Looking back on the past year, we have seen many new scenarios, new applications and new changes in the encryption field. Players are also gradually increasing, but security issues have always plagued the development of the industry. Therefore, SlowMist sorted out the major safety events that will appear in the industry in 2022, and conducted corresponding analysis and interpretation.
According to the SlowMist blockchain hacking event archives (SlowMist Hackedimage description
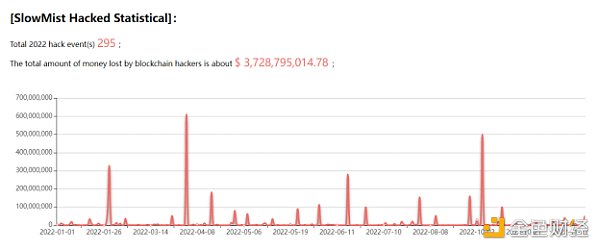
(2022 Security Incident Statistics)
Among them, there were 245 security incidents of various ecological DeFi, cross-chain bridges, and NFT, 10 security incidents of exchanges, 11 security incidents of public chains, 5 security incidents of wallets, and 24 security incidents of other types.
first level title
public chain
public chain
The public chain is the most important infrastructure in the Web3 field, and it is also one of the most competitive tracks in the industry. And the biggest surprise in 2022 is the Terra event. On May 8, the cryptocurrency market saw one of the most devastating crashes in history. The massive $285 million selloff of the Terra network's algorithmic stablecoin UST set off a chain reaction. The price of Terra's native token LUNA suddenly plummeted without warning. In one day, the market value of Luna evaporated by nearly 40 billion U.S. dollars, and the TVL of the entire ecological project almost returned to zero. This incident may become the death button to start the 2022 encryption winter.
DeFi / cross-chain bridge
according toDeFi LlamaThe data shows that as of the end of December, the total lock-up value of DeFi was about 39.8 billion US dollars, a huge drop of 75% year-on-year. Ethereum dominates with 58.5% of the entire DeFi TVL ($23.3 billion), followed by TRON with a TVL of $4.3 billion, and BNB Chain (BNB) was US$4.2 billion. Interestingly, in May 2022, Ethereum’s TVL in DeFi decreased by 35%,according to
according toSlowMist HackedAccording to statistics, there will be about 90 security incidents on BNBChaan in 2022, with a total loss of about US$785 million, ranking first among all chain platforms in terms of loss. There were about 50 security incidents on Ethereum, with a total loss of about US$528 million, followed by about 11 security incidents on Solana, with a total loss of about US$196 million.
datadataaccording to
according toSlowMist HackedAccording to statistics, there will be 15 cross-chain bridge security incidents in 2022, with losses as high as US$1.21 billion, accounting for 32.45% of the total losses in 2022.
secondary title
NFT
NFT will perform extremely well in 2022, according toNFTScanThe data shows that the number of NFT transactions on Ethereum reached 198 million throughout the year, significantly higher than in 2020 and 2021. The annual number of NFT transactions on BNBChain reached 345 million, and the annual number of NFT transactions on Polygon reached 793 million.
On the other hand, according toSlowMist HackedAccording to incomplete statistics, there will be about 56 NFT track security incidents in 2022, with a loss of more than 65.43 million US dollars, most of which are caused by phishing attacks, accounting for about 40% (22 cases), followed by Rug Pull, accounting for about 21% (out of 12).
Wallet/ Trading Platform
On February 8, the U.S. Department of Justice (DOJ) announced that it had seized $3.6 billion worth of bitcoins related to the 2016 hack of cryptocurrency exchange Bitfinex. Ilya Lichtenstein, 34, and his wife, Heather Morgan, 31, were arrested in New York and charged with conspiracy to commit money laundering and fraud. It is also the largest financial seizure ever undertaken by the U.S. Department of Justice.
