first level title
What are RWAs?
RWA, Real World Asset, real world asset. At present, the most popular RWAs mainly include the following categories: cash (USD), metals (gold, silver, etc.), real estate, bonds (mostly U.S. Treasury bonds), insurance, consumer goods, credit notes, royalties, etc.
The asset size of RWA far exceeds that of Crypto Native Asset. For example, the size of the fixed income bond market is about 127 trillion US dollars, the total value of global real estate is about 362 trillion US dollars, the market value of gold is about 11 trillion US dollars, and the current market value of Crypto Native Asset is 1.1 trillion, which is only the market value of gold 1/10 of that.
first level title
How to bring RWA into DeFi?
Smart contracts are often used to create tokens representing RWA while providing off-chain guarantees that issued tokens can always be redeemed for underlying assets.
RWA has the following common application forms in DeFi:
1、Stablecoins:For example, the top stablecoins such as USDT, USDC, and BUSD all belong to RWA. Issuers such as Tether, Circle, and Paxos maintain audited US dollar asset reserves and mint stablecoin tokens for blockchain and DeFi protocols;
2、Synthetic assets:Synthetic assets also belong to RWA. For example, in the form of synthetic assets, stocks, commodities, etc. are traded on the chain in the form of linked derivatives. At present, the best development in the field of synthetic assets is Synthetix, which has more than $3 billion worth of assets locked in its agreement at the peak of the bull market in 2021;
3、Loan agreement:first level title
The development status and cases of RWA track
secondary title
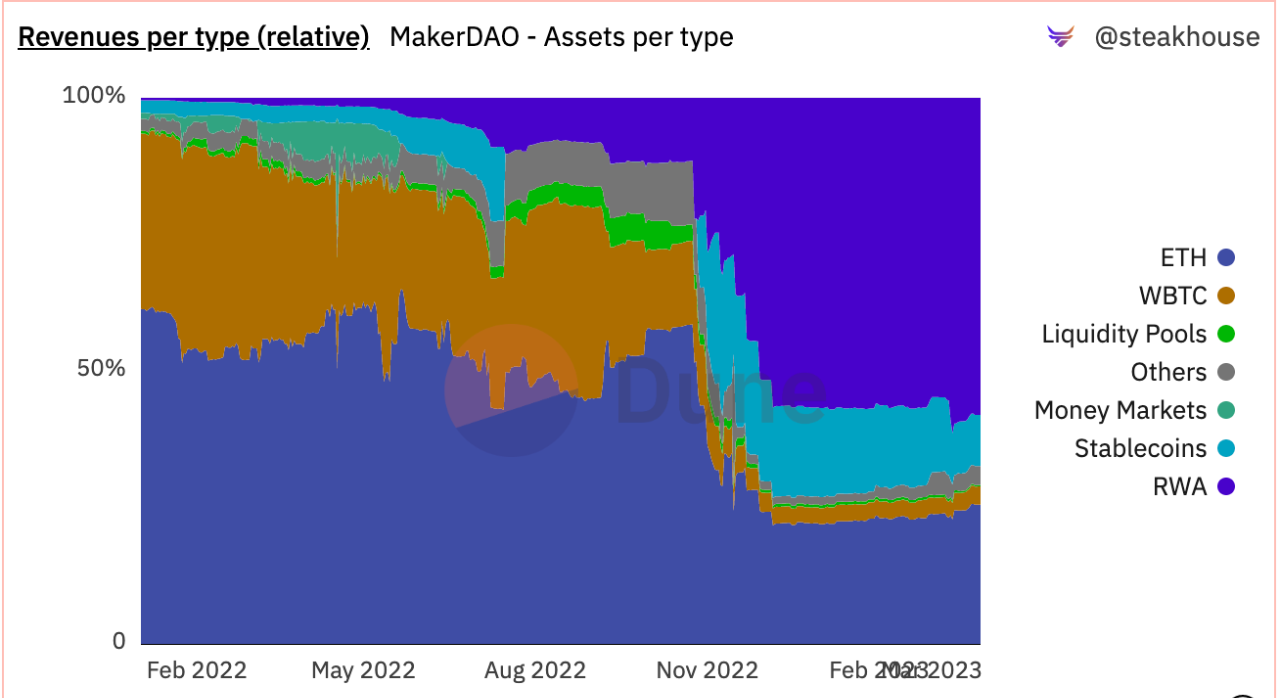
MakerDAO: The RWA business scale exceeds 680 million US dollars, contributing more than 58% of revenue.
