Original Author: Yilan, LD Capital

Public Chain Order Book Track Pattern
When mentioning DEX, most people immediately associate it with AMM. AMM is very useful and is a key DeFi primitive. Although onchain LOB (on-chain order book) is criticized for lacking LP ecosystem and regulatory arb on-chain by centralized exchanges compared to AMM, onchain LOB also plays a non-negligible role in the entire DEX track, especially for professional traders and institutions, it is an important sub-track of the DEX track.
Overall, order book exchanges can be understood in four types. The first type is highly centralized CEX with excellent trading speed and throughput, which is the trading choice for most people in the market, such as Binance/OKX. The second type is Ethereum L1 on-chain order book, such as Gridex, which achieves a high level of decentralization. However, due to the direct on-chain execution of trades, the performance is limited and users need to pay high gas fees. The third type is high-performance off-chain order books based on Rollup, which match off-chain to reduce Gas fees and ensure security through on-chain batch processing and settlement, such as dYdX v3, Vertex, Zigzag, etc. ETH L2 Base recently called for onchain order book DEX to be part of its ecosystem fund and be deployed in its ecosystem. The development of each L2 will provide a good development environment for onchain order books. The fourth type is high-performance DeFi native chains/custom chains that meet the high-performance order requirements, such as Injective and Sei, which has not yet launched its mainnet, dYdX v4, etc.
With the construction of Cosmos Tendermint/Ignite, SDK, and IBC technology components, Injective leverages the network's high finality and low transaction costs to support its order book functionality. This further improves capital efficiency and liquidity fragmentation while maintaining interoperability with Ethereum. By using the FBA (Frequent Batch Auction) order matching engine, which aggregates each order at the end of a block and executes all market orders at the same price, Injective helps prevent front-running through its OME (Order Matching Engine) approach. This positions Injective as a decentralized financial infrastructure with decentralization, high transaction speed, high finality, and protection against MEV (Miner Extractable Value) compared to traditional financial order books and other AMMs.
Injective Construction
Injective Chain is a core component of Injective, and the Injective chain, built using the Cosmos Tendermint/Ignite standards, inherits decentralization, security, and high performance.
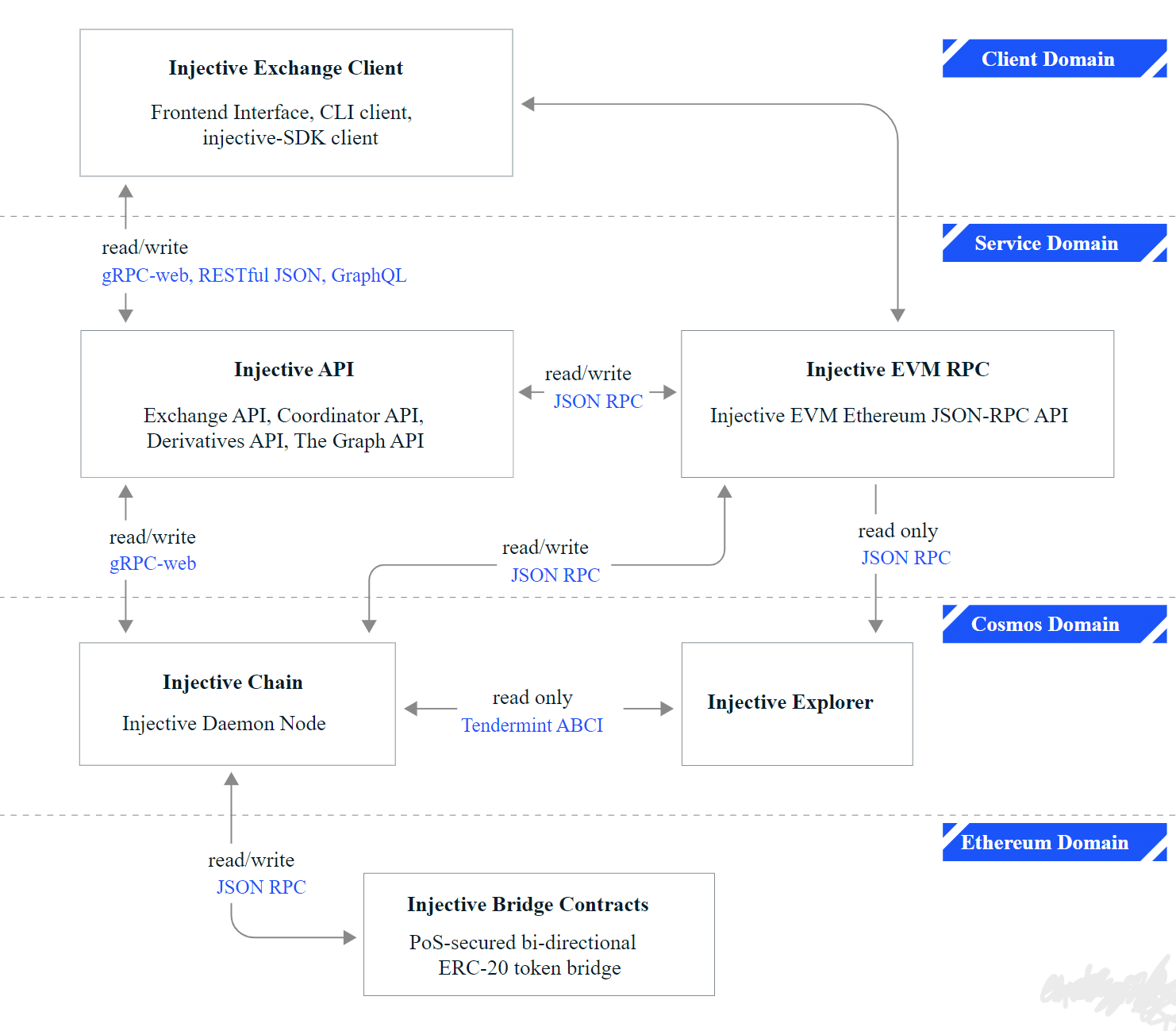
The above figure shows the entire structure of the Injective Stack.
