Original Author: Jill, LD Capital

Preface
Recently, due to Compound founder Robert announcing the establishment of a new company focusing on on-chain US debt, the narrative of Real-World Asset (RWA) tokenization has been sparked, and the Compound token COMP has soared as a result. In addition, RWA leader MakerDAO and lending leader Aave have also seen significant price increases recently.
Compound and Aave have similar product forms, and we have previously published MakerDAO-related business data, so this article mainly looks at the fundamental data of Aave and Compound from three directions: lending business, token emissions, and protocol revenues and expenses.
Summary
Aave has a capital volume 2.6 times that of Compound,secondary title
The security of DeFi protocols is the foundation of project development, and reducing potential risks is the most important task for the team. Both Aave and Compound have risk isolation measures in their product designs. However, Compound's current approach is more aggressive, directly reducing the complexity of the protocol and isolating each asset pool based on different underlying assets. This also means that Compound has given up some market share of altcoins as underlying assets. Aave, on the other hand, is more inclined to be a comprehensive and universal lending protocol, seizing more market share, isolating new assets from the core asset pool, and reducing potential risks of new assets as collateral.
In terms of risk control measures, both have introduced reserve funds as remedies in case of protocol debt losses. In addition, Aave has an embedded safety module, which allows token stakers to serve as the security backstop for the entire protocol. This not only empowers the protocol token but also locks up a portion of token liquidity, reducing market inflation.
In terms of token issuance, the current emission of both is relatively low, and the impact of token selling pressure on the secondary market is minimal. Aave is an earlier protocol, with a token circulation of 90.5%, but the safety module locks up a portion of token liquidity. Compound pioneered liquidity mining, but the liquidity generated through this method will be immediately sold by participants when they obtain substantial returns, which has a significant impact on the protocol. Therefore, Compound has changed its liquidity incentive measures and distributes tokens to real users. Currently, the token circulation is 68.6%.
The prices of COMP and AAVE tokens have risen significantly due to recent RWA narratives. However, it should be noted that the founder's new company for Compound is still in the application stage, while Aave's RWA funds are only $7.65 million, which is only 0.3% of the RWA leader Maker's fund size.
In terms of protocol revenue, Aave has a more diversified income source, and all the interest from stablecoin GHO loans goes to the treasury. Looking at the trend of treasury revenue, it can be seen that Aave's protocol revenue has decreased sharply since the last bull market. However, the current protocol revenue is sufficient to cover the protocol expenses, while Compound still relies on COMP token rewards as subsidies. Compound has a relatively single source of revenue, and Aave's protocol revenue is about four times that of Compound.
1. Fundamental Analysis
1. Product Version
Aave initially started as a peer-to-peer lending platform, but later redesigned it due to inefficiencies in loan matching by adopting Compound's money market lending model to provide high liquidity. Aave is currently in version 3 (V3), which aims to provide higher capital efficiency, greater security, and cross
Higher capital efficiency refers to the efficient mode (eMode), which classifies assets and sets risk parameters based on asset types. When the collateral of the borrower is the same category as the lending asset, a higher loan amount can be obtained. Higher security refers to the isolation mode, which means that newly listed lending assets through on-chain voting will first enter isolation mode. In this mode, the assets will have a debt ceiling, and when used as collateral, only approved stablecoins are allowed to be borrowed, aiming to list more long-tail assets while ensuring the security of the protocol.
These functions are currently available on V3. Cross-chain lending (Portal) functionality was already deployable when V3 was released in March 2022. However, due to security considerations, the team has been cautious about deploying this feature and it has not been officially deployed yet. Aave's cross-chain lending is not controlled by the Aave protocol itself, but it introduces a third-party cross-chain bridge protocol.
Compound was the first DeFi protocol to introduce the concept of money market lending, allowing for the borrowing and lending between mainstream crypto assets. However, in V3, the general lending approach has been changed, and the various asset pools are isolated based on the underlying assets. This is done to mitigate the risks associated with individual assets at the architectural level, avoiding irreparable losses to the protocol.
Specifically, in Compound V2, the protocol allows users to freely deposit (collateralize) or borrow supported assets. Collateralized assets are assets that users borrow. In Compound V3, each pool will have only one underlying asset, but there are no restrictions on collateralized assets. Currently, the first underlying asset pool launched in V3 is USDC, which allows users to collateralize mainstream cryptocurrencies and borrow stablecoin USDC.