On November 6, Binance founder CZ tweeted that he had decided to liquidate all remaining FTT on the books, which triggered a confrontation between the two exchanges. Although Alameda CEO and FTX CEO SBF successively tweeted to try to stabilize user confidence and refute the previously exposed news, it still caused FTX to go bankrupt quickly after the liquidity dried up. In the end, FTX was thundered and SBF was arrested. The opacity of centralized exchanges has once again triggered a crisis of trust among people, and the problem of lack of prudential supervision has become more prominent. Whether it is stricter protection for consumers or clearer rules for institutions, the pace of regulation will become clearer.
After the FTX storm, the sales of hardware wallets increased significantly, and the wallet with the largest number of users, MetaMask, had 30 million monthly active users. according toFinboldAccording to the data, based on the top 21 cryptocurrency storage APP applications, between January 2022 and October 2022, the number of encrypted wallet downloads on Android and iOS devices has reached approximately 102.06 million times. While that figure is lower than the 177.85 million downloads recorded during the 2021 bull run, it is higher than in any year other than 2021. The breakdown of data by month shows that the downloads of encrypted wallets showed a downward trend at the beginning of the year, but after the collapse of Terra/Luna and the thunderstorm of FTX, they both showed a relatively large increase.
other
The irreversible and anonymous features of blockchain technology not only effectively protect privacy, but also provide a "protective umbrella" for cybercrime. As concepts such as the metaverse and NFT are popular, cryptocurrency theft and fraud incidents occur from time to time. Many criminals issue so-called virtual assets under the banner of the blockchain to carry out fraud. Far beyond imagination.
datadataIn 2021, among the payment methods involved in fraudulent payments, the use of cryptocurrency to pay is second only to bank transfers, ranking second, as high as 750 million US dollars; in 2020 and 2019, it will only be 130 million to 30 million US dollars, which has increased significantly year by year The trend is obvious. It is worth noting that cryptocurrency transfers are growing rapidly in "pig killing" scams. In 2021, $139 million of the "killing pig dish" fraudulent funds will be paid in cryptocurrency, which is 5 times that of 2020 and 25 times that of 2019.
According to a report issued by the U.S. Federal Trade Commission (FTC)Report, over a year since the start of 2021, more than 46,000 people have reported experiencingcryptocurrencyscam, with losses totaling over $1 billion. According to the report, the most common type of cryptocurrency scam is investment-related fraud, accounting for $575 million out of a total of $1 billion, and the cryptocurrencies most commonly paid to scammers include BTC (70%), USDT (10%), and ETH (9% ).
2. Attack method
Among the 295 security incidents, the attack methods are mainly divided into three categories: attacks caused by the project's own design defects and various contract loopholes; methods including Rug Pull, phishing, and Scam types; asset losses caused by private key leakage.
The most common attack method in 2022 is caused by the project's own design flaws and various contract loopholes, about 92 cases, resulting in a loss of 1.06 billion US dollars, accounting for 40.5% of the total. Among them, the most important ones are the attacks caused by the use of flash loans, about 19 cases, resulting in a loss of 61.33 million US dollars. Others include re-entry problems, price manipulation, verification problems and so on.
The occurrence rate of asset loss due to the theft of private keys is about 6%, but the amount of losses reached 746 million US dollars, second only to contract loopholes. Among the incidents of private key theft, the largest loss came from the Ronin incident, followed by Harmony , all from the cross-chain bridge.
In the Web3 world, users' security awareness is often uneven, which also leads to various and frequent phishing attacks against users. For example, attackers use malicious means to take official media platforms of various projects (such as Discord, Twitter) as their own, or forge official media accounts and post phishing Mint and AirDrop links, and repost real official account content from time to time to confuse audiovisuals. For example, using advertisements on search engines to promote fake websites or domain names and content that are highly similar to official domain names to make the real ones look like real ones; for example, using fake emails and attractive gift activities to lure you into the game; download link. In any case, it is most necessary to increase security awareness. At the same time, once you find that you have been tricked, transfer assets as soon as possible, stop losses in time and retain evidence, and seek help from security agencies in the industry if necessary.