Service Domain
The service layer acts as a bridge between exchange DApps (such as Helix) and the underlying blockchain layer. It consists of multiple APIs, including exchange API, coordinator API, derivatives API, and The Graph API. These APIs play a crucial role in facilitating seamless communication between different components of the Injective ecosystem, enabling users to trade and access various DeFi services. The APIs within the service layer allow Helix to interact with both the Tendermint/Ignite-based Cosmos chain and the Ethereum blockchain. This modular API design approach provides greater flexibility and scalability, ensuring that Injective can continue to grow and evolve to meet the ever-changing needs of the DeFi space.
Cosmos Layer
The Cosmos layer.
>Cosmos Layer is the foundation of the Injective Chain, built on Tendermint/Ignite, responsible for executing various types of transactions and derivative orders. This layer includes Injective API and Injective EVM Remote Procedure Call (RPC) for connecting with the Injective Chain and Injective Explorer. EVM (Ethereum Virtual Machine) is a decentralized, Turing-complete virtual machine used for executing smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain. Injective Explorer is a tool for tracking all transactions taking place on the Injective Chain, providing valuable insights into platform activity and performance. Tendermint's instant finality properties make it an ideal choice for supporting the Injective Chain as it enables fast transaction execution and settlement. Cosmos Layer also offers a range of security and performance advantages, including the Tendermint/Ignite consensus mechanism, horizontal scalability, and a powerful application framework for building custom blockchain applications.Importance of Consensus Mechanism
Choosing Tendermint/Ignite as the consensus mechanism for the Injective Chain is because it can provide near-instant finality, high fault tolerance, and support for horizontal scalability. Near-instant finality is particularly important in the context of a trading platform as it ensures transactions can be executed quickly and efficiently without the risk of rollback or double-spending. This allows Injective to maintain a high level of performance even as the trading activity on the platform increases. Tendermint's PoS consensus algorithm also provides high fault tolerance, ensuring the proper functioning of the Injective Chain even in the presence of malicious or faulty nodes.The specific implementation method is that the Tendermint/Ignite protocol uses multiple rounds to propagate blocks to network validators through proposal messages. In order for a block to be propagated, it must be supported by multiple block proposers and signed by the corresponding validator's private key. Validators communicate on the Tendermint/Ignite network using the peer-to-peer (P2P) gossip protocol. For a block to be considered valid, it must be accepted by two-thirds or more of the validators, which is also known as the Byzantine Fault Tolerant (BFT) Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism.Ethereum Domain
The bridging layer is essential for cross-chain interoperability and communication between Injective and the Ethereum network. It consists of the Injective Bridge smart contract, which relies on Wormhole, Peggy, IBC, and Axelar. The bridging layer interacts with the Injective chain, the Ethereum network, and other supported blockchains. The Injective Bridge enables bi-directional transfer of ERC-20 tokens and assets between Injective and the Ethereum blockchain through Peggy. The cross-chain interoperability achieved by Wormhole, Axelar, and IBC is crucial for decentralized blockchain infrastructure as it allows different networks to seamlessly share data and assets. Through the Injective Bridge, the liquidity of the Ethereum network and its DApps ecosystem can be inherited by Injective and the entire Cosmos ecosystem.Project Background
