Original author: Xinwei, Severin, Ian, MT Capital
TL;DR
Celestia currently shows a solid staking trend, with a staking rate of 48.88% and a staking annualized rate of return (APR) of 15.74%, and it is predicted that it will reach the ideal staking rate limit by the end of 2024. Since no new tokens will be unlocked before November 2024, it is expected that the actual circulation of its tokens will continue to decrease, thus having a positive impact on the price. At the same time, the Celestia network currently maintains 100 active nodes.
Celestia’s current data usage is only 0.1% of total daily capacity, despite this, its activity is growing compared to Ethereum. As data usage increases, future fees may increase significantly. If the daily data capacity of 46,080 MB is reached throughout the year, the annual fee will be as high as approximately $5.2 million, which is 65 times the current Ethereum data fee. User demand is expected to come from high-TPS applications and games, and a large number of chains based on Celestia RaaS will emerge in the next few months.
EigenDAs adoption of erasure coding, KZG commitment, ACeD and other technologies, as well as the decoupling of DA and consensus, enable EigenDA to provide excellent performance far exceeding the Ethereum DA solution in terms of transaction throughput, node load and DA cost. Compared with other DA solutions, EigenDA also has the advantages of lower startup and staking costs, faster network communication, data submission speed, and higher flexibility.
Comparing Celestia and EigenDA, Celestias competitive advantages lie in extremely low data availability costs and higher data throughput, which makes Celestia more popular among small and medium-sized L2 and application chains. EigenDAs competitive advantage lies in its potentially higher security and Ethereum orthodoxy, which makes EigenDA likely to become a rational choice for more large-scale L2 sources of revenue and expenditure. In the future, Celestia will be able to enjoy the incremental market gains brought by the dual trend of modularization + application chain, while EigenDA will gain more access to the Ethereum-based stock market that has higher security requirements.
The NEAR protocol enhances scalability and decentralization through sharding technology and stateless verification, simplifying data management for L2 projects. Avail optimizes blockchain data processing and storage through a modular system, supports asynchronous interaction between application chains, improves network performance, and enables light clients to effectively verify data integrity. Together, these technologies promote the user-friendliness of blockchain technology and the development of a decentralized digital world.
introduction
The data availability layer has become an important part of the modular architecture. DA has gradually become one of the hottest tracks in 2024. Discussions about Ethereum DA, Celestia and other DA solutions are also endless in the market. This article will conduct an in-depth discussion on the core mechanisms, characteristics, comparisons and future development expectations of Celestia and EigenDA, the core players of the DA track, and scan other players on the DA track to help readers have an overview of the current development of the DA track and understand The future competitive landscape of the DA circuit.
Celestia
Celestia is the first modular Data Availability (DA) network designed to scale securely as the number of users grows. This modularity allows anyone to easily launch an independent blockchain.
Celestia technical features
1. Modular DA Network
Celestia’s design separates execution, consensus, settlement, and data availability. This modular structure allows for specialization and optimization at every level, improving the overall efficiency and scalability of the network.
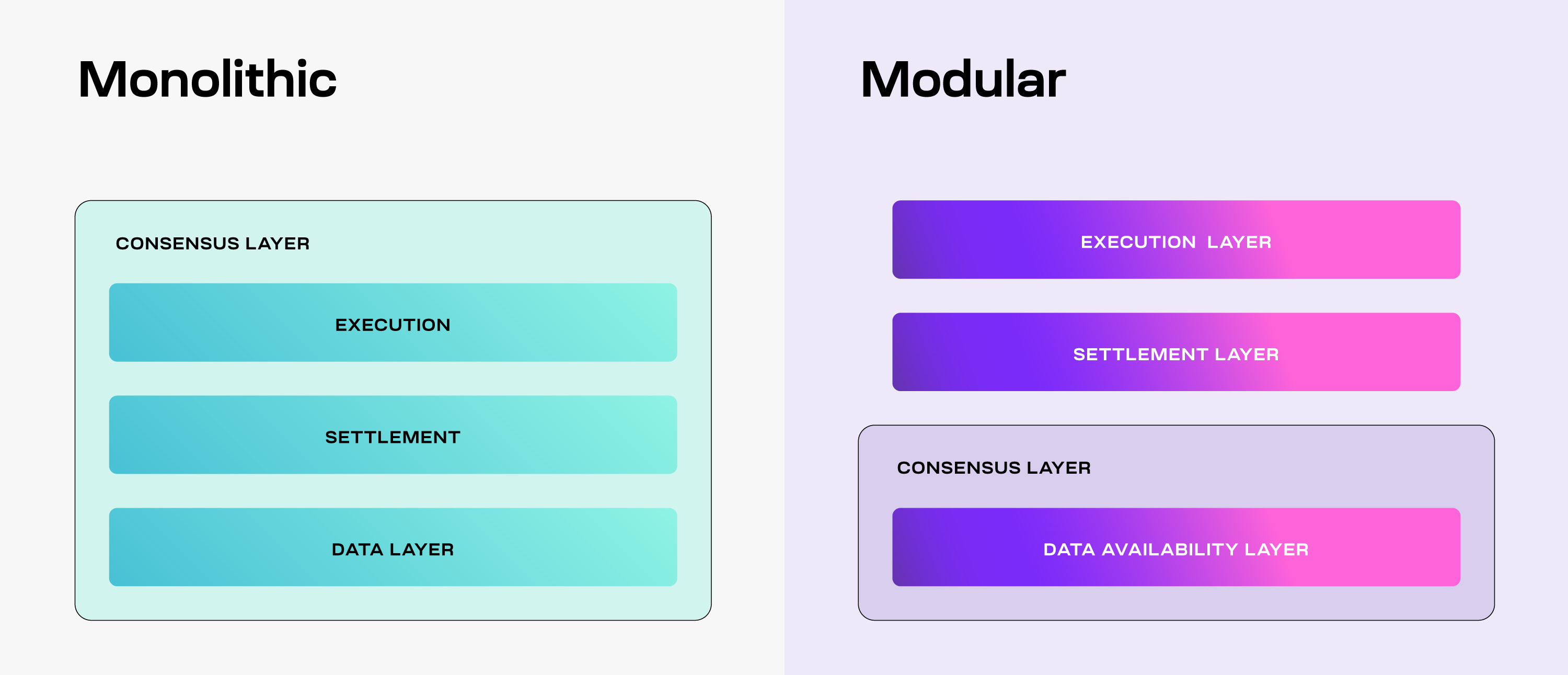
source:https://docs.celestia.org/learn/how-celestia-works/monolithic-vs-modular
2. Data Availability Sampling (DAS)
DAS is a method that allows light nodes to verify the availability of data without downloading the entire block. Light nodes randomly sample data blocks, and if these data can be successfully retrieved and verified, it means that the entire blocks data is available.
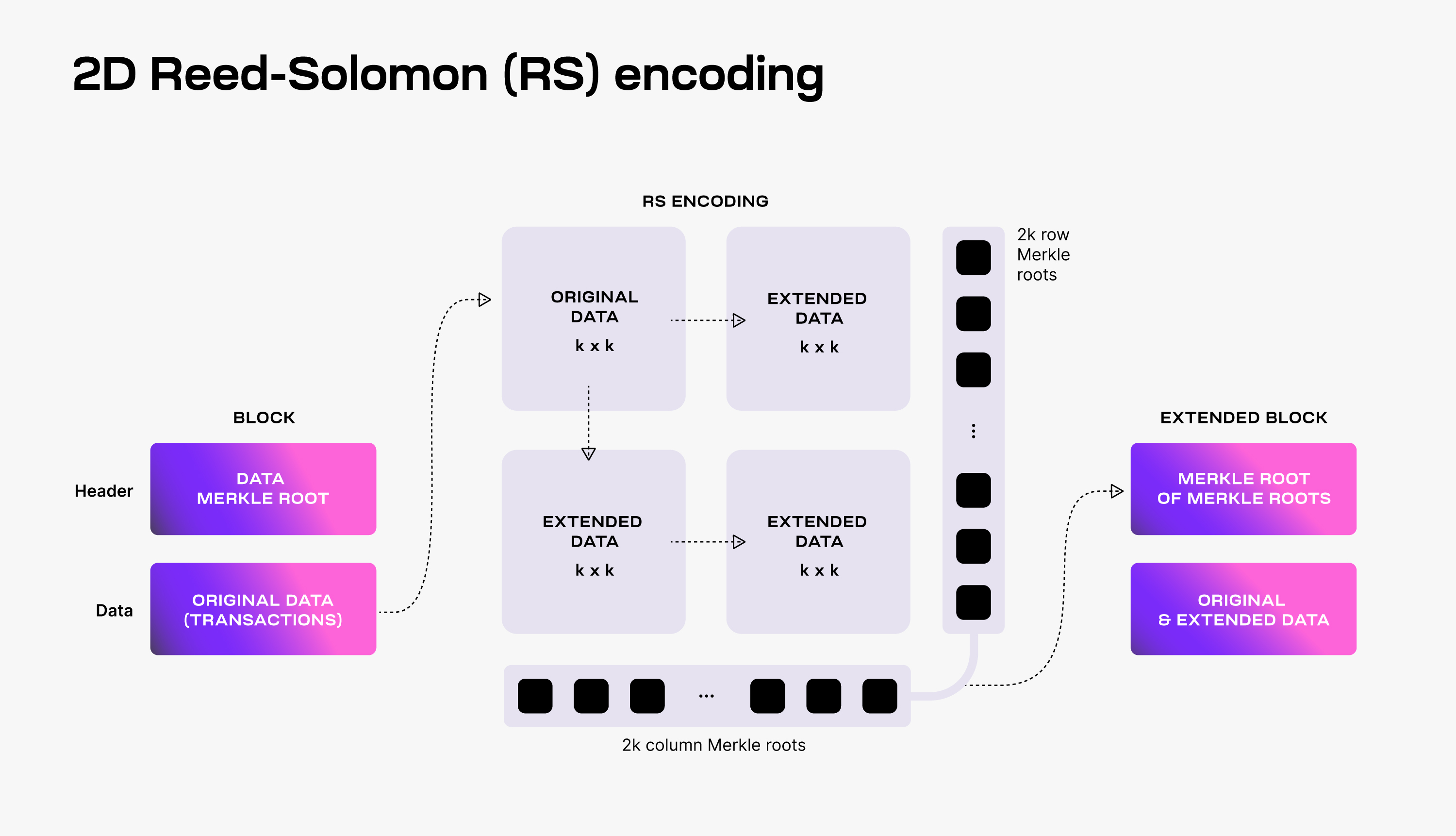
source:https://docs.celestia.org/learn/how-celestia-works/data-availability-layer
3. Namespace Merkle Trees (NMTs)
NMTs enable block data to be partitioned into separate namespaces for different applications. This means that applications only need to download and process the data relevant to them, significantly reducing data processing requirements.
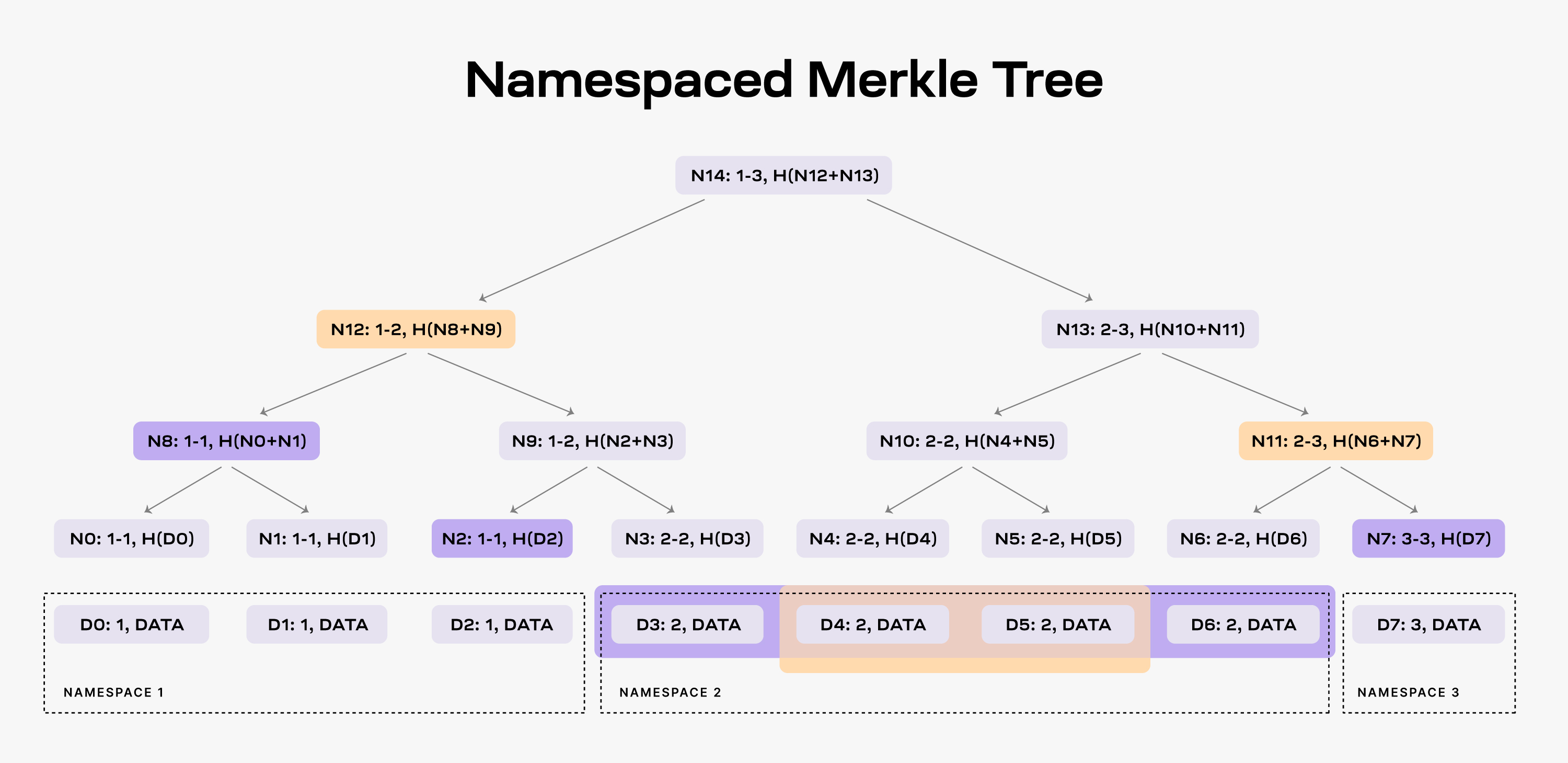
source:https://docs.celestia.org/learn/how-celestia-works/data-availability-layer
4. Achieve scalability through light nodes
The more light nodes participate in data availability sampling, the more data the network can handle. This scalability feature is critical to maintaining efficiency as the network grows.
