentralized ecosystem with global influence, the efficiency that can compete with the existing traditional financial system is only one factor. What is more important is the intangible value created around community membership tokens and user experience. In cryptocurrencies, it is not difficult to see that the value growth of top assets such as Bitcoin, Dogecoin, and NFT most of the time far exceeds the growth of the token value of MakerDAO and other robust Defi protocols. When considering the value of cryptocurrencies purely based on fundamentals It is biased. In other words, referring to the MEME currency to empower tokens such as $MKR and making good use of the intangible value potential of the community is not only an effective means to solve governance problems such as voter apathy, but also a large-scale application of SubDAOs. A shortcut.
2.2 Overall planning
The Endgame Plan product roadmap is divided into 4 main stages: Pregame, Early Game, Midgame and Endgame, aiming to enhance its efficiency, resilience and participation by creating a strong governance balance, thereby providing SubDAOs with a solid foundation for parallel growth and product innovation. Base. The program promotes the optimization of governance structures and the diversification of product innovation in an evolving, community-driven ecosystem. In the short term, Endgame aims to increase the supply of Dai to over 100 billion within three years and ensure the ecosystem continues to accelerate growth in an autonomous and vibrant DAO economy. Additionally, the plan is designed to securely maintain governance equilibrium, ensuring it can scale to any scale.
 I Pregame
I Pregame
As a testing phase of the product, 6 initial SubDAOs will be run and tested to see if their key functions are functioning properly before the Endgame plan is officially launched. Features worth noting include:
Issuance of respective ERC 20 tokens belonging to SubDAOs, and three farms for token distribution by SubDAOs, that is, the three tokens of $DAI, stETHs synthetic assets $ETHD, and $MKR can be used for liquidity mining of SubDAOs tokens. .
Release of Meta Elixir I and Metanomics I. Form a liquidity pool of DAI:ETHD:MKR = 1: 1: 1 and distribute $MKR tokens to SubDAO.
The establishment of a MIP set can be simply understood as a general charter on how to implement the above measures to prepare for the large-scale automatic issuance of SubDAO in the future.
II Early Game
The Endgame plan will be adjusted and released after the Pregame stage, and it will further enter the Early Game stage. This stage can be broken down into five periods:
Phase 1:
The rebranding of the two tokens, $MKR and $DAI, has transformed them from two independent brands into a single cohesive concept that better communicates and embodies Endgames vision. The two tokens will be maintained, and new versions of $DAI and $MKR will be issued, temporarily called NewStable and NewGovToken.

Phase 2:
Six tested SubDAO and NewStable token farms will be officially launched, and SubDAO tokens will also be distributed through NewStable farms. The main tasks of all SubDAOs are to acquire users and maintain decentralized front-ends, but SubDAOs can be divided into FacilitatorDAOs and AllocatorDAOs according to different business focuses:
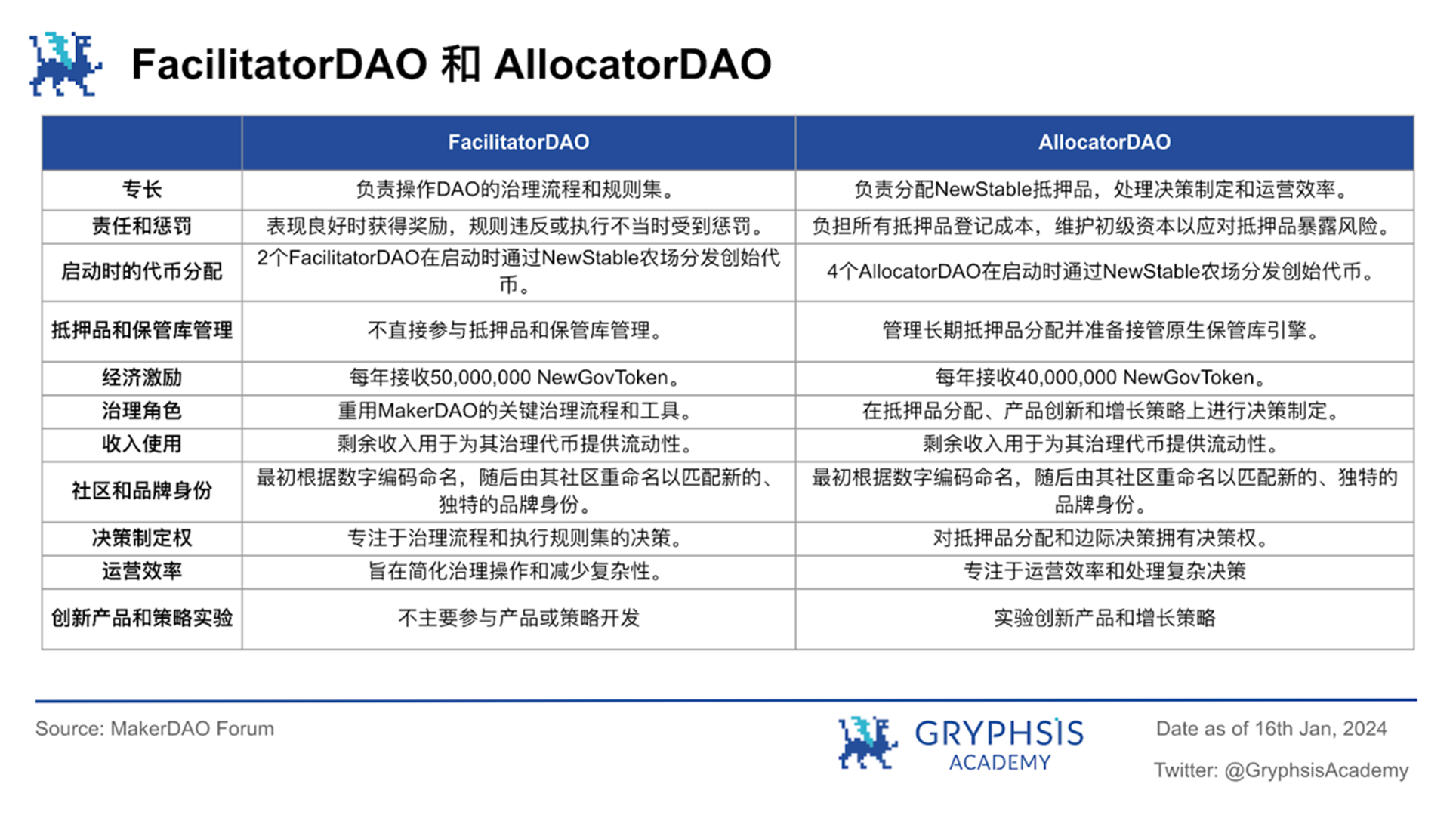 Phase 3:
Phase 3:
After SubDAO is launched, MakerDAO will introduce Atlas to participate in governance and decision-making, making the process more friendly and efficient for NewGovToken holders. Atlas is a giant governance rulebook built as a unified data structure that contains all principles, rules, processes and knowledge for the entire MakerDAO ecosystem. This data is optimized for use with specialized governance AI tools that modify, improve, summarize and interpret Atlas.
Phase 4:
The launch of the Governance Participation Incentive Plan at this stage is a key part of MakerDAOs final plan, mainly through the Sagittarius Lockstake Engine, referred to as SLE, to encourage NewGovToken holders to participate more deeply in DAO governance. At this stage, NewGovToken holders are encouraged to lock up their tokens and delegate voting rights in support of specific governance strategies, a process that occurs through an easy-to-use, gamification-like interface. In order to reward active contributions to the governance process, SLE users will receive 30% of the protocol surplus as NewStable income, or receive SubDAO tokens as rewards. Additionally, to encourage long-term engagement and problem resolution, SLE institutes a 15% exit fee. During the first six months of SLE’s launch, a one-time reward boost will be provided to compensate for the fact that only NewStable users will be able to farm SubDAO tokens in the early stages.
Phase 5:
NewChain release and final end state is the final step towards the Endgame Plan. This phase includes the deployment of NewChain, a brand new blockchain that will host the back-end logic of SubDAO token economics and MakerDAO governance security. The launch of NewChain ensures that NewStable and NewGovToken, as well as $DAI and $MKR, continue to function normally on Ethereum, while gaining additional governance protections through an advanced two-stage bridge design.
The core feature of NewChain is to use hard forks as a governance mechanism to deal with major governance disputes and provide the ultimate level of security for users who rely on Dai and NewStable. In addition, NewChain also has features that optimize the AI-assisted DAO governance process, such as smart contract generation and state leasing, as well as neural token economics emission and each SubDAOs governance Lockstake system, promoting innovation and growth of the entire ecosystem.
The above is the step-by-step plan for MakerDAO starting from Early Game. At present, we have no way to ensure whether Phase 1 to Phase 5 represents the main plan from Early Game to Midgame and finally to Endgame. Therefore, in this $MKR valuation report, we have Contents beyond the currently foreseeable scope will not be discussed.
2.3 Types of collateral
For the short-term income and expenditure analysis of MakerDAO, it is important to understand the underlying assets it introduces. The Endgame plan divides collateral into two types: decentralized assets that can actually guarantee unbiased properties, and real-world assets that can provide reliable liquidity and stability.
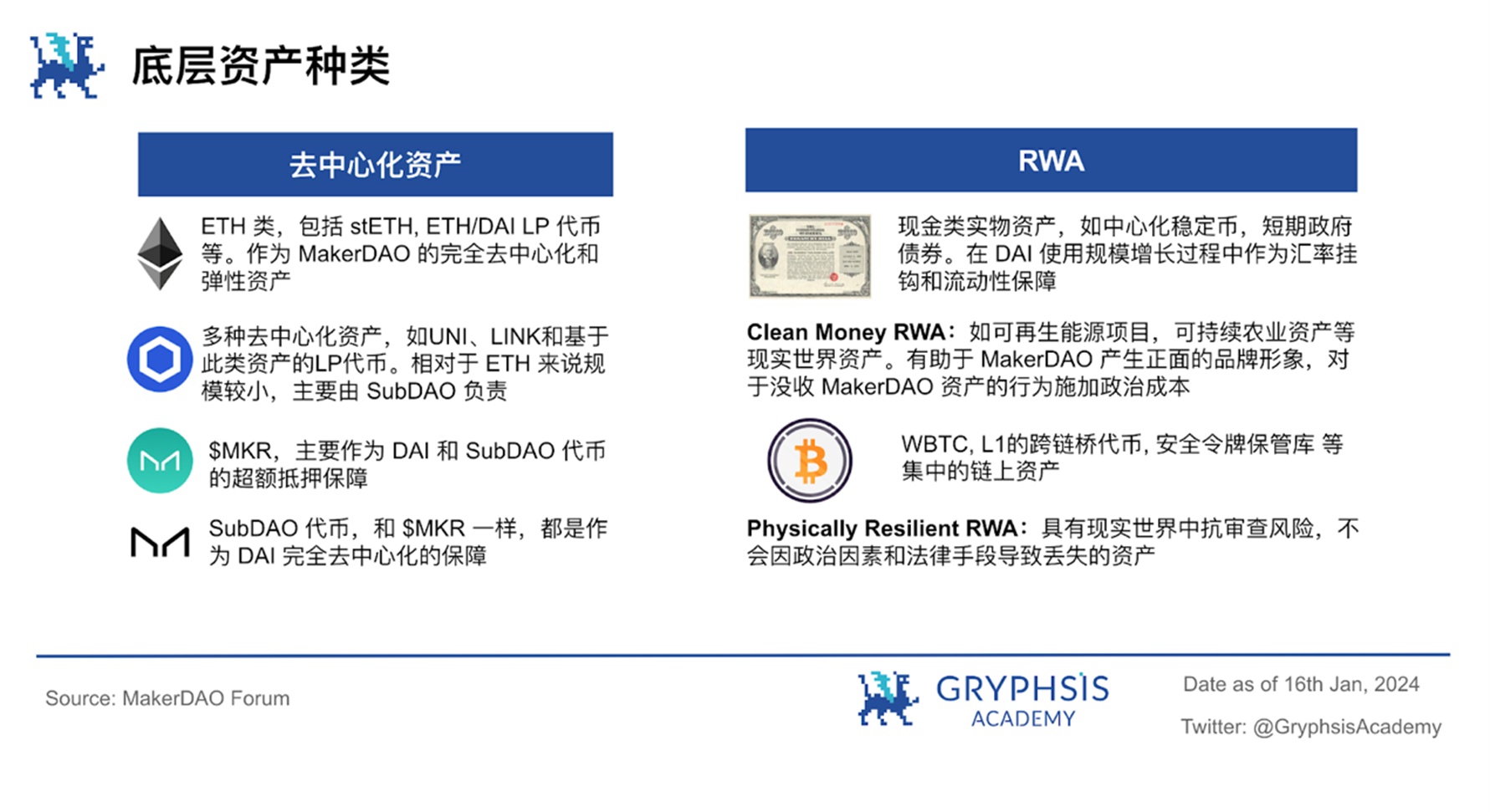 $MKR:The utility of DAIs liquidity support token is reduced, that is, this liquidity support mechanism is changed from mandatory to optional, and whether to enable it is decided based on governance decisions. Instead, if the MakerDAO system suffers losses, it is possible to spread those losses by reducing the target price of DAI (i.e. its price pegged to the US dollar). In Endgames plan, $MKR has become a very useful form of decentralized collateral for DAI through the over-collateralized vault. It can generate stability fees for the protocol and participate in governance. It can also be used to farm SubDAO tokens.
$MKR:The utility of DAIs liquidity support token is reduced, that is, this liquidity support mechanism is changed from mandatory to optional, and whether to enable it is decided based on governance decisions. Instead, if the MakerDAO system suffers losses, it is possible to spread those losses by reducing the target price of DAI (i.e. its price pegged to the US dollar). In Endgames plan, $MKR has become a very useful form of decentralized collateral for DAI through the over-collateralized vault. It can generate stability fees for the protocol and participate in governance. It can also be used to farm SubDAO tokens.
