Original author: Jiang Haibo, PANews
The rise of Bitcoin and the booming development of the Inscription ecosystem constitute the mainstream narrative of the cryptocurrency world this year. Bitcoins rise has been driven by the prosperity of the on-chain ecology, the anticipation of the adoption of spot ETFs, the anticipation of halving and the Federal Reserves interest rate cut. It has also been greatly promoted by the entry of institutional investors. These factors have jointly contributed to its significant growth this year. .
In addition, the inscription ecology, especially the non-fungible tokens (NFT) and fungible tokens (FT) represented by Ordinals, not only brings new vitality and focus to the Bitcoin ecosystem, but also spills over to Other public chains, almost all leading public chains have developed a set of inscription gameplay. Old projects are constantly added to take advantage of the opportunity to regain their vitality.
Bounce’s Bitcoin Ecosystem Project Auction and Layer 2
Bounce Finance is an auction-as-a-service (AaaS) protocol that provides projects with one-stop token issuance services. The platform supports multiple blockchain networks, providing users with the ability to create and participate in various types of auctions, including token and NFT auctions, physical collectible auctions, advertising space auctions, and more.
Recently, Bounce has launched auctions for several Bitcoin ecological projects. The initial valuations were relatively low, and subsequent auctions can use the tokens of previous projects as shovels, so these projects have performed well. Since its own native token AUCTION is also the golden shovel in the auction, the price of AUCTION also rises.
Take the recent auction of GoDID as an example. GoDID is a market aggregator for decentralized identities (DID), providing services for ENS, Space ID, and Bitcoin Ordinals DID. The token of GoDID is BDID, of which 20% is allocated to users who use AUCTION to purchase lottery tickets, 40% is allocated to AUCTION pledgers, 20% is allocated to pledgers of the US dollar stable currency DAII issued by the previous Launch project BitStable, 5 % is allocated to airdrop mining participants using MUBI, BSSB, AUCTION, and WBTC, among which MUBI and BSSB are auction items in previous phases.
In December, Bounce also announced a blockchain solution designed for the Bitcoin ecosystem, BounceBit, a Bitcoin Layer 2 based on Binance Bitcoin BTCB and AUCTION, which is scheduled to launch in 2024.
Uniswap expands to Rootstock
Uniswap is a leading decentralized exchange (DEX). Over time, Uniswap has launched multiple versions and expanded to multiple chains.
Last week, GFX Labs deployed Uniswap V3 to the Bitcoin sidechain Rootstock through Oku. This move is also seen as Uniswap’s expansion into the Bitcoin ecosystem. GFX Labs received funding from the Uniswap Foundation to build Oku, a trading front-end based on Uniswap V3. Oku features order books, price action charts, transaction history, limit orders, and more.
Rootstock (RSK) is a side chain based on the Bitcoin network, compatible with the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM), ensuring security through merged mining with Bitcoin, and has SBTC anchored 1:1 with Bitcoin. RSK introduces a joint guarantor model, a group of entities trusted by the community to manage the transfer of assets from Bitcoin to RSK. These guarantors provide an additional layer of security, ensuring assets are safely transferred between the two networks.
As of December 19, liquidity on Oku was $535,000.
NFT Market Magic Eden
Magic Eden is an NFT marketplace focused on the Solana blockchain. It has a large presence in the Solana ecosystem, providing a user-friendly interface that enables artists, collectors, and NFT enthusiasts to easily buy, sell, and explore NFTs. Its features include low transaction fees, high-speed transactions, and a diverse NFT collection, making it one of the most popular NFT marketplaces in the Solana ecosystem.
In March of this year, with the rise of Ordinals NFT, Magic Eden announced its expansion into the Bitcoin ecosystem as an important step in its multi-chain vision, which further strengthened its position in the multi-chain NFT market.
As shown in the figure below, the transaction volume of Bitcoin ecological NFTs such as bitmap and Bitcoin Frogs is also at the forefront of Magic Eden.
Nostr combines decentralized social networking and micropayments
Nostr is a decentralized social protocol backed by Twitter co-founder Jack Dorsey. Its concept originated in November 2020 and aims to build a global, decentralized, censorship-resistant communication network.