5. Fraud proof of wrong extension data
In response to possible data expansion errors by block producers (whether intentional or unintentional), fraud proofs allow blocks with invalid data to be verified and rejected, enhancing the security of the network.
6. Building a PoS blockchain for data availability
Celestia uses a PoS blockchain, called celestia-app, to facilitate transactions and data availability. This layer is built on celestia-core, which is an improved version of the Tendermint consensus algorithm designed to handle the unique needs of the DA layer.
7. Scalability
There are two decisive factors for scalability: the amount of data sampled centrally (the amount of data that can be sampled) and the target block header size of light nodes (the block header size of light nodes directly affects the performance and scalability of the overall network).
In response to the above two factors, Celestia utilizes the principle of collective sampling, that is, through many nodes participating in partial sampling of the data, it can support larger data blocks (i.e., higher transaction processing per second, tps). This approach can expand network capacity without sacrificing security. Furthermore, in the Celestia system, the block header size of a light node grows proportionally to the square root of the block size. This means that if they are to maintain nearly the same security as a full node, a light node will face a bandwidth cost proportional to the square root of the block size.
Modular Celestia Stack Features
1. Self-sovereignty
Celestias Rollups differ from Ethereum Rollups in that their canonical status is independently determined when running on Celestia. This increases autonomy, allowing nodes to freely decide how they operate through hard and soft forks. This self-sovereignty reduces reliance on central governance and promotes more experimentation and innovation.
2. Flexibility
Celestias execution-independent nature means that its Rollups are not limited to EVM-compatible designs. This openness provides a broader space for virtual machine innovation and helps promote technological development.
3. Easy deployment
Celestia simplifies the blockchain deployment process. Using tools like Optimint, developers can quickly deploy new chains without worrying about the complexity and high cost of consensus mechanisms.
4. Efficient resource pricing
Celestia handles active state growth and historical data storage separately, providing a more efficient resource pricing mechanism. This approach reduces the interaction between execution environments and improves user experience.
5. Trust minimization bridge
Celestias architecture supports the creation of trust-minimized bridges, allowing different chains to interconnect securely. This enhances the security and interoperability of blockchain clusters.
6. Minimal Governance
Celestia’s modular design reduces the need for centralized governance. The execution layer can evolve independently and rapidly, while the consensus layer remains stable. This separation reduces the need for complex social coordination.
7. Decentralized block verification
Celestia emphasizes decentralization of block verification, not just block production. This approach increases the security and trustworthiness of the network.
8. Simplicity
Celestia avoids overcomplication by choosing simple and proven technologies like Tendermint as its foundation. This simplicity benefits system stability and scalability.
Celestia data costs
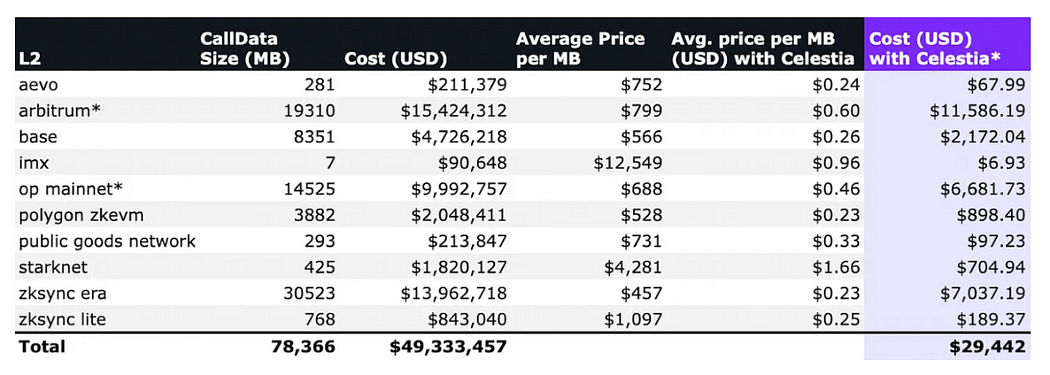
Numia Data recently released a report titled The impact of Celestias modular DA layer on Ethereum L2s: a first look, which compares different Layer 2 (L2) solutions released on Ethereum in the past six months. The cost incurred by CallData, and what they might have incurred if they used Celestia as the data availability (DA) layer (in this calculation, TIA price is assumed to be $12). This report clearly demonstrates the huge economic benefits of a dedicated DA layer like Celestias in reducing L2 Gas expenses by comparing the cost difference between the two scenarios.
Tokenomics
Total supply at creation: 1 billion TIA.
Distribution of TIA at Creation
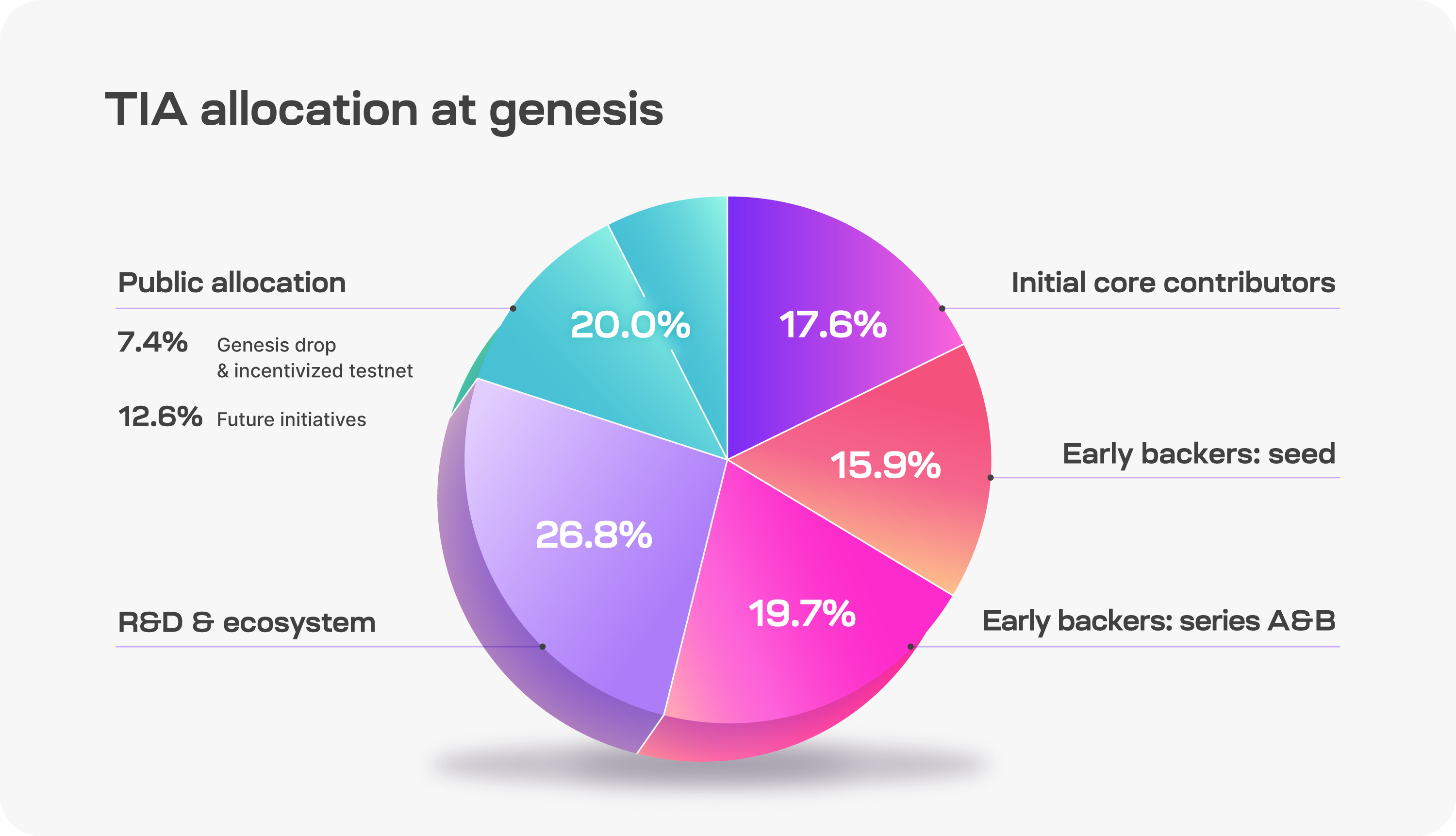
source:https://docs.celestia.org/learn/staking-governance-supply
Inflation plan: Start at 8%, then decrease by 10% each year until reaching an annual minimum of 1.5%
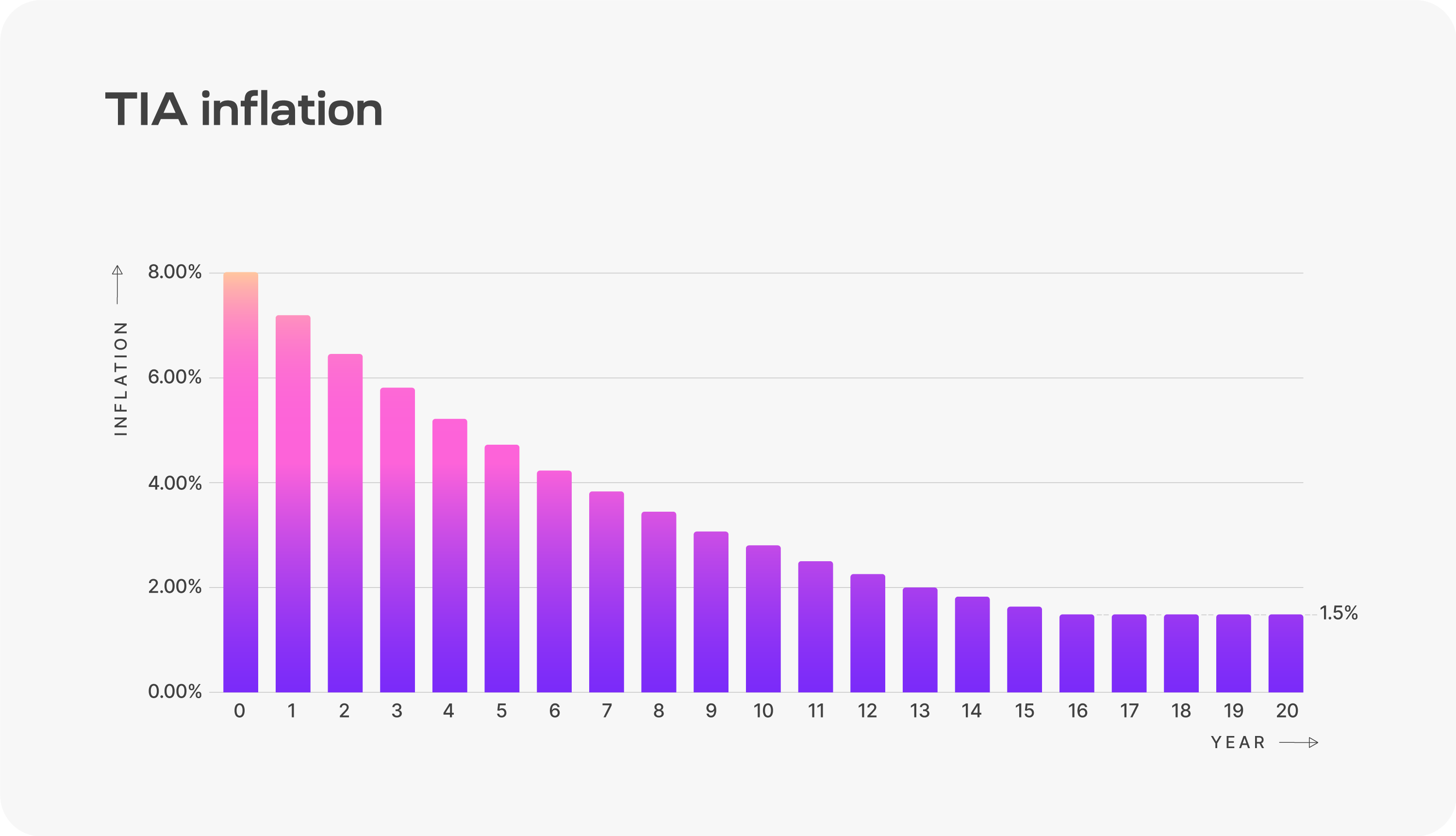
source:https://docs.celestia.org/learn/staking-governance-supply
TIA’s Token Utility
Pay for data space: Developers submit PayForBlobs transactions on Celestia and pay using TIA to use its data availability tier.