Cash type RWA:RWA assets are currently the most widely used by MakerDAO, such as centralized stablecoins and short-term government bonds. This type of asset is currently an important collateral to maintain the stability of the DAI exchange rate, and judging from the recent performance of US Treasury bonds, it is also one of the main sources of MakerDAOs income. However, the risk of seizure of such assets, or the greatest regulatory risk, is why MakerDAO has to go through three different stages to reduce the proportion of such assets in the balance sheet as much as possible.
2.4 Three stages
Terminology:
DSR:DAI deposit interest rate
SFBR:Stability fee basic interest rate (same as the loan interest rate Stability Fee in this report)
TR:A mechanism that continuously changes the DAI target price over time, a positive TR increases the demand for DAI and decreases the supply of DAI. The main purpose of TR is to control MakerDAOs exposure to RWA assets and encourage the generation of DAI through more decentralized collateral such as ETH.
In summary, SFBR and TR can be understood as the rates for all stable pools and the rates specifically for decentralized asset stable pools. Increasing SFBR and TR is equivalent to increasing DSR in disguise, which will lead to an increase in the cost of obtaining DAI through mortgage. Reducing the supply of DAI will also increase the demand for DAI, thereby raising the price of DAI.
Pigeon stage:
When regulatory risks are low and global economic conditions are stable, use Cashlike RWA assets to generate as much income as possible and accumulate ETH to deposit in the treasury to deal with future crises. The original plan is that the dovish stance will continue until 2025, when there will be an expansion of the dovish stance timeline to accumulate more capital if there are no obvious regulatory risks.
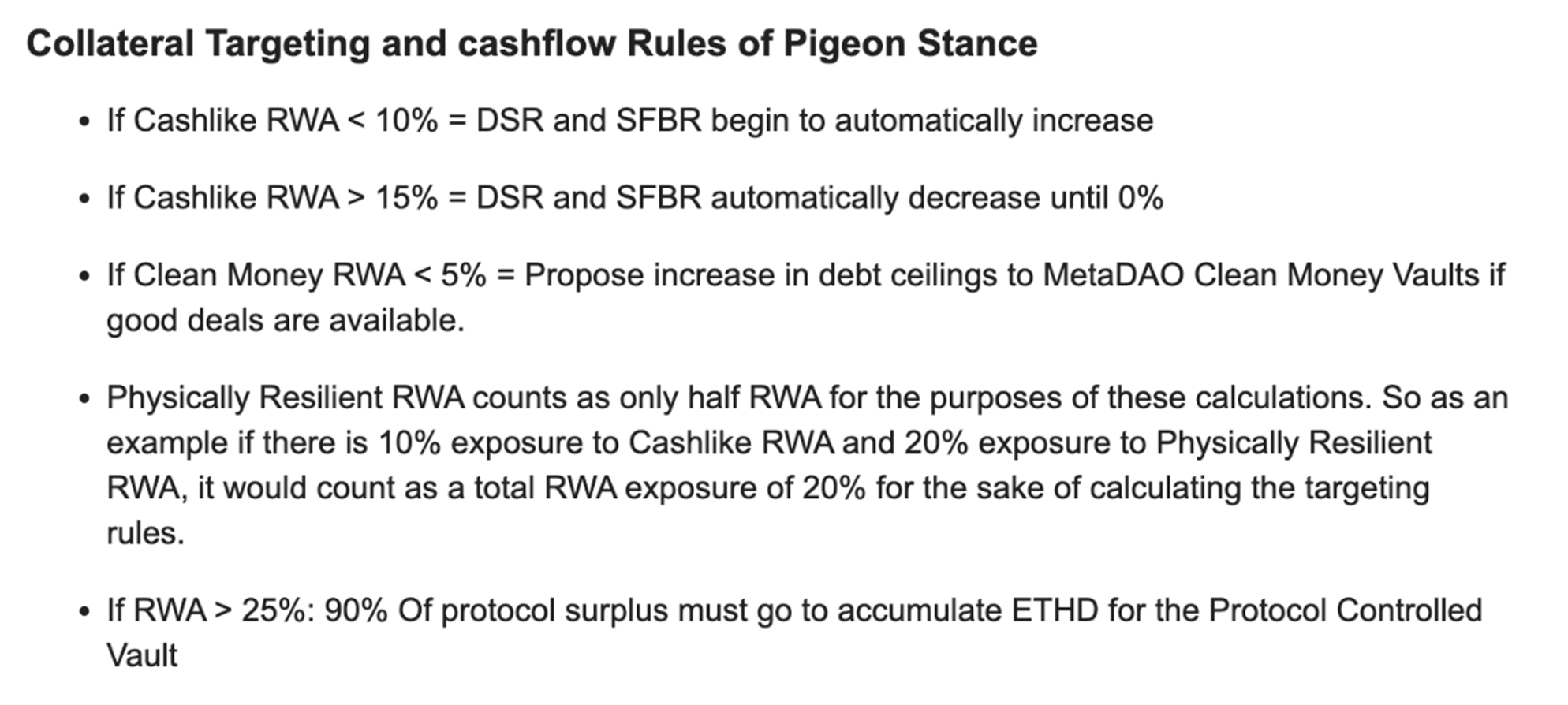
Source: https://forum.makerdao.com/t/endgame-plan-v3-complete-overview/17427
Eagle stage:It ensures that the seizable RWA exposure does not exceed 25%, and decouples DAI from the US dollar when necessary, so that DAI can withstand the most severe regulatory crackdowns without cutting off its connection with real-world assets.
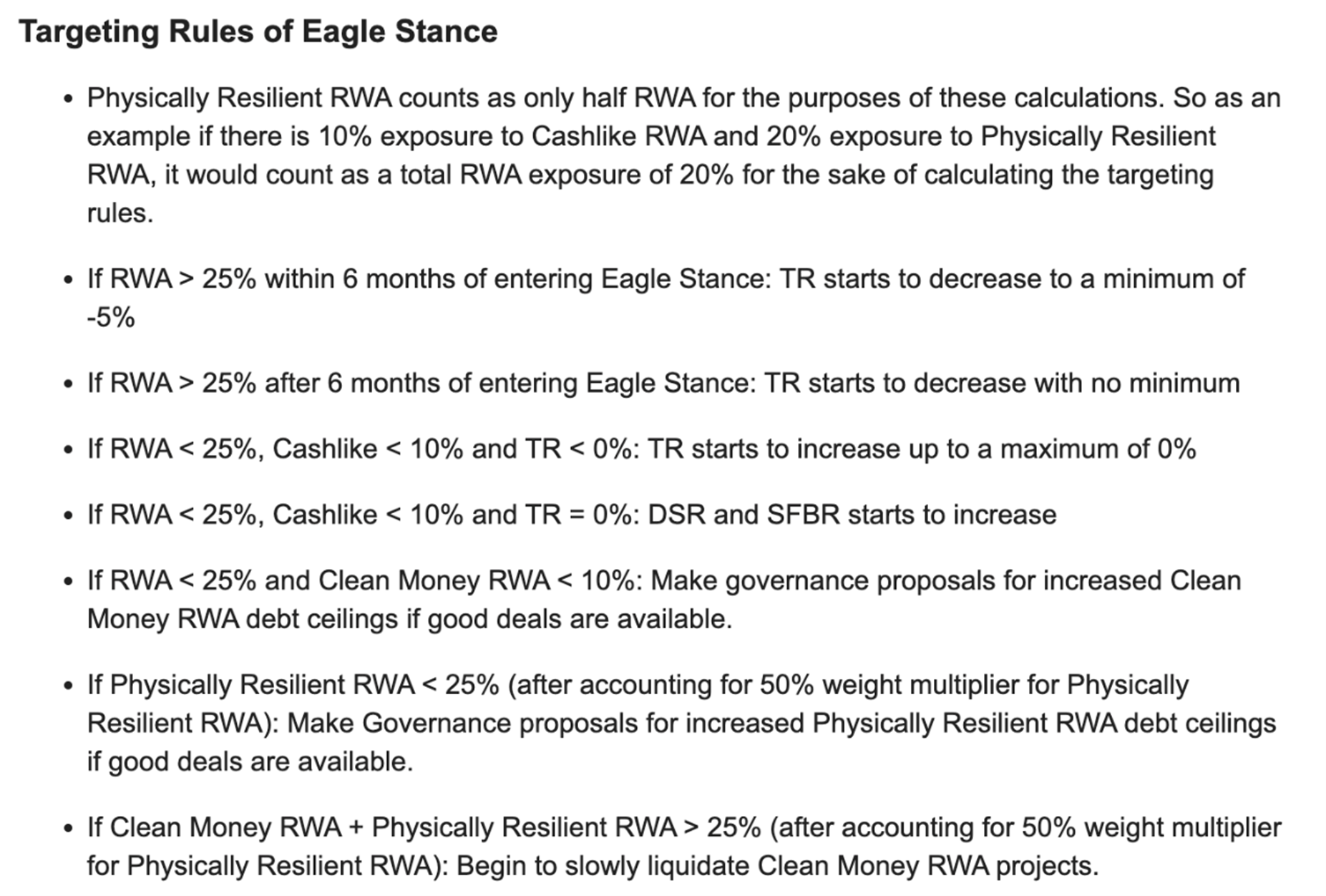
Source: https://forum.makerdao.com/t/endgame-plan-v3-complete-overview/17427
Phoenix stage:
Measures to deal with extreme situations, using only decentralized assets and Physically Resilient RWA assets as collateral, the target exchange rate of DAI will be adjusted based on market price deviations, rather than relying on collateral in PSM.

Source: https://forum.makerdao.com/t/endgame-plan-v3-complete-overview/17427
With reference to the current regulatory attitude and the operating status of MakerDAO, we predict that MakerDAO will be in a dovish state in the next three years. At the same time, its RWA asset proportion planning for the dovish state is not fully applicable. In this valuation report, we based on its current asset proportion Make predictions based on ratios and a rough plan to capture as much gain as possible during the dovish phase.At the same time, until MakerDAO empowers $MKR, we will temporarily regard $MKR as a project token closely related to MakerDAOs revenue.
3. Tokenomics
3.1 $MKR Token Utility
The $MKR token is the core of the MakerDAO ecosystem and serves two key functions. First of all, it represents governance voting rights, allowing holders to vote on MakerDAO proposals and thus directly participate in the decision-making process of the protocol. This includes decisions on system parameters, protocol upgrades, and governance policies. Secondly, when the system has insufficient funds to repay DAI debt, MakerDAO can issue new $MKR tokens to offset bad debts and maintain the stability of the economic system. This mechanism ensures the health of the $DAI stablecoin and the overall stability of the system, while providing $MKR token holders with the ability to directly influence the future of the protocol.
3.2 $MKR Token Distribution
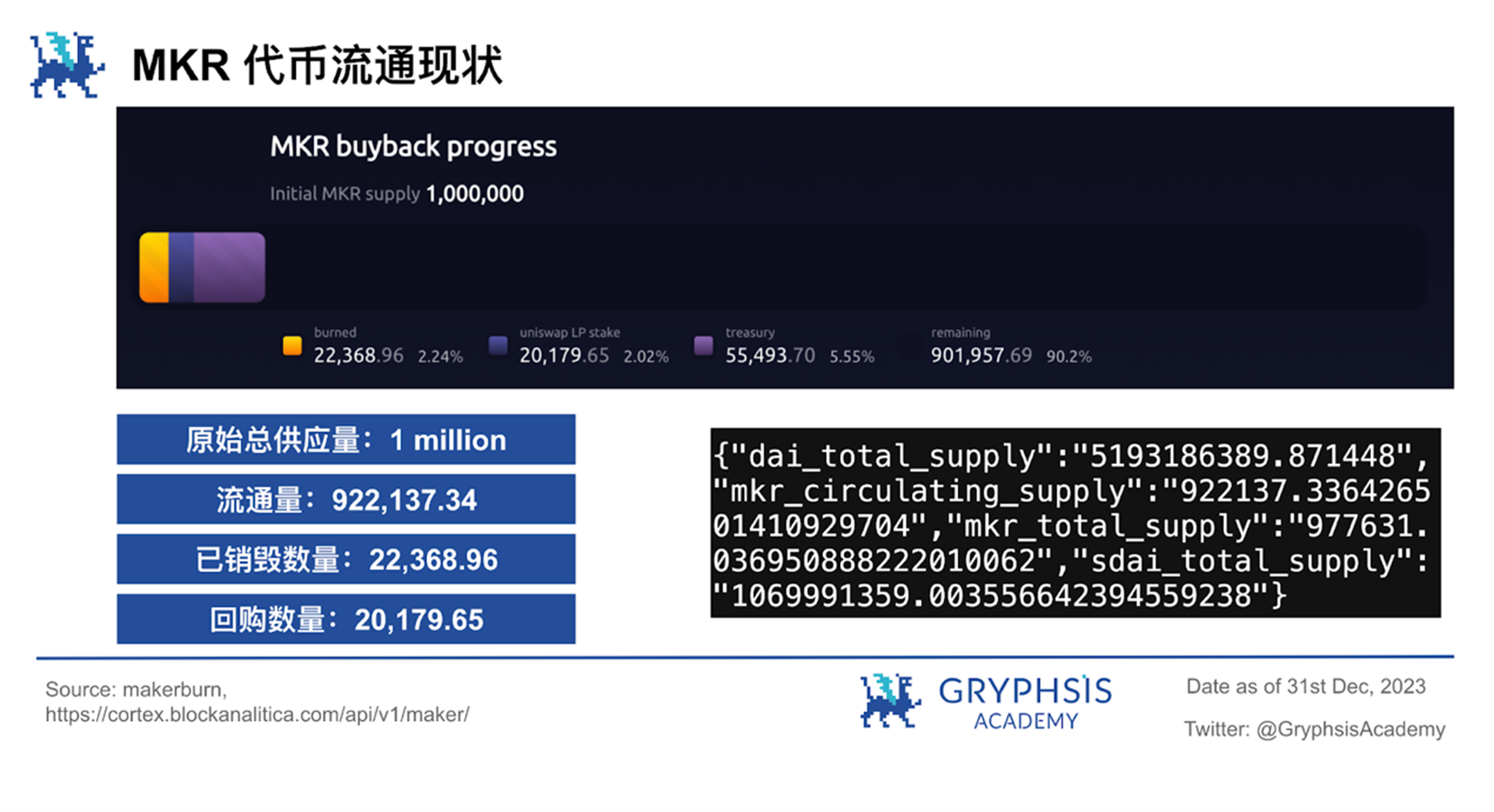
MakerDAO manages and regulates the supply of $MKR tokens through its unique stock buyback model. The core of this model is a mechanism called the Surplus Buffer, which is the primary destination for all revenue from the MakerDAO protocol. The primary purpose of the surplus buffer is to provide a first line of defense against loan shortfalls. When a loan gap occurs, funds from the surplus buffer will first be used to cover the gap. Only if the surplus buffer is insufficient to cover the shortfall, the Maker protocol will make up the difference by issuing additional $MKR tokens.