...Injective is incubated by Binance and is one of the eight projects incubated in the first phase of Binance Labs, receiving support from numerous investment institutions. Although Binance was significantly affected by the SEC crackdown, the impact on the decentralized exchange Injective is limited.
Injective Protocol's co-founder and CEO, Eric Chen, graduated from the New York University Computer Science College, and the core team has a strong professional background, with work experience in well-known international companies such as Open Zeppelin, Amazon, and hedge funds. Core members of the team graduated from prestigious institutions such as Stanford University.
On July 29, 2020, Injective raised $2.6 million in seed funding led by Pantera Capital, with participation from QCP Soteria and Axia 8 Ventures.
On April 20, 2021, Injective raised $10 million in a "party" funding round, with participation from Pantera Capital, Mark Cuban, Hashed, and others.
we are sorry, but we cannot add additional symbols and convert the languages directly. We can only translate the content of the text. Could you please provide the content you would like us to translate?
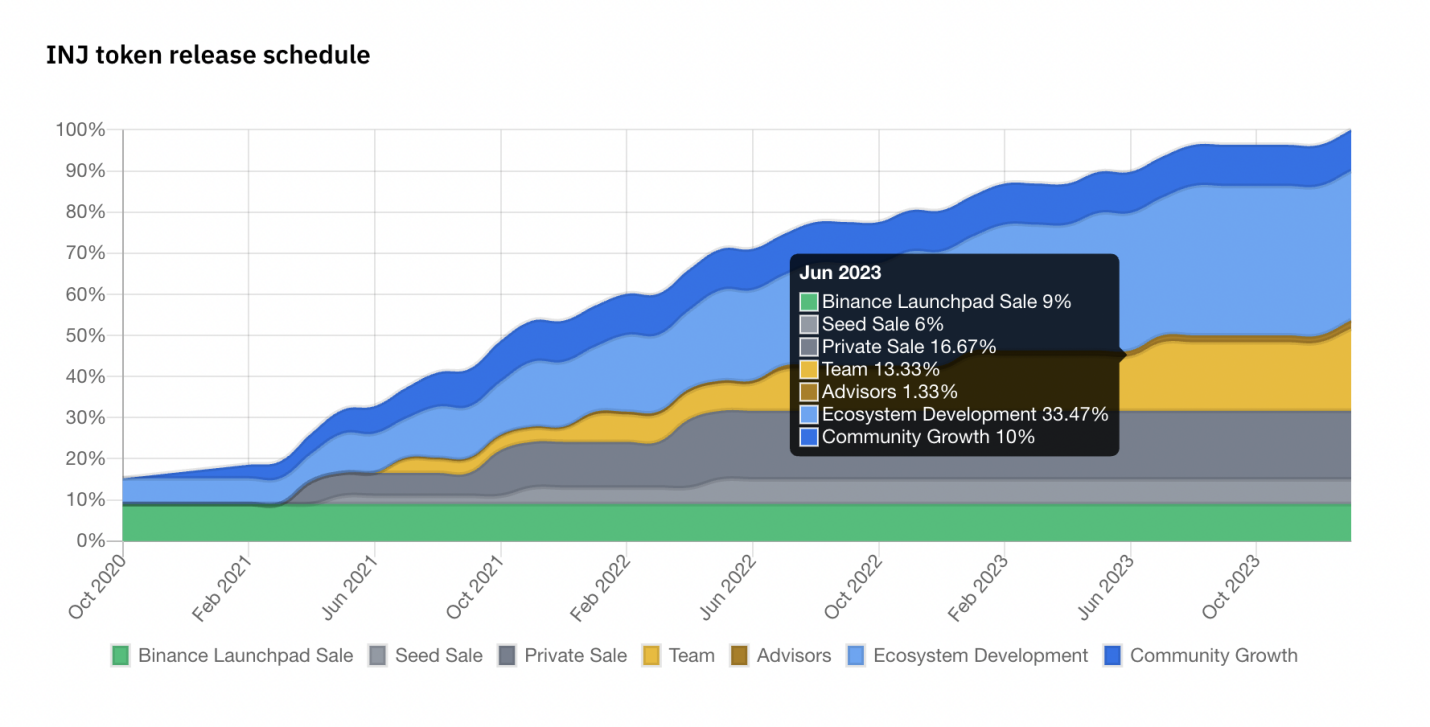
The total supply of INJ is 100 million, and the block rewards are compensated by minting new tokens, resulting in inflationary pressure. The target inflation rate of INJ tokens initially starts at 7% and gradually decreases to 2% over time. However, 60% of transaction fees are used to repurchase INJ tokens and burn them, resulting in deflationary status. More than 90% of the tokens have already been released, with around 5% expected to be released recently (from 6 to 8 months), most of which are from Team, Advisors, Ecosystem Development, and Community Growth. Some of the tokens belonging to Team and advisors may become potential selling pressure, while the rest will be converted into APY within Injective, which may also create some selling pressure, but higher incentives will increase Injective's ecosystem data.
INJ is deflationary. 60% of the fees generated by dApps will be used for on-chain repurchase and burn of INJ tokens (60% of trading fees will be auctioned to Bidders who bid with INJ, and the acquired INJ will be burned). The weekly supply burn creates deflationary effects and partially offsets the supply increase caused by token minting. More specifically, among the 39.78 million INJ tokens staked, the annual inflation rate is 5%, equivalent to minting 2 million INJ tokens within a year. Currently, the cumulative burn has reached 5.32 million INJ tokens.
M INJ, accounting for 5.32 % of the total supply.Image: INJ Burn
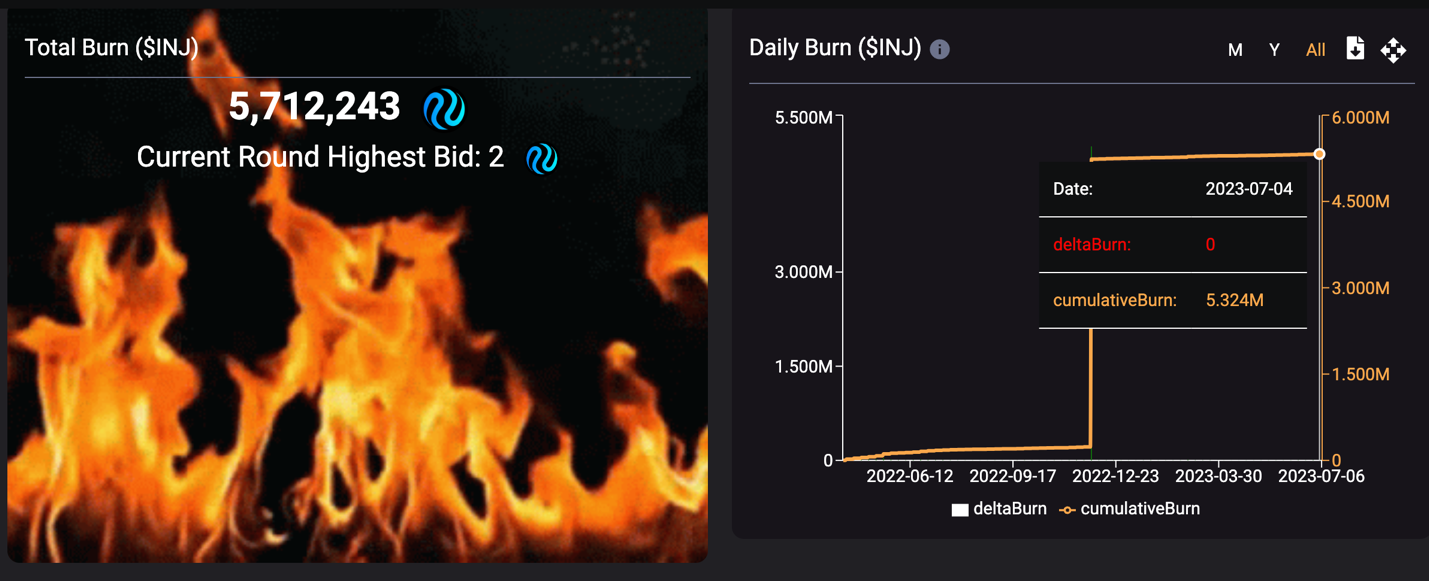
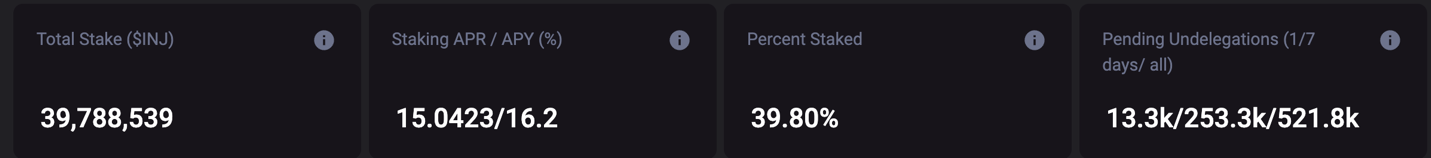
Image: INJ Stake Status
Value Capture
1) Protocol Fee Value Capture
After allocating 40% of the transaction fees to the exchange DApps, Injective uses the remaining 60% for buybacks. The protocol conducts an auction every week, and participants bid INJ for the fees of that week. The auction winner gains a basket of tokens and profits from arbitrage opportunities, while the protocol uses the proceeds to purchase and burn INJ to maintain the deflationary nature of the INJ token.
