Original title: ""All for One and One for All" - An on-chain distribution model for the Arbitrum community》
Original Compilation: The Dark Side of the Moon, PANews
TL;DR
secondary title
• Offchain Labs, Arbitrum Foundation and Nansen jointly designed a token distribution model based on the participation of community members in the Arbitrum ecosystem
• This allocation mode relies on Nansen's on-chain data, and allocates qualification points based on the wallet's on-chain historical activity records. The wallet address must meet at least three point standards to qualify for the airdrop.
first level title
Introduction
IntroductionHow many ARB tokens can you claim? A Quick Look at Arbitrum Token Economics and Airdrop Specifications》)
How many ARB tokens can you claim? A Quick Look at Arbitrum Token Economics and Airdrop Specifications
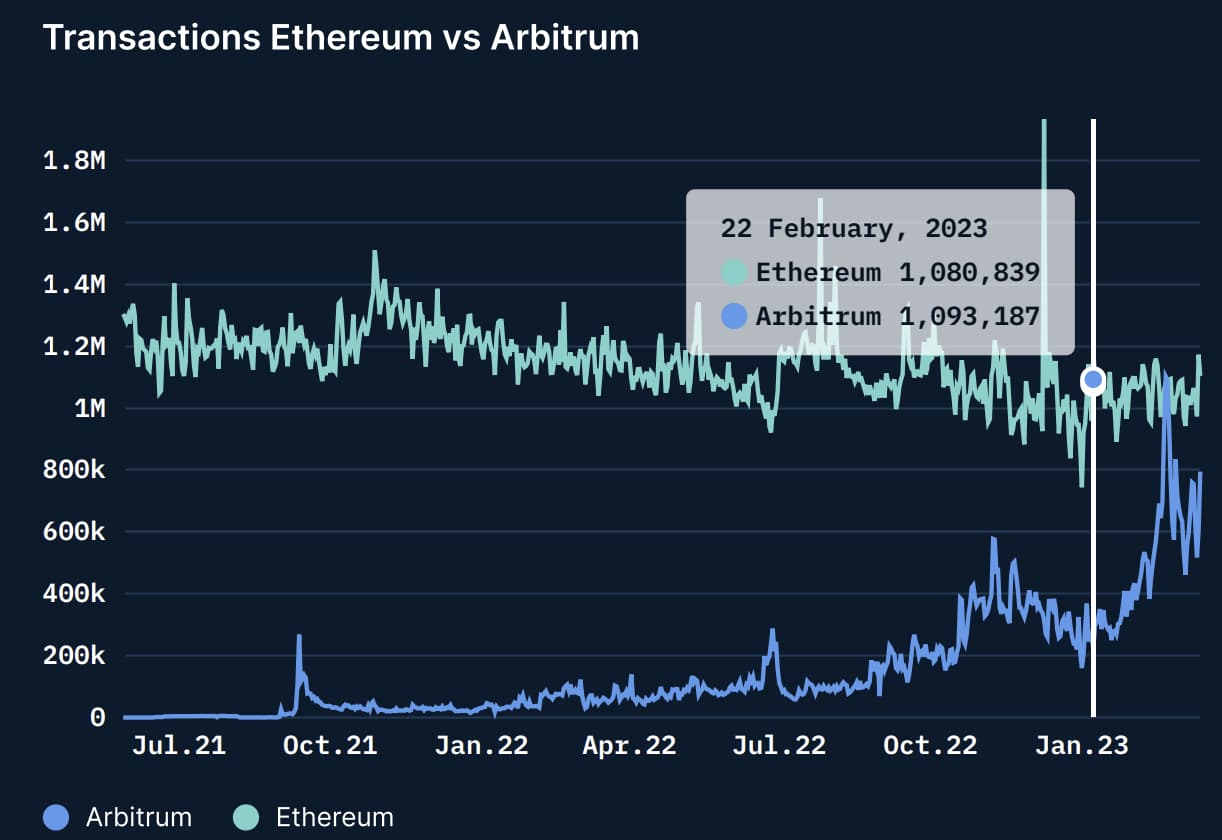
image description
Figure 1: The rise of L2, Arbitrum’s daily transaction volume surpassed that of Ethereum for the first time in February 2023
The Arbitrum Foundation has empowered Nansen to ensure that consideration is given to the number of addresses interacting with the network and airdrops of tokens to users who contribute to the development of the Arbitrum ecosystem.
•The allocation mode will be based on on-chain data: query Arbitrum's past historical data through Nansen Query
• Mechanism design will incorporate multiple parameters and criteria to ensure its safety
• Nansen's analysis will be carried out as envisioned by Offchain Labs, Arbitrum's parent company
In short, on-chain analysis has a part of human planning. Even if strict analysis standards are used, the airdrop distribution model cannot be absolutely accurate.
In this article, we will introduce the specific process and distribution model of the Arbitrum token airdrop.
Parts 1 and 2 review the specific variables and goals of the airdrop program. Section 3 explains the specific process between allocation criteria and on-chain analysis. Sections 4 and 5 detail the eligibility criteria and associated 'points' design. Part 6 introduces the idea of the total anti-witch. Section 7 summarizes the final statistics for eligible wallet addresses. Section 8 focuses on eligible dApps and protocols.
1. The token distribution model is a key factor for the success of the airdrop
In view of the complex operability of token airdrops, it is usually necessary to optimize the process of user participation and governance decision-making. Therefore, the protocol needs to set specific airdrop criteria to support the protocol in achieving its long-term development goals (see section "2. Airdrop Principles and Objectives" below).
