Original Author: Artist, Hins, Freya, Chance, Chad
Summary
Summary
first level title
secondary title
1.1 The Era of Data Explosion
Modern society is in an era of unprecedented information explosion, and it is also a digital era in which data is the main factor of production. While the amount of data is increasing exponentially, it also puts forward higher requirements for the existing data storage system, and a series of requirements such as data storage, data management, and data retrieval come one after another.
secondary title
1.2 Traditional solutions
Traditional centralized cloud storage is a storage solution that puts storage resources on the cloud for users to access. The business model of Internet cloud storage as a service has a long history. Amazon Web Services (AWS), the leader in the track, launched Amazon Web Services (AWS) in 2006, leasing its own servers and storage space to users, reducing the need for developers to create and manage Server infrastructure overhead. By 2022, the entire Internet cloud service market has become very large, with a market size of more than 200 billion US dollars. Foreign companies such as Amazon, Microsoft, Google, and domestic Alibaba represent the leading companies in centralized cloud storage. Under the encirclement of these giants, the entire market is extremely concentrated: Amazon will account for about 34% in 2022, and Microsoft will account for about 34%. 21%, Google 11%, Alibaba Cloud 5%.
Due to the centralization of data by centralized storage, the amount of related data is larger, and it is more vulnerable to batch attacks and leaks, which in turn leads to increased security, privacy and sustainability risks of centralized storage data, and the industry is gradually falling into a bottleneck. On the other hand, under the current centralized storage model, users upload sensitive data, which not only makes users lose control over their own data, but also transfers the risk of data leakage to the cloud storage operator side. If the private information is lost, damaged, leaked or stolen, it may cause great losses to individuals, businesses and society, and discredit cloud storage operators.
secondary title
1.3 Decentralized storage VS centralized storage
Due to the huge risks of traditional storage solutions, decentralized storage solutions emerged as the times require, and are considered to be a broader and more effective storage method in the future storage field. It can not only improve the security of stored data, but also reduce Storage costs, it seems that the market for decentralized storage is huge, and decentralized storage is one of the earliest and most concerned blockchain infrastructures.
secondary title
1.4 The development history of distributed storage
IPFS, the underlying technology of the Filecoin network, is the earliest decentralized storage solution. Its launch date can be traced back to 2014. The vision of IPFS is to replace HTTP, making Internet access and download faster and more secure.

From the perspective of scale, the development trend of decentralized storage is also very gratifying: according to the 2022 annual report released by the Filecoin Foundation, the total storage capacity of Filecoin is close to 19 EiB, accounting for 1% of the total global storage capacity. Over 300 PiB of data is stored on the network via the social layer Filecoin Plus. Nearly 4,000 storage providers have contributed data capacity to the Filecoin network. Filecoin provides storage services for individuals, organizations, and government agencies such as the UnDergrounD Physics Group and Starling Lab of the University of California, Berkeley, and cooperates with LockheeD Martin to plan to deploy IPFS in space.
first level title
secondary title
2.1 Decentralized storage and "Internet of Everything" DApp
With the development of Web3-related technologies, people have gradually discovered that the issue of data ownership is becoming more and more important.
Nowadays, for a user, his own data is often stored in different applications and controlled by different Red Heart storage service providers. An OG may have its own social accounts on Twitter, Youtube, Zhihu, and Weibo. The data of the same Thread is controlled by different companies on different social platforms. They can delete and modify their information at will— — Ownership of user data does not appear to be owned by the user. Is there a way to give users real ownership of their data?
Decentralized storage provides such a possibility. In the decentralized storage infrastructure, user data is no longer owned by a single service provider, but is stored by different nodes in the network after being dispersed. When in use, users can get "shards" from different nodes and restore their own data.
Using the decentralized storage infrastructure, the application can do: no longer hold or store the user's data, but "index" the data published by the user in the decentralized storage facility, and provide corresponding services. For example, Twitter can help users post their thoughts and provide services such as likes and retweets, but the data is still controlled by users. This approach is not against supervision: when a piece of data has a bad influence or violates the law, the application only needs not to index and display the data, but the data itself can still be completely stored in the decentralized system.
It is conceivable that using the above ideas, a user can allow his data to circulate in different applications, breaking the "island of data". In a word, create a DApp world of "Internet of Everything".