In September this year, Nostr carried out NIP-57 upgrade, adding the micro-payment function Zaps, allowing users to make small rewards or payments through the Nostr client, thereby enabling fast and low-cost payments in the Nostr ecosystem. Zaps are mainly implemented through the Lightning Network, and its process is efficient and low-cost.
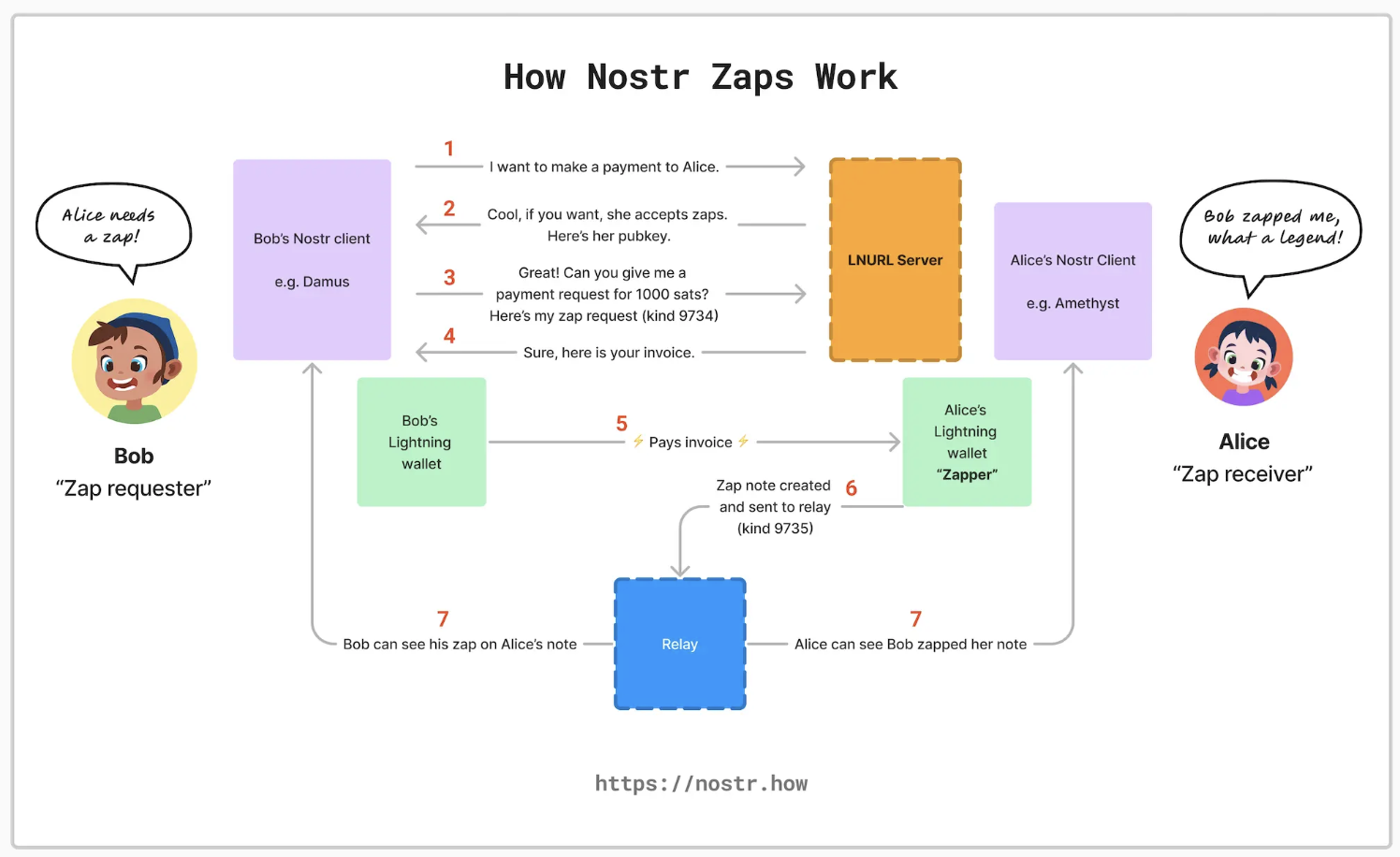
After the user initiates a Zap request on the Nostr client, if the recipients Lightning wallet supports Zaps, the LNURL server will respond and confirm the recipients public key. The client then creates a Zap request containing the key data from the payment, and the LNURL server responds with the required invoice. Once the user completes the payment, the amount is paid directly to the recipient’s Lightning wallet.