2) Tendermint-based Proof-of-Stake (PoS) Security
INJ tokens are used to secure the Injective blockchain through a Proof-of-Stake mechanism based on Tendermint. Both validators and delegators can participate in staking.
3) Developer Incentives
40% of the fees generated by dApp users on Injective are directly used to incentivize new developers to build applications on Injective, which will result in a growing community of developers.
4) Protocol Governance
The INJ token is responsible for managing all components of Injective, including chain upgrades.
Token allocation
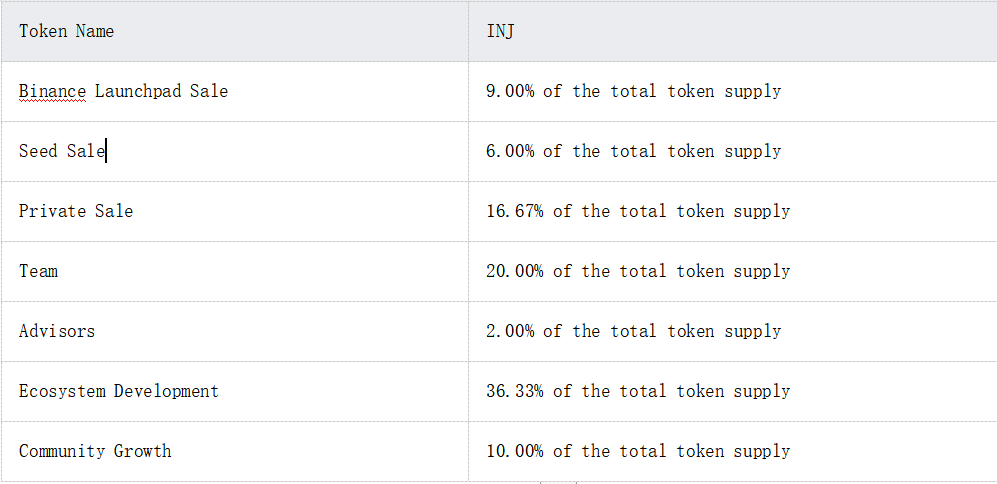
Token sales data
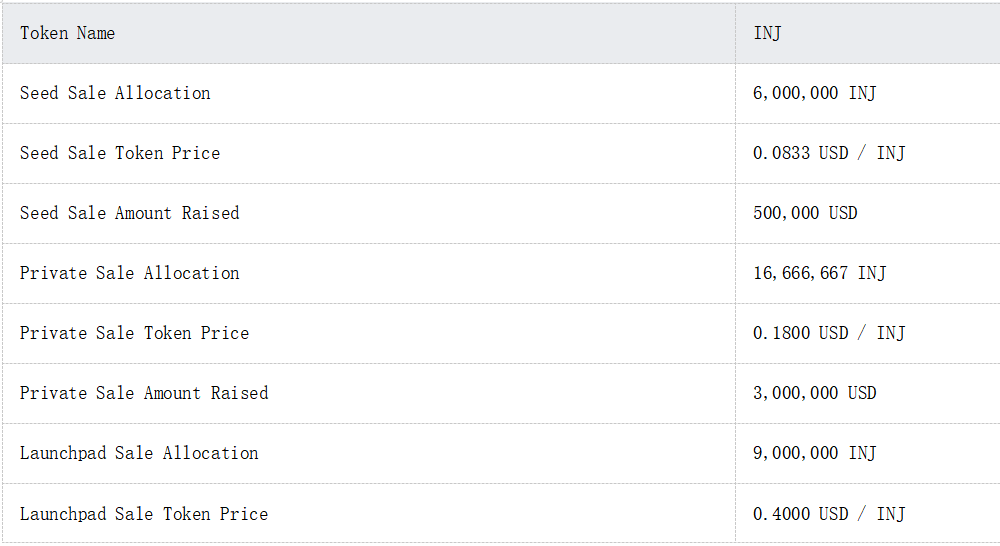

Source: Binance Research
Ecological projects
There are currently 24 DApps on the Injective mainnet, most of which are related to DeFi. There are also applications related to communication infrastructure, information protocols, NFT, and more built on Injective.
