Original author: YBB Capital Researcher Ac-Core

Introduction:
Compared to the V3 version that was released two years ago in May 2021, V4 offers more flexibility in asset composition and significantly reduces the gas fees required for liquidity provision and trading. With the addition of the new feature called Hooks, developers no longer need to develop xxSwap but can customize liquidity and add frontend pages and elements according to their own needs to create a "designated place". At the same time, there is no need to worry about insufficient liquidity in the "designated place". Let's explore how Uni V4 is leading DeFi from the "Lego era" into the "thousands of hooks story".
YBB Capital Researcher Ac-Core DIY
Uniswap V4 - Rare Genuine Innovation in a Bear Market
The iterative upgrade of Uniswap has shown us the infinite potential of the DeFi world, as it has never deviated from the original intent and rules of X*Y=K. The innovation of Uniswap V4 mainly focuses on providing more customizable trading logic, improving gas efficiency and developer experience, as well as enhancing the convenience and efficiency of transactions. Whether it's developers or users, they can enjoy a more open, flexible, and efficient automated market-making service compared to using V3. The following sections will comprehensively introduce the upgrades of V4 and the two most important changes: Hooks and Singleton.
The Game-Changing Introduction: Hooks
The core feature of Uniswap V4 version - Hooks, allows every developer to create a customized DEX that meets specific scenario requirements and build their own "LEGO blocks". Hooks are an important concept introduced in Uniswap V4 and are used as plugins for customizing liquidity pools, swaps, fees, and liquidity provider (LP) position interactions. Through the Hooks mechanism, developers can perform specific actions at key moments in the lifecycle of a liquidity pool, such as before/after a swap or before/after a change in LP position.
Furthermore, Hooks are also smart contracts that interact with the core contracts of Uniswap V4. They can execute custom logic at different "crucial points" within a liquidity pool (crucial points refer to actions before/after a swap or during LP deposits/withdrawals), allowing developers to define and execute custom logic in a flexible manner. Hooks can be bound to specific liquidity pools to control the behavior and interaction of the pools. For example, developers can create a Hook that validates specific conditions before each swap or performs additional actions when LP positions change.

YBB Capital Researcher Ac-Core
Through Hooks, mining pool creators can adjust pool parameters and introduce new functionalities to the AMM. It can even enable the creation of various DeFi strategies within Uniswap, ultimately benefiting LPs/swappers more. It is not difficult to imagine that the introduction of Hooks will bring greater flexibility and innovation space to developers, allowing them to create unique liquidity pools based on their needs and strategies, providing more innovative and personalized trading experiences, such as:
Time-Weighted Average Market Maker (TWAMM): Developers can use the Hooks mechanism to create liquidity pools that support TWAMM strategies, which average out large orders over a period of time.
Dynamic fees: Using Hooks, liquidity pools can dynamically adjust fees based on market volatility or other input parameters to better adapt to market conditions.
Onchain limit orders: Hooks can enable the creation and execution of limit orders on-chain, allowing users to trade at specified prices.
Interaction with the lending agreement: Developers can automatically deposit funds that exceed the liquidity range into the lending agreement through Hooks to maximize the utility of the funds.
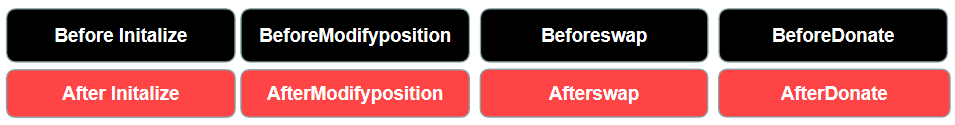
At the same time, Uniswap V4 currently supports eight types of Hooks callbacks as shown in the figure below. These Hooks can be executed before and after the start of a transaction, thereby implementing on-chain limit order functionality. In actual operation, a limit price can be set before the start of the transaction, and then the limit price can be checked after the end of the transaction. If it is satisfied, the transaction is executed; if it is not satisfied, the transaction is canceled.