Bootstrapping new Rollups: Developers can use TIA as a Gas token and currency to launch new blockchains, similar to ETH used in Ethereum-based Rollups. This helps focus on the development of the application or execution layer without the need to issue new tokens immediately.
Proof of Stake: Celestia is built on the Cosmos SDK and uses Proof of Stake to ensure its consensus. Users can delegate TIA to validators and earn a portion of the staking rewards.
Decentralized governance: TIA holders participate in governance, vote to determine network parameters and manage the community pool, which receives 2% of the block reward.
Token unlock
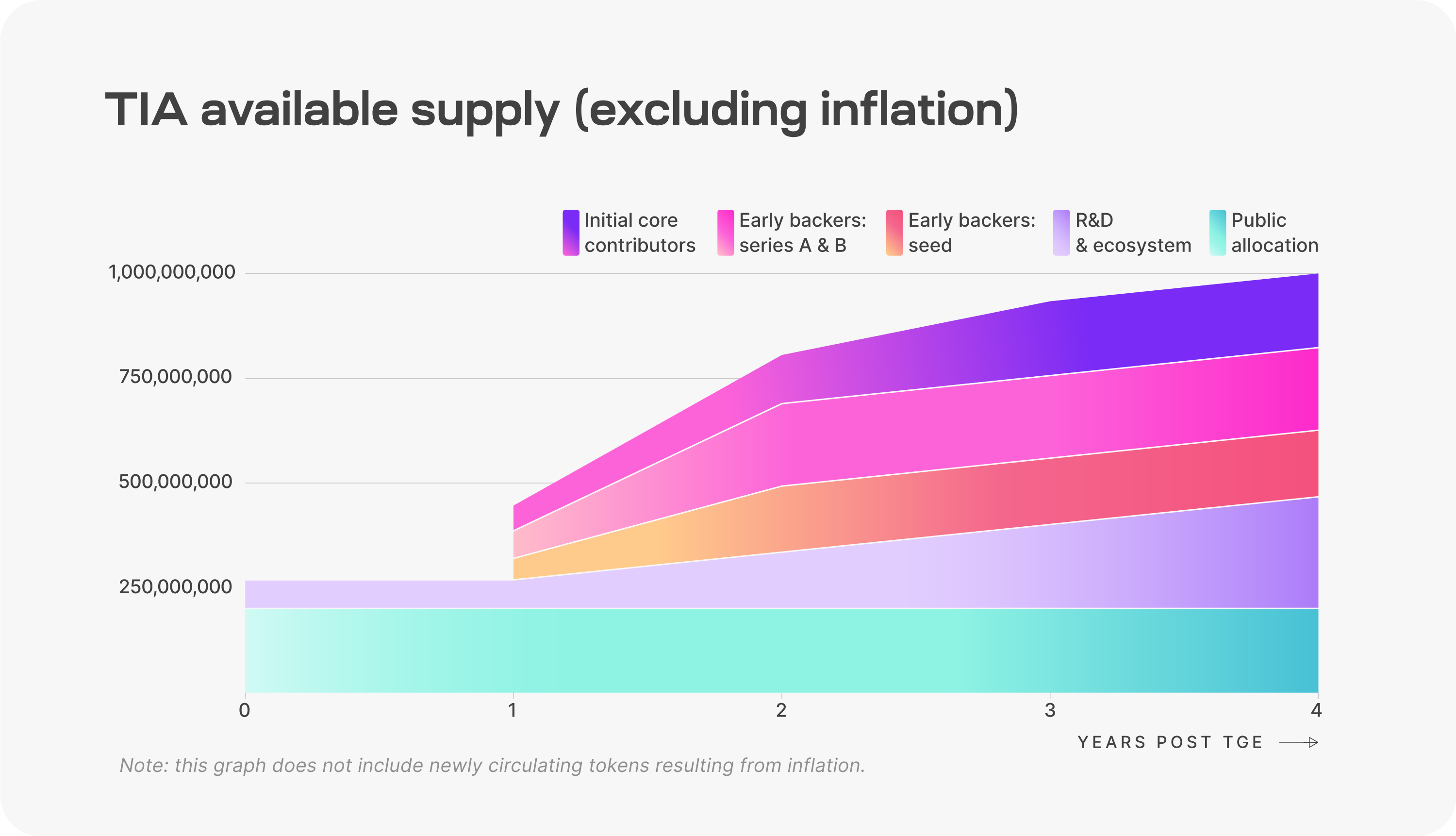
source:https://docs.celestia.org/learn/staking-governance-supply
Pledge situation
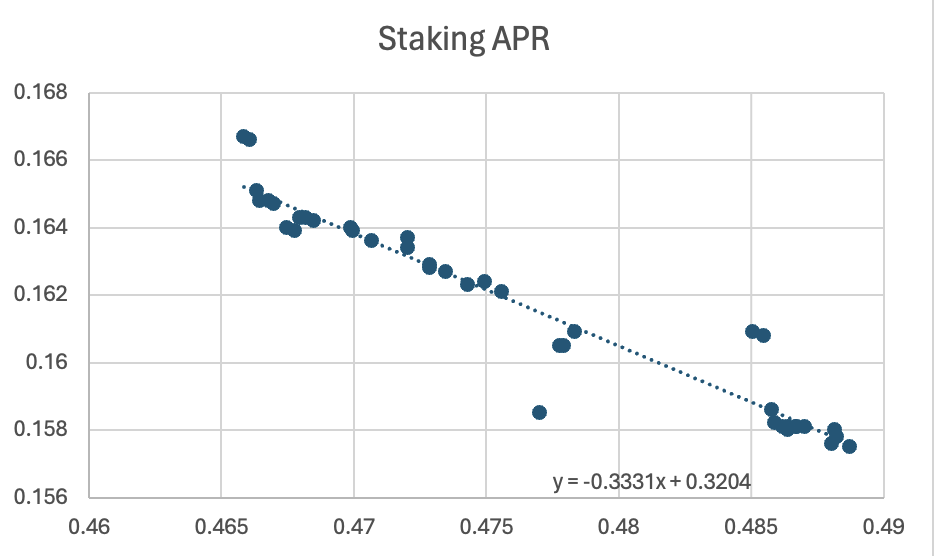
Celestia’s current pledge rate is 48.88%, and the pledge APR is 15.74%.
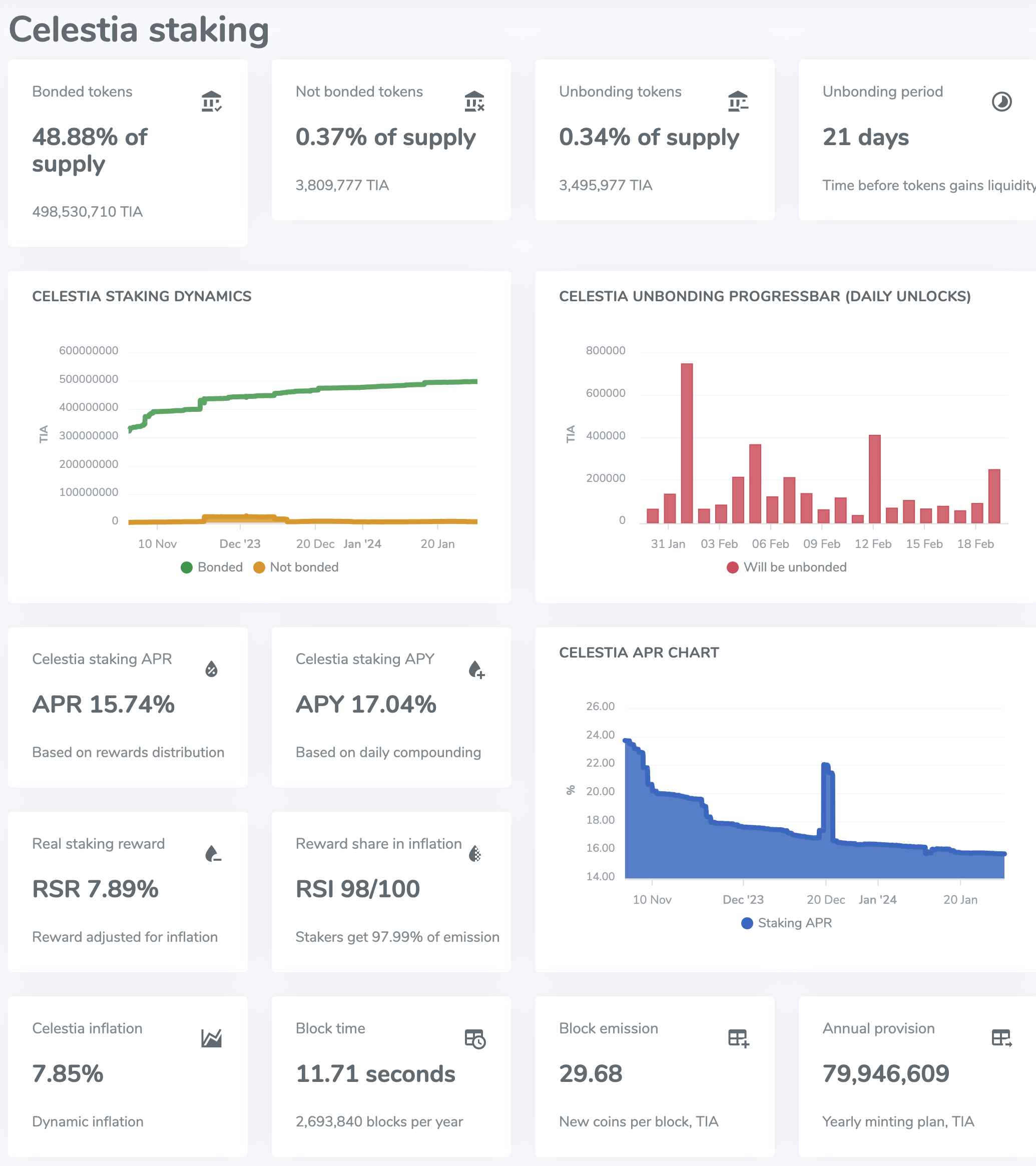
source:https://staking-explorer.com/staking/celestia
According to the current relationship between staking APR and staking rate, the following linear relationship is fitted:
Staking APR = -0.3331 Staking rate + 0.3204
source:MT Capital
It is known that Celestias minimum staking APR is its own inflation rate, which is 7.85%. The ideal limit that can be obtained for the pledge rate is 72.6%.
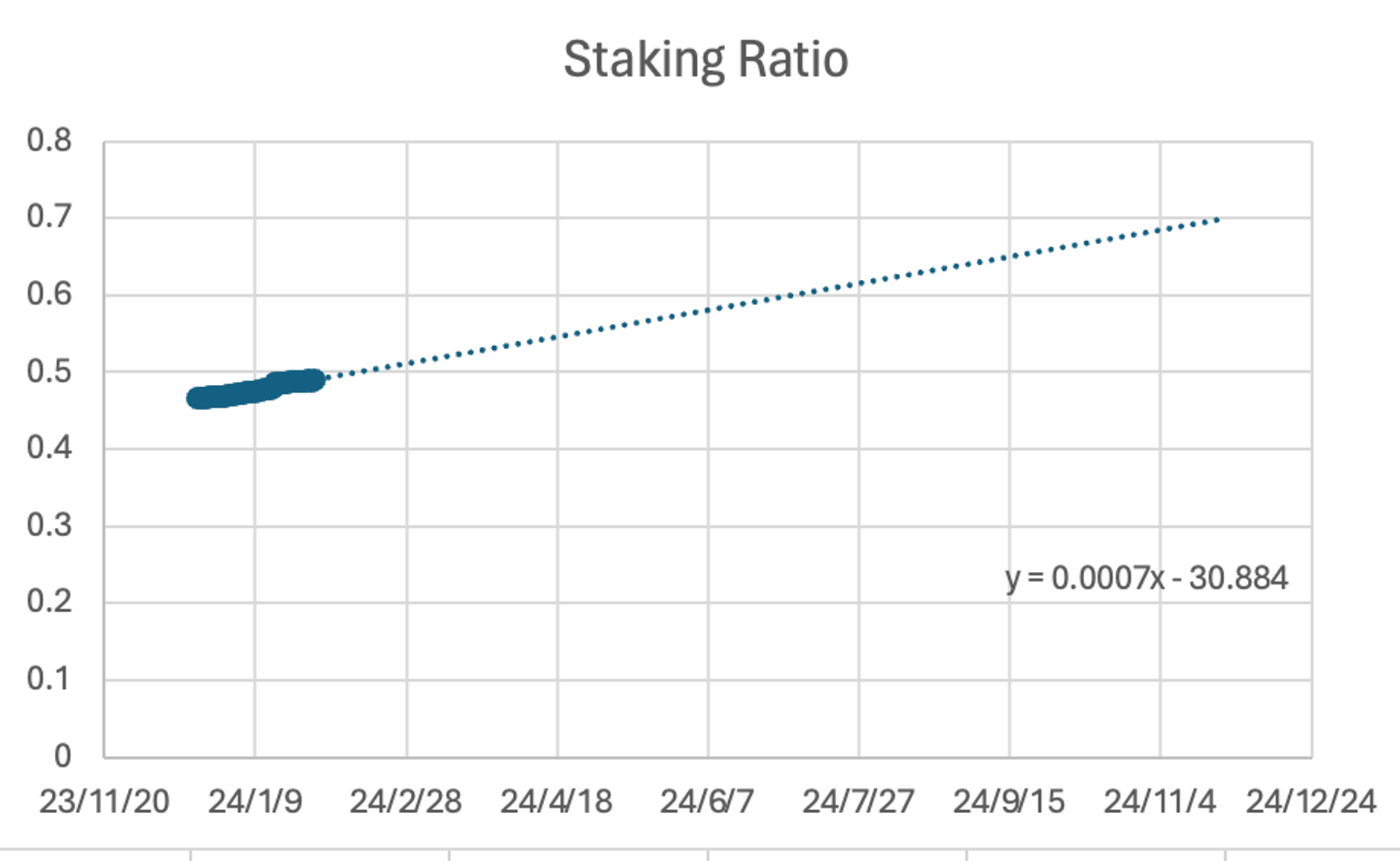
According to fitting the data of pledge rate changes over time, it can be seen that the pledge rate reaches its limit around the end of 24.
source:MT Capital
And because there will be no new unlocks for Celestia before November 24, we can think that the actual circulation of Celestia will continue to decrease before November 24. We estimate the token price of Celestia before November 24. Continue to be optimistic.