2. Lending Business
When choosing a lending protocol, the primary consideration for users is the security of the assets. On the premise of asset security, users usually prefer protocols with larger fund sizes because a larger fund size typically means better liquidity. In addition to that, other factors to consider include which party offers better interest rates, supports a wider range of assets, lending incentives, etc. We will compare the two protocol products based on the above dimensions.
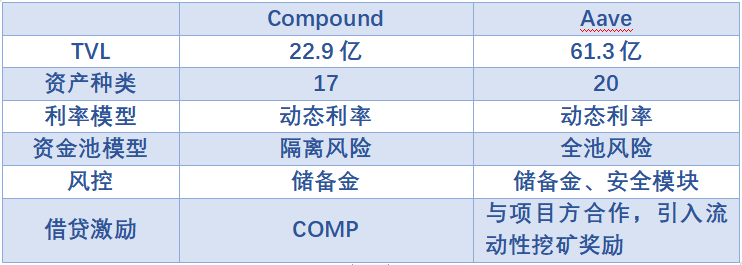
TVL data comes from defillama.com, since the last bull market, the overall size of DeFi protocols has experienced a significant retracement. Compound and Aave are the leading protocols in the DeFi lending field, with Aave's funds being 2.6 times that of Compound, making it the largest protocol in the lending field.
Both Aave and Compound have now deployed on multiple chains. However, Aave entered Polygon and other chains as early as '21 and is in a leading position on other chains as well, occupying a larger market share. Compound, on the other hand, only began deploying on other chains this year. However, the Ethereum chain remains the primary lending venue. Aave supports more types of altcoins, but some of these tokens are frozen due to potential risks. Currently, Aave supports a similar number of tokens as Compound V2. Compound V3 supports very few asset types, with USDC as the main collateral including ETH, WBTC, COMP, UNI, LINK. In the ETH market, the collateral assets are only wstETH and cbETH. Aave has supported stETH as collateral since February 2022, but Compound only started offering wstETH and cbETH in January this year. From this perspective, Compound's progress in multi-chain development is slow, while Aave is more aggressive in business expansion, gradually widening the gap.
Both use dynamic interest rate lending, with Ethereum blocks as the interest calculation unit, prioritized by Compound. The core of the interest rate model is
Utilization rate of funds, which is calculated based on market borrowing demand, does not vary much. When the utilization rate of funds is high, the interest rate will also be higher, and both introduce optimal interest rates. When the utilization rate of funds reaches a certain threshold, the borrowing interest rate will increase sharply, thereby restricting borrowing and preventing liquidity depletion. The fund utilization efficiency of stablecoins and altcoins in Aave is higher than Compound. In terms of the fund pool model, both have measures for risk isolation. However, Aave's fund pool is still a fully pooled risk model. However, for the sake of protocol security, newly listed assets will enter isolation mode first, thereby reducing the risk of these assets being used as collateral through specific risk parameters and specific underlying assets. Compound V3 isolates each asset pool based on the different underlying assets, isolating risks from a system architecture perspective. However, it also means that Compound has abandoned some altcoins as a market share of underlying assets. To address potential risks that may occur in the system, Compound introduces the concept of "reserves". The system will allocate a portion of the borrowing interest as reserves according to the reserve factor to address protocol losses. In addition to charging reserves, Aave also uses a safety module to backstop the protocol. AAVE token stakers will bear up to 30% of the security risk of the entire protocol. In return, stakers can receive AAVE token rewards and protocol income dividends. Compound pioneered the concept of liquidity mining, using COMP tokens as rewards, and is gradually reducing the reward amount. Aave protocol was launched earlier, and the token is basically in a fully circulating state. Currently, it can only collaborate with other projects to incentivize liquidity, such as its partnership with Polygon in June 2021.Aave Polygon provides over $8.5 million in token rewards for market liquidity mining.3. Other Businesses
Stablecoin: Aave's stablecoin, GHO, went live on the mainnet on July 15th with a borrowing interest rate of 1.5%, making it more competitive than other stablecoins. All GHO interest income goes to the treasury. Within two days of going live, GHO's borrowing volume reached 2.21 million tokens, and the team's efforts to promote liquidity will be monitored closely. Compound currently has no plans to issue stablecoins.