In the Arbitrum token airdrop, Nansen focused on the design of the distribution model parameters to help the Arbitrum Foundation as much as possible to formulate the distribution criteria and determine the recipient list of the token airdrop. However, the following factors are also strongly correlated with the airdrop distribution model:
•Demand-side factors: mainly related to the use of tokens in protocol governance, on the basis of which the demand for tokens needs to be determined
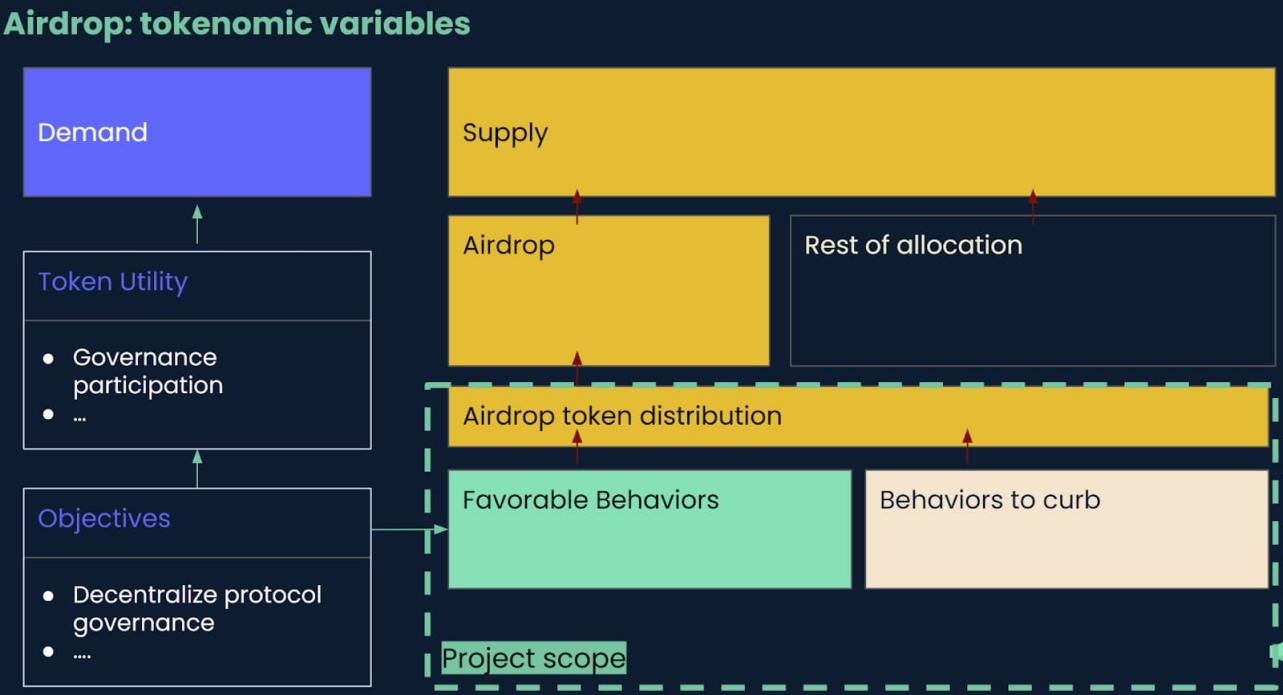
image description
Figure 2: This round of airdrop distribution model variables
2. Principles and objectives of Airdrop
The Arbitrum Foundation hopes to optimize the decentralization of Arbitrum protocol governance through airdrops. So one way to think about it is to try to define organic activity. "Organic" activities include active transactions on Arbitrum, as well as helping to develop on-chain dApps and other protocols, or actively contributing to Arbitrum's governance. The above behaviors can be measured in on-chain data and categorized by wallet activity on the Arbitrum chain.
However, some wallet addresses with multiple transactions are not necessarily real demand, and there is no guarantee that these addresses will continue to be active after the airdrop. Therefore, one goal of on-chain data analysis is to help identify sybil-like wallet addresses, such as those purported to qualify for this round and future airdrops. The second goal is by introducing a "negative criterion" highly correlated with Sybil behavior, which was designed by Offchain Labs anti-Sybil attack researchers based on Nansen Query Arbitrum and Ethereum on-chain data.
3. Distribution standards and on-chain data analysis: an iterative process
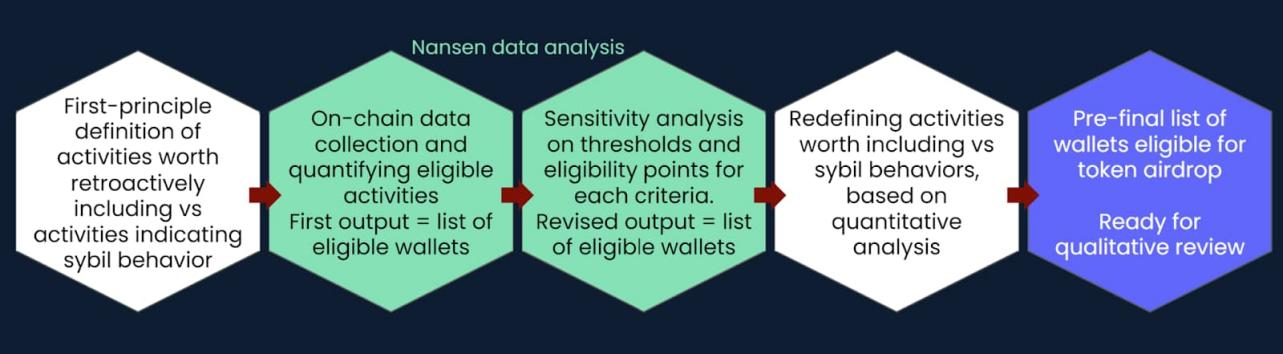
image description
Figure 3: Project flow, from first-principles criteria to data validation
The research generally followed the following steps:
Step 1: According to the goal of the airdrop, define the activity of distributing tokens according to the first principle
This step defines ex-ante criteria for on-chain activity to qualify as “organic”. At this point, we are trying to answer the following question before looking at the on-chain data: How many transactions should a wallet initiate to be eligible for an airdrop? What should organic behavior look like over time? What is the corresponding dollar value to bridge and spend?