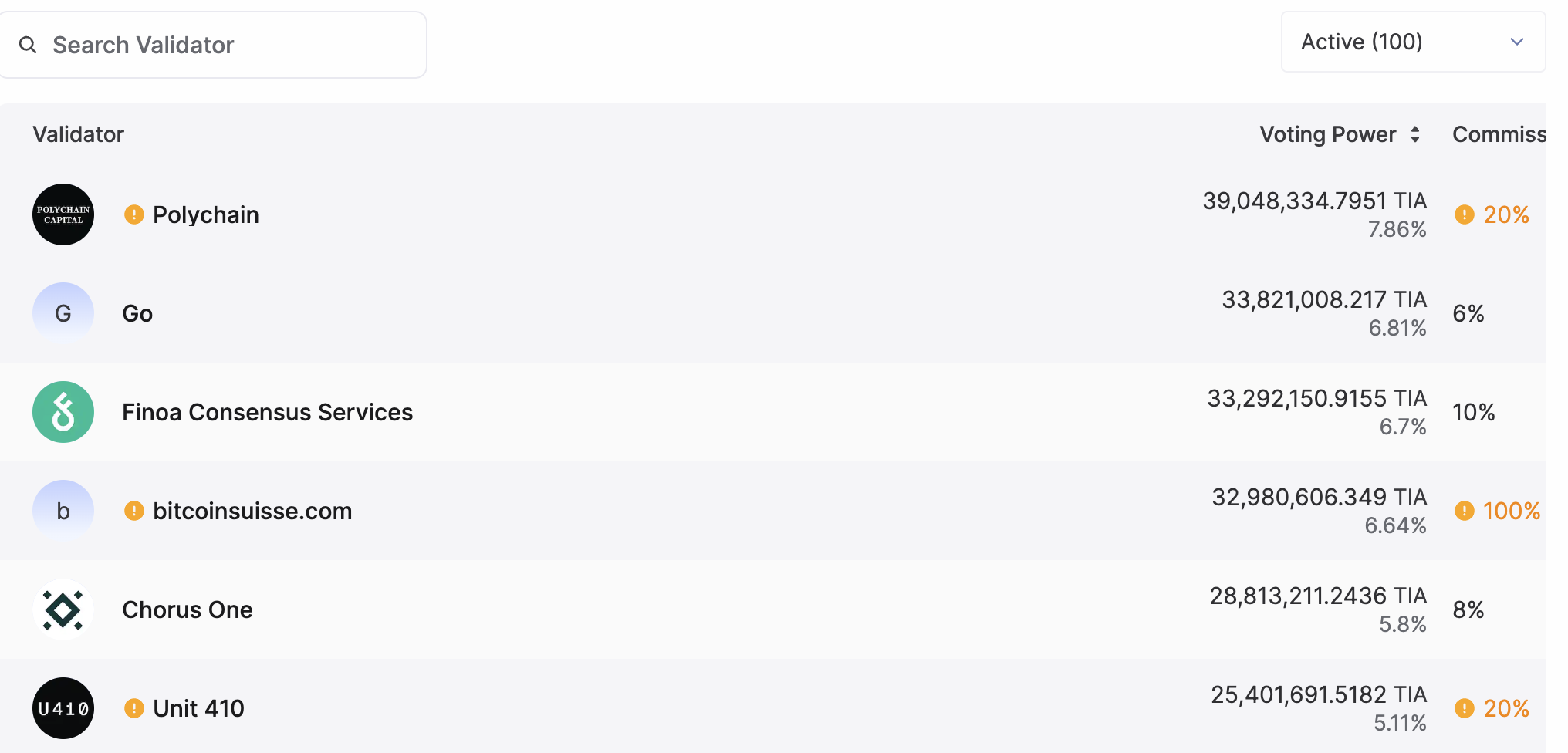
The current number of active nodes in Celestia is 100.
source:https://wallet.keplr.app/chains/celestia
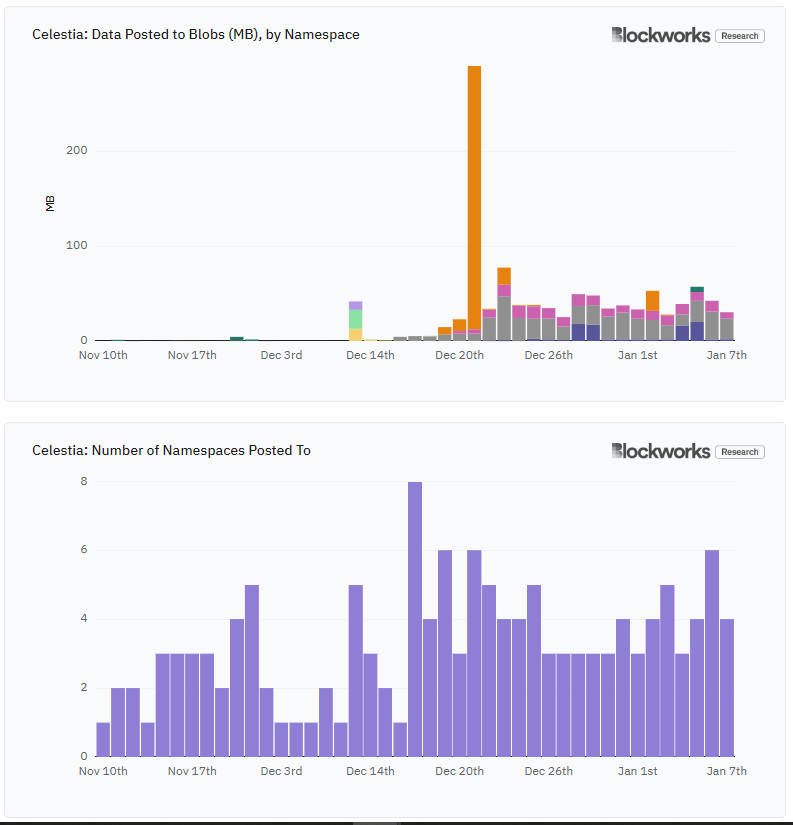
Compared to the Ethereum mainnet, Celestia data costs are reduced by 99.9%. Users can publish data to namespace-containing blobs and access the data by filtering on specific namespaces. Since Celestia has been running for two months, users have published a large amount of data to different namespaces, but 87% of it is concentrated in the three main namespaces.
source:https://twitter.com/smyyguy/status/1744419436449222864
Celestias current daily data usage is just 0.1%, well below the 46,080 MB of data it can support per day. Still, Celestias activity is growing compared to Ethereums current 15 rollups and 700 MB of data per day.
Currently, Celestias fees are relatively low, but if data usage grows, the fees could increase significantly. In the future, if Celestia achieves a full years worth of daily data capacity of 46,080 MB at a TIA price of $13, the network will generate annual fees of approximately $5.2 million. This would be 65 times the data currently posted to Ethereum. The networks fee structure can lead to bidding wars between users, driving up fees.
Future user demand may come from various applications, such as high TPS general chains, specific applications or games. While it is currently difficult to predict the exact source of demand, gaming and high TPS rollups are likely to be key drivers. In the coming months, we will see an influx of chains launching into the market leveraging Celestias RaaS.

source:https://twitter.com/smyyguy/status/1744419436449222864
Celestia’s new valuation model
Considering that Celestia is the first modular public chain DA layer, and the Cosmos community is very generous with airdrops for Celestia stakers (Dymension’s airdrop has covered the cost of Celestia stakers), there will be a large number of modular public chain related projects in the future. The project will airdrop to Celestia pledgers, so there will be the following valuation ideas:
Price (TIA) = Accumulation of value to the DA layer + Currency premium of TIA as a “modular currency” + Value of all future airdrops
Celestia Ecological Project
Cevmos
Cevmos is a rollup stack jointly developed by the Cosmos EVM application chain Evmos and Celestia. The goal is to provide the best settlement layer for EVM-based rollup on Celestia. The name is a combination of the abbreviations for Celestia, Evmos and Cosmos. Cevmos aims to provide a dedicated settlement layer for rollups to reduce costs and improve efficiency as part of its mandatory settlement rollup approach. Cevmos, as the settlement layer, is built based on Evmos and implements EVMs recursive rollup on top of it.
Unlike the existing Tendermint Core consensus engine on Cosmos, Cevmos uses Optimint (Optimistic Tendermint), a replacement for Tendermint BFT that allows developers to leverage existing consensus and data availability (such as Celestia) to deploy rollups. Since Cevmos itself is a rollup, all rollups built on top of it are collectively called settlement rollups. Each rollup implements the redeployment of existing rollup contracts and applications on Ethereum through a minimal two-way trust bridge with Cevmos rollup, reducing migration workload. All rollups will use calldata on Cevmos rollup, and Cevmos batches the data through Optimint and publishes it to Celestia.
As a restricted EVM environment, Cevmos rollup also attempts to meet the challenge through a single round of fraud proof. Cevmos not only avoids the need to design and maintain complex consensus mechanisms, but also brings the efficiency of rollup and the interoperability of EVM to the entire Cosmos ecosystem, providing a practical modular solution for the widespread application and popularization of the Cosmos ecosystem.
Dymension
Dymension is a Cosmos-based sovereign rollup platform designed to greatly simplify application-focused custom rollups through its Dymension Chain (settlement layer), RDK (RollApp Development Kit) and IRC (inter-rollup communication) capabilities. for rollApp) development process.
Dymensions self-built settlement layer, called Dymension hub, is a chain that adopts the Tendermint Core state replication model and is based on the PoS consensus mechanism. RollApp built on the Dymension hub not only inherits the security of the hub, but also implements mutual communication through the RDK and the dedicated module group supported by the hub.
RollApps consists of two key parts: client and server. As the application side of RollApp, the server side is responsible for implementing customized business logic and building pre-packaged modules of the RollApp development kit RDK. The client component, named dymint, is derived from Celestias Optimint. As a direct replacement for Tendermint, it is responsible for block production, peer-to-peer network message dissemination and inter-layer communication. Since RollApp itself does not undertake consensus tasks, dymint can provide the low-latency performance required by modern applications.
Similar to Cosmos, Dymension RollApps aims to create application-specific blockchains that reduce consensus overhead. RDK adds new modules and modifies existing modules based on Cosmos-SDK to ensure RollApps compatibility with the Dymension protocol while still being compatible with other Cosmos ecosystem tools. RollApps are able to interact with any IBC-enabled chain through the Dymension Hub, so they are also part of the Cosmos ecosystem.
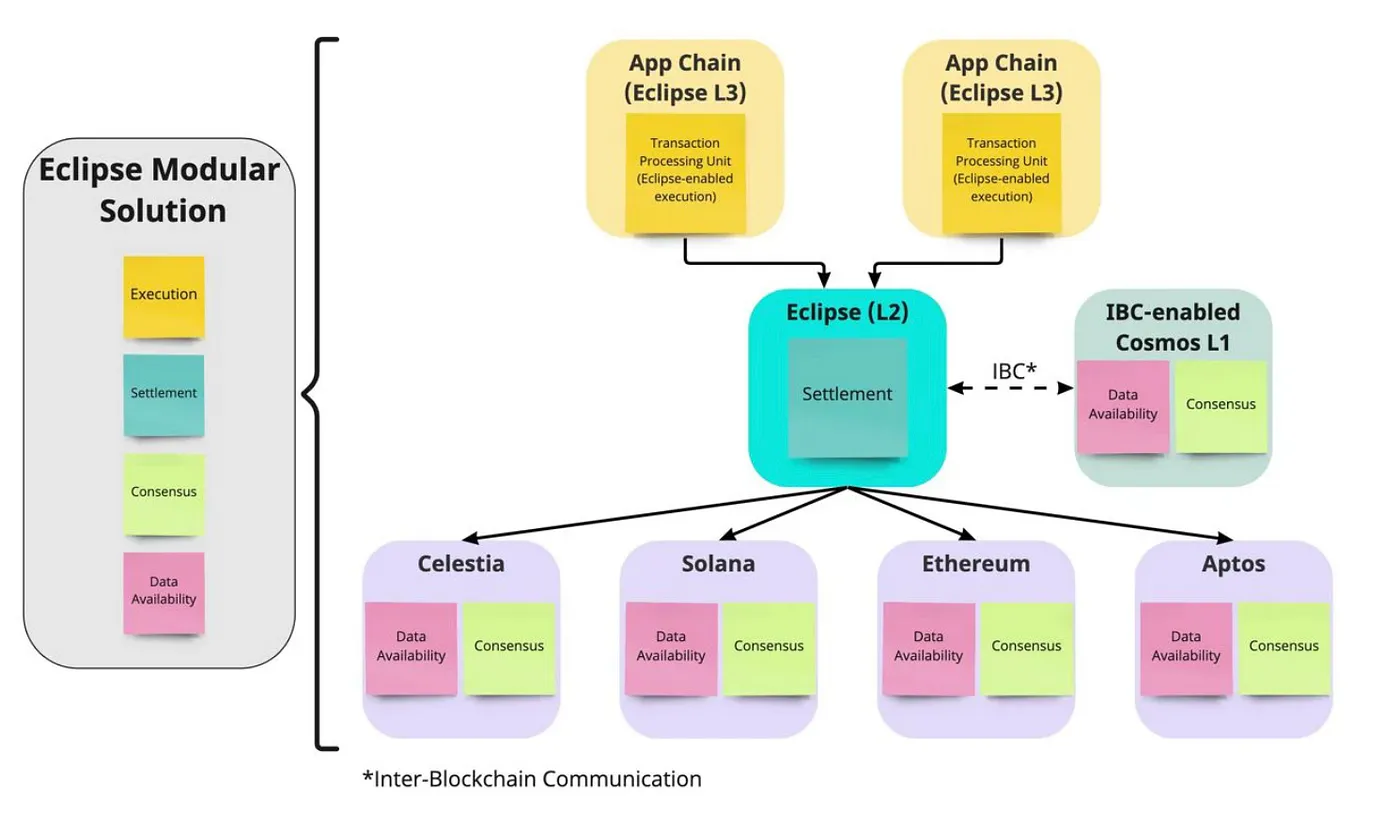
Eclipse
Eclipse is a sovereign rollup project based on the Cosmos ecosystem, which specifically allows the use of Solana VM on any chain to build customizable and modular rollup settlement layers. In the early stages, Eclipse plans to use Celestia as its consensus layer and data availability (DA) layer, and Solana VM as the execution and settlement environment. The ultimate goal of Eclipse is to provide customized rollup execution layers for different Layer 1 heterogeneous blockchains and connect various blockchains through a modular approach. In addition, Eclipse plans to further develop the settlement layer rollup based on Solana VM into Optimistic rollup and zk rollup in the future, thereby expanding its functionality and application scope.