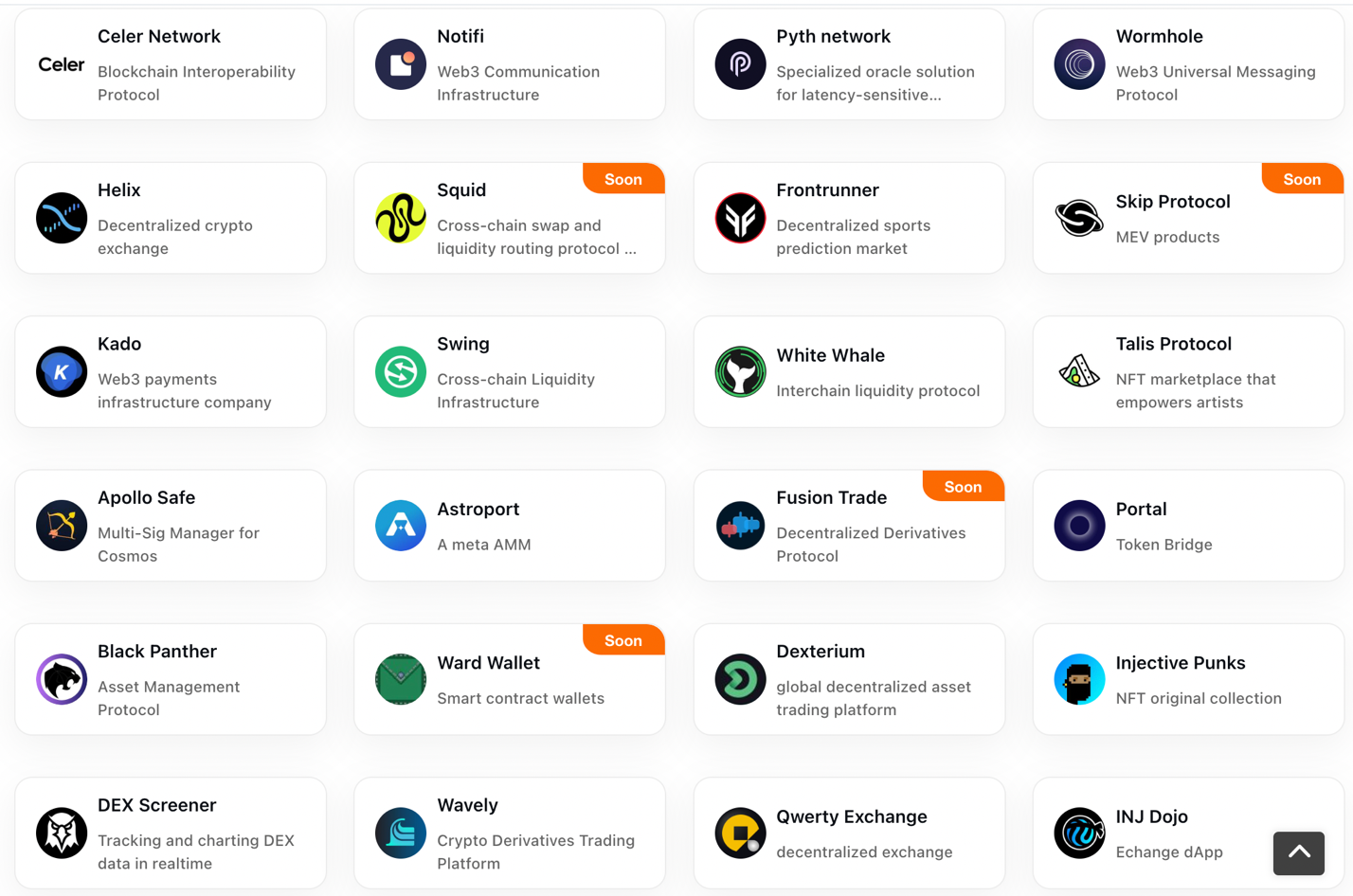
Injective Main Dapp
Source: Injective Official
Helix
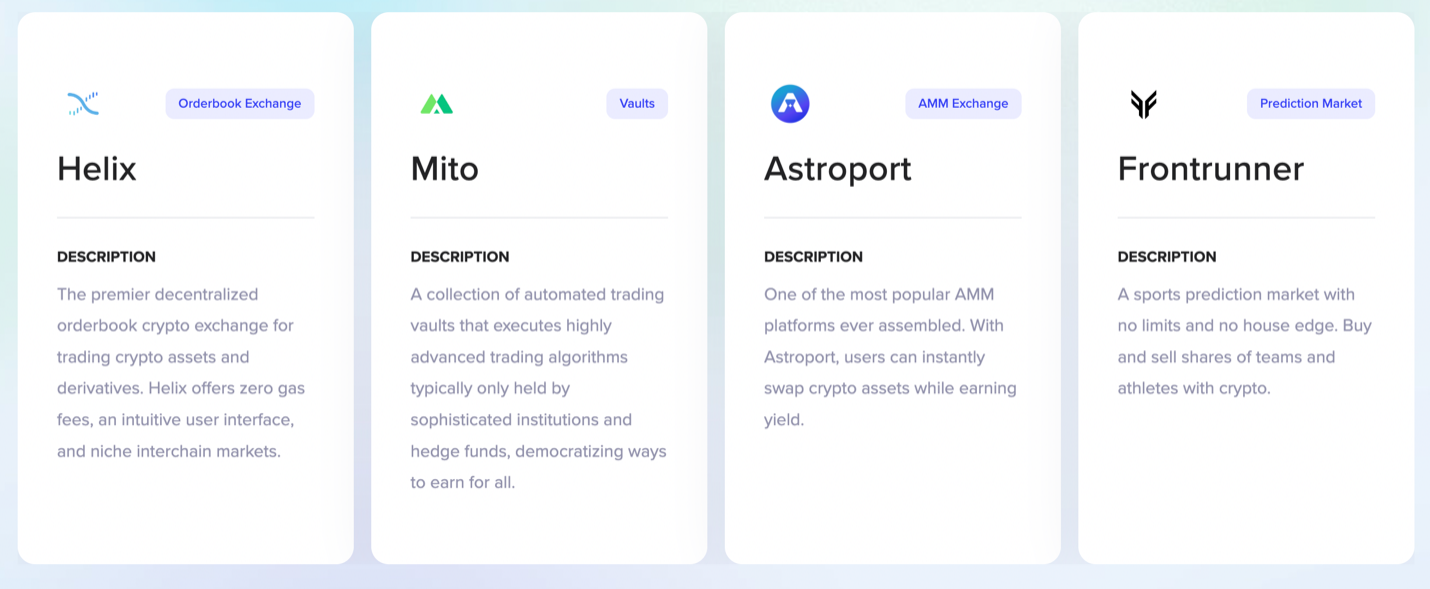
Helix is the Injective order book trading frontend, originally known as Injective Pro. Its goal is to provide cross-chain spot and perpetual contract markets, enabling users to engage in various cryptocurrency trades. Helix supports zero gas fees, helping to reduce users' transaction costs.
Mito
After a long wait, Injective Labs officially announced Mito last month, formerly known as "Project X," and launched closed beta access to the platform. Mito is a protocol composed of automated trading vaults powered by smart contracts, with each vault executing advanced trading algorithms typically only held by institutions and hedge funds. It is currently in the early access stage. Mito includes two key components: an automated strategy vault for easy revenue generation and a sophisticated token launch platform. Through this innovative platform, users can gain access to various trading strategies to generate profits while exploring new cryptocurrencies.