Step 2: Collection of on-chain data and quantification of qualified behavior
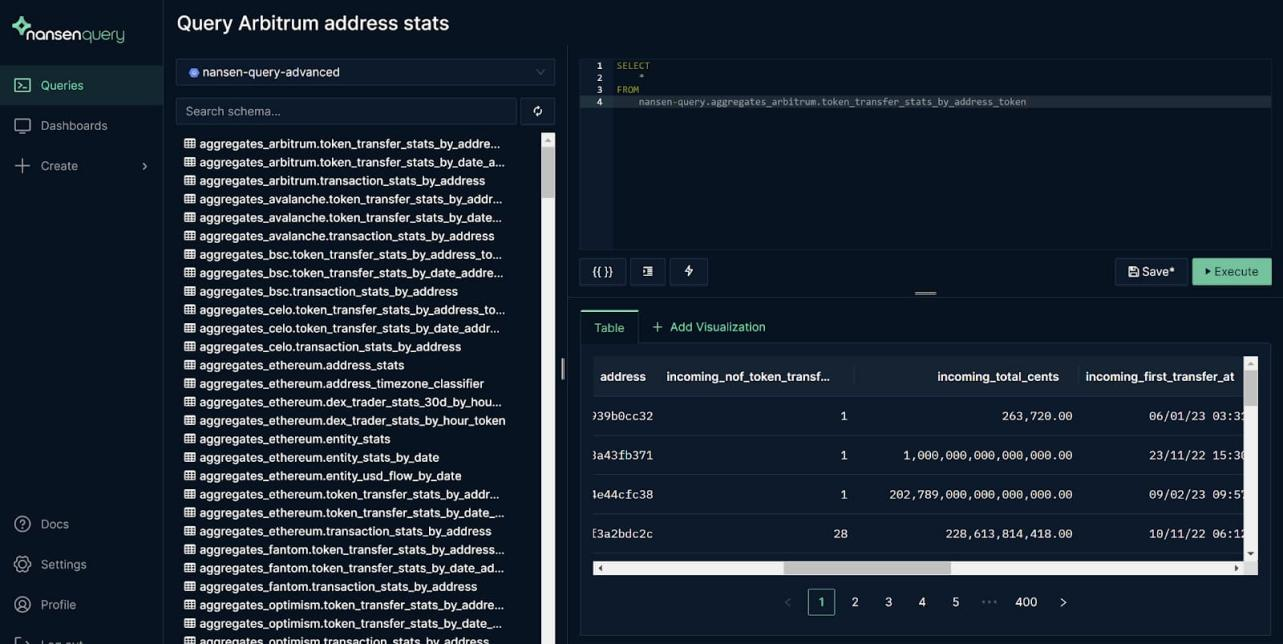
Figure 4: Nansen query interface: wallet address transfer activity data on the Arbitrum One chain
text
Step 3:: Sensitivity analysis
We build an ad-hoc model by setting eligibility criteria in the allocation model and combining it with address lists that have been created before. The model can attribute a certain number of positive or negative points to the criteria.
We reviewed a portion of the address data to assess whether our criteria and points design were too strict, as they only captured address data too far ahead of addresses on Arbitrum, and vice versa, also needed to be checked to see if the criteria were too lenient. We can illustrate this process by visualizing the distribution of criteria (Figures 5 to 8).
This step requires several iterations to eventually arrive at reasonable thresholds and criteria. For example, the model must capture data for addresses that score above the median threshold shown in