Fuel
Although Fuel and Celestia are similar, they have significant differences. Celestia focuses on the optimization of data availability and consensus, handling data sorting, while Fuel is positioned as a modular execution layer.
One of the main differences of Fuel is the new virtual machine architecture it runs on - FuelVM, as well as the supporting Sway language and tool chain. FuelVM is a custom virtual machine specifically designed for executing smart contracts. It is capable of processing transactions in parallel and is designed to prevent fraud from the beginning. It is suitable for the transaction execution layer of Optimistic rollup.
FuelVM combines WASM, EVM and Solanas SeaLevel features, but its unique feature is that it uses a UTXO model instead of an account model. This means that Fuel VM requires each transaction to explicitly specify the UTXO it will touch. Because the execution engine is able to precisely identify the states involved in each transaction, it can easily identify transactions that are processed in parallel without disputes. This design makes Fuel VM more efficient and secure when processing transactions.
Celestia Summary and Future Outlook
As the first modular DA network, Celestia focuses on scaling securely as the number of users grows. Its modular design makes launching independent blockchains simple. The network’s core technologies include Data Availability Sampling (DAS), which allows light nodes to verify data availability without downloading entire blocks, and Namespace Merkle Trees (NMTs), which enable applications to process only relevant data. , greatly reducing data processing requirements.
According to the relationship between the current staking rate and APR, it is expected that there will be no new unlocks of Celestia before November 2024. According to the current staking trend, the Celestia staking rate will continue to increase, the actual circulation will continue to decrease, and its token price is expected to continue rising. In addition, Celestia’s data cost has been reduced by 99.9% compared to the Ethereum mainnet, and its daily data usage is only 0.1%, which is far lower than the 46,080 MB data volume it can support every day, showing huge expansion potential.
The value of Celestias TIA token is not only based on its application and innovation in blockchain technology, but also includes the airdrop value it may receive in the future. With the development of blockchain technology and the further popularity of modular public chains, Celestia and its TIA token may show greater potential and value.
Celestias ecosystem includes multiple innovative projects such as Cevmos, Dymension, Eclipse and Fuel. These projects use Celestias modular features to provide customized solutions for specific applications, reflecting Celestias importance in the field of blockchain technology. status and development potential.
Given its unique approach and technological innovation, Celestia is poised to play an important role in the blockchain industry. Its focus on solving the blockchain trilemma, especially scalability, without sacrificing security or decentralization has made it an important player in the growing blockchain ecosystem.
EigenDA
Introduction to EigenDA
EigenDA is EigenLayers first AVS product. EigenDA aims to rely on the security of Ethereum to make the re-pledge node become the verification node of EigenDA and support Rollup to publish data to EigenDA to obtain data availability services with lower cost and higher transaction throughput.
EigenDA technical architecture
EigenDA follows the final expansion path of Ethereum Danksharding. Therefore, the technical path of the DA layer adopted by EigenDA is also highly related to the technical path of Ethereum Danksharding expansion. Furthermore, EigenDA’s adoption of technologies such as erasure coding, KZG commitment, ACeD (Authenticated Coded Dispersal), and the decoupling of DA and consensus can provide far greater benefits than Ethereum Danksharding in terms of transaction throughput, node load, and DA cost. Excellent performance of DA scheme.
The specific implementation process of EigenDA is as follows:
First, after Rollups sorter creates the data blob, it needs to send a request to split the data blob to Disperser. (Disperser can be run by Rollup itself, or third-party Dispersers such as EigenLabs can be used)
Secondly, after receiving the data blob, Disperser needs to split the data blob into different data blocks and use erasure coding to generate redundant data blob data blocks and the corresponding KZG commitment and KZG multi-reveal proof (KZG multi-reveal proofs).
Then, Disperser will distribute the data blocks, KZG commitments and KZG multi-reveal proofs to different EigenDA nodes (Ethereum re-staking nodes are registered as EigenDA nodes). EigenDA nodes need to use KZG multi-reveal proofs and KZG commitments to verify the validity of data blocks. After verification, the node needs to save the data and send the signature to Disperser.
Finally, Disperser will aggregate the signatures and send them to the EigenDA contract on the Ethereum mainnet. The signature in the EigenDA contract will be further verified. If the verification is correct, the process ends.
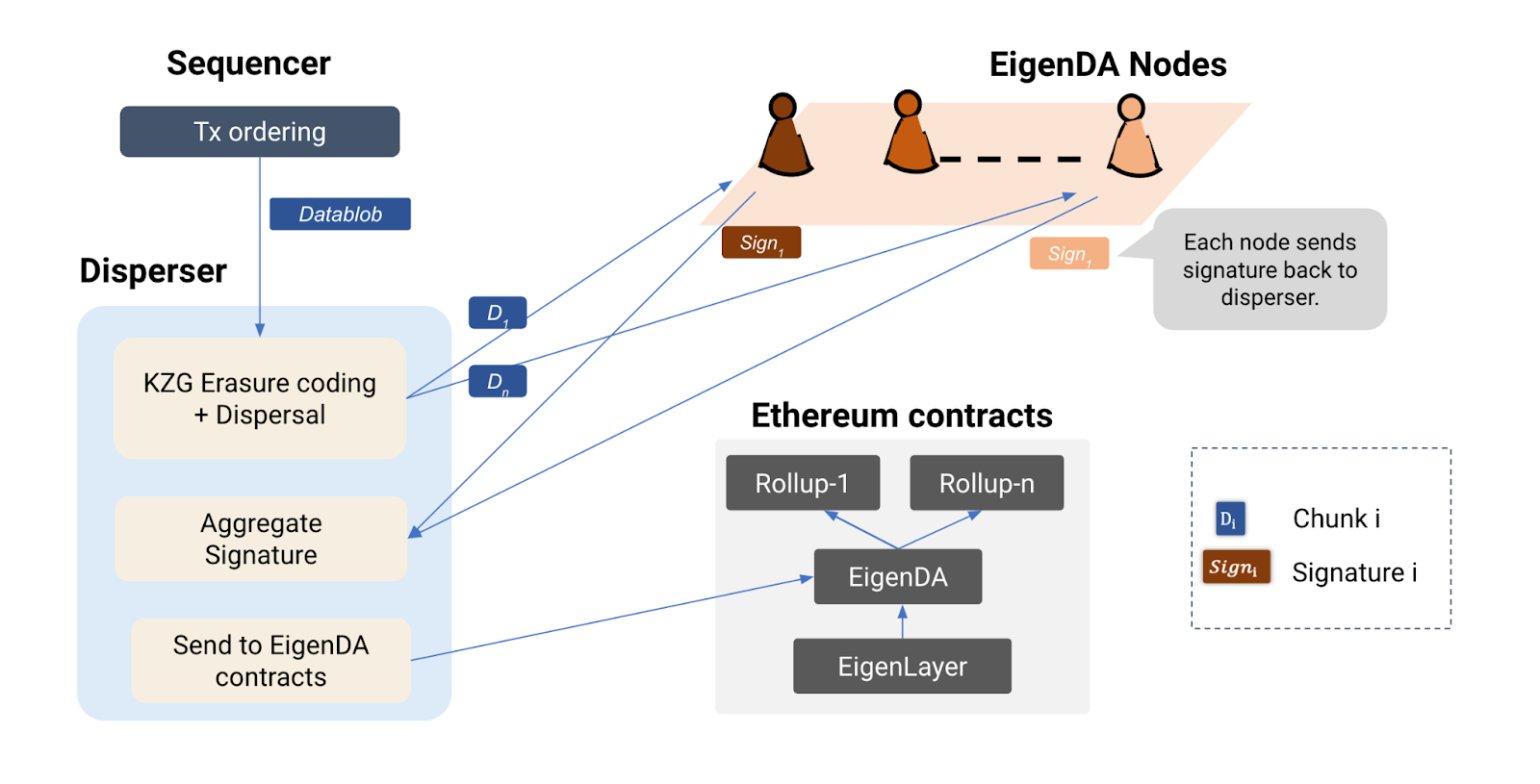
source:https://www.blog.eigenlayer.xyz/intro-to-eigenda-hyperscale-data-availability-for-rollups/
Similar to other DA solutions, the core idea of EigenDA is to use DAS technology to reduce the storage and verification load of a single node, while improving the throughput of the global DA consensus, and using erasure coding redundancy to ensure data security. The difference is that EigenDA chose the KZG commitment verification technology that is at the same frequency as Ethereum upgrade in terms of specific technology selection. Moreover, EigenDA does not rely on consensus protocols and P2P network propagation, but uses unicast (Unicast) to further increase the consensus speed.
In addition, EigenDA has some more refined designs in ensuring node data storage and node verification.
EigenDA ensures that the EigenDA node actually stores the data in the data block through Proof of Custody. Each EigenDA node must regularly calculate and submit the value of a function, and the node must store the corresponding data block to calculate the value of the function. The ETH of nodes that fail to successfully pass Proof of Custody will be punished by forfeiture.
EigenDA further guarantees the validity of the DA consensus through Dual Quorum certification. EigenDA will have at least two independent sets of Quorum to prove data availability. For example, one group of Quorum is composed of ETH re-pledgers, and the other group is composed of Rollup native token stakers. A DA that must be verified simultaneously by two independent Quorums will be confirmed to be valid.
EigenDA feature analysis
In order to better distinguish the differences, advantages and disadvantages of EigenDA from Ethereum DA and other DA solutions, we will compare the two separately.
Compare Ethereum DA, EigenDA:
EigenDA nodes do not need to download and store all the data, but only a small portion of the data blocks, which significantly reduces the nodes operating and operating costs.
EigenDA decouples DA from consensus so that nodes do not need to wait for the sorting process of serial processing and can directly process the proof of data block availability in parallel, thus significantly improving network operation efficiency. Moreover, through erasure coding and KZG commitment, nodes only need to download small pieces of data for storage and verification, resulting in higher network throughput.
Since EigenDA only inherits part of the security of the main network, EigenDA is still weaker than Ethereum DA from a security perspective.
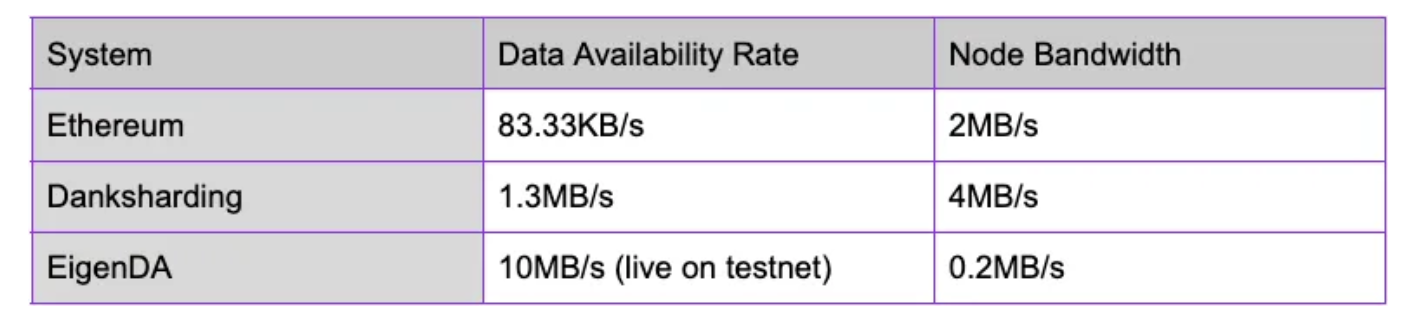
Compared to other DA solutions, EigenDA:
EigenDA nodes are a subset of re-pledge nodes in the EigenLayer network, and there is no additional staking cost to become an EigenDA node.
EigenDA decouples DA from consensus and directly unicasts it, so that the propagation of data blocks is no longer limited by the constraints of the consensus protocol and P2P network throughput, which can greatly shorten communication, network delays and confirmation times, and increase the speed of data submission.