2.2 Why Decentralized Storage is Needed
text
2.2.1 Data ownership and security requirements
In the field of storage, data security has three important definitions (CIA):
Confidentiality. That is, the user's data privacy is not leaked.
Integrity. That is, the user's data will not be easily added or deleted, and the user can get the complete data stored by himself.
Availability. That is, users can get their own data at any time, and there will be no data unavailability due to system downtime or being banned from access by users.
Over time, people have become more and more aware of the importance of data security and data ownership. Under the current centralized storage mode, users upload personal data to the centralized storage service, and it is difficult to avoid the problem of privacy data leakage. At the same time, cloud storage service providers may add, delete, and modify user data due to political or related interest issues. In this way, the integrity of user data is often bound with the credit of the service provider. The service provider's storage system, faced with increasing demand and performance pressure, may also experience problems such as downtime, which in turn damages the availability of user data.
Bitcoin is the first time that people can decentralize the power of the system. Since the release of Bitcoin, there has been almost no downtime in the entire network. The decentralized storage system itself has better confidentiality and anti-censorship capabilities. People began to imagine whether decentralized storage can provide better protection in terms of data ownership and security.
2.2.2 The needs of smart contracts and DApps
Since the introduction of smart contracts and EVM on Ethereum, the blockchain has become a decentralized, programmable distributed ledger. The invention of smart contracts has promoted the emergence of scenarios and applications such as NFT and Defi.
image description
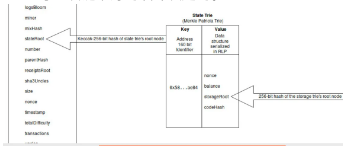
Ethereum Data Storage Design Diagram
In Ethereum, the balance of each account, Nonce value and other information are not directly stored in the block, but each node calculates the entire world state tree (including the information of each account), and the hash value of the root of the state tree stored in blocks. The information of each account and the information stored in each smart contract (a smart contract is a special account) are stored in the state tree. In the design of the Ethereum client, these data are actually saved by each node in LevelDB or RocksDB under the chain, and the state tree root is used for consensus. Therefore, storing data directly into smart contracts on the blockchain is more expensive.
secondary title
2.3 Basic technology of decentralized storage
The decentralized storage infrastructure uses a number of key technologies of cryptography and distributed systems to make the entire system have high availability, and at the same time ensure that the stored data has high confidentiality and integrity.
On the whole, the core idea of the decentralized storage infrastructure is to divide a user's file into multiple fragments, repeat each fragment multiple times, and then store the results in different nodes or partitions . When the user needs to obtain the original data, he can initiate a request to each node of the whole network with a certain logic to restore his original data. Techniques that may be used include:
Distributed Hash Table (DHT): DHT is a distributed key-value storage system that can efficiently store and retrieve data between different nodes. By using DHT, decentralized storage can find the location of data in the network for fast access.
Data sharding (SharDing): In order to improve storage efficiency and data security, decentralized storage systems usually divide data into multiple shards and distribute these shards on different nodes. This can reduce the storage pressure of a single node and improve data redundancy and reliability.
Data encryption: In order to protect the privacy and security of user data, decentralized storage systems usually use encryption technology to encrypt data. In this way, even if the data is intercepted during transmission, the attacker cannot obtain the original data content.
Error Correcting Codes: It increases the error tolerance of data by adding redundant information. In decentralized storage, erasure codes can help recover data in the event of data loss or corruption, improving system reliability.
In addition, in order to ensure the availability of data in the network, consensus on each node is generally required. In order to ensure the decentralization of the network, more nodes are required to participate in data storage and consensus, which involves the following key technologies:
Consensus algorithm: Decentralized storage usually uses blockchain technology to achieve autonomy and transparency. The consensus algorithm is the core technology in the blockchain system, which can ensure that all nodes in the network reach a consensus on the state of the data.