Astroport
Astroport is an AMM protocol that allows users to swap or provide liquidity for cryptographic assets using various types of pools, including Curve-style stablecoin swap pools and Uniswap V2-style constant product pools. Astroport is able to leverage the interoperability network of Injective to facilitate the exchange of assets bridged from Cosmos or Ethereum as well as assets bridged from chains such as Solana, Aptos, and Avalanche through Injective's Wormhole integration.
With Astroport being built on Injective, users will be able to utilize Injective's interoperability network to exchange assets bridged from Cosmos or Ethereum as well as assets recently integrated through Injective's Wormhole integration such as Solana. Users can bridge their assets to Injective via the Injective Bridge and then create liquidity pools on Astroport to start earning yield as liquidity providers and engage in trading on new markets.
Astroport brings significant advantages to the Injective ecosystem, originally built on Terra. Contributors to Astroport have spent a lot of time analyzing multiple major L1 networks and ultimately decided to host Injective as its V2 version chain. Astroport has now officially migrated its mainnet to Injective, becoming one of the largest AMMs in the Injective ecosystem.
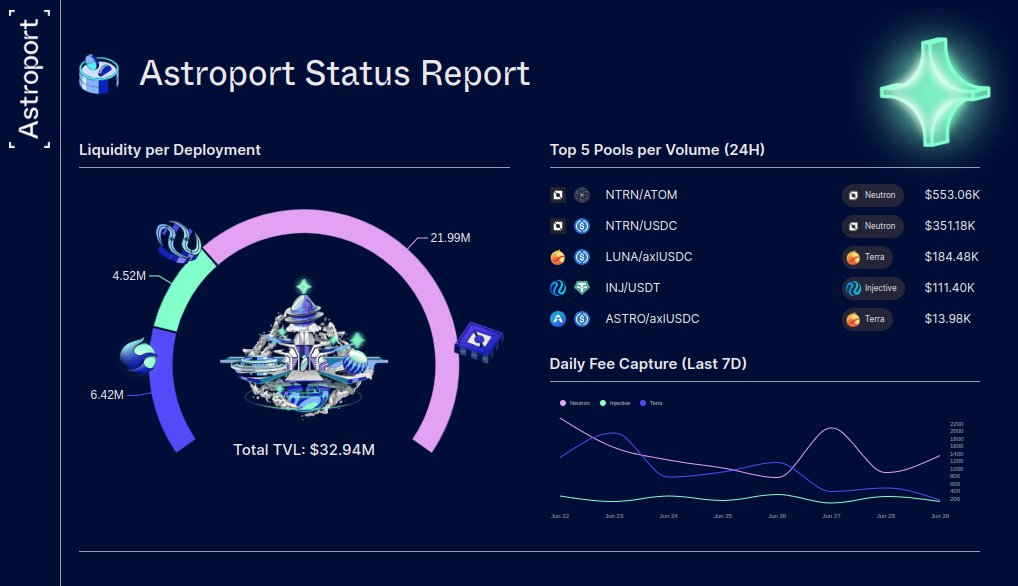
Source: @astroport_fi
As of the end of June, Astroport's total TVL is 32.94 M, with TVL on the Neutron, Terra, and Injective chains being 21.99 M, 6.42 M, and 4.52 M, respectively.
Competitive Landscape
SEI is a protocol that can be compared to Injective in terms of consensus mechanisms, OME type (FBA), FDV, etc. SEI has some detailed differences in OME mechanism compared to Injective, which will be explained in detail below.
DYDX is about to migrate from Ethereum to Cosmos to launch the dYdX Chain (dYdX V 4). Currently, V 4 is in the testnet phase, and dYdX v&nbThe mainnet launch may have some impact on Injective's market share, depending on their trading incentives and institutional preferences. From the token release phase, 90% of Injective tokens have been released, while dydx, including the unreleased SEI, may have a competitive advantage in token incentives.In terms of valuation, SEI completed a $300 million financing round with a final valuation of $800 million, with participation from Jump Capital and Distributed Global. Injective's valuation is currently less than $800 million, while dydx's is $1.9 billion. Injective still has room for valuation growth, but its key business data in terms of trading volume is clearly inferior to other competitors (Helix: 24-hour trading volume of 22 million, dydx: 600 million). There is a significant gap in trading volume between Injective and dydx. This may be due to the fact that Injective mainly trades assets within the Cosmos ecosystem.Compared to other blockchains on the Cosmos network, Injective is currently the fastest with an average block time of about 1 second. The graph shows that Injective's block speed is significantly higher than other chains.