EigenDA inherits part of the security of Ethereum and is generally more secure than other DA solutions.
EigenDA also supports Rollup to flexibly choose different pledge token models, erasure coding ratios, etc., for greater flexibility.
Since the final confirmation of EigenDA relies on the EigenDA contract on the Ethereum mainnet, the time overhead of final confirmation will be significantly higher than that of other DA solutions.
EigenDA introduces the latest progress and use cases
EigenDA will launch testnet testing in mid-November 2023. Initially, EigenDA limited the number of node operators in the test network to 30 and set an initial throughput target of 1 Mbps. EigenDA plans to gradually expand the number of operators so that EigenDA can eventually approach the target throughput of 10 Mbps.
Currently, according to EigenDA test network data, the number of node operators in the EigenDA test network has expanded to 200, but the average network throughput in the past seven days is only 0.45 Mbps, which has not yet reached the initial target of 1 Mbps.
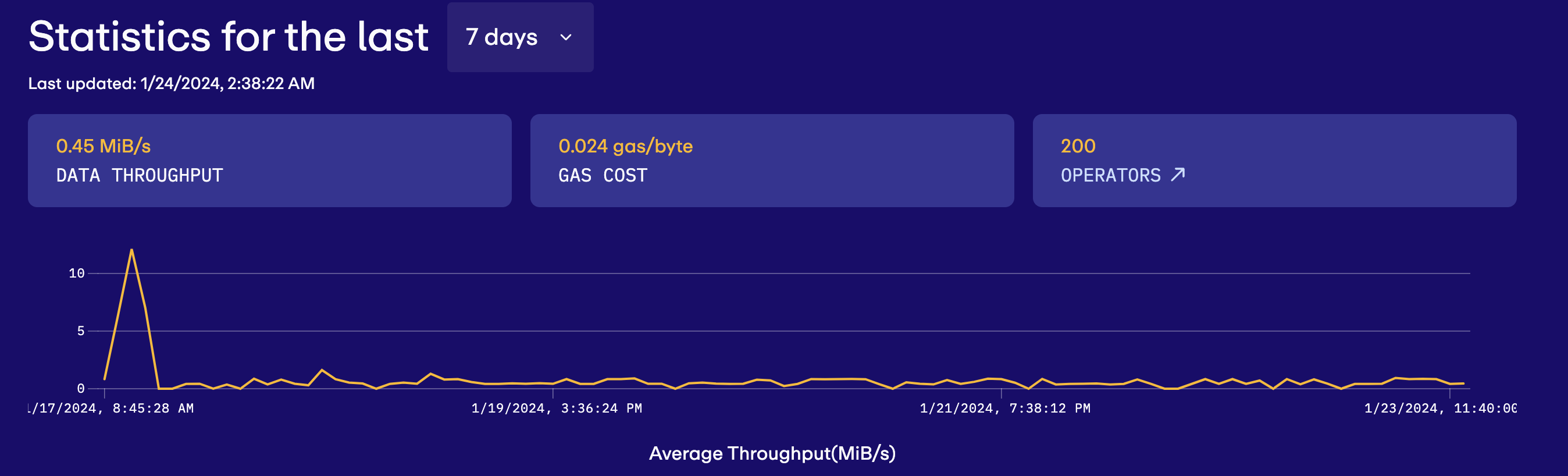
source:https://blobs-goerli.eigenda.xyz/?duration=?P7D
Currently, the total TVL in the EigenDA test network is approximately 3.5 M, among which Ankr, Lido and Staders LST are the top three pledged assets with the largest proportion. The total number of operating nodes has reached 200, and the total number of pledgers has reached 29.4k.
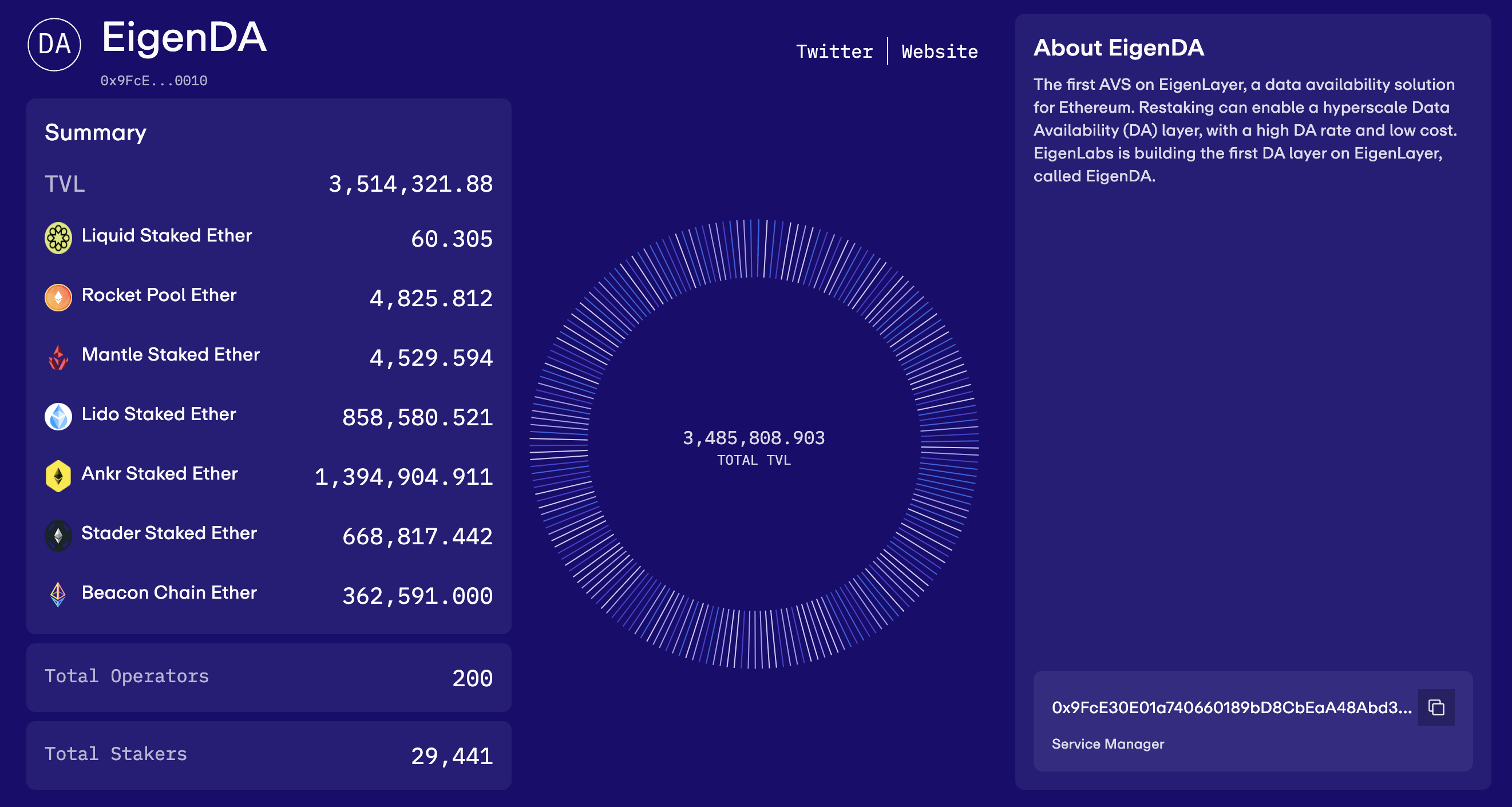
source:https://goerli.eigenlayer.xyz/avs/eigenda
Although EigenDA is still in the testnet stage, we might as well make a simple comparison between the current EigenDA testnet data and Ethereum-related data to see how far EigenDA is from its final vision.
Inherit the security of Ethereum:
The current TVL of the EigenDA test network is about 3.5 M, while the FDV of Ethereum is about 264 B. From the perspective of asset value, EigenDA only inherits 0.001% of the security of Ethereum.
Currently, the number of pledge verification nodes on the EigenDA test network is 29.4k, while the number of pledge verification nodes on Ethereum is 904k. Judging from the number of pledge verification nodes, EigenDA has inherited about 3.2% of the security of Ethereum.
Improvement of network throughput:
The current throughput of the EigenDA test network is about 0.45 Mbps, while the throughput of Ethereum is about 0.083 Mbps. Although the network throughput of EigenDA is still an ideal situation of reaching 1 Mbps - 10 Mbps or even 1 Gbps, it is compared to Ethereum. The throughput is still improved by about 500%.
At present, EigenDA has also launched a partner program. Currently, 8 project parties including AltLayer, Caldera, Celo, Layer N, Mantle, Movement, Polymer Labs and Versatus have reached cooperation with EigenDA and plan to use EigenDAs data availability service.
Summarize
EigenDAs adoption of erasure coding, KZG commitment, ACeD and other technologies, as well as the decoupling of DA and consensus, enable EigenDA to provide excellent performance far exceeding the Ethereum DA solution in terms of transaction throughput, node load and DA cost. Compared with other DA solutions, EigenDA also has the advantages of lower startup and staking costs, faster network communication, data submission speed, and higher flexibility. EigenDA is expected to host some of Ethereums DA services and become a new competitor in the DA market.
Comparison and future prospects of Celestia and EigenDA
DA comparison:
Data availability sampling:
Celestia supports data availability sampling, allowing light nodes to randomly sample data blocks for download and verification. EigenDA does not support data availability sampling. Supporting data availability sampling allows Celestia to safely increase the block size through more light nodes, ensuring the minimum requirements for node verification without increasing the burden on nodes. Increasing the number of light nodes can also increase the decentralization of the network.
Coding proof scheme:
Celestia uses a fraud proof model to ensure that the original data is correctly encoded, while EigenDA uses KZG commitments for validity proof. In comparison, Celestias fraud proof has a lower threshold for implementation, a relatively higher level of technical maturity, and does not require the additional cost of generating KZG commitments. However, EigenDA using KZG commitment will be faster in verifying data accuracy than Celestia using fraud proof, because under the fraud proof mechanism, light nodes need to wait for a short period of time to receive the fraud proof from the full node.
Consensus mechanism:
Celestia uses the Tendermint consensus mechanism, which requires point-to-point network communication. EigenDA decouples DA from consensus and directly unicasts it, so that the propagation of data blocks is no longer limited by the consensus protocol and P2P network throughput, and the network communication time and confirmation time are faster.
However, EigenDA needs to rely on the EigenDA contract on the Ethereum mainnet to complete the final verification and confirmation. Therefore, in terms of the final confirmation time of the block, Celestia only takes 15 seconds, which is significantly faster than EigenDAs 12 minutes.
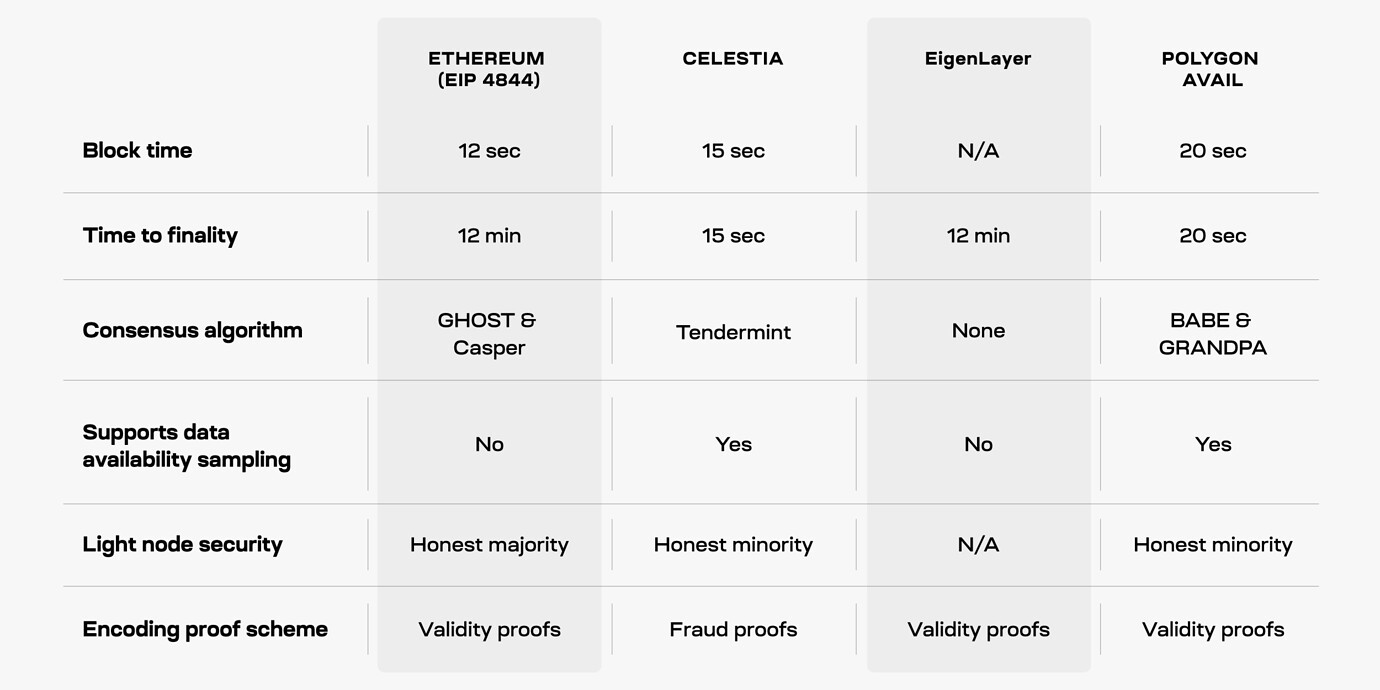
source:https://forum.celestia.org/t/a-comparison-between-da-layers/899
Node load:
Since Celestias full node needs to bear the functions of broadcast, consensus and verification at the same time, Celestia has 128 MB/s download and 12.5 MB/s upload data bandwidth requirements for the full node. EigenDAs nodes do not need to be responsible for broadcast and consensus functions. Therefore, EigenDAs bandwidth requirement for nodes is very low, only 0.3 MB/s.