It is worth noting that the surplus buffer has a set upper limit. When the funds in the surplus buffer exceed this limit, additional Dai will be used to repurchase $MKR tokens, and the repurchased $MKR tokens will be destroyed before June 2023. This mechanism is designed to reduce the total supply of $MKR, thereby providing value to existing $MKR holders. In the long term, this buyback and burn mechanism will result in a reduction in the supply of $MKR. To date, 22,368.96 $MKR tokens have been repurchased and burned, which accounts for 2.237% of the total supply. This ongoing buyback and burn activity reflects the financial health of the MakerDAO protocol and the scarcity of the $MKR token, having a somewhat positive impact on the market value of $MKR.
Since June 2023, in MakerDAOs updated smart combustion engine, funds exceeding the newly set surplus buffer will be used to purchase $MKR tokens, and the purchased $MKR will be composed of the corresponding amount of ¥DAI trading pairs and provide liquidity on Uniswap V2. The generated liquidity provision tokens (LP Tokens) are then transferred to addresses owned by the protocol. The main purpose of this move is to further control the supply, liquidity and other mechanisms of the circulation of $MKR tokens and DAI tokens under the agreement. In essence, it is to regulate the supply of $MKR tokens in the open market, which can be understood as a Active market making.
At the same time, the smart burning engine is based on a valuation model that optimizes the process of burning tokens when the $MKR token price is low. When $MKR market cap falls below its valuation target, the protocol will burn accumulated Elixir ($MKR/$ETH/$DAI liquidity tokens). Additionally, the plan introduces an annual new issuance of $MKR tokens to offset the concentration of holders caused by burning. This mechanism is designed to create a dynamic balance where an equal amount of $MKR is burned and issued each year, thus supporting a healthy circulation of the token. The value of $MKR will be driven by a combination of its burning mechanism, the SubDAO token yield available to active voters, and the ability to generate low-interest, high-collateralization $DAI for active voters.
3.3 MakerDAO profit model
3.3.1 Lending interest income (Stability fee)
Before the introduction of RWA assets, MakerDAOs main source of income was loan interest income, which is the loan interest paid when users mortgage crypto assets in exchange for $DAI. The following is MakerDAOs on-chain mortgage pool and corresponding interest:
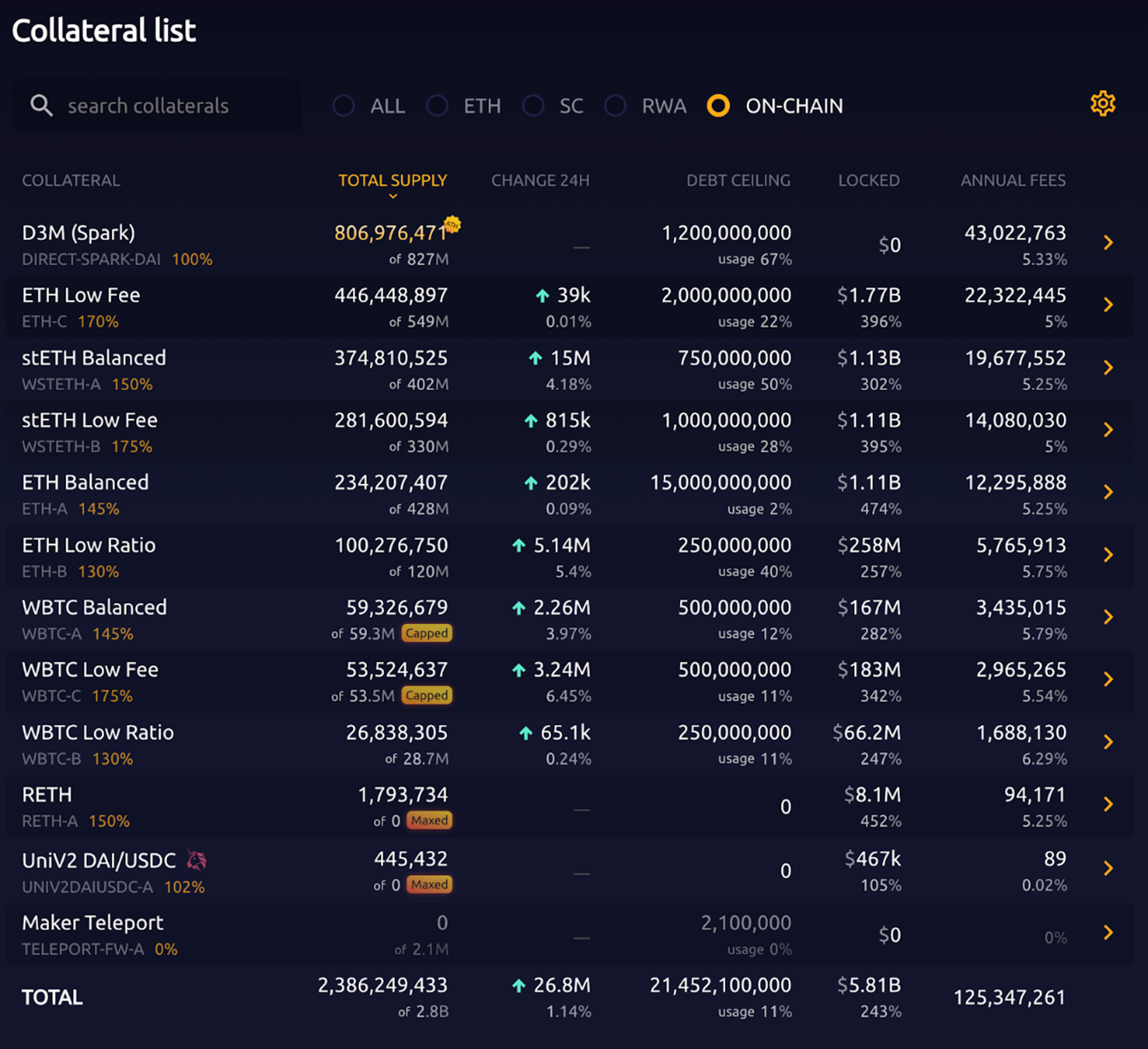
Source: makerburn
Combined with Dunes data, most of MakerDAOs income before October 2022 comes from the interest income of the above $ETH lending pools. In 2022, due to the collapse of $UST, a large number of users have withdrawn from the encryption market, and stablecoin TVL has dropped significantly. MakerDAO needs to take interest rate cuts to try to retain users and stabilize its own financial situation; at the same time, the lending rates of competitors such as Aave have also dropped to 0 %; and MakerDAO’s plan to exchange stable currency reserves such as $USDC into interest-bearing assets such as government bonds has begun to be implemented.
The stable fee rate of almost 0 in 2022 makes 2022 a year where MakerDAO can barely make ends meet, so starting in 2023, income from RWA assets such as treasury bonds gradually began to account for the majority of MakerDAOs total income.
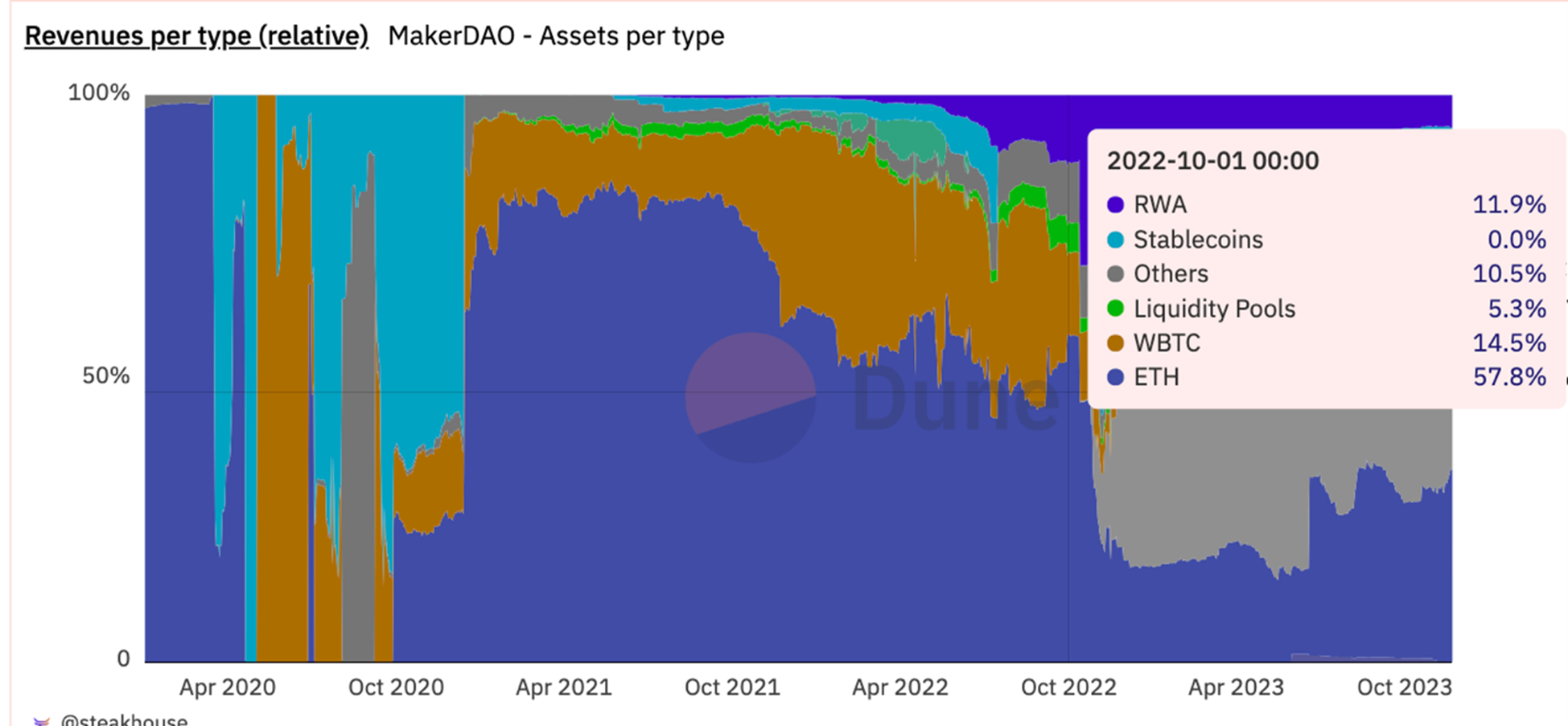
Source: https://dune.com/steakhouse/makerdao
3.3.2 Real world asset income (RWA income)
As U.S. Treasury bond yields have gradually increased since the end of 2021, the income from MakerDAOs U.S. Treasury bond reserves has also increased until today this source of income accounts for more than half of MakerDAOs total revenue.