Figures 5 through 8: For example, the threshold for the “different number of months a transaction was made” criterion is set to two months or more, and higher than one Median of months.
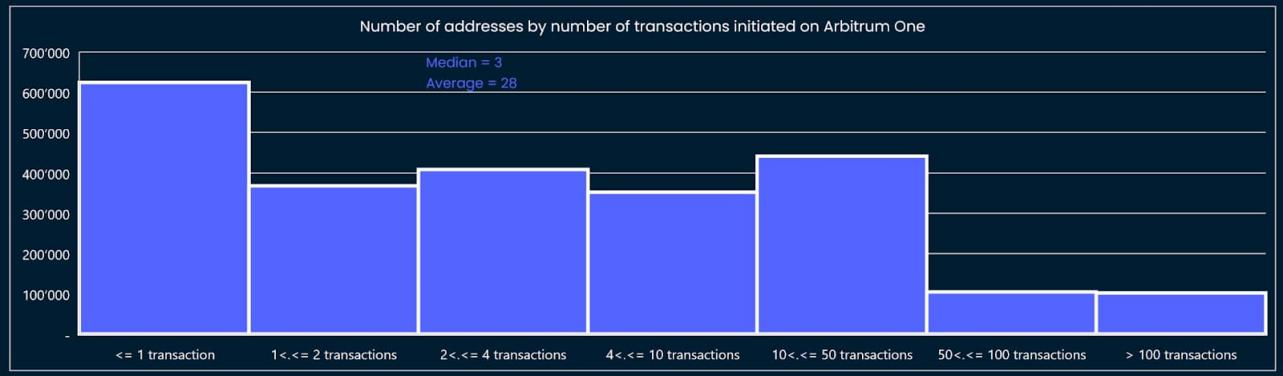
image description
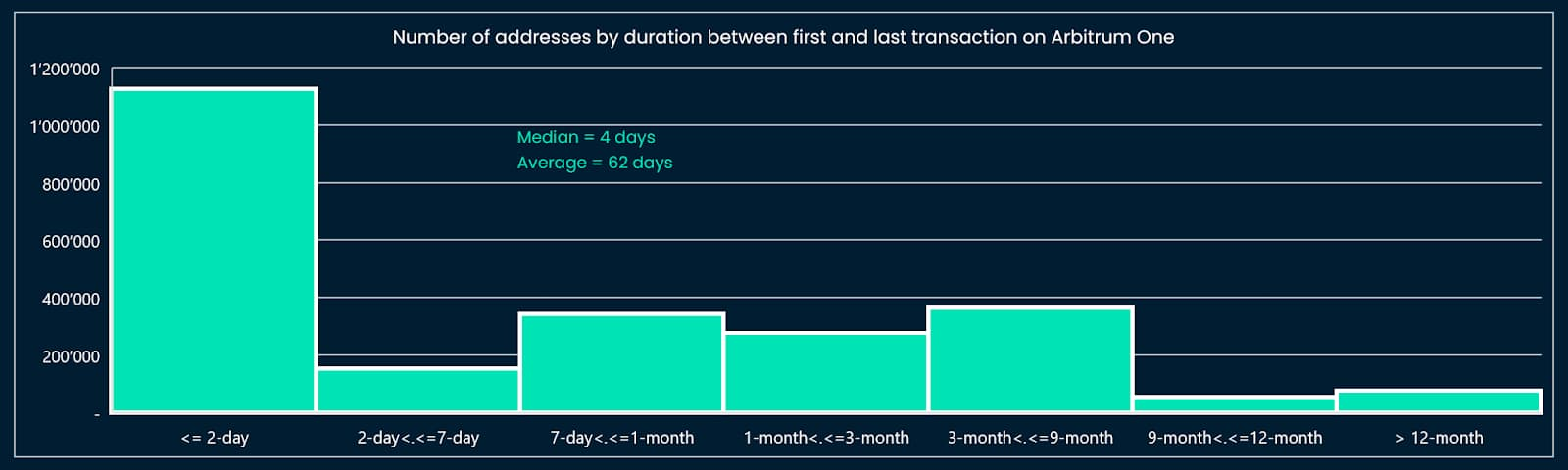
image description
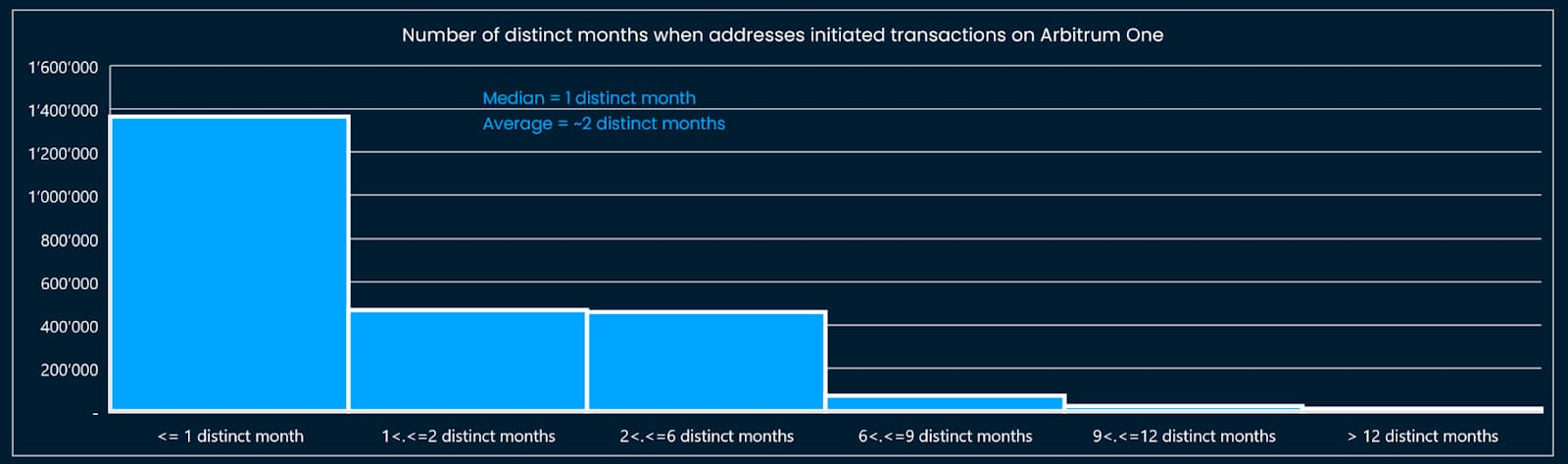
image description
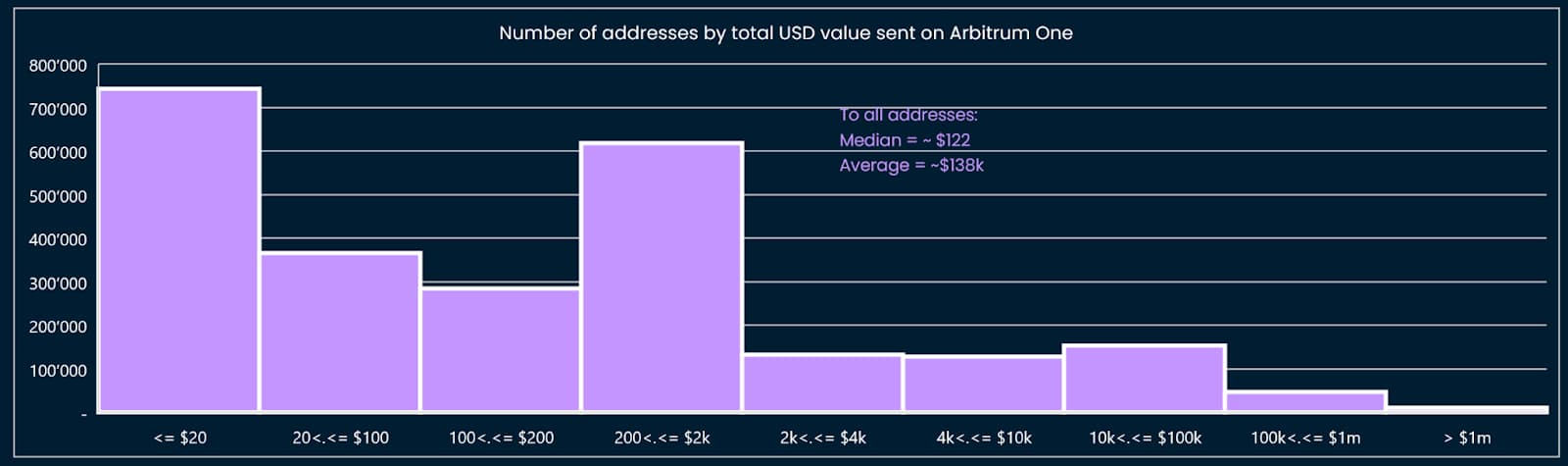
image description
Figure 8: Wallet addresses denominated in USD, snapshot on February 6, 2023 (Arbitrum One)
Step 4: Determine the final standard and anti-witch design
Determine the criteria for eligible and ineligible activities and revise the points system based on the results of on-chain analysis. At this stage, Arbitrum Nova is added as a supplementary standard to Arbitrum One. So re-invoke the model until a satisfactory result is obtained.
Offchain Labs researchers also designed an anti-Sybil attack model, they modeled historical transactions and data on Arbitrum and Ethereum. Removed the address wallet that would partly involve witches.