Throughput:
Celestias data throughput is approximately 6.67 MB/s. The current throughput of EigenDAs test network is 0.45 MB/s, which is still far from the expected goal of 1 MB/s - 10 MB/s. At this stage, Celestias throughput has significant advantages over EigenDA.
Start-up costs:
Celestias DA solution is highly dependent on the security of its PoS network. Therefore, becoming a Celestia node requires a sufficient amount of Tia tokens to be pledged. Celestias DA plan has some start-up costs.
The security of EigenDA is inherited from Ethereum. To become an EigenDA node, you only need to register as a pledge node. There is no need to pay additional pledge costs and avoid initial startup costs.
The cost:
Celestia currently charges Manta a DA cost of $3.41/MB. According to EigenDA test network data, the current usage cost of EigenDA is approximately 0.024 Gas/Byte. In comparison, Celestias DA solution still has a huge cost advantage over EigenDA.
safety:
Celestias security is guaranteed by its network value. The higher the value of Celestias network, the higher the cost for an attacker to attack and the lower the probability of a successful attack. Currently, the pledge value of Celestia is approximately 1.2B, which means that a malicious attacker needs to pay at least more than 0.8B to attack the Celestia network.
EigenDA security is a subset of Ethereum security. The size of EigenDAs security depends on the value of re-pledged assets in the EigenDA network and the proportion of node operators in the Ethereum main network. From a TVL perspective, based on current testnet data, EigenDAs network value only inherits 0.001% of the security of Ethereum. If EigenDA is to achieve security that exceeds Celestias current level, the value of the re-pledged assets in the EigenDA network needs to account for more than 0.45% of the value of the Ethereum network. Currently, EigenDA is still in the test network stage, and the asset deposits open to EigenLayer are limited. It is expected that after the EigenDA mainnet is launched and EigenLayer is fully liberalized, the value of re-pledged assets in the EigenDA network will further surge, surpassing Celestia in terms of network security.
Of course, the number of nodes is also one of the factors that cannot be ignored in network security. Currently, Celestia has about 100 pledge verification nodes, and the EigenDA test network has 200 nodes. From the perspective of the number of nodes, EigenDA will also be more secure than Celestia.
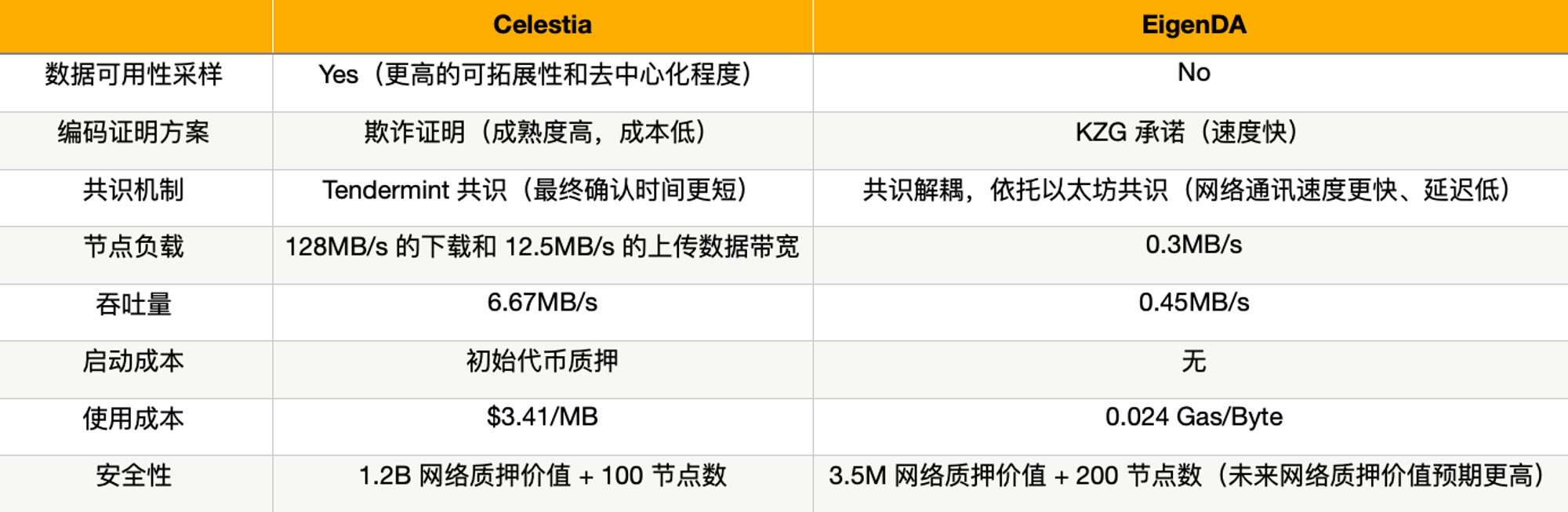
source:MT Capital
Although Celestia and EigenDA currently have different solutions in terms of data availability sampling and encoding proof schemes, as DAS and KZG technologies continue to mature, their choices may become more consistent. According to @sreeramkannan, EigenDA will also consider introducing DAS in the future to support more light nodes. @likebeckett also suggested that Celestia could also change its coding proof scheme if the validity proof scheme based on KZG commitments becomes more attractive than the fraud proof scheme. Therefore, the difference in DA technical architecture between the two may not become the core difference in the future.
The most significant differences between the two in the future are likely to be the gap in network security, usage cost, and throughput.
DA future outlook
According to our comparison between Celestia and EigenDA in the previous section, network security, usage cost and throughput may become the core considerations for different projects to choose different DA solutions. In addition, the Ethereum legitimacy of EigenDA itself is also one of the key factors that cannot be ignored.
From the perspective of network security, although the network security currently displayed by the EigenDA test network still lags behind Celestia. However, we believe that with the launch of EigenDA mainnet, EigenLayers relaxation of restrictions on re-pledged assets and the explosion of restaking narratives in the second half of the year, the value of assets pledged in EigenDA will increase exponentially, and the number of nodes in EigenDA will also increase significantly. Increase. EigenDAs network security may far exceed Celestias network security. Projects that rely more heavily on security may prefer EigenDAs solution.
The current FDV of Ethereum is about 277 B. Only 0.4% of Ethereum participating in EigenDA can achieve security exceeding Celestia, which is obviously very easy to achieve.
In terms of the usage cost gap, the current usage cost of Celestia is still significantly lower than the usage cost of EigenDA. Small L2s and more application chains that are more sensitive to profitability may prefer Celestias DA solution. The migration of Lyra and Aevo to Celestia DA is the best example. Profitability is first of all an issue that every small and medium-sized L2 must consider. In the early days when there is not enough prosperity in the ecosystem to generate income, increasing revenue and reducing expenditure is undoubtedly the wisest choice. Blindly pursuing Ethereums brand premium may hinder its own development. For Application Chain, lower costs also give Application Chain more room for asset control, and it can more flexibly formulate profit sharing incentives, liquidity incentives, and user activity incentive policies based on its own development to guide its own value. Development of the Internet.
Taking aevo as an example, migrating to Celestia can reduce its data availability costs by 90%+.
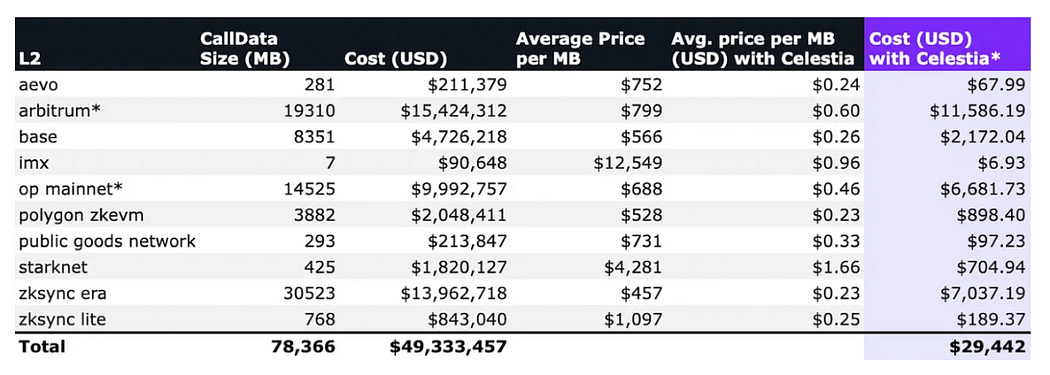
In terms of throughput gap, based only on comparing the existing Celestia throughput data with the EigenDA test network throughput data, Celestias throughput still has a significant advantage of more than 10 times. Celestia with higher throughput will obviously be more favored by application chains with higher performance requirements. Moreover, Celestia can also flexibly increase the block size according to actual needs, giving the application chain higher scalability and transaction throughput support. Of course, the current test network data of EigenDA can only be used as a reference. EigenDA can sometimes run a performance of 6 MB/s - 8 MB/s. The specific performance still needs to wait for EigenDA to finally go online, and a more fair judgment can be given during actual operation.
In terms of Ethereum legitimacy, projects using EigenDA will still be regarded as having orthodox Ethereum origin. However, with the passage of time and the deepening of the concept of modularity, the situation of being scorned or being called deviant for using Celestia DA is also expected to gradually decrease. The concept of Ethereum legitimacy will be used in the future of massive L2 and massive application chains. Fading into the waves. However, in the short term, it should be difficult for us to see the shining DeFi on Ethereum and the migration of L2 kings. Grasping Ethereum is still one of their core narratives.
To sum up, Celestias extremely low DA cost and higher throughput performance make Celestia extremely attractive to small and medium-sized L2 and application chains. L2 and application chains, which have saved high DA costs, have more room for asset disposal and can better allocate revenue and profits to stimulate the development of their respective ecosystems and liquidity. In contrast, EigenDA’s competitive advantage relies more on the security and legitimacy attached to Ethereum. In the short and medium term, EigenDA may become a more rational choice for large L2s compared to Ethereums expensive DA.
Therefore, after detailed comparison, we believe that Celestia can enjoy more incremental market gains brought by the dual trend wave of modularization + application chain, while EigenDA will gain more from Ethereum, which has higher security requirements. It is a stock market.
Nowadays, the competition between Celestia DA and Ethereum-based DA has gradually become the focus of market discussion. In addition, third-party DA solutions such as Near DA and Polygon Avail have also begun to surface. This article will continue the main players of third-party DA, Near DA and Polygon Avail, to peek into the rest of the development path of the DA track.
Near DA
Cost-effectiveness
Using NEAR DA significantly reduces data storage and transmission costs. The cost of publishing a Blocks calldata on NEAR is only $0.0016, while the cost of publishing the same amount of data on Ethereum L1 (after the Cancun upgrade) is about $7.73, indicating that NEARs cost efficiency is as high as 5,000 times.
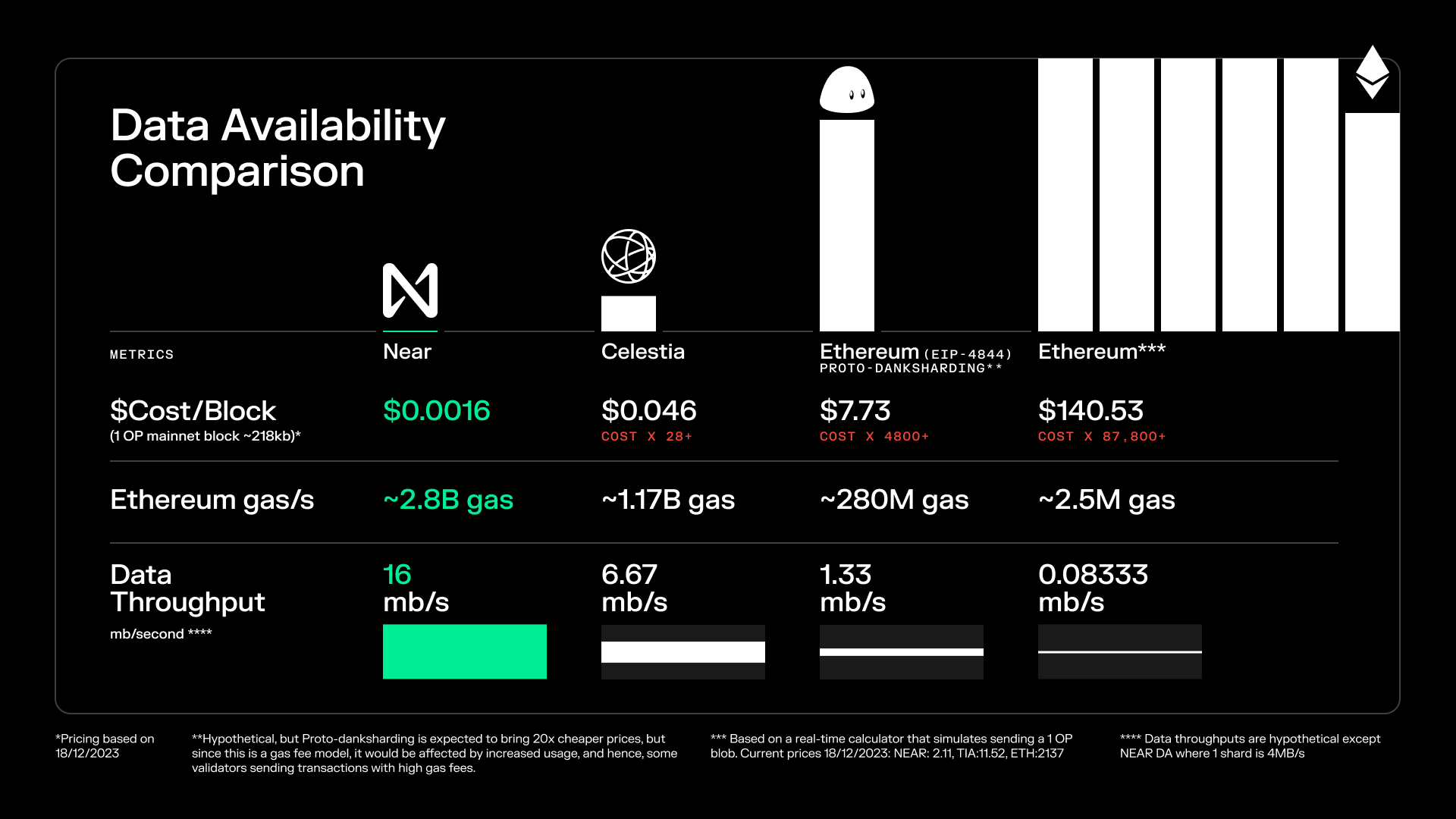
source:https://near.org/data-availability
Technical principles
The Blob Store contract is a key component on the Near blockchain, designed specifically for processing and storing DA blobs. The Blob Store contract stores blobs by utilizing Nears consensus mechanism. When a block producer processes a piece of data, a consensus is formed around the data.