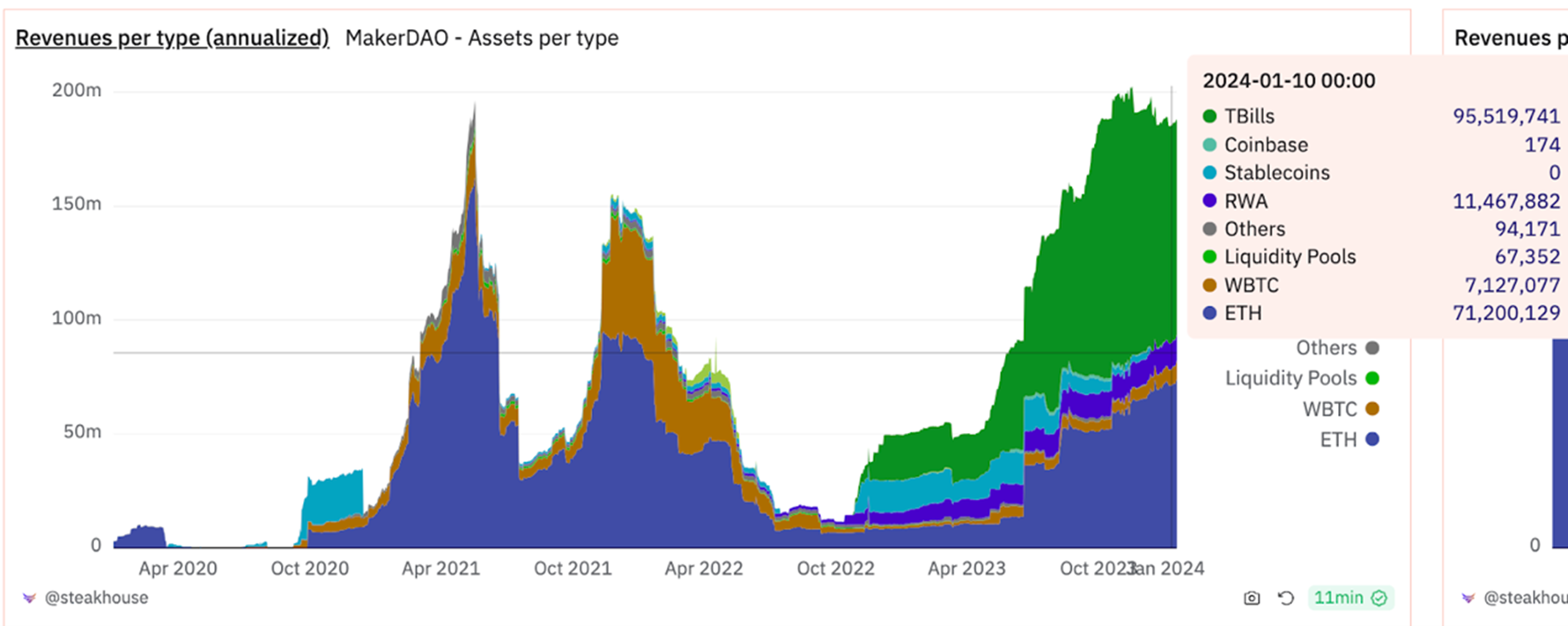
Source: https://dune.com/steakhouse/makerdao
3.3.3 Liquidation income
When the price of the users crypto assets drops rapidly to the liquidation line, MakerDAO will liquidate the users crypto assets and charge a certain fee. This part of the revenue once helped MakerDAO obtain certain profits when the market fluctuated greatly in 2022, but the market fluctuations were relatively stable. At this time, we do not expect to maintain MakerDAOs operations through liquidation revenue.
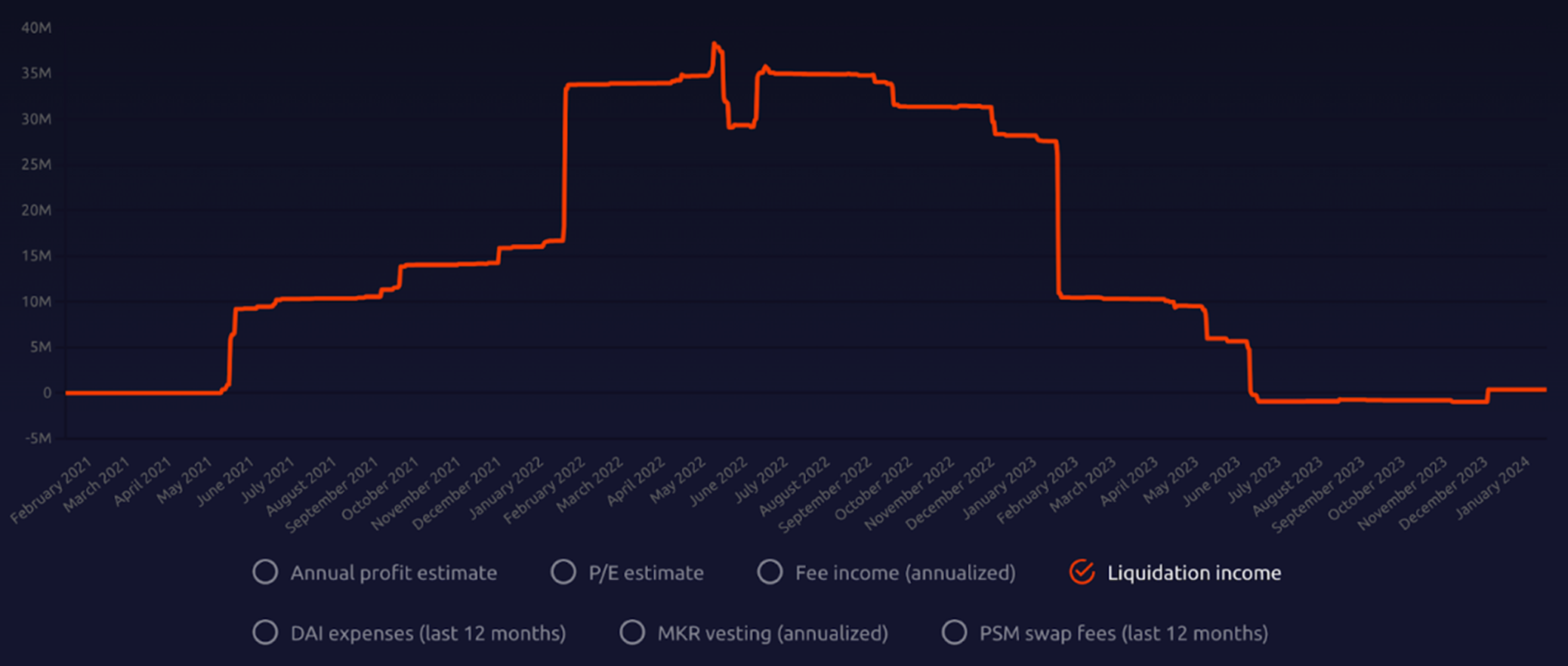
Source: Makerburn
3.3.4 PSM(PSM revenue)
Users can swap $DAI with other stablecoins (such as $USDC) at a ratio very close to 1:1 through PSM. The small fee levied during this exchange process is the PSM exchange fee. This fee is used to regulate the supply of $DAI, helping to maintain its value stability and as part of the system’s revenue. During periods of market volatility, PSM allows MakerDAO to effectively regulate $DAI’s liquidity and its price peg in this way.
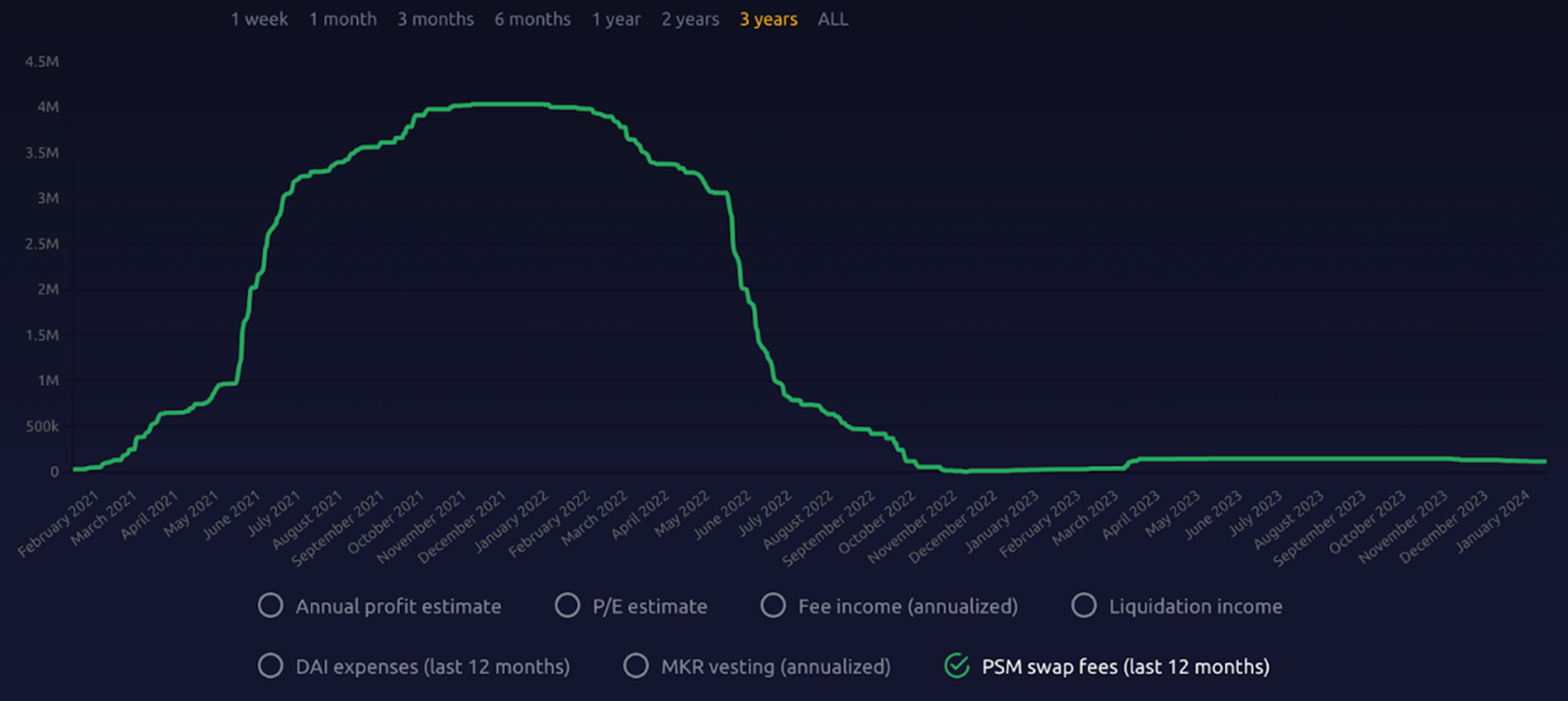
Source: Makerburn
4. Valuation Model
Our valuation is based on the Discounted Cash Flow Analysis (DCF) methodology, which is included in our valuation model (MKR Valuation Model) has a more detailed derivation, and the valuation can be adjusted accordingly based on actual future market conditions. Below is a detailed description and explanation of the valuation method.
4.1 Discounted cash flow analysis (DCF)
For ease of understanding, MakerDAO can be regarded as a temporarily unregulated currency issuer similar to a bank. If initial users need to use the decentralized stable currency $DAI to trade, they must obtain $DAI through over-collateralized assets and pay to MakerDAO borrows interest. At the same time, MakerDAO also uses the interest fees paid by borrowers to provide DSR, providing depositors of $DAI with exposure to regular savings interest.
Initially, MakerDAOs main sources of income include users over-collateralizing crypto assets and real-world assets to lend stablecoins $DAI to collect a certain loan interest (Stability fee), and liquidation fees (Liquidation income) collected when the value of users mortgage assets falls below the liquidation line. ) and PSM’s stablecoin transaction fees (PSM revenue). Starting from the end of 2022, MakerDAO will gradually replace most of its PSM underlying assets from stable currencies such as USDC to real-world assets such as U.S. bonds and U.S. bond ETFs that can bring stable income. This additional fixed income (RWA income) has now become MakerDAO’s current The largest source of income, followed by interest income from ETH lending.
Based on the above conditions, we believe that the discounted cash flow method is most suitable for the valuation of $MKR currency price. Discounted cash flow (DCF) is an absolute valuation method used to estimate the value of an asset based on its expected future cash flows. The principle is that the value of a company is calculated based on the cash flows it can generate in the future, which is equal to the cash flow discounted at a discount rate that reflects its risk. Our model is based on the data before December 31, 2023, takes 3 years as the prediction period, and uses the terminal value to represent the future long-term cash flow under the ongoing operation of the agreement, estimating the $MKR token on March 1, 2024 the value of.
4.1.1 Assumptions
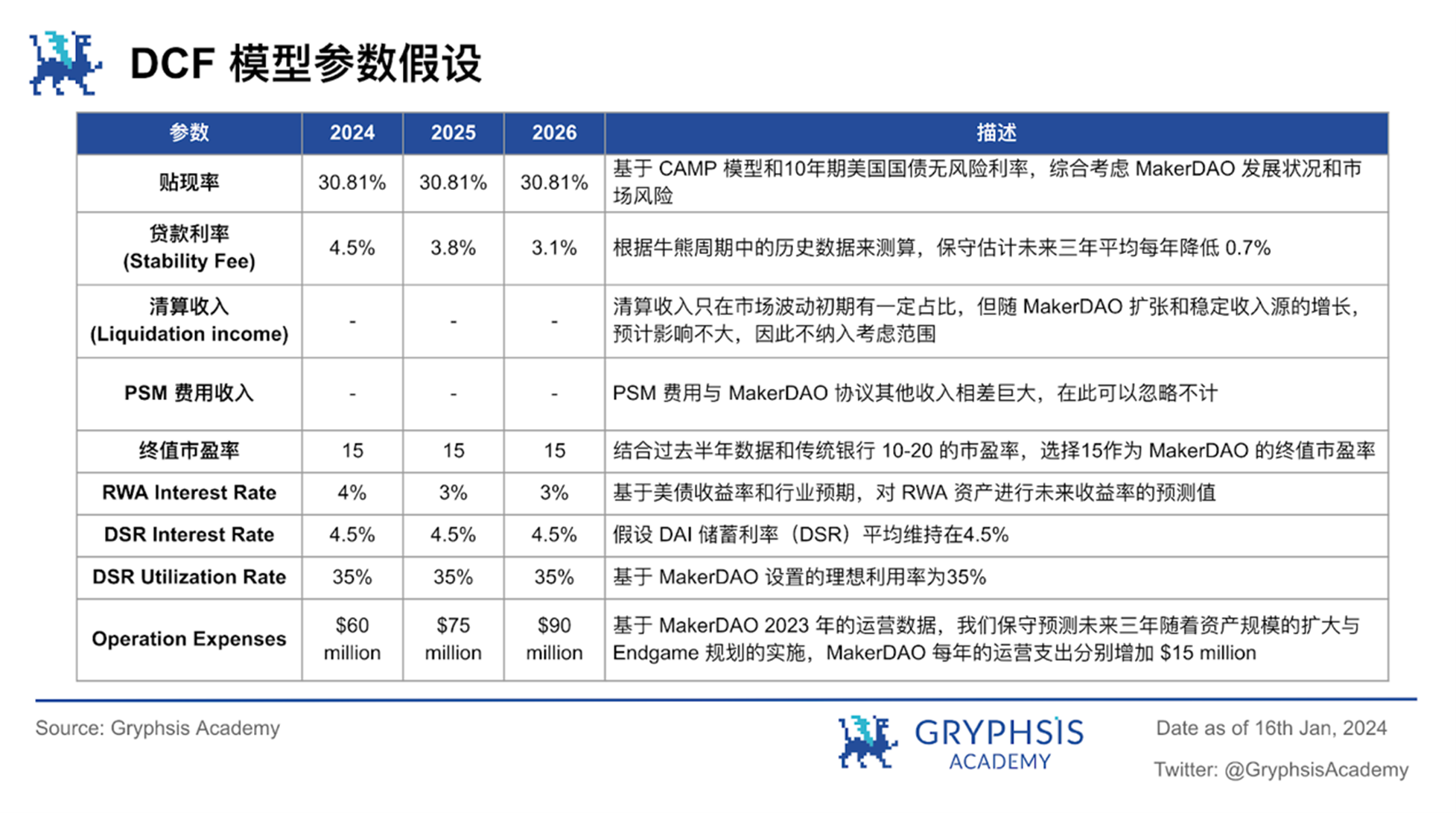
The construction of this model is based on a series of key premises and takes into account Endgames data such as the proportion of RWA assets at different stages and the U.S. Treasury bond interest rate cut cycle, reflecting the predictive valuation of MakerDAOs development trend in the next three years. These assumptions are the cornerstone of model evaluation and have been integrated into our valuation framework, allowing flexibility to adapt to changing market conditions. A detailed description of the assumptions can be found in the following sections.