Step 5: Pre-selected list of wallet addresses eligible for token airdrop
The model finally came up with qualified wallet addresses. Which are marked as "functional" wallet addresses such as exchanges, fund pools, addresses for "burning" and cross-chain bridges. List of wallet addresses is ready for final eligibility review.
4. Compliance Standards and Other Token Allocation Standards
The above process resulted in final specific standards defined around the following broad categories (see Figure 9):
• Quantitative thresholds for the volume, value and time span of wallet-initiated transactions or transfers
• The actions of these wallets bring liquidity to Arbitrum
• Experiment with new Arbitrum chains like Nova
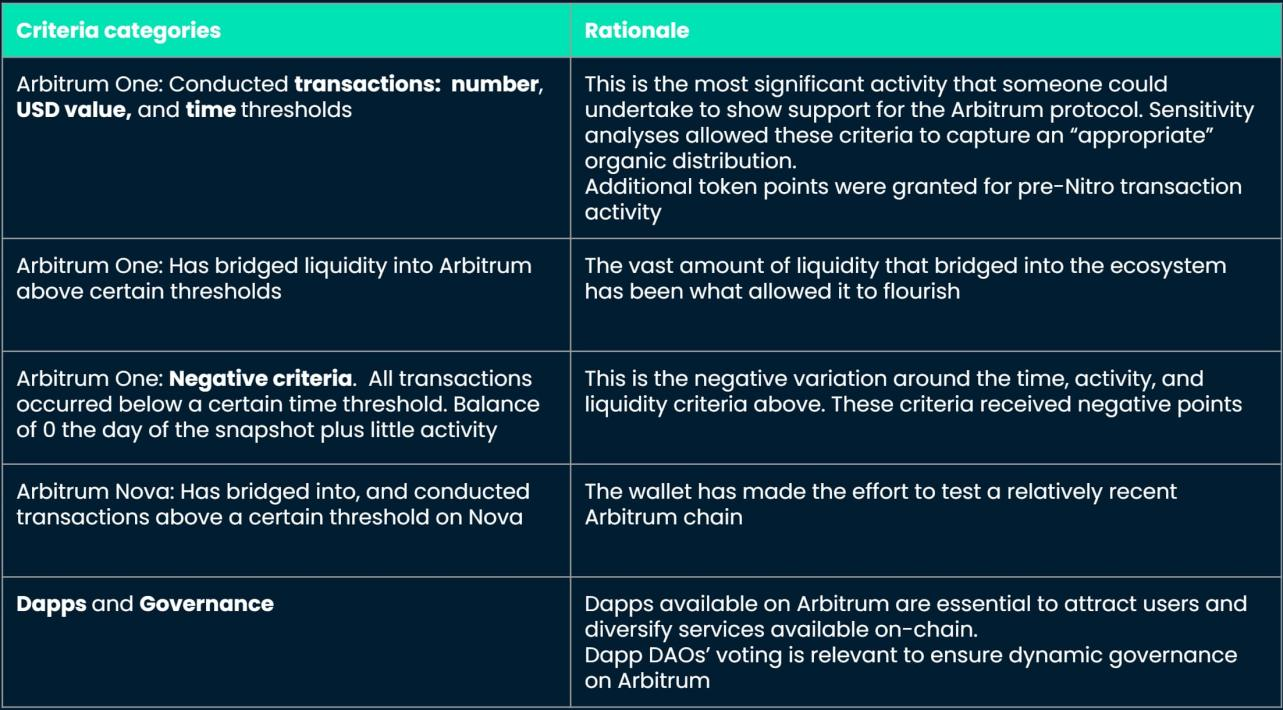
image description
Figure 9: Airdrop breakdown criteria
Historical data collected by Nansen from the genesis block of Arbitrum One:
August 31, 2022 block number 22, 207, 817, that is, before the Arbitrum upgrade to Nitro
February 6, 2023 block number 58,642,080 to account for increased Nitro activity after Arbitrum
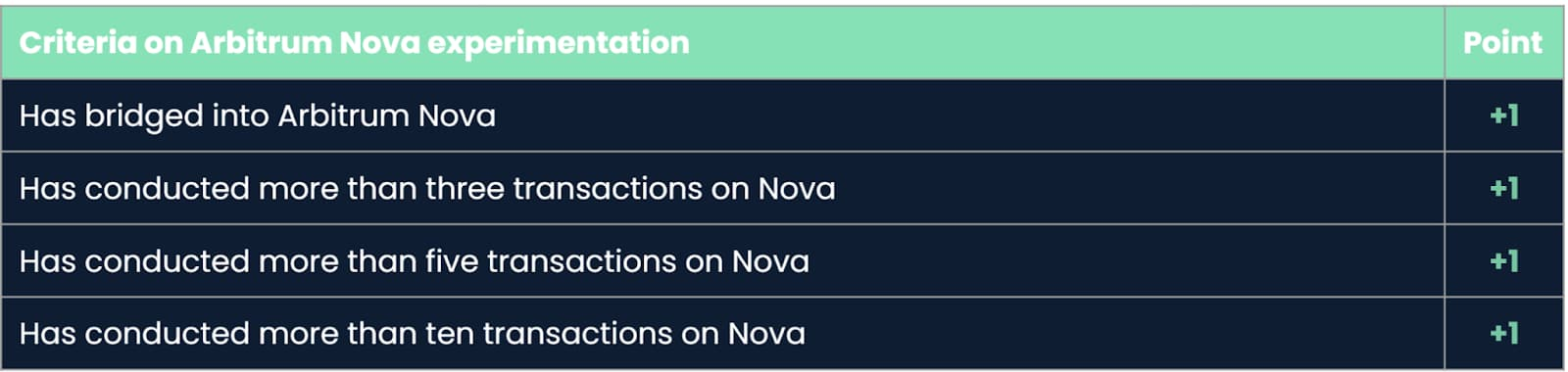
Added supplemental eligibility criteria to cover another chain, Arbitrum Nova, to reward wallet addresses for early active participation in testing this new chain. However, the points will be slightly below the standard on Arbitrum One, and the points earned in our distribution model will be lower. The snapshots on Arbitrum Nova are:
October 2, 2022 block number 499, 342
February 6, 2023 block number 2, 108, 676
Each "organic" activity earns positive (encouraged behavior) or negative (discouraged behavior) points. The amount of tokens a wallet address receives in an airdrop depends on how many points it has collected. The minimum participation standard is that the wallet address must reach three points. The more points you get, the higher the proportion of participating in the distribution. Scores from all snapshot dates are combined to determine the final score for each address.