Data Pruning: Once a block contains the receipt and is processed, the receipt is no longer needed for consensus and can be pruned. The pruning time is at least 3 NEAR epochs of 12 hours each, but in practice it is usually five epochs.
Archive Node: Once the receipt is pruned, the responsibility for storing transaction data is transferred to the archive node. This data is also available from indexers.
Blob Commitment Verification: By checking the blob commitment, we can verify that the blob was retrieved from the ecosystem participant in the submitted format. Blob promises are created by splitting a blob into 256-byte fragments and creating a Merkle tree where each leaf is the Sha-256 hash of a shard. The root of the Merkle tree is the blob commitment, provided to the L1 contract in the form of [transaction_id ++ commitment], which is 64 bytes of data.
Key advantages
Consensus Validation: Near validators provide consensus around blob submissions.
Data persistence: Function input data is stored by full nodes for at least three days, and archive nodes can store data for longer.
Efficient use of consensus: Consensus that doesn’t take up more data than needed.
Indexer Support: The data is currently indexed by all major browsers on NEAR.
Long-term availability of commitments: Commitments are easy to create and easy for anyone to build with limited expertise and tools.
Currently, the data availability layer product NEAR DA launched by Near has been integrated with developer stacks such as Polygon CDK and Arbitrum Orbit. Developers can use it to build their own L2 or L3 networks.
The NEAR-Polygon CDK integration allows developers building their own rollups to become part of the Polygon ecosystem. This is the first integration of NEAR DA with a ZK-based L2 stack, adding options to developers looking for scalable DA solutions. This integration also builds on the NEAR-Polygon research collaboration to build zkWASM, a new prover for the WASM blockchain. In the future, builders can even create zkWASM chains based on NEAR DA. NEAR DA and zkWASM technologies will jointly play an important role in scaling the EVM and Wasm ecosystems in parallel while maximizing the future interoperability of multi-chains.
The Arbitrum Orbit chain leverages the Arbitrum Nitro technology stack, a technology developed by Arbitrum to scale Ethereum. It allows developers to create their own blockchains that can settle transactions on Arbitrum One, Arbitrum Nova, or the Ethereum mainnet, provided the Arbitrum DAO grants an L2 license. These Orbit chains use Arbitrums Rollup and AnyTrust protocols, offering customization in throughput, privacy, gas tokens, and governance to meet specific use cases and business needs. For example, rollup developers looking for cheaper data availability (DA) alternatives can now leverage NEAR DA in the Arbitrum Orbit stack. In this way, developers can build self-managing, configurable blockchains with more control over their functionality and governance while gaining the security guarantees of Ethereum.
Polygon Avail
Avail started as a Polygon project in 2020 and became an independent entity in 2023. The team, led by Polygon co-founder Anurag Arjun and former Polygon head of research Prabal Banerjee, aims to deliver industry-leading data availability solutions. Polygon Avail is a modular blockchain solution focused on the data availability layer, designed to build scalable data availability solutions. It adopts a series of technologies, including light clients, data availability sampling, KZG (Kate-Zaverucha-Goldberg) polynomial commitment and erasure coding, etc., to improve the throughput of on-chain data and solve performance bottlenecks.
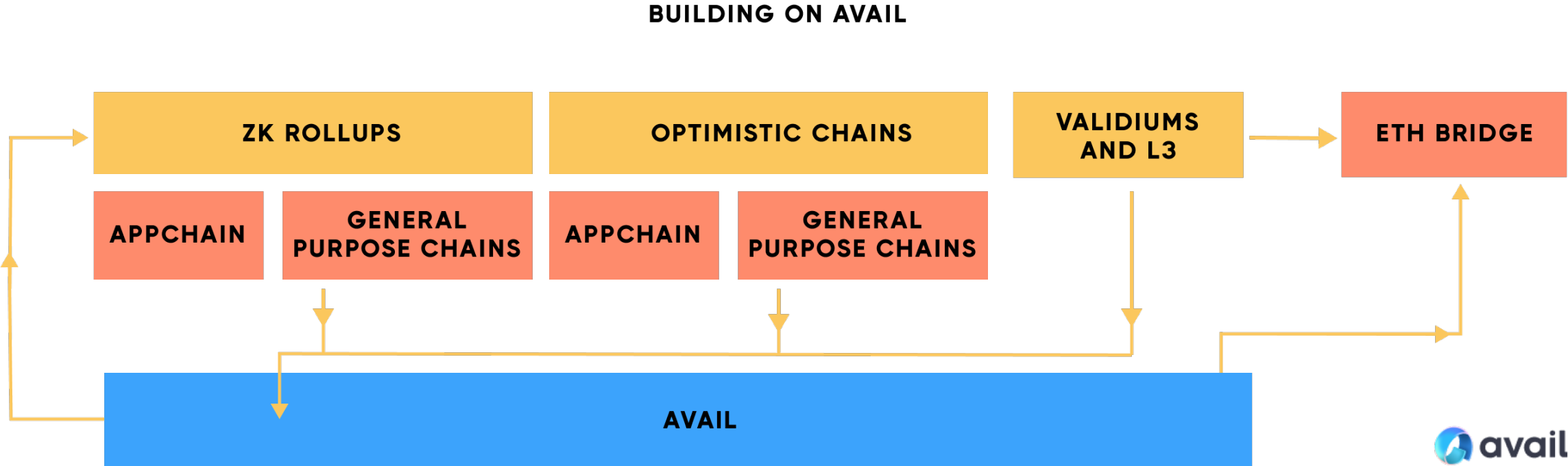
source:https://blog.availproject.org/the-avail-vision-reshaping-the-blockchain-landscape/
Avail design features include:
Consensus Mechanism: Uses the BABE and GRANDPA consensus mechanisms from the Polkadot SDK, combining liveness and security to provide network resilience and be able to withstand temporary network partitions and large number of node failures.
Decentralization: Using Polkadots Nominated Proof of Stake (NPoS) to support up to 1,000 verification nodes and reduce the risk of stake centralization through effective reward distribution. Avails full nodes and light clients use the Data Availability Sampling (DAS) method for verification, allowing for the same security guarantees as traditional full nodes while reducing reliance on full nodes.
Validity Proof: Avail uses KZG polynomials to promise to reduce memory, bandwidth, and storage requirements and provide an efficient verification process. This is different from the fraud proof technology used by Celestia. Avail has many similarities at the data availability level, but its core difference lies in the method of validity proof.
Data availability and security: Avails design philosophy focuses on establishing a data availability layer and providing a universal data availability solution. It does not rely on honest majority assumptions, light clients can determine data availability on their own through random data sampling, and blocks can be reconstructed from light nodes even if a full node goes down or attempts are made to censor data.
Technical implementation: Avail utilizes data redundancy, fraud-resistant proofs, and commitment mechanisms to ensure data validity. It uses KZG polynomial commitment to ensure that the data is still valid after erasure, including data redundancy, anti-fraud proof, and commitment mechanisms, so that full nodes can include all transaction data of light nodes.
Avails practical applications include managed independent chains, side chains and off-chain expansion solutions, with the goal of providing a full-scenario data availability solution for the application layer. For example, in the Ethereum Layer 2 solution, Avail can be used for transaction ordering and data availability, ensuring the availability of data on the chain while alleviating the data volume limitations of the main chain.
The future of Near DA and Polygon Avail
The NEAR protocol has demonstrated its scalability and future development blueprint through its sharding approach and NEAR DA technology. The engineering team’s recent shift to stateless verification marks a further evolution of sharding technology, aiming to enable more shards and a higher degree of decentralization by reducing validator hardware requirements and moving state into memory. This will increase the overall processing power of the NEAR protocol and eliminate the need for projects and developers to compete for block space. As the number of shards increases, the data storage requirements of a single shard decrease, and each account could theoretically become its own shard, allowing lightweight RPC nodes to be run. This means more efficient data management for L2 projects using NEAR DA. Although data availability sharding is still in the research and development stage, it has demonstrated the important advantages of the NEAR protocol for various builders and ecosystems. With the development of the Web3 field, NEAR not only solves the scaling challenges faced by Ethereum by providing fast, low-cost data availability solutions for rollup, but also prepares for the future of multi-chain and cross-chain, promoting NEAR DA technology be at the forefront of this change.
Avail’s future outlook is focused on increasing the efficiency and accessibility of the blockchain ecosystem. Through its modular system, Avail aims to independently optimize data processing and storage, improving overall network performance. It places special emphasis on enhancing data availability and ensuring that even if the data is not directly stored on the chain, it can be effectively verified, which is crucial for maintaining transaction transparency and security. Avail also plans to support asynchronous interaction of multiple application chains, similar to a microservice architecture, to improve overall flexibility and scalability. For ordinary users, Avail uses advanced technology to enable light clients to verify data integrity without downloading the entire blockchain, which makes blockchain technology more user-friendly. Since becoming independent from Polygon, Avail has begun exploring new cooperation opportunities with diverse partners to demonstrate its potential in multiple application scenarios. Ultimately, Avails goal is to provide developers with an easy-to-use environment that inspires them to create innovative applications while promoting a more open, connected, and decentralized digital world.
Reference
https://www.chaincatcher.com/article/2111784https://docs.celestia.org/learn/how-celestia-works/monolithic-vs-modular
https://staking-explorer.com/staking/celestia
https://twitter.com/smyyguy/status/1744419436449222864?s=46
https://docs.eigenlayer.xyz/eigenda-guides/eigenda-rollup-user-guides/building-on-top-of-eigenda
https://www.blog.eigenlayer.xyz/intro-to-eigenda-hyperscale-data-availability-for-rollups/
https://www.blog.eigenlayer.xyz/launch-of-the-stage-2-testnet-eigenlayer-eigenda/
https://www.reflexivityresearch.com/free-reports/exploring-eigenlayer
https://forum.celestia.org/t/a-comparison-between-da-layers/899
https://mirror.xyz/edatweets.eth/ zZG 84 zO 6 EjGo 9 sieBvHUEYYjsY 1935 n 2 XMkc_ 12 _ 678
https://twitter.com/sreeramkannan/status/1595863300679831552
https://blog.celestia.org/ethereum-off-chain-data-availability-landscape/
https://www.odaily.news/post/5189320
https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/45728
https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/45308
https://www.panewslab.com/zh/articledetails/z7f4srnb.html
https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/52079
https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/51570
https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/42095
https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/20581
https://twitter.com/smyyguy/status/1744419436449222864?s=46
https://near.org/data-availability
https://pages.near.org/blog/arbitrum-integrates-near-da-for-developers-building-ethereum-rollups/
https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/51873
https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/46036
https://foresightnews.pro/article/detail/48885
https://dodotopia.notion.site/Celestia- f 86 a 7 f 5 e 0 a 154 e 229 a 2 fddf 9 a 90 c 37 ea
https://docs.celestia.org/concepts/how-celestia-works/data-availability-layer
https://fuel-labs.ghost.io/beyond-monolithic-the-modular-blockchain-paradigm/
https://medium.com/alliancedao/the-case-for-parallel-processing-chains-90bac38a6ba4
https://docs.dymension.xyz/learn/dymension-hub
https://mirror.xyz/neelsalami.eth/ rvhK 5 mEcFTOjyu_DFsqS 2cYR7U6Fjvbw3nf8tI-pr-Q?ref=twitter
https://polygon.technology/solutions/polygon-avail/
https://rainandcoffee.substack.com/p/the-modular-world
https://www.techflowpost.com/article/detail_ 15557.html
MT Capital
MT Capital, headquartered in Silicon Valley, is a crypto-native fund focusing on Web3 and related technologies. We have a global team, and our diverse cultural backgrounds and perspectives allow us to have an in-depth understanding of the global market and to seize investment opportunities in different regions. MT Capitals vision is to become the worlds leading blockchain investment firm, focused on supporting early-stage technology companies that can generate significant value. Since 2016, our investment portfolio covers Infra, L1/L2, DeFi, NFT, GameFi and other fields. We are not just investors, we are the driving force behind the founding team.
Official website: https://mt.capital/
Twitter: https://twitter.com/MTCapital_US
Medium: https://medium.com/@MTCapital_US