Incentive and punishment mechanism: In order to attract more participants to join the decentralized storage network, the incentive mechanism is crucial. By setting appropriate rewards and penalties, the incentive mechanism can encourage participants to provide more storage resources and bandwidth to the network. For example, in order to incentivize miners to provide stable services, the Filecoin network requires miners to invest a part of block rewards as collateral. If a miner terminates the contract early or goes offline, the miner will be punished and the collateral will be burned, this process is called "punishment". And honest miners will be punished for their work. In this way, the entire system can not only incentivize miners to store data in the first place, but also incentivize miners to store data durably and correctly, and maintain their commitment to users and the network.
first level title
secondary title
3.1 The "Big Three" of decentralized storage
Decentralized storage essentially serves the application layer of the Web3 ecosystem, so the solution is more inclined to meet the needs of end users, that is, to perform data storage, calculation and call in a more efficient and cost-effective manner. Arweave, Filecoin and Storj have formed independent three head decentralized storage networks.
3.1.1 Filecoin

As a decentralized storage system, Filecoin aims to provide safe and reliable storage for humanity's most important information. It employs an innovative incentive mechanism that enables network participants to provide storage space and receive corresponding rewards. Filecoin can be used in conjunction with various DApp development platforms to provide developers with highly reliable storage solutions to ensure data security and accessibility.
Filecoin and IPFS are two separate complementary protocols, both created by Protocol Labs. IPFS allows peers to store, request, and transmit verifiable data with each other. Filecoin aims to provide a persistent data storage system. It follows Proof-of-Spacetime and Proof-of-Replication to guarantee that miners have correctly stored the data they promised to store.
advantage
advantage:
Decentralization — Instead of a centralized network that stores information in one place, Filecoin creates a decentralized network where data is replicated in multiple locations and accessible from anywhere.
Extremely low-cost — Filecoin is trying to disrupt the current storage market with an extremely low-cost alternative to ephemeral storage.
shortcoming:
shortcoming:
Payment method - does not support one-time payment to store data, but only supports system storage data based on monthly contract. Filecoin wants to rent excess data storage on servers around the world. The owners of these servers can rent out the space to you and me to keep our data on a monthly basis. Similar to how Airbnb became a (sometimes) cheaper option to staying in a hotel, Filecoin aims to be a cheaper option than the big players in the cloud storage industry. Mainly Filecoin's economic model: contract-based storage can be thought of more simply as a pay-as-you-go model. Users pay a network of nodes to permanently store data, and it also provides trustless assurances that someone is actually there to store the data they say it is, and for an agreed upon amount of time.
In fact, every business has its own alternative use case, in that case if they need permanent storage, and only need to pay once to store data permanently, instead of paying monthly contract fee and fixed time like filecoin store data, then Arweave will come in handy.
3.1.2 Arweave

Arweave is a blockchain-based decentralized storage platform that uses an innovative sustainable and permanent donation mechanism to support data storage. It was released in 2018. They created Arweave to provide people and businesses with permanent, low-cost, and decentralized storage. To incentivize miners and provide payment for storage services, Arweave employs a native token called AR.
Arweave introduces an entirely new economic model to the market, never seen before the advent of permissionless encrypted networks: permanent storage. The easy way to interact with Arweave is to use BunDlr, since it is persistent data storage, Arweave (and BunDlr) does not support mutable data. But updated versions can be uploaded, so a system can be built to facilitate the presence of variable data, but with a permanent edit history.
advantage:
advantage:
Arweave uses persistent storage, where users only need to pay a one-time upfront fee to store data permanently. The protocol does this by leveraging cryptoeconomic game theory and creating an endowment fund that compensates miners for ensuring data availability, reliability, and durability. Arweave is the first to use economics to incentivize long-term storage of data. This combination makes public or private data permanent. The Arweave blockchain is capable of handling over 5,000 transactions per second.
shortcoming:
The Arweave feature can be applied to data preservation based on HTML 5 webpages to establish a decentralized H 5-APP. However, in actual use, the application scenarios for issuing this certificate are relatively narrow. At present, it can be seen that the data currently stored on Arweave Screenshots of some anti-government remarks on Twitter are the most popular, and the increase in explicit anti-government applications is worrying.
The characteristic of Arweave is that it can never be tampered with, which is particularly difficult in program development, because the program uploaded by the developer to Arweave must be free of any errors. If there is an error, even if it is a punctuation, the previously uploaded content will be invalidated. Re-uploading will inevitably cause a lot of useless garbage to accumulate. In addition, due to the openness of the blockchain, the content uploaded by Arweave is open to the whole society, and it is not suitable for uploading personal content.