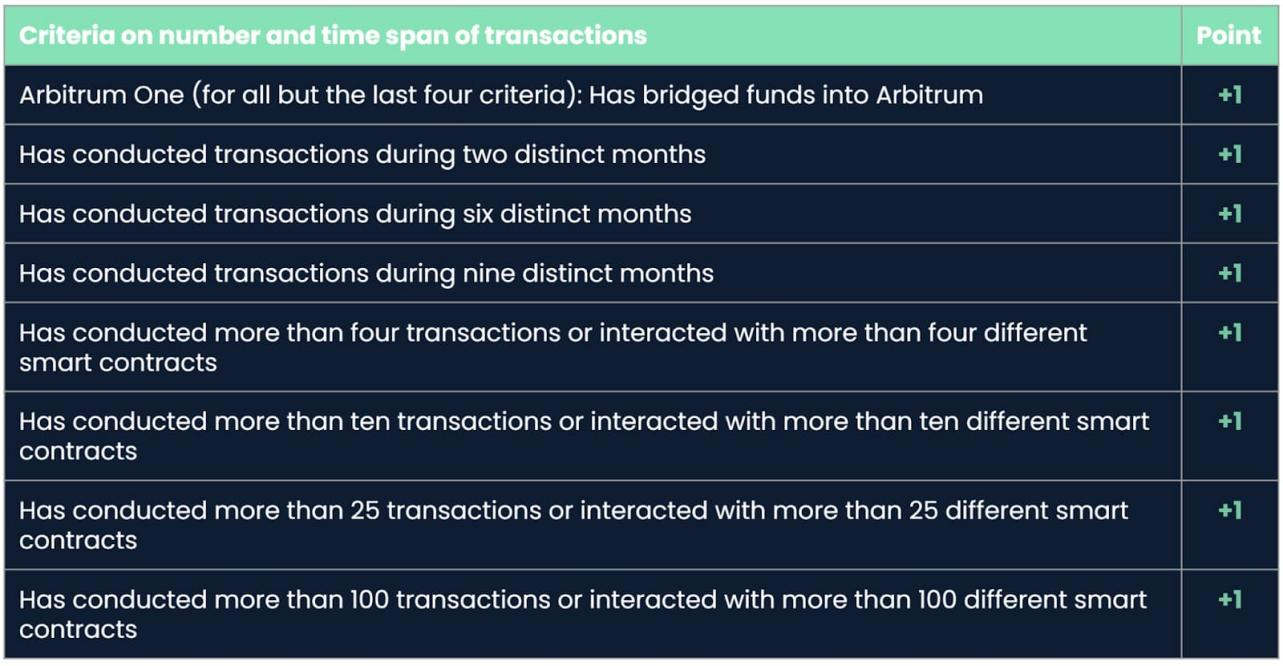
image description


Over 620,000 addresses received airdrops, detailed explanation of Arbitrum airdrop data and anti-sybil strategy
In summary, we have obtained various behavioral data of eligible wallet addresses, such as:
• Bridged to Arbitrum One's wallet address with more than a dozen transactions in two different months and had a non-zero balance at the time of the airdrop snapshot
• Bridge to wallet address on Arbitrum One and Arbitrum Nova requires at least 25 transactions through Arbitrum One in two different months, on Arbitrum Nova wallet requires more than ten transactions
• A wallet address that sent over $250,000 worth of assets into Arbitrum One made over 100 different transactions over nine different months, and on Arbitrum Nova, the same wallet initiated over a dozen transactions
6. Recognizing "Sorceress" Addresses
Among the addresses initially eligible to receive the Arbitrum airdrop tokens, some of which were not for utility purposes but focused on obtaining possible future airdrops (see Figures 11 and 12), these addresses are considered unlikely to have been using Arbitrum , and are less likely to actively participate in governance.
Sybil addresses are often difficult to distinguish from real behavior addresses, as was the case with airdrop data in the past. Both different types of addresses can exhibit the exact same pattern on-chain, but they have different goals, one for real use and one for potential airdrops.
Therefore, tracking sybil addresses requires a qualitative evaluation step, which requires a human assessment of whether the model used to detect sybils will violate the airdrop goals.