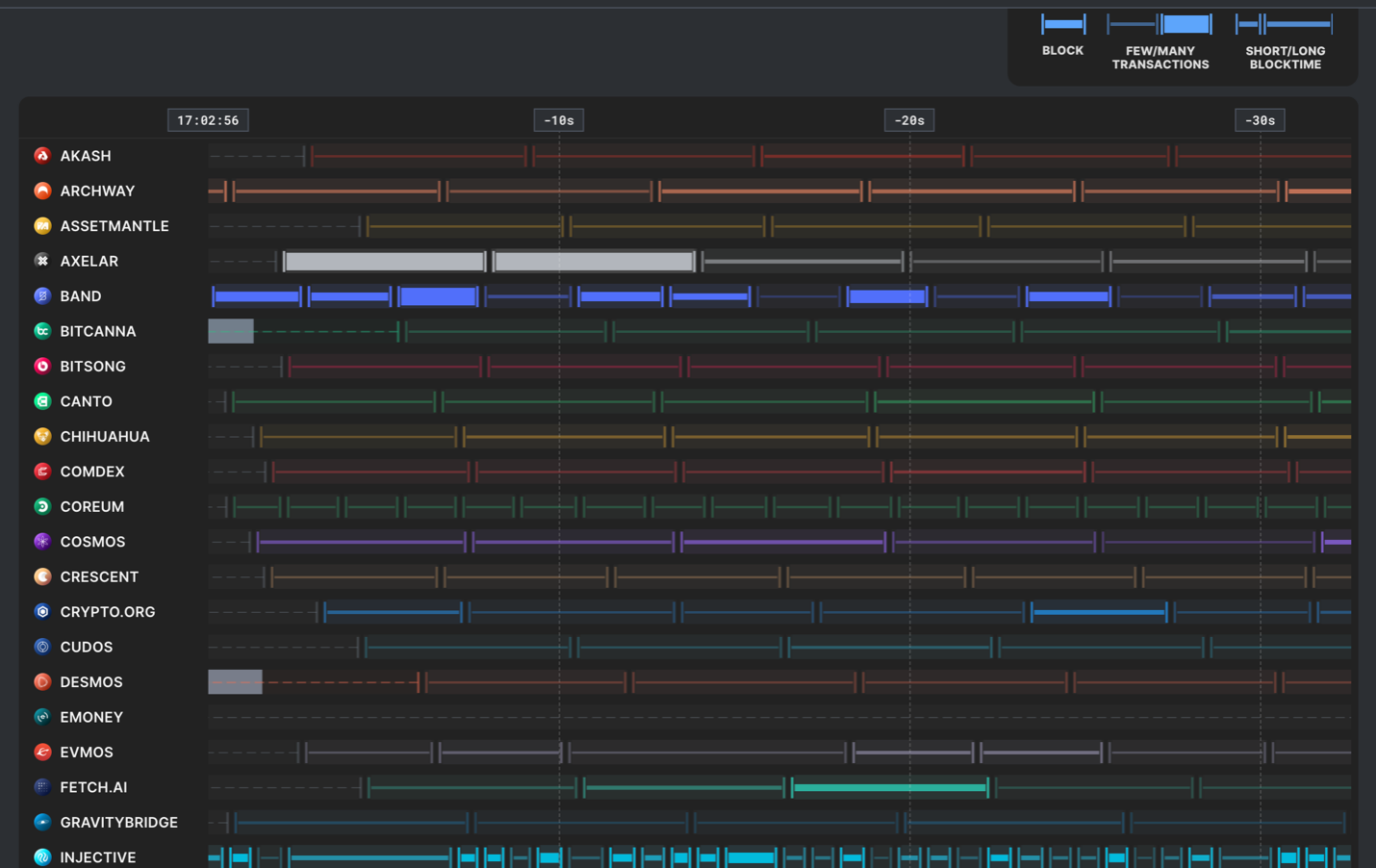
Source: https://hub.mintscan.io/chains/monitor
Comparison of Order Matching Engine (OME)
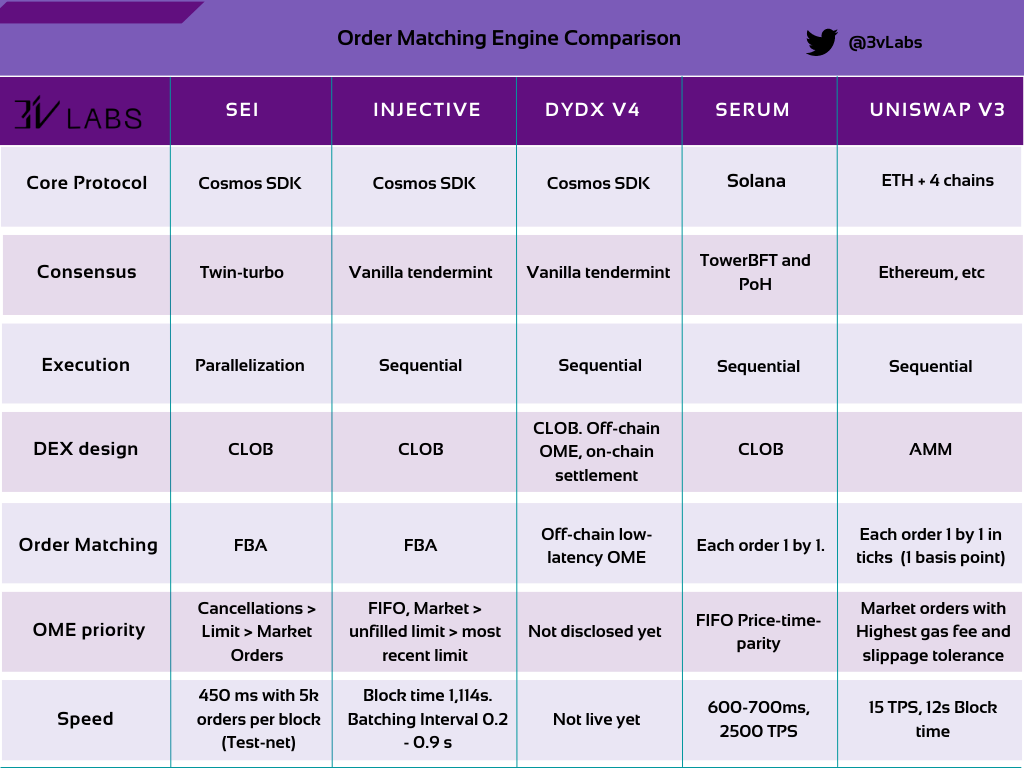
Source: OME Comparison by 3 V labs
The above image is a comparison of the order matching mechanisms of SEI, Injective, dYdX V 4, Serum, and Uni V 3 by 3 V Labs.
Order book defense against MEV is a requirement for handling large-scale institutional order flow. Currently, most public chain-based order book DEXs minimize adverse MEV through frequent batch auctions (FBA). In addition to FBA, Off-Chain Low Latency OME is the order matching model for dYdX V 4.
For Injective, the FBA matching mechanism is an important upgrade, which uses a frequent batch auction model. The result is to maintain fast transaction times, approach market prices through higher liquidity, and narrow spreads.
Injective's frequent batch auction (FBA) is widely proposed as a clear solution to the inefficiency issue of capital related to CDA. One benefit of FBA is improved market fairness and liquidity through the elimination of front-running transactions.