Second, and most abhorrent of all, is the Rug Pull. Rug Pull usually means that the developer of the project abandons the project and runs away with the funds, and more often the project party actively commits crimes. It can happen in many ways: For example, when the developer starts the initial liquidity, pushes up the price, and then withdraws the liquidity. The funds invested by the users were swept away, the encrypted assets were dumped, and eventually disappeared, and the users who invested in the project will also suffer huge losses. Another example is launching a website but closing it after attracting hundreds of thousands of deposits. In 2022, there will be 50 RugPull incidents, with a loss of about 188 million US dollars, which often occur in the BSC ecology and NFT fields.
Other relatively new methods in 2022 are front-end malicious attacks, DNS attacks, and BGP hijacking; the most bizarre is the loss of assets caused by human configuration errors.
3. Phishing/scam techniques
This section only selects some of the phishing/scam techniques disclosed by SlowMist.
Malicious browser bookmarks steal Discord Token
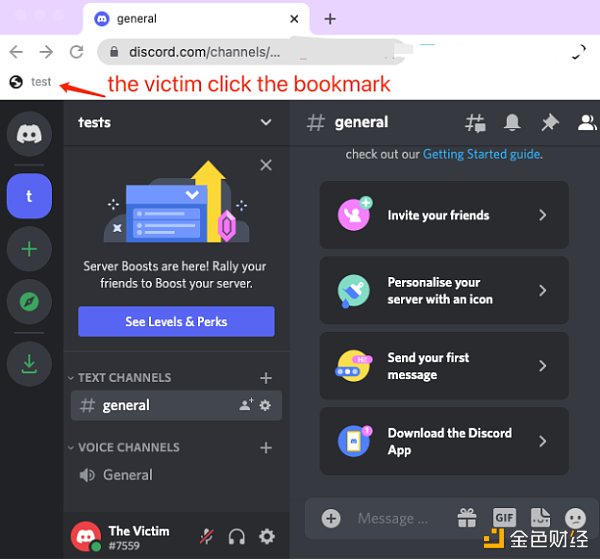
Today's browsers have their own bookmark managers, which provide convenience but are also easy to be exploited by attackers. By carefully constructing a malicious phishing page, you can insert a piece of JavaScript code into your favorite bookmarks. With this, you can do almost anything, including obtaining information through the webpackChunkdiscord_app front-end package packaged by Discord. When the Discord user clicks, the malicious JavaScript code will be executed in the Discord domain where the user is located, and the Discord Token will be stolen. After the attacker obtains the Discord Token of the project party, the attacker can directly and automatically take over the project party's Discord account-related permissions. The attacker who gets the Token is equivalent to logging in to the Discord account, and can do any equivalent operations of logging in to Discord, such as setting up a Discord webhook robot, posting false news such as announcements in the channel for phishing. Here is an example of a victim clicking on a phished bookmark:
The following is a demonstration of the JavaScript code written by the attacker to obtain Token and other personal information, and receive it through the webhook of the Discord Server.
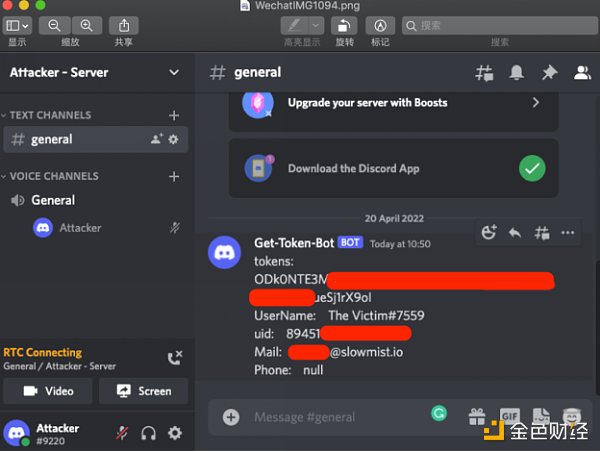
It can be seen that on the premise that the user logs in to Discord on the web, assuming that the victim adds a malicious bookmark under the guidance of the phishing page, and clicks on the bookmark when logging in on the Discord web, triggering the malicious code, the victim’s Token and other personal The information will be sent to the attacker's channel through the Discord webhook set by the attacker.