DAI Total Supply:
The growth of the total supply of DAI has a significant impact on valuation because it directly drives total interest income (Stability fee), which is currently the second largest source of income, and indirectly affects liquidation income (Liquidation income). According to the last research report, we will predict the total supply of DAI through the share of CDP stablecoins in the stablecoin market and the market share of DAI in CDP stablecoins.
The first is the stablecoin TVL. Referring to the growth rate from April 21 to April 22, it is divided into the following three situations:
Current: 130, 646.0 million
Bear: 2024 - 10% ;2025 - 20% ;2026 - 30%
Base: 2024 - 15% ;2025 - 30% ;2026 - 45%
Bull: 2024 - 20% ;2025 - 40% ;2026 - 60%
Our view is that we are currently in a rate hike cycle.A method like MakerDAO that can bring the interest of off-chain risk-free income assets to the chain and distribute it to stablecoin holders, that is, DSR, is compared to the traditional $USDC and $USDT that treat this part of the income as the project party’s profit. It will be more favored by the market, but because the current ecosystem is still developing, decentralized stablecoins have a series of problems such as difficulty in depositing and withdrawing funds, and are not user-friendly, so their market share is still hovering at a low level of 7%.(Most of the interest given by DSR comes from MakerDAO’s mortgage loan income, but in theory it can use the additional income from RWA as DSR interest)
In view of the fact that the introduction of RWA assets enables CDP stablecoins to generate stable interest at present, we make a rough prediction of the share of CDP stablecoins in the stablecoin market based on three different market conditions:
Bear: 2024 - 12% ;2025 - 15% ;2026 - 18%
Base: 2024 - 17% ;2025 - 20% ;2026 - 23%
Bull: 2024 - 22% ;2025 - 25% ;2026 - 28%
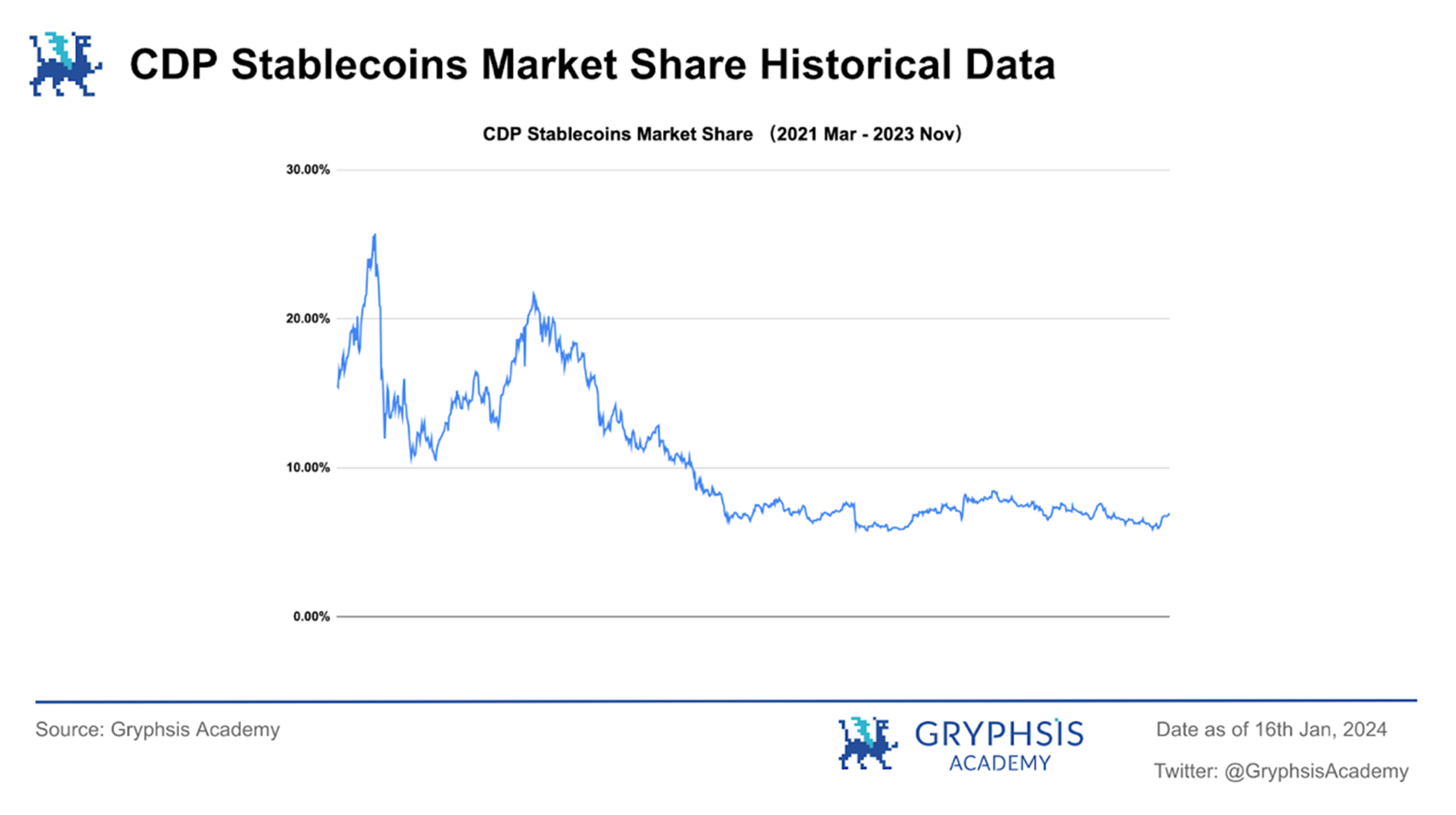
At the same time, in the CDP stablecoin market, since CDP TVL became relatively stable in July 2022, DAIs proportion in CDP stablecoins has been hovering around 60% - 70%. We can predict that the increase in the CDP stablecoin market share in the future will lead to a greater Many project parties such as Aave are working on similar stablecoin projects. As competition becomes more intense and technical barriers in this field are almost negligible for leading projects, DAI’s market share of CDP stablecoins in the next three years can be divided into the following three situations. :
Bear: 2024 - 65% ;2025 - 55% ;2026 - 45%
Base: 2024 - 65% ;2025 - 60% ;2026 - 55%
Bull: 2024 - 65% ;2025 - 70% ;2026 - 75%
RWA asset proportion:
The current proportion of RWA assets in MakerDAOs total assets is 46.40%. According to the Endgame plan, the proportion of U.S. debt assets will gradually decrease in response to different regulatory situations. It is expected to drop to 15% around 2025. We assume that RWA assets will account for 10% of MakerDAOs total assets in the next three years. The ratio is:
Bear: 2024 - 40% ;2025 - 22% ;2026 - 4%
Base: 2024 - 44% ;2025 - 30% ;2026 - 16%
Bull: 2024 - 58% ;2025 - 63% ;2026 - 68%
The remaining numerical predictions are detailed in the table below:
 $MKR token deflation:
$MKR token deflation:
In view of the fact that MakerDAO will start to rebrand the $MKR token in early 2024, with expectations of additional issuance and deflation of the smart combustion engine, as far as its plan is concerned, it will keep the circulation of $MKR tokens unchanged. The valuation is based on the existing The circulation volume is calculated.
4.1.2 DCF Model
The following are the corresponding DCF results in the three scenarios:
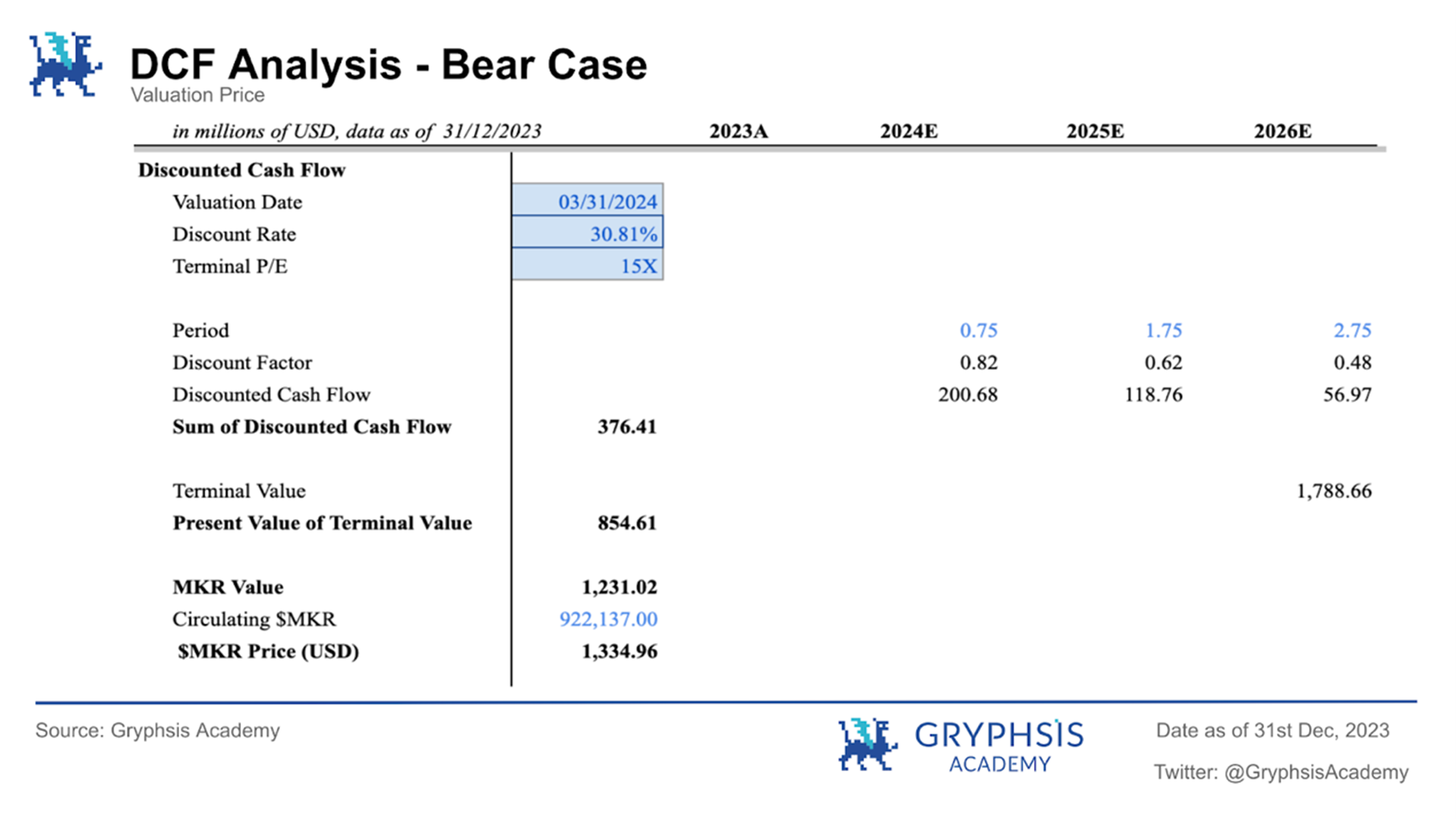
Bear market situation:
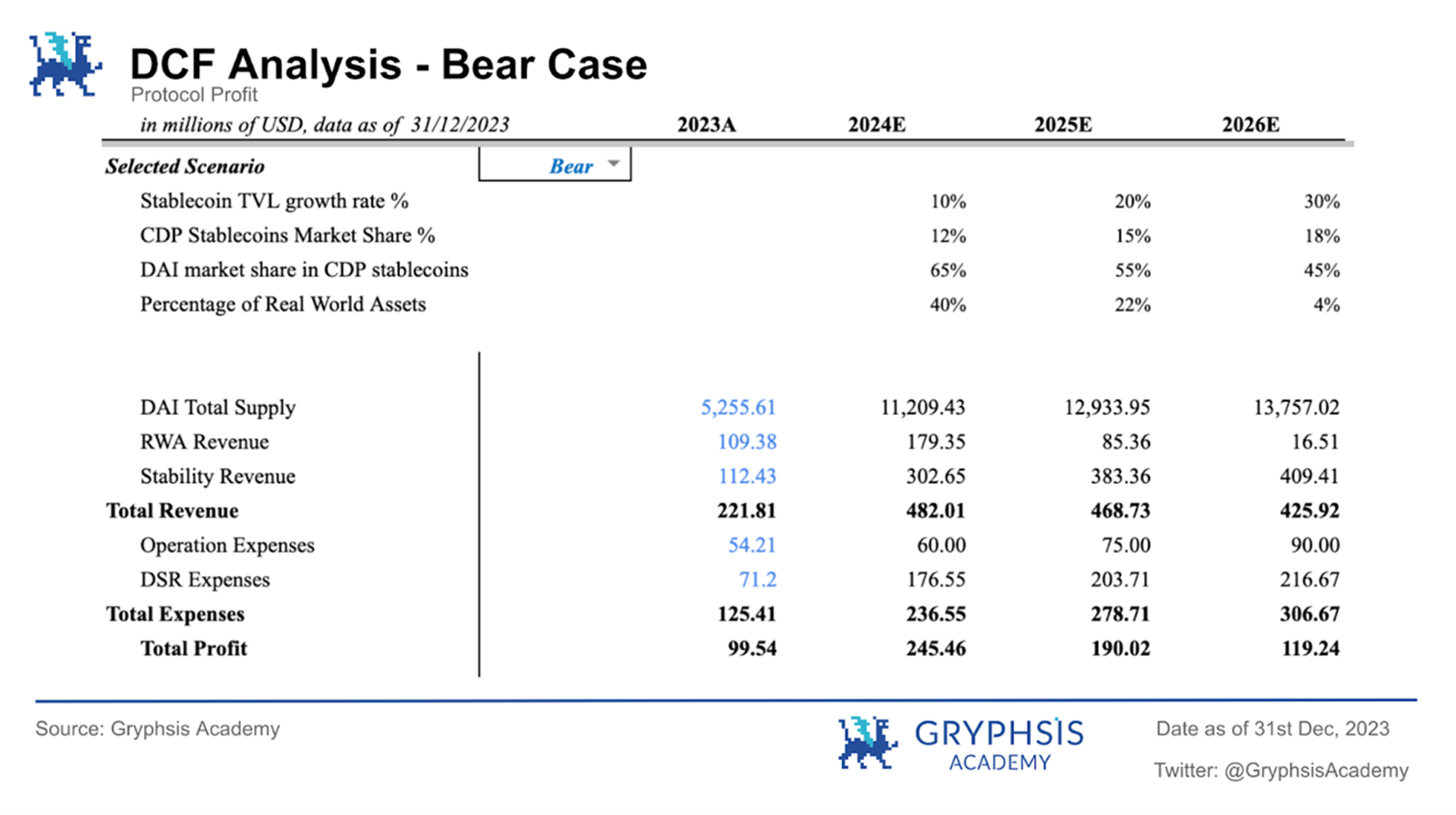
During the bear market, the $MKR token price is expected to be $1,334.96, with the protocol valuation on March 1, 2024 being $1.231 billion.