YBB Capital Researcher Ac-Core Homemade
Another Hooks in V4 - "Action Hooks"
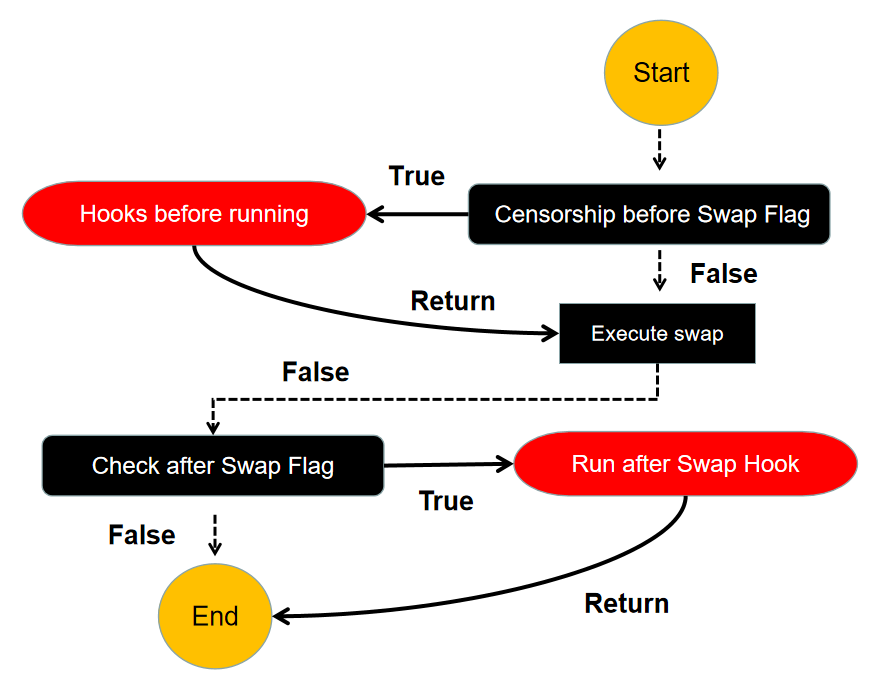
In addition to Hooks, there is another "Action Hooks" in the Uniswap V4 version. It can only trigger the execution of contracts when the Flag condition is met, so it can call logic during the execution of contracts. Refer to the following flowchart to explain that before our asset exchange, the contract needs to check the Flag to evaluate the volatility of the liquidity pool. If the liquidity is high, the Flag will become True and our Hooks will be executed. If the liquidity is insufficient, the Flag will become False and the Hooks will be rejected to keep the interaction unchanged. Through the operation shown in the figure below, "Action Hooks" enables a more gas-efficient method to execute the Hooks we need. Next, the Singleton structure and Flash accounting will be introduced to achieve a cheaper asset exchange and contract deployment experience in V4.
YBB Capital Researcher Ac-Core Homemade
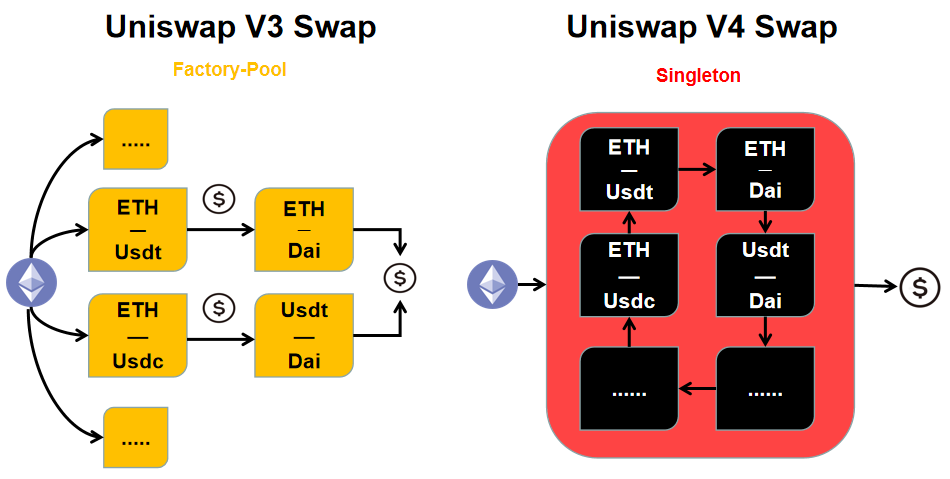
New Singleton Structure: Singleton
In previous versions of Uniswap, Factory-Pool is the contract architecture that has been used since V1 and is also the most commonly used contract architecture for DEX and derivatives in the DeFi world. However, in V4, it abandoned Factory-Pool and replaced it with a singleton contract structure named "Singleton". In V3, each time a liquidity pool is created, a completely new contract needs to be deployed, which is very expensive. But in V4, all liquidity pools are stored in a single contract through the singleton structure, which maximizes the reduction of gas consumption in creating liquidity and cross-chain pools (contracts). This means that token transactions do not need to be transferred between different contracts, and even 99% of gas fees can be reduced compared to V3.