RWA: Aave is the second DeFi protocol to introduce RWA (Real World Asset) after Maker. It operates the RWA market separately from the Aave lending market through a collaboration with Centrifuge Tinlake. The current funding size is approximately $7.65 million, far below Maker's $2.3 billion. Currently, only the USDC market provides deposit and borrowing APY, while other markets no longer offer this. Users who have successfully passed KYC only need to deposit USDC in the USDC market to receive a base APY of 2.83% and a wCFG liquidity mining yield of 4.09%.
Source: Aave Official Website
From the perspective of the development of lending business, Compound, although pioneering the concept of capital pool lending agreement, has been lagging behind in terms of team effort and business expansion, while Aave has seized the opportunity of multi-chain development and has a team with innovative ideas, gradually pulling ahead of Compound and becoming the leader.
2. Token Demand and Emission
In July 2020, Aave released a new version of its economic model, replacing the original token LEND with AAVE at a ratio of 100:1. The LEND token is in full circulation. The total supply of AAVE tokens is 16 million, of which 13 million are available for the replacement of the original LEND tokens, and the remaining 3 million are issued for the Aave ecosystem reserve.
The main use cases of AAVE in the protocol are governance and staking. Aave has a built-in Safety Module (SM) component in the protocol, where token holders can stake their funds to provide a backstop in case of a debt shortfall in the Aave protocol. In return, stakers can receive AAVE token incentives and share in the protocol's revenue.
From the official website's staking interface, it can be seen that the current daily emission of AAVE tokens is 1,100.
There are a total of tokens, based on Coingecko's price of $80.56 on July 15, the value is approximately $88.6 thousand dollars, and the current circulation of AAVE tokens has reached 90.52%.
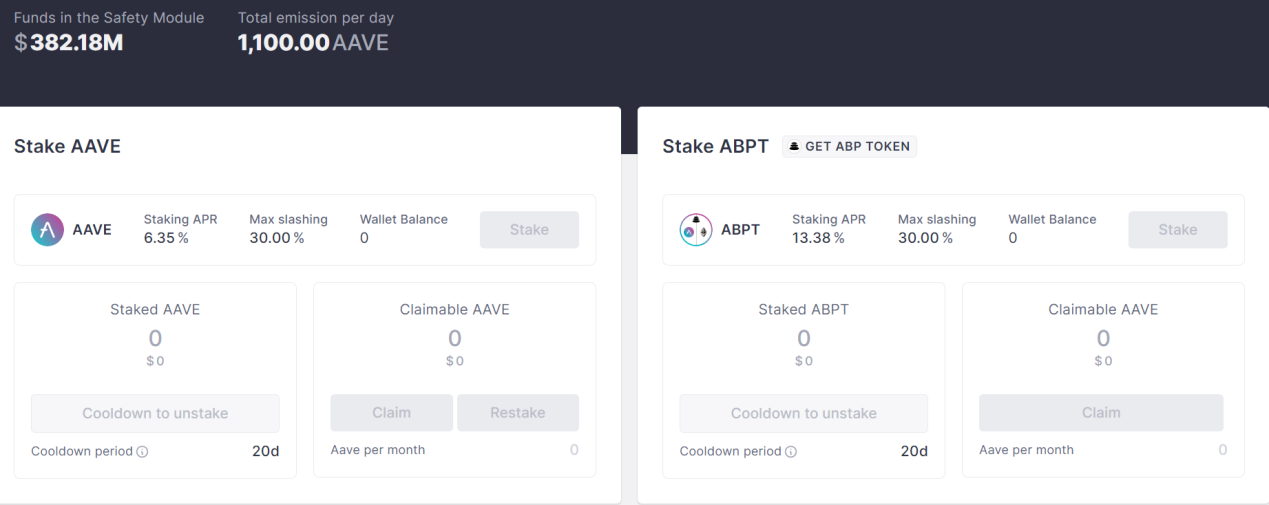
Source: Aave Official Staking Interface
Compound token is COMP, officially launched in June 2020, with a total supply of 10 million. COMP is the governance token of the Compound protocol, mainly used for protocol governance (proposal voting) and as liquidity incentives for the lending market. The initial allocation plan for COMP is as follows:
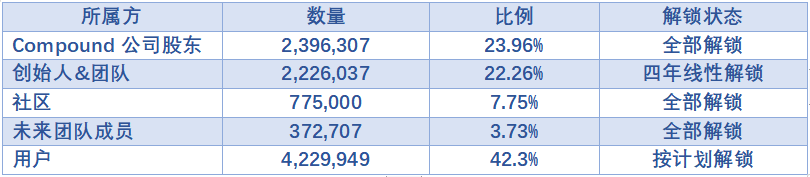
The continuous unlocking pressure of the token currently mainly comes from the founders and the team, as well as the portion allocated to users, with unclear plans for the portion allocated to the founders and the team, while the portion allocated to users mainly serves as incentives for lending activities.