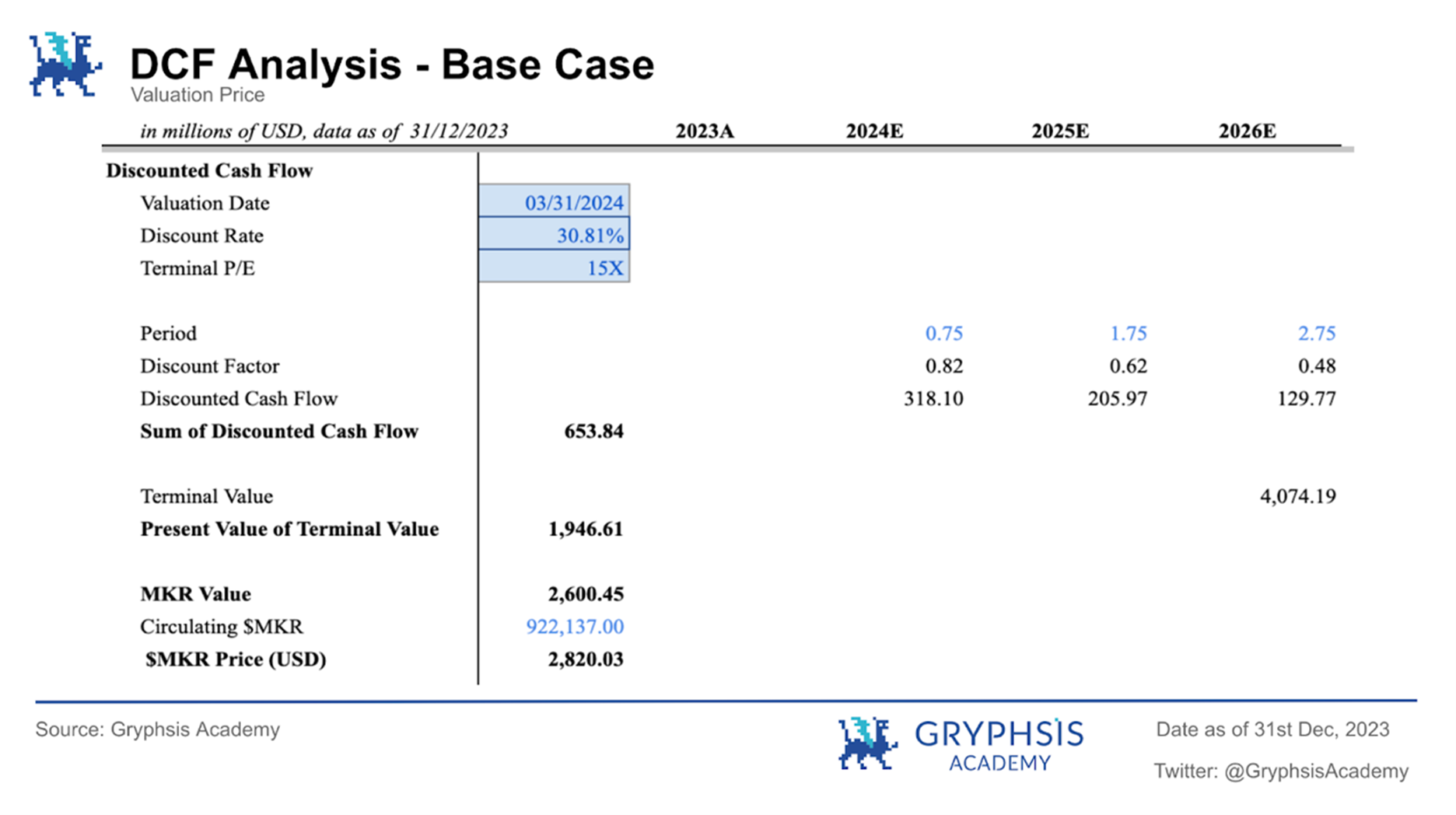
Baseline case:
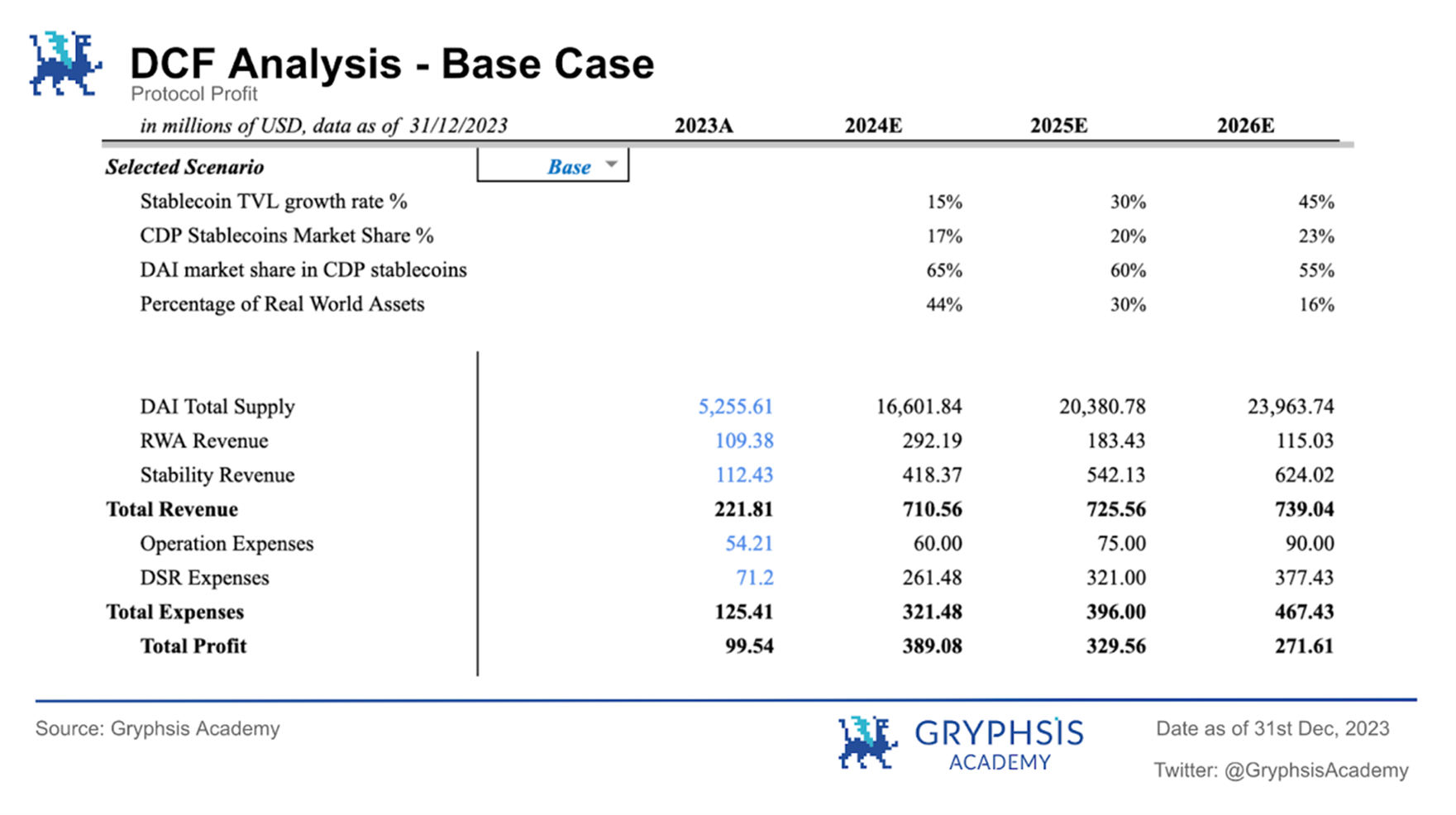
In the base case, the $MKR token price is expected to be $2,820.03, with the protocol valuation on March 1, 2024 being $2.600 billion.
Bull market situation:
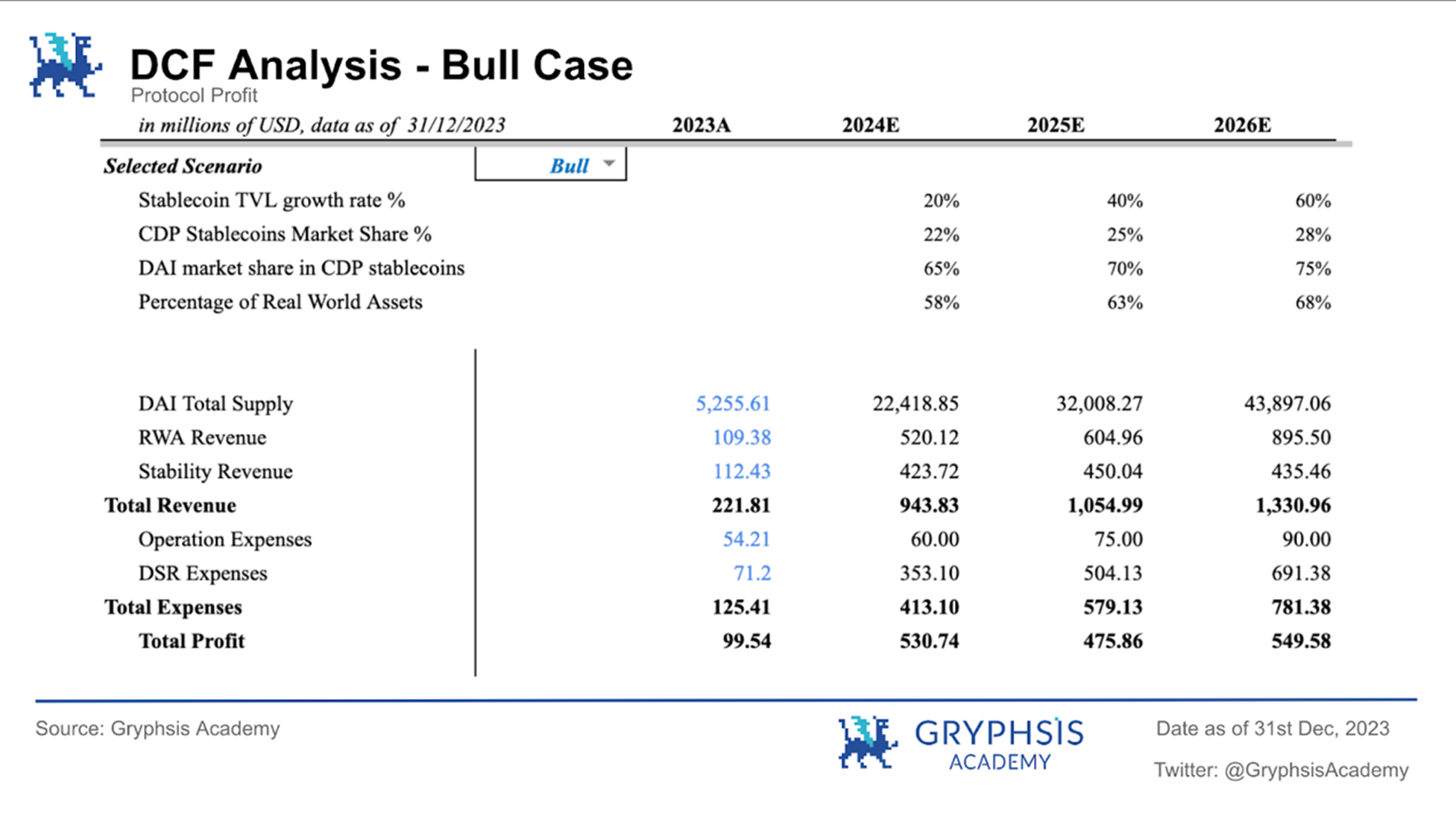 During the bull run, the $MKR token price was expected to be $5,349.17, with the protocol valuation on March 1, 2024 at $4.933 billion.