Arweave mainly focuses on one-time payment and permanent file storage. This model is relatively simple, and there is a certain risk that homogeneous projects will use the same storage concept and start a price war.
3.1.3 Stroj

Stroj is a decentralized content storage and distribution network, designed to provide fast, secure, and low-cost P2P cloud storage services, mainly for enterprise customers, benchmarking against Amazon Web Services (AWS) S 3 . Storj was established in 2014 and launched in 2017. Storj is currently running a version called Storj Next, which will be launched in February 2023. This version introduces permanent storage functions and token storage rewards. The decentralized storage service provided by Stroj simply means that users upload the files they need to store to the network, and the files are distributed and stored in computers (storage nodes) that are willing to contribute storage space around the world. When users need to use files, Then retrieve the location of the file from the network, and then download it to the local computer.
However, unlike other decentralized storage networks, there are not only users and storage nodes in the Storj network, but also satellites as a third role, forming an independent and interdependent relationship between the three.
User: Use the Uplink client for content transmission, and Uplink is responsible for data encryption/decryption and fragmentation.
Satellite: Connecting users and storage nodes, the coordinator in the network. Responsible for storing node address information, metadata, maintaining node reputation, paying and managing node fees, auditing nodes, and managing user account authorization. The satellite will help the user find the node with the fastest upload speed, and record the expenditure and income of the user terminal and the node at the same time.
Storage nodes: provide users with storage space and network bandwidth.
advantage:
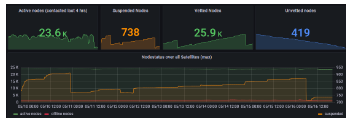
advantage:
High-level encryption Fast data retrieval Affordable price Easy-to-use user experience
shortcoming:
secondary title
3.2 Classification of storage facilities
Firstly, research the existing decentralized storage infrastructure, mainly from three aspects: its structure and characteristics, current usage, and usage cost, and analyze which facilities are more suitable for DApp to "live" in it. According to whether the infrastructure itself relies on a complete blockchain design, we divide it into Off-chain storage facilities and On-chain storage facilities:
In Off-chain decentralized storage facilities, each node does not exist in the form of a blockchain, but a P2P decentralized network, and data is directly dispersed and stored in each node.
secondary title
3.3 New "Challengers"
3.3.1 BNB Greenfield
In March, Binance released BNB Greenfield. Greenfield is a blockchain and storage platform focused on facilitating decentralized data management and access, aiming to transform the data economy by simplifying the storage and management of data and linking data ownership with the BNB SmartChain (BSC) context.
As a part of the "one currency and three chains" in the BNB world, the difference between Greenfield and the existing centralized and decentralized storage infrastructure is:
Allows data and assets to be created and managed in the form of Ethereum-compatible addresses.
BNB is allowed to be used as a basic asset, and native cross-chain with BSC is allowed to provide cloud storage for applications on BSC.
Provides developers with API primitives and performance similar to popular existing Web2 cloud storage.
Greenfield is essentially a blockchain, consisting of two layers: the blockchain itself and the storage provider (Storage Provider).
On-chain, the Greenfield blockchain maintains user ledgers and records storage metadata as general blockchain state data. Its native token is used to pay fees and governance is BNB, which is transferred from the BNB smart chain. User requests to store or retrieve files from Greenfield will actually be wrapped in blocks.
Off-chain, a storage provider (SP) is a storage service infrastructure provided by an organization or individual that uses Greenfield as the ledger and the only source of truth. Each SP is responsible for responding to user requests to upload and download data, while also acting as a gatekeeper for user permissions and authentication.
BNB Greenfield blockchain and SP together form a decentralized object storage system. It is worth mentioning that applications using Greenfield as the storage infrastructure can easily cross-chain with BSC and BNB Beacon Chain.
Since the Greenfield test network has just been released, and the main network will be released in the third quarter of this year, there are not many ecological settlements yet.
In my opinion, the BNB Greenfield storage facility is mainly a part of the BNB-related community and will definitely have a positive impact on the value of BNB. Greenfield makes BSC have a better user experience and get higher recognition. As more and more projects and users choose to use BSC, the overall demand and value of BNB and Greenfield will increase. Through cross-chain switching and the interconnection of the entire ecosystem, BNB can be more widely used in various applications in the ecosystem to build a mutually beneficial and win-win ecosystem.