This singleton structure is also equipped with a new "Flash Accounting" system. In V3, assets need to be transferred between liquidity pools at the end of each interaction. But in V4, this system only transfers assets on the "net balance". Each operation (exchange/deployment) only causes changes in the internal balance, and the asset balance is represented in units of "delta". At the end of the exchange, it only exchanges the net "delta" balance after a series of calculations. This means that a more efficient system can provide additional gas savings for Uniswap V4.
With the help of "Singleton" and "Flash Accounting", Uniswap V4 supports Native ETH. Users can directly trade using Ether (ETH) without the need for additional conversion operations, thereby improving transaction convenience and saving gas fees. This closely integrates the Uni and ETH ecosystems and benefits Ethereum.
In terms of contract structure, there have been significant changes in the storage and encapsulation of liquidity positions in V4. In the V2 version, liquidity was distributed across the entire range (as shown in Figure 1), so the Uni protocol used homogeneous tokens (ERC-20) as liquidity certificates. In the V3 version, due to the introduction of limit order liquidity, the corresponding liquidity display changed to non-homogeneous tokens (ERC-721). In the V4 version, we speculate that liquidity display will not be tokenized, but will be managed using the address of each wallet. In addition, the "transient storage" of the Cancun upgrade, as specified in EIP-1153, is also beneficial for the V4 system, which helps achieve further cost optimization.
YBB Capital Researcher Ac-Core Homemade
How to Allow Custom Oracles and Distribute Internalized MEV to LP Holders
UniSwap V4 is a decentralized trading protocol designed to enable trustless token trading on Ethereum. It provides higher liquidity and better trading experience by utilizing custom oracles and an internalized MEV (Maximize Extractable Value) distribution mechanism. To allow custom oracles and distribute internalized MEV to liquidity providers (LP holders), the following steps can be considered:
1. Design a custom oracle: You need to develop an oracle that can provide customized price data. An oracle is a contract that retrieves external data and provides real-time market prices and other information to smart contracts. You can develop an oracle contract tailored to your needs based on trade pairs, time, or other factors.
2. Implement the internalized MEV distribution mechanism: MEV refers to the profit generated in blockchain transactions due to changes in transaction order. UniSwap V4 distributes these profits directly to liquidity providers through the internalized MEV distribution mechanism. You can design a mechanism to allocate a portion of the earnings directly to the corresponding LP holders when MEV occurs.
3. Contract integration and deployment: Integrate the custom oracle and internalized MEV distribution mechanism into the smart contracts of UniSwap V4. Simply modify and extend the respective contracts to support these functionalities. Ensure adherence to security best practices during contract development and modification and conduct thorough testing and auditing.
4. Notification and incentive mechanism: Promote this new feature to liquidity providers and provide them with appropriate incentives. Communication with users can be done through social media channels or other means to let them know the benefits of the new customized Oracle and internalized MEV distribution mechanism.
5. Monitoring and improvement: After deployment, closely monitor the operation of the system. Monitor the effectiveness of transactions and MEV distribution and make improvements as needed. Feedback and participation in community suggestions are essential for further optimizing this mechanism.
Advantages of Customized Liquidity Pools
Uniswap V4 introduces the concept of customized liquidity pools. However, customization is recommended based on centralized liquidity, so this change not only affects the development pattern of Fork Swap, the significance of aggregators, but also brings many advantages to liquidity providers and traders.
Expanded options for liquidity providers: Traditional AMM models usually have fixed rules and parameters, which limits the choices for liquidity providers. However, Uniswap V4 allows customization of liquidity pools through Hooks mechanism, enabling liquidity providers to create different types of liquidity pools according to their preferences and strategies. This allows for a variety of liquidity pools of different scales in the market, providing users with more choices and flexibility.
Reduced fees and improved efficiency: Uniswap V4's architecture centralizes all liquidity pools in one smart contract by introducing the "Singleton" contract. This architecture reduces transaction costs, improves transaction efficiency, and simplifies contract deployment and maintenance. In addition, customized liquidity pools can set more suitable fee structures according to specific needs to meet the needs of different users.