During the bull run, the $MKR token price was expected to be $5,349.17, with the protocol valuation on March 1, 2024 at $4.933 billion.
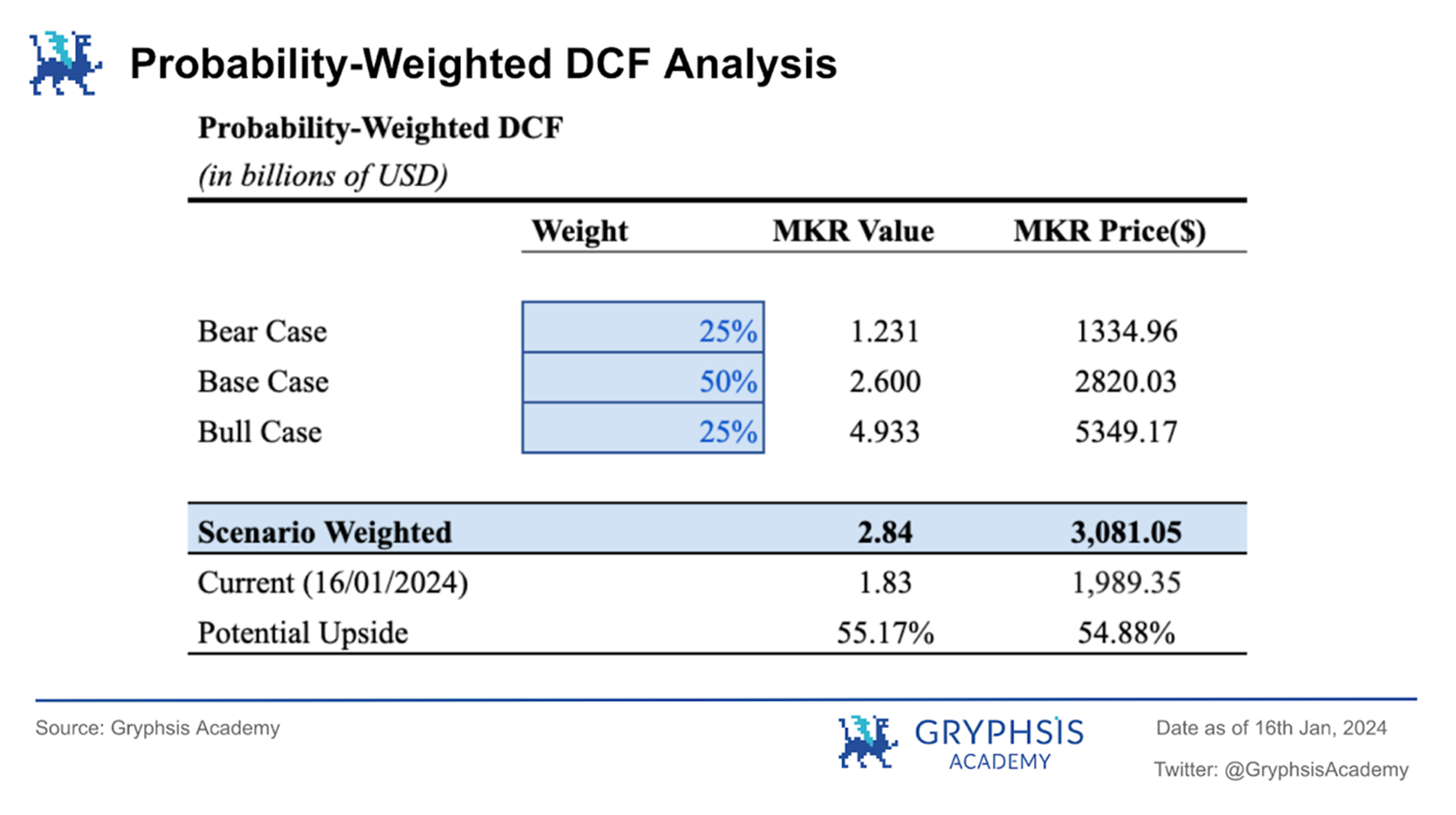
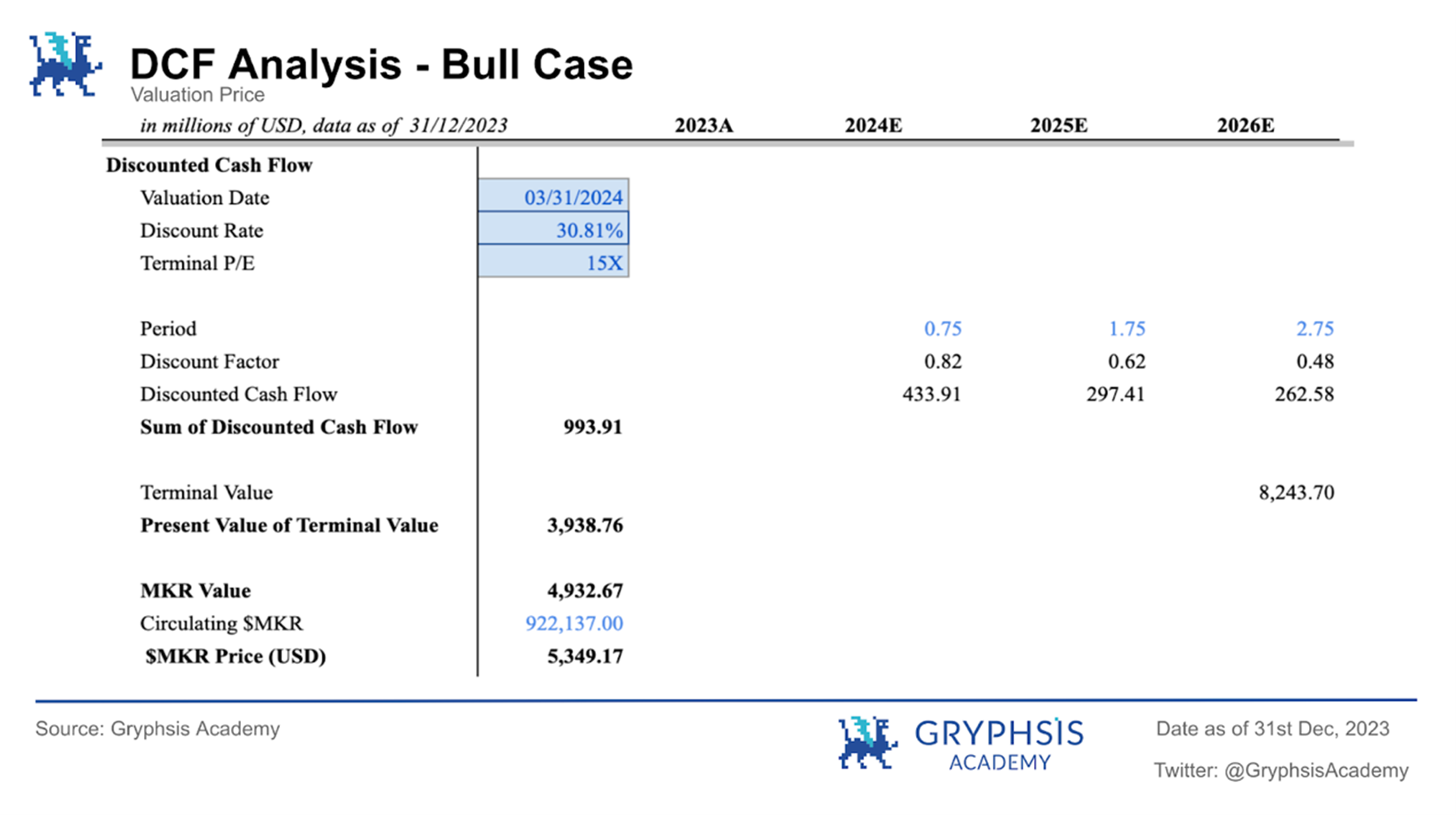 4.1.3 Probability weighted scenario analysis
4.1.3 Probability weighted scenario analysis
We assign a probability of 25% to the bull and bear markets respectively, and a probability of 50% to the baseline scenario. The probability-weighted DCF valuation of the $MKR token price is $3,081.05, valuing the protocol at $2.84 billion. The price of the $MKR token on January 16, 2024 was $1,989.35, still with a potential upside of 54.88%.
4.2 Comparable analysis
Comparable analysis is a commonly used valuation method that performs valuation by comparing it with similar companies in the same industry. The basic assumption is that similar companies should have similar valuation multiples, such as price-to-sales (P/S) and price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios. Of course, it needs to be stated that there may be certain limitations when using this valuation method to value these lending protocols in the field of decentralized finance, because reliable sales revenue data may not be available.
When conducting a comparability analysis, it is critical to select businesses that are as similar as possible in terms of industry, business model, risk profile and market dynamics. By ensuring comparability in these aspects, the impact of external factors is reduced, allowing us to focus on the intrinsic value drivers of the companies being analyzed. If the comparable companies we select belong to the decentralized lending industry and have similar business nature and risk profile as MakerDAO, this can enhance the effectiveness of the comparative analysis. Here we select AAVE, Curve Finance and Compound, three companies that are also leaders in the lending business and have certain business similarities with MakerDAO, for comparability analysis.
4.2.1 Valuation assumptions and variable considerations
Price/Earnings Ratio: The Price/Earnings Ratio helps investors evaluate the investment value and risk level of the project by considering the relationship between the token price and the protocol profit. The P/E ratio of different industries and project types may vary greatly. , so it is usually necessary to compare with blockchain projects in the same industry or market averages.
Price/Sales Ratio: The price-to-sales ratio is often used to evaluate the valuation of companies in the same industry based on revenue. For decentralized lending protocols, protocol revenue (known as “sales revenue” in traditional companies) is a key factor in assessing their financial performance and sustainability. Use the price-to-sales ratio to understand how the market assesses the protocols earning power.
PEG indicator (price-to-earnings ratio/net profit growth rate): For lending protocols like MakerDAO, the recent introduction of U.S. debt assets as underlying assets has significantly increased the protocol revenue. Using the past average protocol revenue to calculate the price-to-earnings ratio/price-to-sales ratio for valuation will inevitably lead to errors. Biased. We introduce the PEG indicator to make up for the shortcomings of PE valuation in evaluating the dynamic growth of the protocol. When PEG > 1, the price-to-earnings ratio is higher than the protocols profit growth rate, which is overvalued; PEG< 1, it means that the company is developing rapidly, but this development is not reflected by the price-earnings ratio for the time being, and it is undervalued. Based on the PEG indicator, we can roughly make a more comprehensive judgment on comparable valuations.
Average P/S ratio: We adopt the market multiplier method commonly used in the encryption industry and use the weighted average of the price-to-sales ratios of four comparable protocols as the market multiplier 1. By calculating the weighted average of the price-to-earnings ratio or price-to-sales ratio obtained by the agreement through FDV/Market Cap, we basically take into account the upper and lower limits of comparable projects and the weight of projects with different market capitalizations, providing a more balanced market multiple estimate. Therefore, we choose to use the weighted average of comparable items as a quantitative market multiplier to avoid the potential bias that may arise from relying solely on the maximum or minimum value. However, please note that due to the accuracy limitations of revenue and other data, this value is for comparative reference only. .
Median: Statistically speaking, the median is not affected by extreme values in the distribution sequence, which improves the representativeness of the distribution sequence to a certain extent. Therefore, we believe that choosing the median as the market multiplier of 2 is reasonable.
Fee revenue (Annualized Total Revenue): By analyzing the revenue generated by a blockchain project, its ability to generate revenue and maintain operations can be evaluated. Revenue is a key indicator of a projects financial health and growth potential. The evaluation of protocol fee income helps to understand the revenue streams directly related to lending activities and the profitability of the lending agreement. Protocol income can come from various sources within the lending agreement, including lending interest, RWA proceeds, etc. By considering protocol fee revenue as a variable, analysts can evaluate the diversification of revenue streams. This helps assess a protocol’s ability to withstand market fluctuations and long-term viability.
Profit (Annualized Revenue to $MKR Holders): In the traditional stock market, earnings in P/E refers to the net profit actually earned by the company during a specific period of time (usually quarterly or annual), which is what investors focus on An important financial indicator used to measure a companys profitability and financial health. However, in the blockchain space, the concept of “earnings” may not be applicable. This is because DeFi projects don’t make money in traditional ways, and they typically don’t have net profits or earnings per share similar to traditional companies. Instead, their economic models may involve token transaction fees, liquidity mining rewards, loan interest, etc. being converted to net income for the project or token holders. When valuing the $MKR token in PE, we refer to Makerburn’s method and use its net profit for calculation.