image description
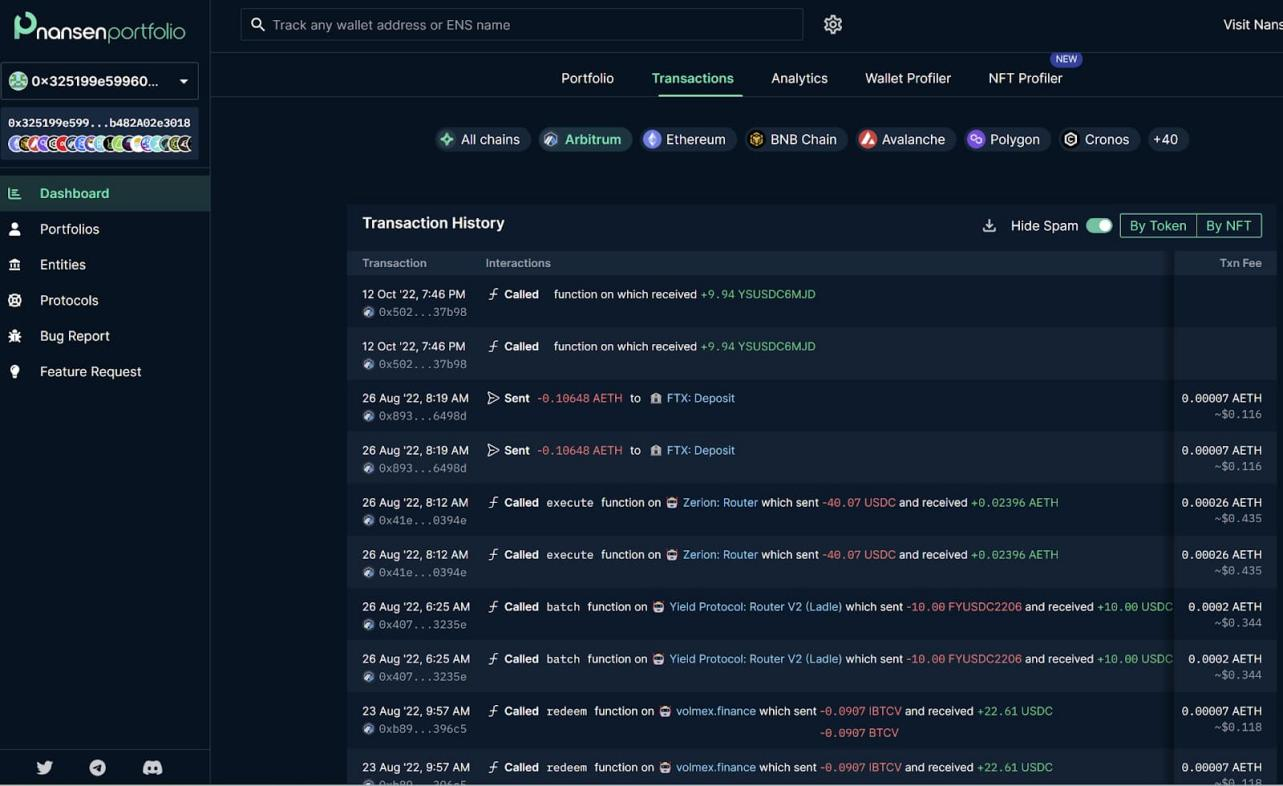
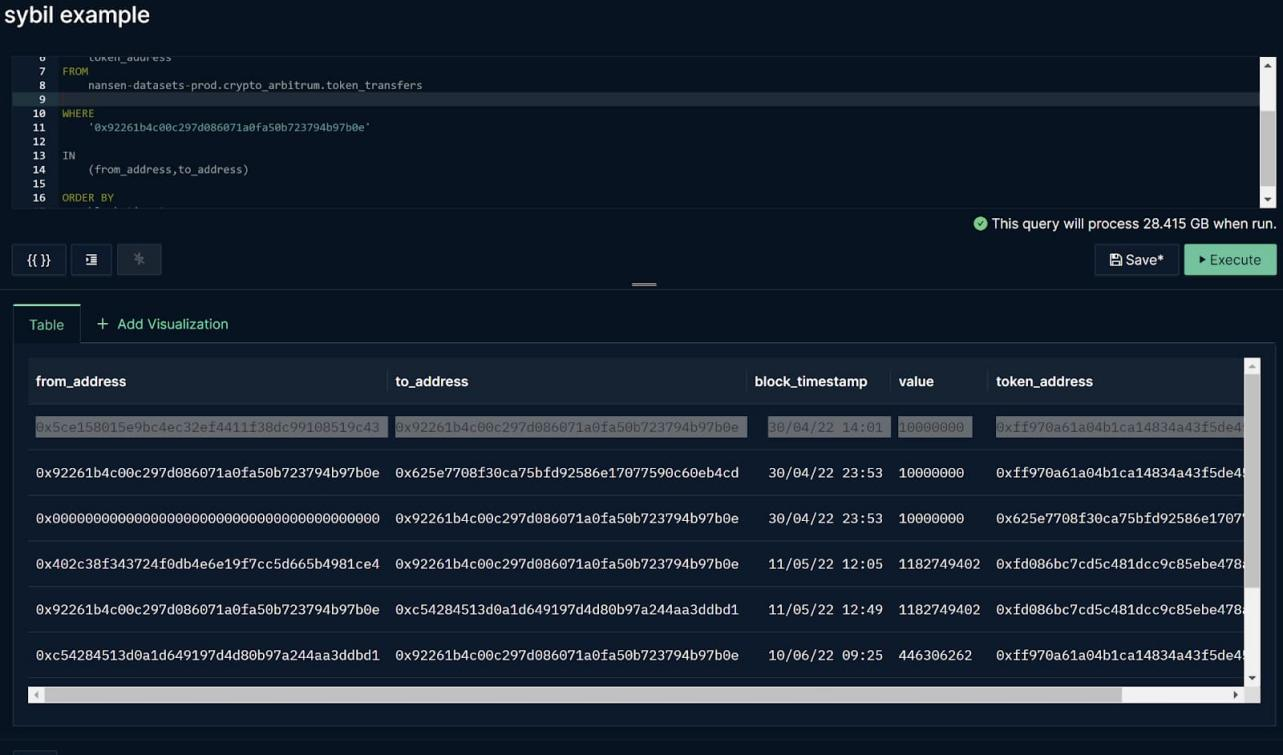
image description
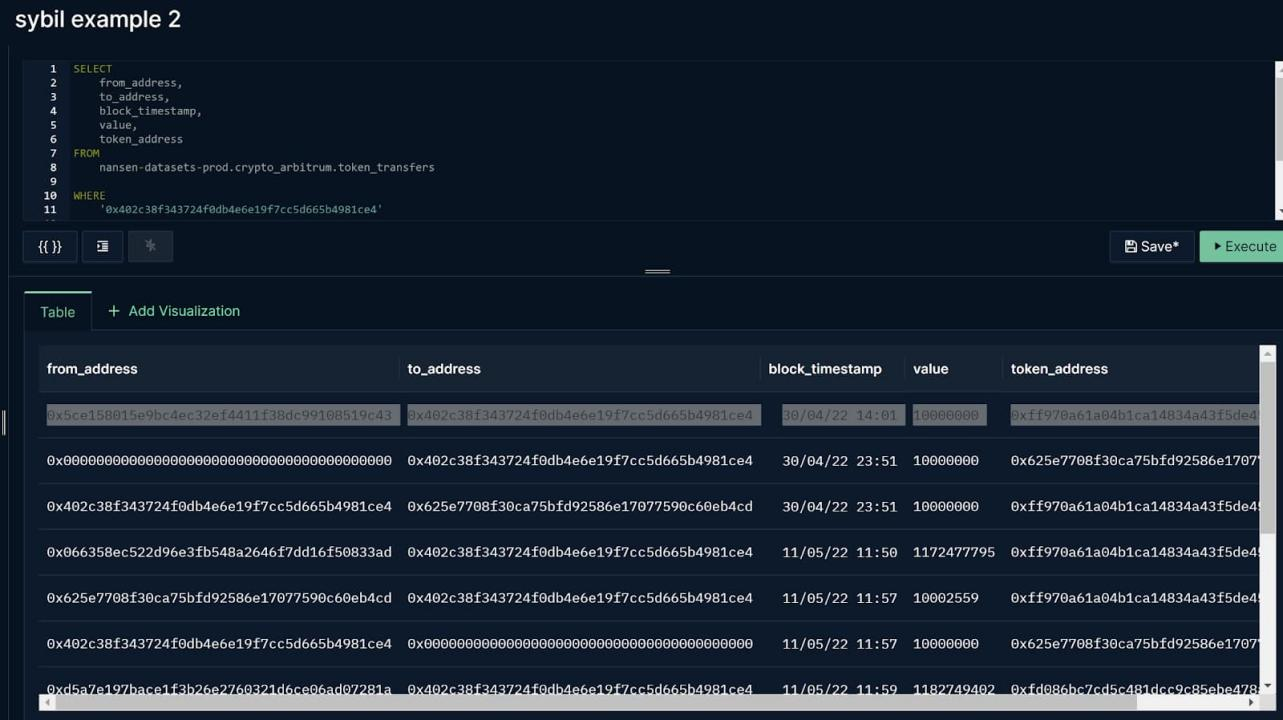
Over 620,000 addresses received airdrops, detailed explanation of Arbitrum airdrop data and anti-sybil strategy
7. Eligible wallet list and statistics overview
Of the approximately 2.3 million wallets bridged to Arbitrum One by February 6, 2023, 625,143, or approximately 28%, earned more than 3 points and became eligible for newly issued Arbitrum tokens. This qualification number is ex-sybil ex-functional-entity. About 37,000 addresses are associated with functional wallets, such as bridging smart contracts, centralized exchange wallets, or burn addresses, which are excluded. About 135,000 addresses identified as Sybil addresses were also excluded.

image description
Figure 13: Eligible wallets by number of tokens available
8. Decentralized governance
The above criteria do not cover all positive contributions to the Arbitrum ecosystem. In addition to the technology stack part, Arbitrum is also a community composed of developers, builders and users, and