According to the proposal passed on July 15, 2023, the incentives for users participating in the V2 market for USDC and DAI deposit and borrowing have been lowered from 161.2 COMP to 111.2 COMP. The total rewards for borrowing and lending in the V2 market are 111.2 * 4 = 444.8 COMP per day (with deposit and borrowing market incentives at 0.015 COMP per block). Simultaneously, the proposal also lowers the borrowing rewards for the V3 lending market from 481.41 COMP to 381.41 COMP, while increasing the supply rewards from 0 to 100 COMP per day, transferring part of the borrowing incentives to the supply market. Therefore, the total rewards in the V3 market remain at 481.41 COMP.
Based on the above proposal, the current deterministic daily emission of COMP is 926.21 tokens, and based on the price of $74 on Coingecko on July 15, it is worth approximately $68.5 thousand. The circulating supply of COMP tokens currently reaches 68.56%.
As one of the earlier DeFi protocols to go live, Compound and Aave
The current token emission is relatively low, and the impact of token selling pressure on the secondary market price is minimal. The protocol tokens of the two are mainly used for governance and incentivizing protocol users. The difference between them is that Compound distributes tokens to users who participate in lending activities to attract liquidity, while Aave provides incentives for token holders to pledge their tokens. It can be used to backstop protocol debt and reduce token inflation. Currently, there are about 4.68 million tokens pledged in the safety module, so the actual circulating supply of AAVE is around 61.3%.
III. Protocol Revenue and Expenses
The Aave treasury consists of system reserves and treasury collectors. The sources of Aave protocol revenue are: 1) the interest rate differential on loans, which varies depending on the lending market rates; 2) flash loan fees, which are typically 0.09% of the borrowed amount, with 30% going to the protocol treasury and the remaining 70% distributed to depositors; 3) GHO minting revenue; 4) in V3, there will also be instant liquidity fees, liquidation fees, and gateway fees paid through bridging protocols, but the latter two are not yet activated.
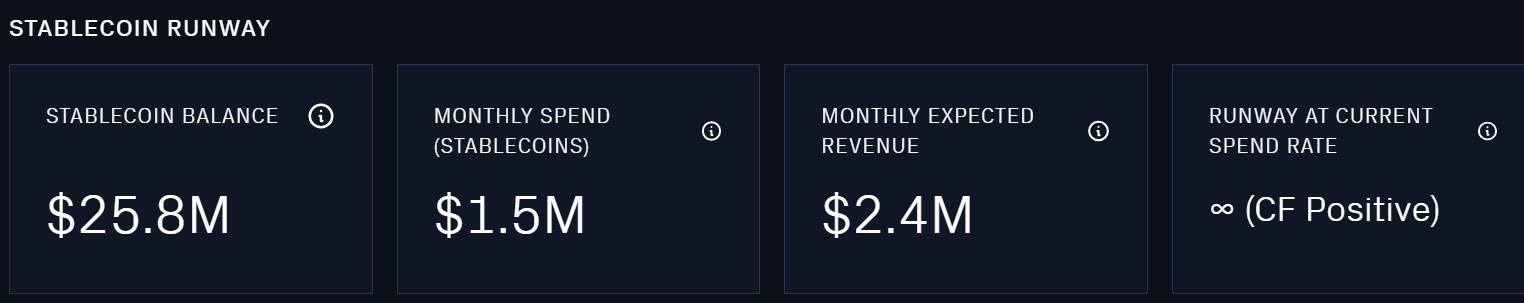
The Aave treasury currently has a cumulative value of $130 million, including $9.15 million (1.2 million tokens) in the form of AAVE tokens as ecosystem reserves, and the remaining $25.8 million in stablecoins.