Because the rate of return of the traditional financial system is now higher than that of the DeFi protocol, for example, the rate of return of U.S. Treasury bonds is about 3.5%, while the rate of return of the top DeFi mortgage lending agreement is about 2%, which gives the DeFi protocol a sustainable income opportunity.
In order to manage the RWA business, MakerDAO established the RWA Foundation. Depending on the type of collateral, different foundations may be established, and each SPV can also choose the most suitable management jurisdiction/legal structure according to business needs. Its basic structure is as follows:
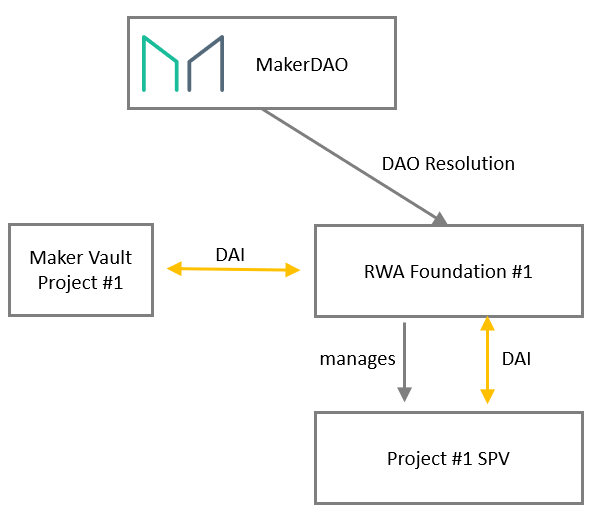
MakerDAO has made some adjustments in the business logic of mortgage lending for RWA's off-chain assets. The main reason is that the liquidation part is not performed through the public auction on the chain, but is enforced by a third party off the chain. Smart contracts that implement new functions mainly include:
RwaLiquidationOracle: a liquidation beacon that acts as an off-chain executor;
RwaFlipper: acts as a virtual liquidation module in case of logout;
RwaUrn: This helps to borrow DAI and deliver to the designated account;
RwaOutputConduit and RwaInputConduit: pay and repay DAI;
RwaSpell: deploy and activate a new collateral type;
RwaToken: represents the RWA collateral in the system;
TellSpell: Allows MakerDAO governance to initiate a liquidation process;
CureSpell: Allows MakerDAO governance to cancel liquidation procedures;
CullSpell: Allows MakerDAO governance to write off loans that are being liquidated.
MakerDAO calls the RwaLiquidationOracle via tell() when they deem it necessary. This will start a countdown, and after the repair period is over, the oracle will start reporting that the position is being liquidated. If the reason for triggering liquidation is remedied, MakerDAO governance can return to normal state by calling Cure() after remediation; etc.) can report that the position is liquidated by calling good(). If there is still debt remaining on the position at the end of the liquidation process, and MakerDAO believes that the debt will not be settled, it can trigger the cancellation by calling cull() . A write-off occurs by setting the system's collateral value to zero, which will cause the position to be liquidated on-chain via bite(), etc. Unlike liquidation modules for existing collateral types, the dedicated liquidation module, RwaFlipper, does not attempt to sell the underlying collateral, but simply marks losses on the system's balance sheet by allowing system debt to be created.
MakerDAO has made great progress in adopting RWA. Currently, MakerDAO has over $680 million worth of RWA-backed decentralized stablecoin DAI.