3.3.2 Filswan
In January of this year, Binance Labs announced the launch of the fourth season incubation plan. The selected projects have the opportunity to receive initial capital investment and various support for project development provided by Binance Labs. Among them, Filswan was successfully shortlisted for the fourth season incubation and received a total of 3 million USD financing.
FilSwan recently announced that its first cross-chain product, multichain.storage, was successfully launched on the Polygon mainnet. The product enables users to pay for IPFS/Filecoin storage through Polygon stablecoins, successfully lowering the operational threshold and simplifying the development process of dApps in Web3 storage.

FilSwan is a team from Canada. Since 2017, he has been deeply involved in the cloud computing and blockchain industry, and the cooperative institutions include Canada's Mcgill University and Concordia University. It has won several R&D grants from the Canadian government and the Canadian Natural Science Foundation in the direction of blockchain cloud computing, and it is also a Canadian next-generation network excellence project. FilSwan is committed to creating a decentralized storage and computing solution. FilSwan's products and services are greatly enhanced through edge computing technology, IPFS/Filecoin storage technology and decentralized ledger technology. FilSwan products are widely used in universities, VR/AR and high-performance computing companies. Users of FilSwan can perform computing tasks at the lowest cost on the nodes closest to them.
3.3.3 OORT
OORT: Decentralized cloud service + public chain, Web3 and metaverse infrastructure, providing users with enterprise-level decentralized underlying infrastructure cloud services. OORT can provide a complete set of Internet-scale Web3 data solutions, aiming to bring Web2 native user experience to end users and developers.
Advantages: security, openness, anti-censorship, resistance to single point of failure, resistance to data leakage (all data is encrypted at the edge node) network attack, Internet-scale scalability, 99.99% + availability, ultra-low latency, 99.99% + durability .
first level title
secondary title
4.1 The advantages and effects of distributed storage on DApp
In DApp applications, distributed storage is often used to store smart contract code, user data, transaction data, authentication data, and more. For developers, the reasonable application of distributed storage technology can bring some other advantages besides security and reliability, such as:
1) High availability and security
Since data is stored on multiple nodes, even if a node fails, the data can still be accessed from other nodes. In distributed storage, data is usually distributed and stored on multiple nodes, and each node only stores a part of the data, so that once a node fails, other nodes can also provide services normally, ensuring data reliability.
2) High performance and responsiveness
secondary title
4.2 DApp development framework and technology selection
Ethereum + IPFS: Ethereum is the most popular DApp development platform today, with its high programmability and smart contract functions, it has become the platform of choice for building decentralized applications. IPFS (InterPlanetary File System) is a popular decentralized storage system that solves the challenges of traditional centralized storage through distributed protocols. Combined with Ethereum and IPFS, developers can build reliable, secure and highly scalable decentralized applications in a powerful environment.
Truffle Suite: Truffle Suite is a suite of development tools designed specifically for the Ethereum ecosystem. Among them, Truffle is a development environment, testing framework, and asset pipeline that is widely chosen for building DApps. Through the integration with IPFS, Truffle Suite can realize decentralized storage and provide developers with comprehensive functions and convenience.
Embark: Embark is a framework that simplifies the process of DApp development and deployment. With Embark, developers can easily create and manage all aspects of DApps, including smart contracts, front-end interfaces, and storage and Whisper communication functions. Embark integrates with decentralized technologies such as IPFS to provide developers with convenient storage and communication capabilities, further enhancing the decentralized nature of DApps.
HarDhat: HarDhat is a powerful development environment for compiling, deploying, testing and debugging Ethereum software. It provides comprehensive support to enable developers to efficiently develop and debug smart contracts. HarDhat can be integrated with IPFS or other decentralized storage solutions to meet DApp's needs for reliable storage.
Ganache: Part of the Truffle Suite, Ganache is a powerful tool for creating private Ethereum blockchains. By using Ganache, developers can test and debug DApps in a safe and deterministic environment. It provides a fast and reliable way for developers to simulate different blockchain scenarios and ensure the stability and consistency of DApps in various situations.