"Zero Yuan Purchase" NFT Fishing
For example, the following phishing website, the signature content is
Maker: user address
Taker:0xde6135b63decc 47 d 5 a 5 d 47834 a 7 dd 241 fe 61945 a
Exchange: 0x7f268357A8c2552623316e2562D90 e 64 2bB 538 E 5 (OpenSeaV2 contract address)
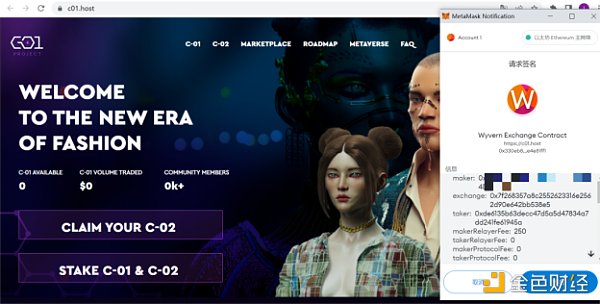
This is a more common way of NFT phishing, that is, scammers can buy all your authorized NFTs with 0 ETH (or any token). In other words, this is a sales order that deceives users into signing NFTs. NFTs are held by users. Once users sign this order, scammers can directly purchase users’ NFTs through OpenSea, but the purchase price is determined by scammers, that is, It is said that scammers can "buy" users' NFTs without spending any funds.
In addition, the signature itself is stored for the attacker. You cannot revoke the validity of the signature through websites such as Revoke.Cash or Etherscan, but you can cancel your previous pending order authorization, which can also avoid this phishing risk from the root.
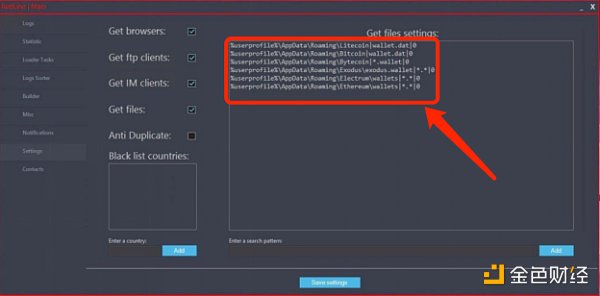
Redline Stealer Trojan Stealing Coins
This kind of attack is mainly through Discord to invite users to participate in the internal testing of new game projects, under the guise of "giving discounts", or send a program for you to download through private chats in the group, usually by sending a compressed package and decompressing it It is an exe file of about 800 M. Once you run it on your computer, it will scan the files on your computer, and then filter the files containing keywords such as Wallet and upload them to the attacker's server to achieve the purpose of stealing cryptocurrency.
RedLine Stealer is a malicious Trojan that was discovered in March 2020 and sold separately on underground forums. The malware harvests information such as saved credentials, autocomplete data, and credit cards from the browser. When run on a target machine, it collects details such as usernames, location data, hardware configuration and installed security software. The new version of RedLine has added the ability to steal cryptocurrency, which can automatically scan the installed digital currency wallet information of the local computer and upload it to the remote control machine. The malware has the ability to upload and download files, execute commands, and periodically send back information about the infected computer. Often scan for cryptocurrency wallet directories and wallet files:
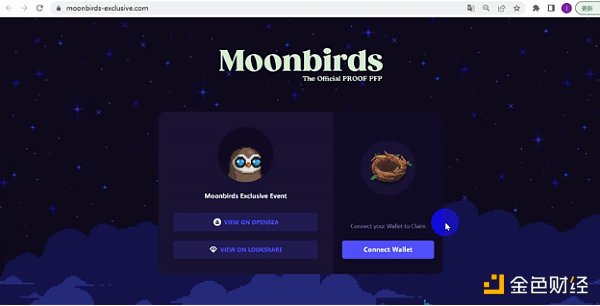
Blank Check eth_sign Phishing
After connecting the wallet and clicking Claim, a signature application box will pop up, and MetaMask will display a red warning at the same time, and it is impossible to tell from this pop-up window what is required to sign. In fact, this is a very dangerous type of signature, basically Ethereum's "blank check". With this phishing, scammers can use your private key to sign any transaction.