To date, Zap has made more than 50,000 payments.
ALEX’s B 20 and Oracle
ALEX was originally a DeFi (decentralized finance) platform on Stacks. Its main product is a DEX, as well as Launchpad, cross-chain bridge, staking, mining, lottery and other functions. DefiLlama data shows that ALEX’s TVL is $38.8 million, accounting for approximately 82.3% of Stacks’ TVL. If judged only by the positioning of a public chain head DEX, then the valuation of ALEX is very limited, especially the liquidity and trading volume are not high.
After the popularity of Inscription, ALEX developed a decentralized exchange called B 20 specifically for trading BRC 20 tokens. ALEX also provided STX tokens to new entrants to pay for the gas fee of the ecosystem. In B 20, these BRC 20 tokens can be traded with sUSDT as the base currency, which is USDT cross-chained from the BNB chain to Stacks.
Additionally, ALEX plans to launch the first Bitcoin oracle for the BRC 20 token, an effort in collaboration with BRC 20 creator and ALEX advisor @domodata as well as key existing players including BestinSlot, OKX, Hiro, Unisat, and more This is done together with the off-chain indexer. It hopes to leverage Stacks’ programmability and readability of Bitcoin state to spearhead decentralized consensus for the BRC 20 index, also known as the “indexer of indexers.” The goal of the Bitcoin oracle is to verify every BRC 20 event and update the global balance in a decentralized, on-chain contract.
The inscriptions of various public chains contend
Inscriptions represented by Ordinals are prevalent on Bitcoin, with ORDI and SATS each having a market cap of over $1 billion. Projects like Ordinals allow users to attach data (such as text, images, etc.) to specific parts of a transaction, thereby associating this data with a specific Satoshi. When such a transaction is packaged onto the blockchain, the specific satoshi carries the user-attached data. These specific satoshis can be viewed as unique digital assets, and users can trade them to others, thereby enabling the transfer of specific assets.
If inscriptions add a new method of asset issuance to Bitcoin, which originally did not support smart contracts, then do inscriptions that are popular on other chains still have meaning? According to incomplete statistics, there are more than 30 public chains that have released or are preparing to release inscriptions, such as Ethereums ETHS, Solanas SOLS, and Avalanches AVAV. The process of casting inscriptions has even caused short-term downtime in many networks such as Arbitrum, TON, and IOST. machine.
On the evening of December 19, the casting of the first inscription INJS on Injective sparked a farce. Since every minting of INJS requires a fee of 0.03 INJ to be paid to contract deployers, the project has caused dissatisfaction among Inscription players. When INJS began casting, Injective’s official Twitter tweeted asking users not to participate, saying the Injection team’s practice of charging fees was inappropriate. After that, INJS announced that it would stop minting and would allow users to participate for free in the future. This also reflects users’ pursuit of Free Launch.
What is the difference between inscription transfer on the smart contract chain and transfer through smart contracts? Taking the inscription project Ethscriptions on Ethereum as an example, the transfer fees of Ethscriptions may be lower than ordinary smart contract transfers because they reduce transaction costs by using calldata and avoiding traditional smart contract storage and execution. This makes Ethscriptions a more cost-effective way to perform operations on the blockchain.
But bypassing traditional smart contract storage and execution may introduce new security vulnerabilities or unforeseen behavior, especially when dealing with complex data structures or logic. Additionally, if only calldata is used, Ethscriptions may not take advantage of all the functionality and flexibility offered by smart contracts, potentially limiting their usefulness in certain applications.
summary
In the development of the Bitcoin ecosystem, Bounces unique auction gameplay has brought a good wealth creation effect, and it also plans to develop Bitcoin Layer 2; Nostr combines decentralized social networking with micropayments; ALEX developed the BRC 20 trading market , also plans to launch the first decentralized Bitcoin oracle; Uniswap and Magic Eden have respectively expanded their trading business to the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Inscriptions have been successfully extended to almost all public chains worthy of attention. For non-smart contract chains such as Bitcoin, inscriptions are even more important; for Ethereum, inscriptions reduce on-chain storage and execution costs in traditional smart contracts, but may also be introduced There are new security issues, and the functionality is not as flexible as smart contracts.