Providing a wider range of trading strategies and risk management tools: Customized liquidity pools provide traders with more opportunities for trading strategies and risk management tools. For example, by supporting the TWAMM strategy, large orders can be averaged over a period of time, reducing the impact on market prices. In addition, customized liquidity pools can be integrated with other DeFi protocols, such as lending protocols and custom oracles, to provide users with more comprehensive trading solutions.
Enhancing flexibility and creativity: Customized liquidity pools offer greater flexibility for liquidity providers. They can customize the management of their liquidity based on market demands and strategies. This flexibility and potential for innovation can incentivize more liquidity providers to participate and provide traders with diversified liquidity choices.
Questions Worth Considering

YBB Capital Researcher Ac-Core Homemade
1. What problems does Curve solve for Uni V3?
The Uni V3 AMM model is based on the concept of X*Y=K. During our actual combination of LP, we found that when extreme conditions occur, not only the total value is at risk of loss, but also the exchange rate of the liquidity pool can exceed the range. Curve and Uniswap V3 are two different decentralized trading protocols, each facing slightly different problems and goals.
Compared to V3, Curve solves the following problems:
1. Profiting from low liquidity ranges: Uniswap V3 concentrates liquidity within specific price ranges, resulting in a lack of liquidity in other price ranges. This leads to higher transaction costs and limited liquidity for trading within larger price ranges. In contrast, Curve focuses on trading between stablecoins and increases liquidity within price ranges using an adaptive liquidity curve. This allows users to trade stablecoins with lower slippage within larger price ranges.
2. Low-cost trading: Because Curve focuses on trading between stablecoins, which have a fixed price relationship, it adopts specific algorithms and strategies to reduce slippage and costs for transactions. This enables users to trade stablecoins at more competitive prices.
3. Better price discovery: Curve provides liquidity across a wider range, especially when trading between stablecoins, it can offer better prices to be discovered. This means that users can obtain more accurate market prices for stablecoins, resulting in better trading decisions.
4. Efficient and Stablecoin Trading: Curve utilizes a specially optimized algorithm and liquidity curve designed to provide efficient stablecoin trading. This allows users to quickly and securely exchange stablecoins without significant price slippage or costs.
2. DEX with Dual Token Economy Model Created Using Uni V2: Camelot
Camelot was originally a project launched on Fantom and was called Excalibur. It later collapsed due to the use of UST as the stablecoin and migrated randomly to the Arbitrum ecosystem, where it was renamed Camelot. Unlike GMX, Camelot focuses more on providing liquidity guidance for new projects. Its main innovative mechanism is the permissionless "Nitro Pools," allowing projects to have complete control over incentive measures and establish the required liquidity types for their own development.
It is important to highlight that Camelot has a dual token economy model, combining the decentralized trading protocols of Uniswap V2 and Curve. It supports trading of volatile and stable tokens, with liquidity spread across the entire range from zero to infinity. Most importantly, it allows project teams to set the ratio of transaction fees based on market conditions and specific protocol requirements, aiming to manage dynamic and targeted transaction costs.
In addition, Camelot has a permissionless custom launchpad for projects to issue tokens and generate more liquidity. Furthermore, every project launching or partnering with Camelot AMM can configure specific transaction rates for their liquidity providers, adapting to their own liquidity strategy needs.
Summary
Uniswap V4, as a significant upgrade for decentralized exchanges, brings greater flexibility and creative space to the DeFi ecosystem by introducing Hooks and customizable liquidity pools. The Hooks mechanism allows developers to create unique liquidity pools tailored to their requirements and strategies, providing a wide range of trading strategies and risk management tools. Customizable liquidity pools expand the choices provided by liquidity providers, reduce fees and increase efficiency, and offer a broader range of trading strategies and risk management tools.
However, the emergence of V4 is bound to once again rebuild the underlying foundation of DeFi. It provides a large liquidity pool that developers can use to deploy their own Hooks or ecosystems, even without the need for a single function xxSwap to obtain high liquidity. This allows more developers to develop various multifunctional ecosystems on the Uniswap platform. Will the combination of Hooks + SingLeton with the advantages of Curve+Camelot affect the next development trend of DeFi? Let's wait and see.