This eth_sign method can sign any hash, so it can naturally sign our signed bytes 32 data. Therefore, the attacker only needs to obtain our address to analyze and query our account after we connect to the DApp, and then construct any data (such as: native token transfer, contract call) for us to sign through eth_sign.
In addition, there is another kind of phishing: after you reject the above sign, it will automatically display another signature box in your MetaMask, and cheat your signature while you are not paying attention. And look at the signature content, the SetApprovalForAll method is used, and the target of Approved asset is displayed as All of your NFT, that is to say, once you sign, scammers can steal all your NFTs without restraint.
This phishing method will be very confusing to users. MetaMask will intuitively display the data that the attacker wants us to sign for the authorized phishing we encountered in the past. And when the attacker uses the eth_sign method to get the user to sign, what MetaMask displays is only a string of bytes 32 hashes.
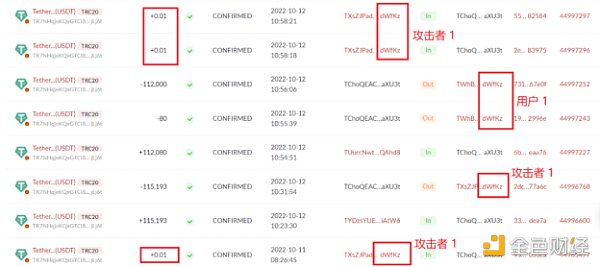
Same ending number + TransferFrom zero transfer scam
In the user's address transfer records, 0 USDT transfers to unfamiliar addresses continue to appear, and this transaction is completed by calling the TransferFrom function. The main reason is that the TransferFrom function of the token contract does not mandate that the authorized transfer amount must be greater than 0, so a transfer of 0 can be initiated from any user account to an unauthorized account without failure. Malicious attackers use this condition to continuously initiate TransferFrom operations on active users on the chain to trigger transfer events.
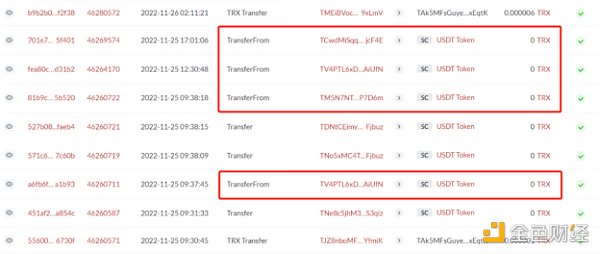
In addition to the 0 USDT transfer harassment, the attackers continue to airdrop small amounts of Tokens (such as 0.01 USDT or 0.001 USDT, etc.) to users with large transaction sizes and high frequency. For the last few, the user accidentally copied the wrong address when copying the address in the historical transfer record, resulting in asset loss.
The above are just examples of some common attack methods and scenarios. In fact, the way is as high as the magic, and the attack methods of hackers are always innovating. What we can do is to continuously improve our knowledge.
For individual users, most risks can be avoided by complying with the following security rules and principles:
Two safety rules:
zero trust. Simply put, it is to remain skeptical, and to remain skeptical at all times.
Continuous validation. If you want to believe, you must have the ability to verify your doubts and make this ability a habit.
Safety principles:
For the knowledge on the Internet, all things refer to information from at least two sources, corroborating each other, and always remain skeptical.
Do a good job of isolation, that is, don't put all your eggs in one basket.
For wallets with important assets, do not update easily, just enough. What you see is what you sign. That is to say, what you see is what you expected to sign. When you sign and send out, the result should be what you expected.
Pay attention to system security updates, and act immediately when there are security updates.
Do not mess up the program.