Web3.js / Ethers.js: Web3.js and Ethers.js are two popular JavaScript libraries for enabling applications to interact with the Ethereum blockchain. These libraries provide a wealth of functionality, including interaction with smart contracts, account management, data query, and more. Whether used in conjunction with IPFS or other decentralized storage systems, Web3.js and Ethers.js provide developers with powerful tools to easily build Ethereum-based applications.
Moralis: Moralis is a fully managed backend service designed for DApp development. It provides powerful features that enable developers to focus on front-end development without worrying about complex back-end architecture. Moralis supports IPFS as a decentralized storage solution, providing developers with a reliable storage solution that allows them to easily store data in the IPFS network.
Arweave: Arweave is a decentralized storage network that uses an innovative sustainable and permanent donation mechanism to support data storage. With Arweave, developers can achieve large-scale, permanent data storage without worrying about data loss or tampering. It provides developers with a reliable and long-term data storage solution, and provides persistence guarantee for DApp data management.
Filecoin: As a decentralized storage system, Filecoin aims to provide safe and reliable storage for humanity's most important information. It employs an innovative incentive mechanism that enables network participants to provide storage space and receive corresponding rewards. Filecoin can be used in conjunction with various DApp development platforms to provide developers with highly reliable storage solutions to ensure data security and accessibility.
secondary title
4.3 Distributed social media platform
The development of the decentralized social media platform is very meaningful to the development of web3. If you want an open and free Internet, you need an open and free social media network. Most internet users spend most of their time on major social media platforms. Traditional social media platforms dictate what users can and cannot see, have the right to censor content/profiles they don't like, and control all user data. The web2 social platform is not portable. Everyone's profile, friendships and content are locked to a specific network and owned by the network operator. And behaviors such as banning accounts may occur at any time. Based on this, a distributed social media platform has been born in the web3 ecosystem, which can unlock network effects for developers. This is a huge moat for major centralized platforms.
Mask Network, RSS3, Lens Protocols, and CyberConnect are currently four representative distributed social media protocols. They are all committed to providing users with more secure, decentralized, and efficient data storage and access services. The following will compare them from four perspectives: data storage, data access, data security, and reward mechanism.
data storage:
Mask Network runs on Ethereum, Binance Smart Chain and Polygon, and features community governance and decentralized data storage.
RSS3 uses a data format called RSS3 Core, which is based on the JSON-LD language for easy data exchange and sharing, and also supports other data formats. The data storage of RSS3 adopts the decentralized IPFS protocol.
Lens Protocols is based on the two main blockchain platforms of Ethereum and Polkadot, and connects them through a cross-chain bridge. Users can freely transfer digital assets between the two platforms, achieving cross-chain interoperability.
CyberConnect uses a distributed storage protocol similar to IPFS and Filecoin to store data, and also combines smart contracts and encryption algorithms to ensure data security.
data access:
Mask Network enables easy data access, sharing and exchange through user-friendly Chrome extensions and interfaces to social media platforms.
In addition to being connected to Ethereum, Polygon, BSC, Arbitrum, Flow, and xDAI, RSS3 also provides data indexing and distribution for ecological projects such as Mask Network, Polygon, Arweave, Misskey, and ShowMe.
Lens Protocol uses a cross-chain bridge to connect Ethereum and Polkadot to realize cross-chain transfer of assets. The cross-chain bridge adopts a multi-signature mechanism to ensure the security and reliability of assets.
CyberConnect provides an interface called CyberConnect Gateway, through which users can find and access data stored on the network.
Data Security:
Mask Network uses encryption algorithms and smart contracts to protect the security of user data, and also supports technologies such as multi-signature to ensure the security of transactions and storage. Allows users to encrypt and decrypt content on social media through public key cryptography.
RSS3 uses distributed storage and encryption algorithms to protect the security of user data, and also supports authentication and other technologies to prevent unauthorized access.
Lens Protocol provides users with a liquidity pool, enabling users to conduct asset transactions and liquidity provision. The protocol supports two liquidity pools, AMM and pricing model.
CyberConnect uses distributed storage protocols similar to IPFS and Filecoin to ensure data security, and also uses technologies such as encryption algorithms, smart contracts, and identity verification.
bonus system:
Mask Network users can perform the following activities on Twitter and Facebook (without leaving the site or installing another app): trade tokens through the Uniswap DEX; donate funds and send cryptocurrency via red envelopes; utilize Initial Twitter Offering (ITO) to raise funds for crypto projects ; Upload and attach (optionally encrypted) files to your posts via a decentralized file storage service.