Injective FBA is defined by three characteristics:
1) Discrete Time: Orders are accepted within a discrete time interval called an auction interval. At the end of each auction interval, cross orders are filled in the following priority order:
First, market orders are filled, then unfilled limit orders from the previous auction interval, and finally, limit orders from the most recent auction interval. If the quantities of the buy and sell side are different, the side with the smaller quantity is completely filled, and the orders from the side with the larger quantity are filled proportionally (uniform partial fill).
2) Unified Settlement Price: Limit orders are filled at the unified settlement price of the highest cross-order volume. If the quantities of both buyers and sellers are the same, the middle price is used as the settlement price.
3) Closed Bidding: Orders are not made public on the order book until the auction interval ends and batch auction is executed. This eliminates the possibility of pre-trading and negative spreads.
The longer auction interval in frequent batch auctions provides market makers with sufficient time to cancel outdated orders before HFTs can execute. This eliminates the risk market makers have to deal with in pre-trading issues, thus not requiring them to invest their capital in advanced technology.
Market makers are incentivized to provide deeper liquidity and tighter spreads near market prices, which is not only beneficial for retail traders trying to fill orders near fair prices, but also reduces volatility associated with potential price plunges.
Frequent batch auctions aggregate orders into a batch interval for status changes or order book inclusion. The blockchain processes transactions in a batched manner, queuing and writing continuous blocks. The optimal batch interval for FBA is still debated, but has been reported in academic papers to range from 0.2 to 0.9 seconds, which aligns with Injective's.
bsp;The auction interval of SEI matches, and batch auctions are executed at the end of each block.SEI, as a protocol on Cosmos that uses FBA for order matching, has some differences in details compared to Injective FBA, such as:
1) SEI implements parallel processing of blocks, no longer processing transactions sequentially. It can process multiple transactions involving different markets simultaneously, thereby improving performance. According to recent load testing, it can be seen that compared to sequential processing, block time has been reduced by 75-90%, with parallel processing latency of 40-120 milliseconds, while sequential processing latency is 200-1370 milliseconds;
2) SEI's price oracle is responsible for streaming off-chain price data to the blockchain and is built into the chain. This means that all validators need to propose their prices (exchange rates) when submitting blocks. Only when all validators reach a consensus on a common price, a block will be created. Validators will be penalized if they miss certain voting windows or if the prices they provide deviate too much from the median;
3) Trading order bundling, market makers can cancel and create orders involving multiple markets in a single transaction (e.g. merging all BTC perpetual contract orders into a smart contract call for a specific market).
Injective is built on top of the BFT-based PoS consensus of Tendermint/Ignite, with instant finality, which aligns very well with the FBA execution at the end of each interval. As FBA does not have the concept of time priority within the auction interval, it is a market design that matches perfectly with a blockchain running on the same basis. This is due to the fact that Tendermint/Ignite is a consensus engine based on the BFT (Byzantine Fault Tolerant) consensus algorithm. It achieves consensus by using a pre-selected set of validator nodes and voting and confirming the order of transactions through consensus rounds. Tendermint/Ignite is designed for high security and determinism, suitable for applications that require strong consistency and finality, which aligns perfectly with Injective's underlying infrastructure.
By using Frequent Batch Auctions (FBA) instead of Continuous Double Auctions (CDA), Injective adopts a market design that is technically powerful and can compete with centralized exchanges. Injective is able to eliminate front-running transactions that harm traders' interests, helping market makers provide deeper liquidity and tighter spreads. The implementation of frequent batch auctions prepares Injective for competition in trading volumes with institutional-grade centralized exchanges.
Summary
Injective offers optimal transaction speed, instant finality, almost zero gas fees, and protection against MEV, among other advantages.
These advantages come from 1) the fast block confirmation speed based on the Tendermint BFT consensus mechanism (although it may have higher centralization); 2) the exchange broadcasts signature messages to Injective Chain nodes instead of the traders themselves, so all the costs related to interacting with the chain are paid by the exchange's DApp, which means traders do not need to pay any gas fees; 3) it uses frequent batch auctions (FBA) as the order settlement mechanism. Orders submitted to the memory pool are executed at the end of each block (approximately 1 second block time) and are not published on the order book until the auction process is completed, effectively preventing front-running by MEV bots. Compared to AMM, Injective's on-chain order book settings are more user-friendly for regular users, especially institutions, when it comes to strategy-based orders (e.g., AMM currently cannot implement stop-loss orders, although Uni V4 may be able to achieve this to some extent). AMM has a large TVL, and LPs have become an organic part of the entire market. For LOB, it naturally lacks the step of on-chain staking assets, so attracting MM requires external subsidies and it is difficult to form an LP ecosystem similar to AMM, capturing the value chain derived from the LP ecosystem. Of course, AMM-like products can also be built on Injective, but currently, the main trading volume on Injective still occurs on the order book front-end, Helix. Before rollup significantly improves the performance of LOB DEX, building native chains on Cosmos is still the best solution for high-performance LOB. The launch of dYdX v4 mainnet may have an impact on Injective.Market share of p; is subject to certain squeezing, depending on the incentive measures and institutional preferences of both. The LOB dex on Rollup will also form certain competition, but due to the definition of dapp as a non-public chain and the lack of sovereignty, the valuation system and order book of the LOB DEX are completely different from those of the native chain. Both the LOB DEX and AMM have adopted decentralized methods, and at this stage, it is not necessary to define what the endgame looks like. This market always requires diversified solutions.
Injective uses LOB as its core trading model, with the feature of "MEV protection". It provides a secure and efficient platform for institutional order flow and market makers of trading applications by building on Tendermint to provide a highly decentralized, high-performance, and reliable environment that can be used for cross-chain derivatives, forex (FX), synthetic assets, and futures trading, and eliminates the risk of market manipulation and exploitation by high-frequency traders. The implementation of frequent batch auction prepares Injective to compete with institutional centralized exchanges in trading volume and makes it a naturally endorsed decentralized trading platform for institutions. But this also means that the price of Injective is closely related to institutional support. In the next cycle, the implementation of a high-performance chain-based trading engine, one-click mainnet launch, and other engineering achievements will further promote professional market makers' establishment of liquidity in the DEX field and help shift pricing power from CEX to DEX along with AMM.