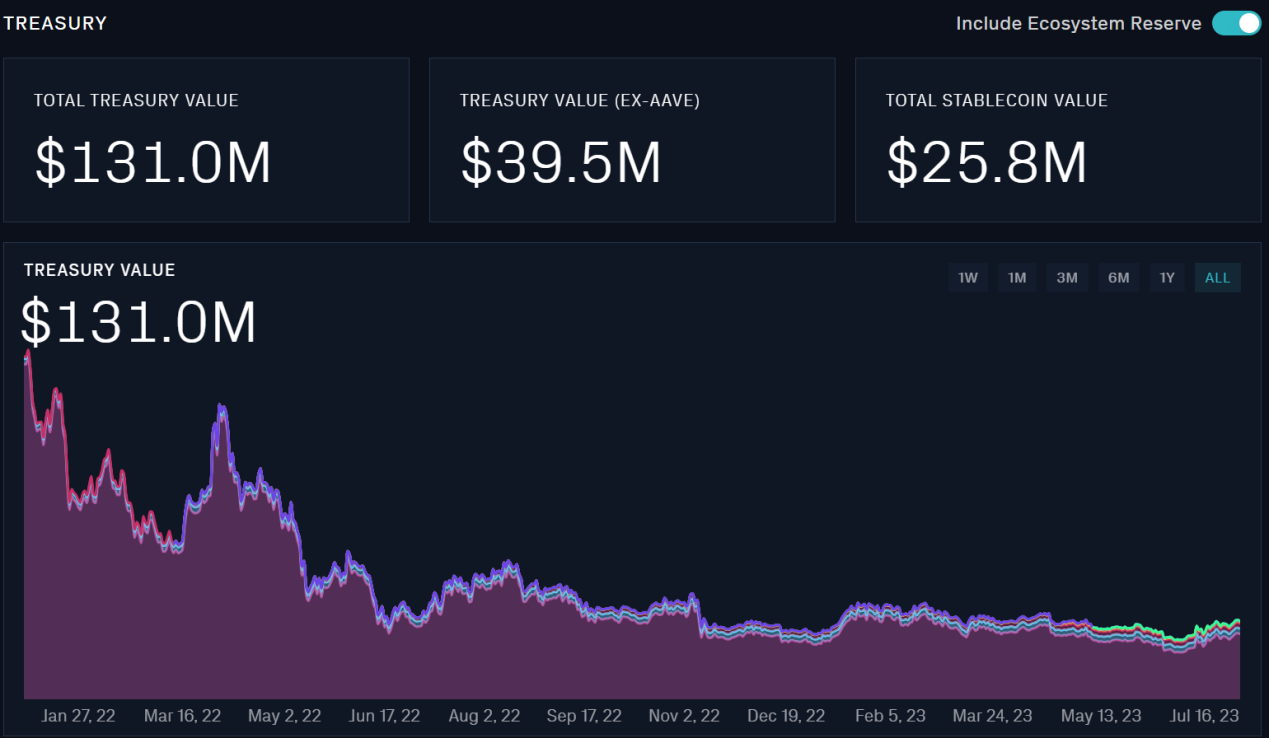
Source:llama.xyz
The above data is from llama.xyz, a website recognized by Aave. However, the data on this website is only available from January 2022 onwards. Taking the revenue and expenditure in June 2023 as an example, the monthly consumption (token incentives) is $1.5 million, the monthly income is $2.4 million, and the surplus is $0.9 million. This data is consistent with Token Terminal data.