4.2.2 Valuation using comparable analysis method
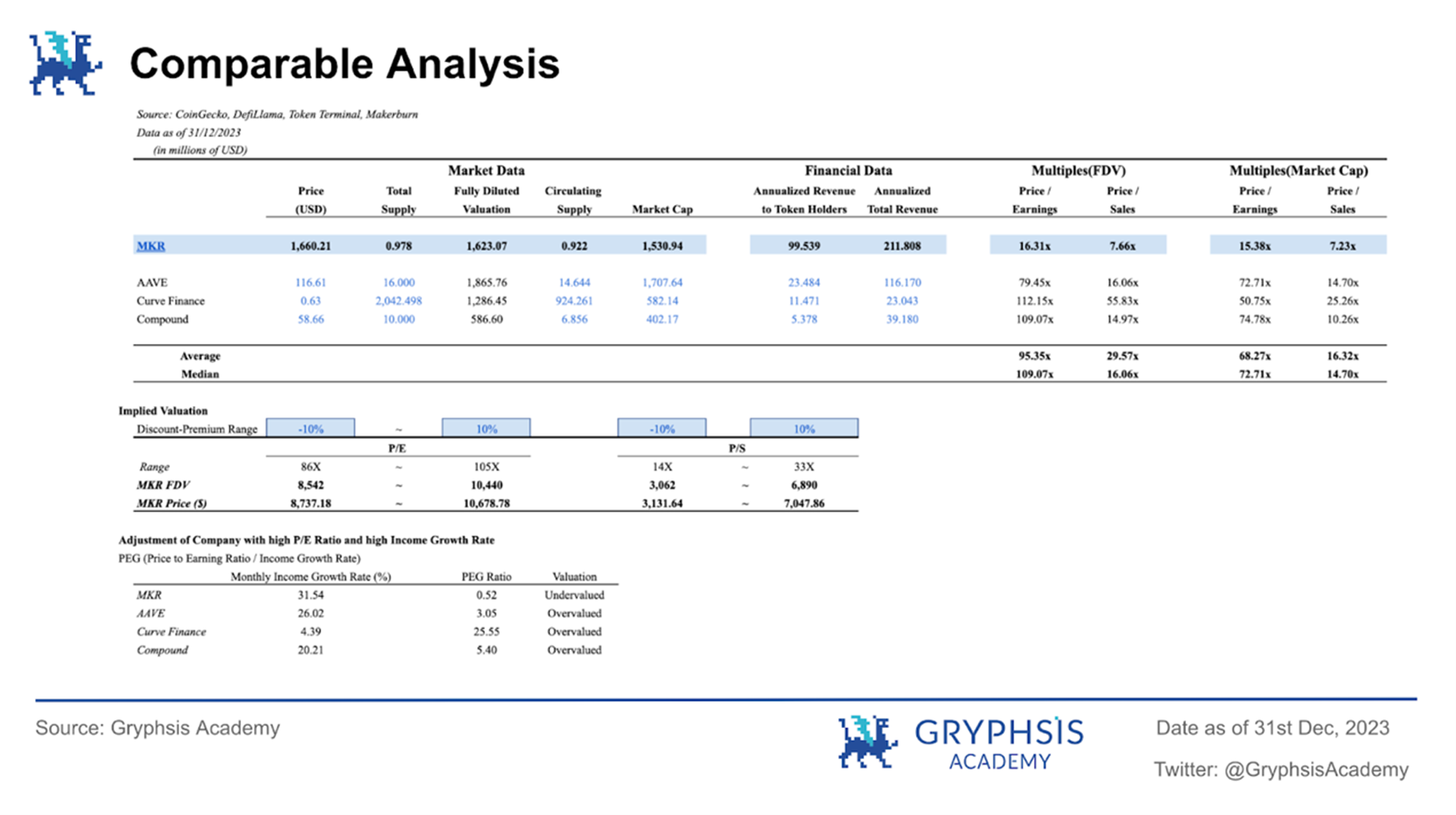 The chart above shows the project valuation and token price based on Price/Earnings Ratio and Price/Sales Ratio. We used data from January to December 2023 to estimate the projects fee income and net income for the entire year. MakerDAOs estimated annualized total revenue is US$211 million, which shows that as one of the leaders in the lending industry, combined with the current considerable U.S. bond yields, it has good income-generating capabilities. Additionally, $MKR has a low price-to-earnings ratio relative to the average ratio of selected decentralized lending protocols, which is also reflected through the PEG metric, and $MKR may be undervalued compared to the other three protocols. Finally, based on the P/E ratio, the $MKR token price range is between $8,737.18 - $10,678.78; based on the P/S ratio, the $MKR token price range is between $3,131.64 - $7,047.86.
The chart above shows the project valuation and token price based on Price/Earnings Ratio and Price/Sales Ratio. We used data from January to December 2023 to estimate the projects fee income and net income for the entire year. MakerDAOs estimated annualized total revenue is US$211 million, which shows that as one of the leaders in the lending industry, combined with the current considerable U.S. bond yields, it has good income-generating capabilities. Additionally, $MKR has a low price-to-earnings ratio relative to the average ratio of selected decentralized lending protocols, which is also reflected through the PEG metric, and $MKR may be undervalued compared to the other three protocols. Finally, based on the P/E ratio, the $MKR token price range is between $8,737.18 - $10,678.78; based on the P/S ratio, the $MKR token price range is between $3,131.64 - $7,047.86.
4.3 Comprehensive analysis
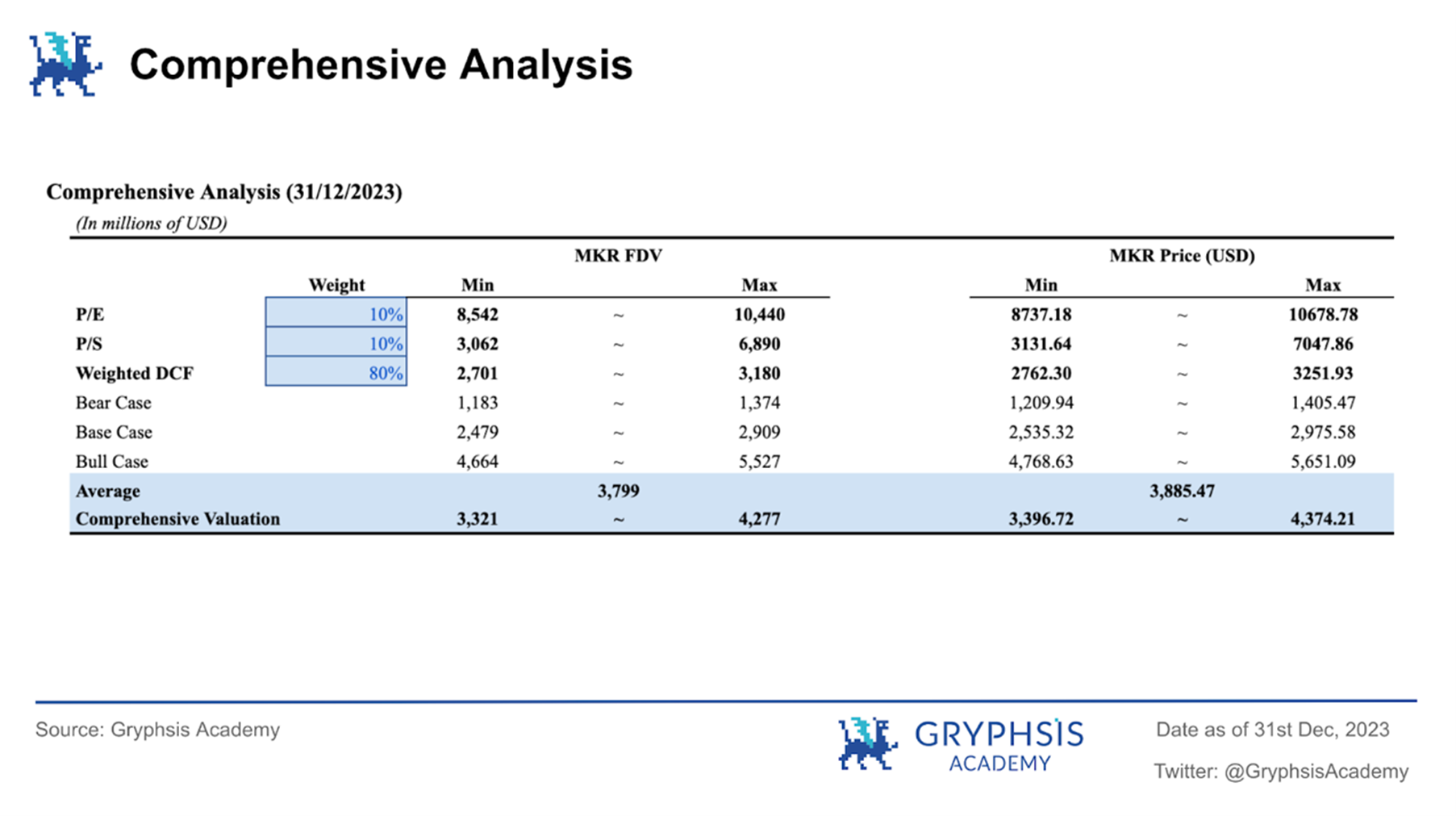 Combining the results of DCF valuation and comparable analysis valuation, we conduct a comprehensive valuation of the $MKR token:
Combining the results of DCF valuation and comparable analysis valuation, we conduct a comprehensive valuation of the $MKR token:
First, we conducted a sensitivity analysis on the key variables in the DCF valuation model, and selected the maximum and minimum values of the probability-weighted DCF valuation under different termination price-earnings ratios and discount rates based on the sensitivity analysis results. In the comparable analysis, since MKRs price-to-earnings ratio/price-to-sales ratio is quite different from other agreements in the industry, taking into account the accuracy of the data, we gave the P/E and P/S valuation models a weight of 10% each, and the other 80%. % is assigned to the weighted DCF valuation. Comprehensive analysis results show that the token price range of $MKR is $3396.72 - $4374.21, and the fully diluted valuation (FDV) range is $3.321 billion - $4.277 billion
In addition, as the above PEG indicator points out, our current valuation of the $MKR token based on the P/E indicator is a relatively conservative valuation. Compared with its rapid growth in net income after the introduction of RWA assets, the current P/E estimate is The value is an underestimate.
The establishment of the valuation model and the derived token price are based on the current data provided and market operations. Actual future market dynamics and MakerDAOs operating performance will ultimately determine its true market value.
5. Risks
5.1 $MKR Distribution
Dilution risk of $MKR tokens: A key feature of MakerDAO’s operating mechanism is the issuance of new $MKR tokens in the event of a shortage of loans. Although this measure is to maintain the stability and liquidity of the system, it also brings the risk of dilution of $MKR tokens. At the same time, the issuance of new tokens may expose existing token holders to the risk of a decrease in value. This dilutive effect could have a negative impact on the market price of $MKR, especially if market demand for $MKR remains unchanged.
5.2 Regulatory risks
Impact of Endgame Planning: The Endgame planning currently being considered by MakerDAO involves several different operational postures, including hawk and phoenix postures. The selection and implementation of these strategies will have a significant impact on MakerDAOs overall earnings and market positioning. In particular, adopting a hawkish stance or a phoenix stance could lead to fundamental changes in operating strategies and risk management approaches, which could impact the value and appeal of the $MKR token.
Potential Impact of Decoupling DAI from the U.S. Dollar: The planned decoupling of MakerDAO stablecoin $DAI from the U.S. dollar is a major strategic adjustment that may lead to user loss and market uncertainty in the short term. As a key DeFi asset, $DAIs connection to the U.S. dollar directly affects its stability and user trust. Any decoupling efforts will need to be carefully managed to avoid negative impacts on the overall ecosystem.
6. Summary
This article uses cash flow analysis (DCF) to reasonably calculate the value of the $MKR token. By probability weighting, MakerDAO is valued at $2.84 billion and $MKR has an expected price of $3,081.05, with a potential upside of nearly 54.88%. Finally, combining the P/E and P/S valuation methods, a comprehensive analysis concluded that the token price range of $MKR after the end of the first quarter of 2024 is $3396.72 - $4374.21, which is consistent with the current token price of $MKR on the market. In comparison, there is still some upside potential.
In the rapidly evolving and highly competitive DeFi market, MakerDAO’s long-term survival and success will be highly dependent on its ability to adapt to regulatory changes and market demands. The Endgame plan is a big step for MakerDAO and even Defi. It remains to be seen whether MakerDAO, which is trying to cross the river by feeling the stones, can really become the efficient and innovative organization it dreams of. We will continue to pay attention to developments in relevant fields in order to provide investors with accurate and timely market analysis.
References
https://forum.makerdao.com/t/endgame-plan-v3-complete-overview/17427/2
https://forum.makerdao.com/t/the-5-phases-of-endgame/20830
https://dune.com/steakhouse/makerdao
https://makerburn.com/#/estimate
https://cryptorank.io/price/maker
https://etherscan.io/token/0x9f8f72aa9304c8b593d555f12ef6589cc3a579a2
https://www.coingecko.com/en/coins/maker
https://coinmarketcap.com/currencies/maker/
https://tokenterminal.com/terminal/projects/makerdao/financial-statement
https://expenses.makerdao.network/
[Statement] This report is produced by@GryphsisAcademy Contributors@yelsanwongCompleted original work, tutored by Gryphsis Academy@CryptoScott_ETH and@Zou_BlockGive suggestions for modifications. The authors are solely responsible for all content, which does not necessarily reflect the views of Gryphsis Academy, nor the views of the organization that commissioned the report. Editorial content and decisions are not influenced by readers. Please be aware that the author may own the cryptocurrencies mentioned in this report. This document is for informational purposes only and should not be relied upon for investment decisions. It is strongly recommended that you conduct your own research and consult with an unbiased financial, tax or legal advisor before making any investment decisions. Remember, the past performance of any asset does not guarantee future returns.