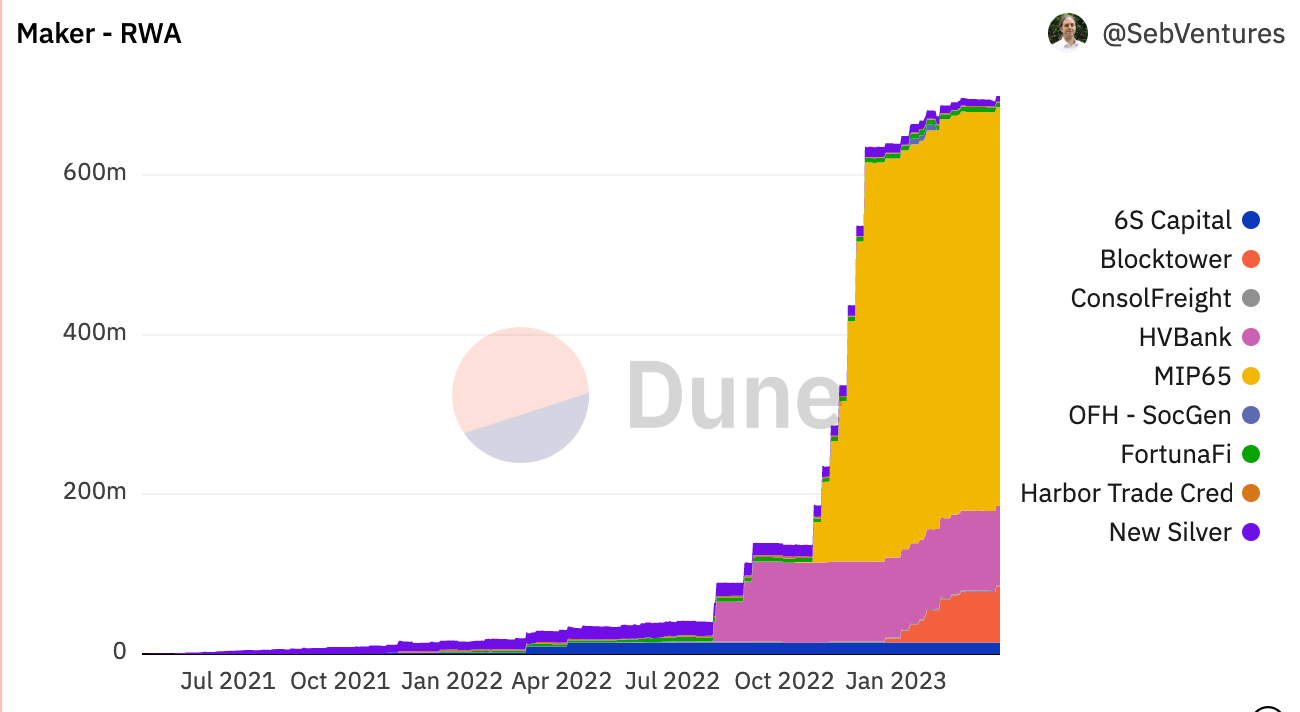
In terms of RWA, MakerDAO disassembled and analyzed its $680 million RWA. There are three specific cases:
1. The majority of MakerDAO’s RWA collateral (~$500 million) is in the form of U.S. Treasury bonds managed by Monetalis (MIP 65). These assets provide the MakerDAO protocol with a source of yield on idle USDC collateral;
2. MakerDAO also launched a vault backed by $100 million worth of loans from a Philadelphia-based commercial bank called Huntingdon Walley Bank (HVB). HVB used MakerDAO to support the growth of its existing business and investments around real estate and other related verticals, and became the first example of a business loan between a US regulated financial institution and a decentralized digital currency;
3. In a separate vault, Societe Generale borrowed $7 million from MakerDAO, and its position was backed by €40 million worth of AAA-rated bonds as OFH tokens.
secondary title
Centrifuge: Bringing RWAs into the Crypto ecosystem in the form of NFT, with a TVL exceeding $170 million.
Centrifuge brings real-world assets into the Crypto ecosystem in the form of NFTs. The dApp of the Centrifuge protocol is called Tinlake, and the product logic of Tinlake is mainly as follows:
1. Asset promoters use Tinlake to bridge real-world assets. The asset is converted into an NFT, which includes relevant legal documents;
2. Asset promoters can use tokenized real-world asset NFT as the underlying collateral to create asset pools;
3. When creating a pool, two Tokens will be created——DROP Token and TIN Token;
4 Investors can decide which pool to provide funds to and purchase DROP or TIN Token according to their personal risk preference;
5. DROP Token holders have guaranteed income, which is determined by the cost function. Each pool has fixed interest, compounded every second;
6. On the other hand, TIN Token holders have no guaranteed income. They receive a variable rate of return based on pool investment return, which may be higher than the return of holding DROP Token;
7. TIN Token holders take higher risks, because if the borrower defaults, they will bear the first loss.
first level title
Opportunities and Risks of RWA
The trust assumption of RWA: Since Tokenization’s RWA is off-chain after all, it cannot enforce liquidation through smart contracts, and also relies on the endorsement of traditional financial institutions, the trust attributes of these RWAs may never be able to reach the same level as Crypto Native Asset. At the same time, due to the existence of the RWA trust assumption, it is difficult for a completely permissionless DeFi protocol to support RWA. Therefore, the current RWA Tokenization project generally still has the role and influence of a centralized entity in the processing of RWA assets.
Potential opportunities for RWA: STO (Security Token Offerings) has historically been seen as a limited implementation of RWA. Since many STOs are typically niche securities available only on permissioned platforms, their adoption has not yet reached the same level as RWAs on public blockchains. The current STO is one of the few asset tokenization schemes approved by regulation in the blockchain industry. The development path of STO in embracing regulation may also be explored by RWA.