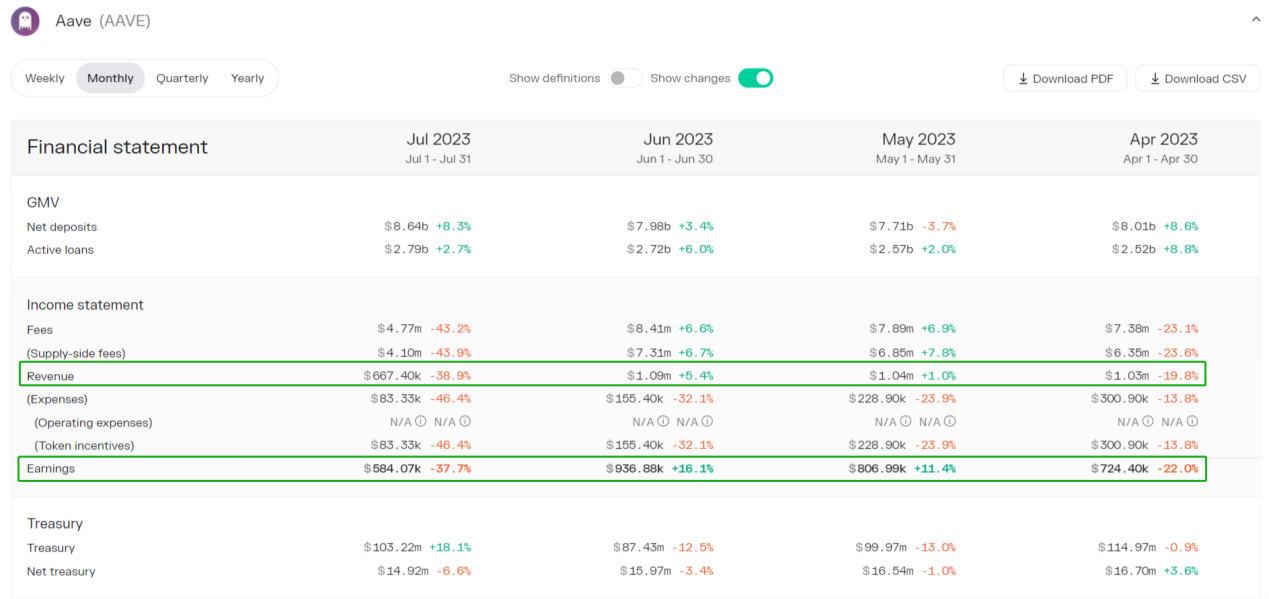
The income source of the Compound protocol is only the interest spread from lending and borrowing because there is no official statistical website. To maintain consistency, Token Terminal data is used as a reference.
Source: Token Terminal
In Token Terminal's calculation, protocol revenue = fees paid for borrowing - supply-side fees, and earnings = protocol revenue - liquidity incentives.
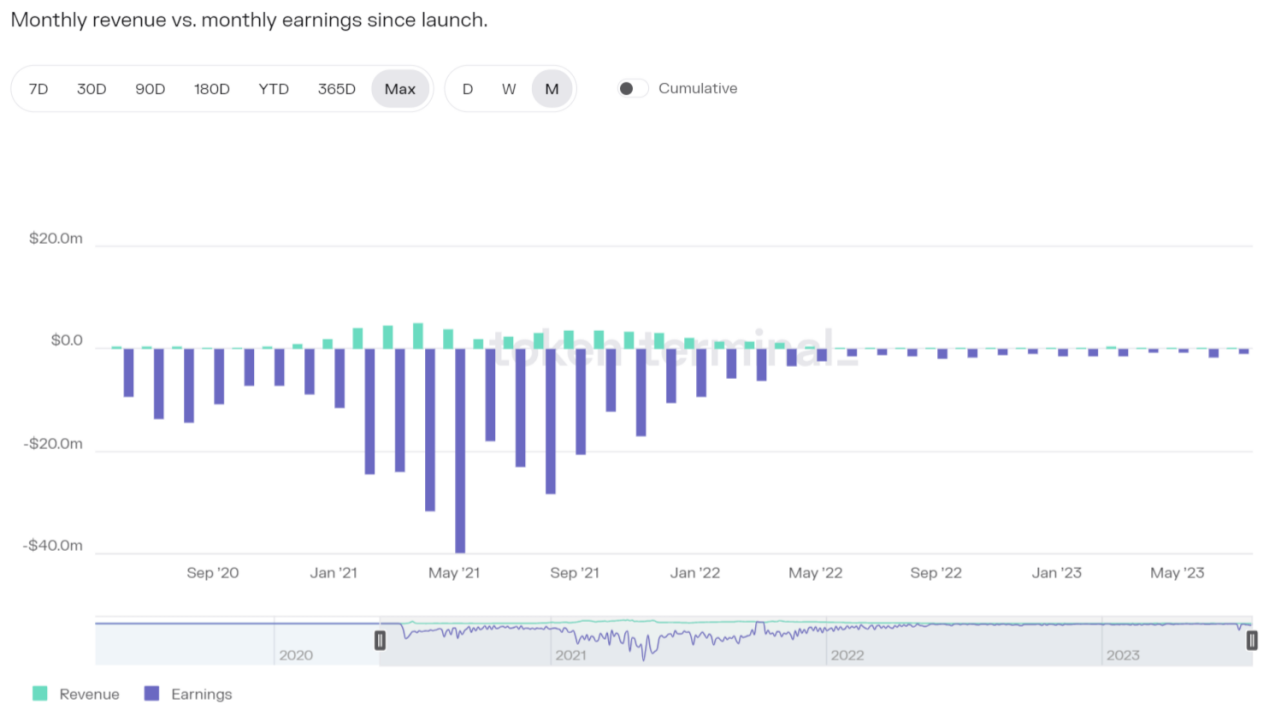
Aave's protocol revenue started gradually rising in May 2021, reaching its peak from September 2021 to November. Afterward, the revenue gradually declined, and by April 2022, it significantly decreased to a monthly revenue of $1.9 million. By October 2022, the monthly revenue dropped to only $0.86 million, which is 12.6% of the peak period = (86/680) * 100%, and it continues to decrease. From March 2023, the protocol revenue started to recover, reaching a monthly revenue of $1.3 million.