one of the main goals is to evolve into a decentralized governance community. Therefore, a portion of the airdrop is allocated to the community treasury on Arbitrum to be distributed according to the value of each sub-community. These entities cover various dApps and protocols running on Arbitrum.
• Based on time deployed to Arbitrum
• Does not distinguish between Arbitrum native, Arbitrum + Ethereum or other multi-chain protocols
• Based on total transaction volume and daily transaction volume data
• The economic value of these transactions
• Need to be proportional to the activity statistics of each dApps (Figure 14 shows the contract log by entity and the transaction share within each entity since the establishment of Arbitrum One)
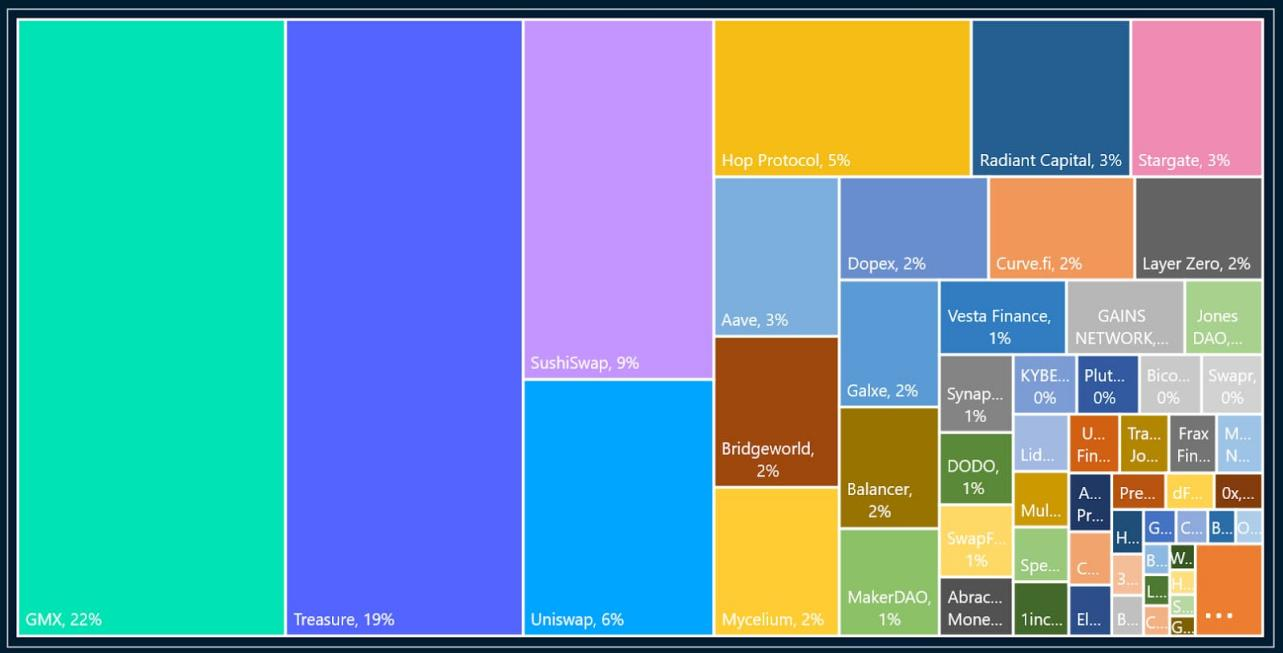
first level title
in conclusion
in conclusion
By using on-chain analysis to extract wallet addresses eligible to receive Arbitrum airdropped tokens, the Arbitrum Foundation and Nansen are attempting to answer the question: "How do we fair the efforts of all those who have helped and will likely continue to help the Arbitrum ecosystem?" .