The reward mechanism of RSS3 is based on RSS3 tokens. RSS3 tokens are mainly used to motivate users to share and access data, and can also be used to support the development of applications and communities. Users can obtain RSS3 tokens by sharing their own data and participating in community governance.
first level title
secondary title
4.4.1 Genaro Network
Genaro Network is a blockchain-based storage network that provides a decentralized platform on which users can store and share data.

data storage:Genaro Network uses a distributed storage solution called Genaro EDen. This solution is similar to IPFS and Swarm, but it pays more attention to data security and reliability. Genaro EDen supports various types and structures of data, including files, pictures, videos, etc.
data access:Genaro Network provides a user-friendly interface through which users can easily find, retrieve and access data stored on the network. In addition, Genaro Network also provides an application called Genaro Sharer, through which users can share their data.
Data Security:Genaro Network takes data security very seriously. It uses a technology called SPoR (Sentinel Proof of Retrievability), which ensures the security of data during storage and transmission. In addition, Genaro Network employs encryption and authentication technologies to protect user data from unauthorized access.
bonus system:Genaro Network has a unique reward mechanism through which users are incentivized to share data, provide storage and access services. Users can get GNX (Genaro Network Tokens) as rewards by sharing data and providing storage space. This reward mechanism helps maintain the stability and security of the distributed network.
4.4.2 Mirror
Mirror is a blockchain-based publishing platform that allows creators to create, own and monetize their creations.

data storage:Mirror implements permanent storage of data through Arweave, including the content published by the creator and all related changes, all the information needed to verify the authenticity of the author's identity. Arweave not only provides permanent data storage, but only pays once for the first upload.
data access:Mirror provides a user-friendly web interface through which users can easily find, retrieve and access content stored on the platform. Additionally, since all content is stored on the blockchain, anyone can use Ethereum tools to directly access the data.
Data Security:Mirror uses blockchain encryption technology to protect the security of user data. Each user has an account associated with their Ethereum wallet, and only through this wallet can users publish or modify their content. This ensures that only the true owners of the content have control over it.
bonus system:secondary title
4.5 Summary discussion: How far are we from information interconnection?
Information interconnection refers to the interconnection and communication of various devices, systems, software, services, etc. through the network, and is one of the infrastructures of the digital age. In the past few decades of development, the continuous progress and popularization of information interconnection technology has promoted the rapid development of society, economy, culture and other fields. However, the current information interconnection technology also has some shortcomings. Among them, the centralized storage of data centers and the service model dominated by cloud computing are the two most obvious problems.
Traditional "cloud storage" means that all user data is stored centrally in a small number of data centers. Such a storage method has the risk of a single point of failure. If one of the data centers fails, it will affect a large number of users. In addition, centralized storage also has problems such as data privacy leakage and abuse, and user data is completely controlled and managed by centralized service providers.
The service model dominated by cloud computing means that most online services are realized through cloud computing, and these services are usually monopolized by a few large Internet companies. This situation has led to the circulation and processing of data being mainly controlled by a small number of large companies, resulting in the problems of data monopoly and centralized control.
With the development and application of blockchain technology, the application of distributed storage technology has also been more widely promoted. The integration between Ethereum and IPFS makes the development and use of DApp easier and more effective, and also provides new ideas and possibilities for the development of information interconnection. Traditional centralized applications have problems such as privacy leaks, data dependence, system crashes, etc., while DApps are based on decentralization, through blockchain technology and smart contracts, making applications more transparent, secure, reliable and more High degree of decentralization. With the continuous advancement of technology and the continuous expansion of application scenarios, DApp will play a more important role in the future development.
references
references
Summary at the end of 2022: the status quo and future of decentralized storage - ODAILY
Why do we need decentralized storage? -Foresight News
Decentralized Storage Report: The Cornerstone of WEB3.0 Development-ODAILY
Web3 Storages : Arweave vs IPFS vs Filecoin, which to choose? | by makeDEVeasy | CoinsBench
Storj Network Statistics - Grafana (storjstats.info)
Storj: Subverting AWS' distributed storage network? | Web3 World (web3 sj.com)