Source:token terminal
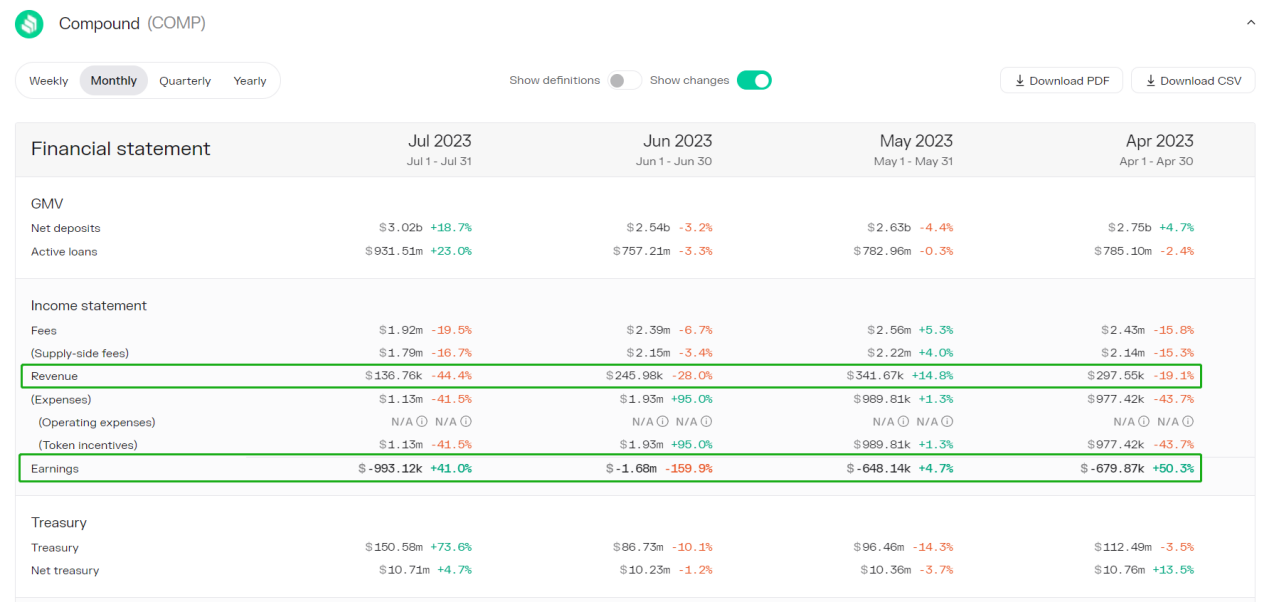
Since January 2021, Compound protocol revenue has gradually increased, with the peak in March to April 2021, with monthly revenue around $5 million. Starting from February 2022, Compound revenue has declined significantly, with monthly revenue remaining around $1 million. By May 2022, the revenue dropped to $460,000 and has been declining ever since.
Compound pioneered the lending and mining model, with a relatively strong token incentive. Therefore, when Earnings were low, after April 2022, Compound changed the token incentive model, gradually reducing COMP rewards, and the COMP token price also experienced a significant decline. Earnings have slowly been recovering. However, the current protocol revenue is far from covering the token incentive expenses.
Source: token terminal
Source: token terminal
According to LinkedIn data, Aave currently has 98 employees, while Compound has 18 employees. Aave has five times more employees than Compound, which may result in larger personnel expenses.
Looking at the protocol revenue of both, Aave has a more diversified income source while Compound has a more single-source income. If we consider the revenue from June, Aave's monthly revenue is 4.4 times that of Compound (105/24.5). Aave's protocol revenue is currently able to cover token incentive expenses whereas Compound is still subsidized by COMP tokens.