Original Author: Marvelous Akpere
Original title: A comparison of Aptos and Sui
Functional Layer1 has a good foundation for pumping the ecosystem over the last year. These pumps are tied to L1 with higher throughput, lower fees, native dApps, risky meme coins, large APY, etc. As savvy investors, we know that when an ecosystem is doing well, buying the base token can serve as a versatile basket for handsome profits.
L1 attempts to solve the blockchain trilemma - decentralization, security and scalability.
If mass adoption of cryptocurrencies is our vision, scalability is still unresolved at the moment. Like Ethereum, Solana, and some other L1 chains are no exception to the structure of oligopoly.
Many L1 chains are just passers-by, while others are still very successful chains, and now another L1 chain is about to become one of them. This new L1 chain is called Aptos.

Aptos is an L1 PoS chain created by Meta's Diem team. It claims to be a more secure and scalable L1. It also claims to solve the blockchain trilemma.
As a blockchain, Aptos is currently being built using Move, a specialized language dropped from Diem. Move allows smart contracts to interact with validators in a deterministic, airtight (predictable, non-polluting) and quantifiable way (preventable against DOS attacks).
Using Move, Aptos combined with an improved leader-based BFT consensus mechanism ensures low latency and zero downtime for block submissions, clearly the most reliable iteration of HotStuff.
secondary title
So, how does Aptos scale?
Aptos scales by decoupling the interdependent execution and consensus layers through an eventually synchronized parallel execution engine.
secondary title
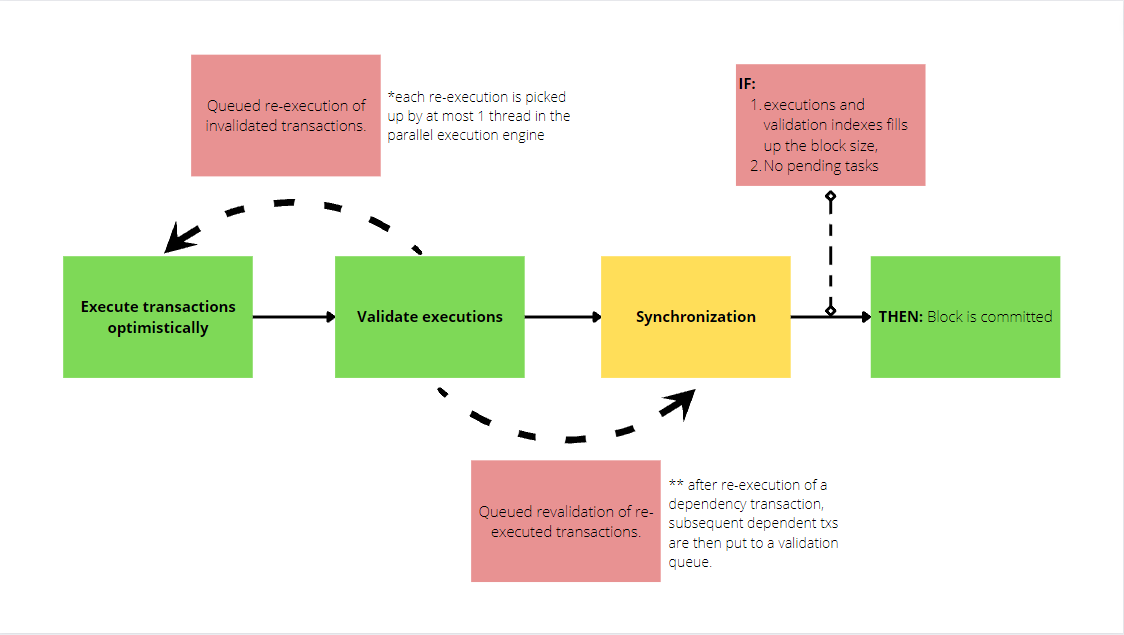
But what if a conflict is detected?
They can only be picked up by at most one thread in the parallel execution engine and re-executed against the execution queue before being revalidated with their subsequent txs through the queue.
Block-STM algorithms are able to handle seamless operations and can separate abstraction from trivial execution verification. This is all due to preset indexed orders that map transactions throughout the execution and validation cycle.
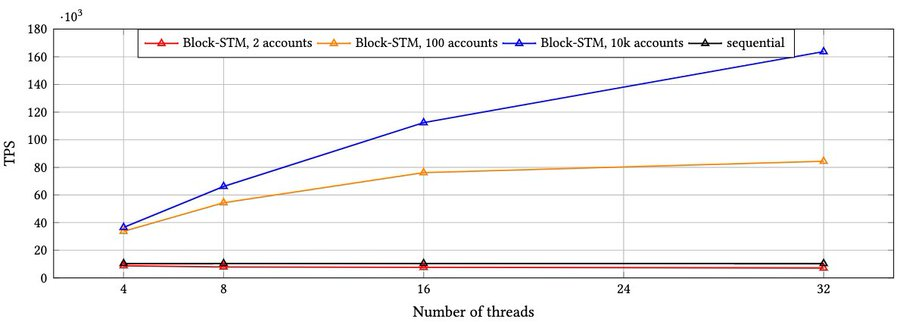
secondary title
Key Features of Aptos
1. Thanks to the cooperation with Google Cloud, Aptos nodes can be set up within 15 minutes.
2. Minimum stake. TBD (Mainnet date unknown)
3. Less demanding compared to key similar products. The process includes, Testnet -> Phase 1: 100 validators -> Phase 2: 200 selections -> Phase 3: 1000 selections -> No limit in Phase 4 so far.
4. Security. A consensus mechanism in addition to Move's security features;
l Separation of validity, security audit and formal verification
l The management of validators is done on the chain
l Responsiveness of the reputation system leading nodes in turn
l Deterministic (only based on the information contained in the ledger state)
l Measurability (to defend against denial-of-service attacks at the transaction execution level)
l Rotation of private/consensus keys.
scalability
scalability
l Testnet outperforms major peers in terms of time to finality and TPS (independent txn execution and consensus mechanism).
l Txns can be verified in two network trips, while similar products require multiple rounds of voting.
l Improved data structure and storage
l State synchronization
Continued testing with no downtime in the private mainnet. In the event of a network outage, an on-chain reputation system automatically mitigates the effects of validator downtime.
Network Architecture
l Provide developers with less technical complexity and social coordination
l Lower latency
l Improved composability
l Improve application communication and functionality
decentralized
decentralized
l Reduced barriers to running nodes
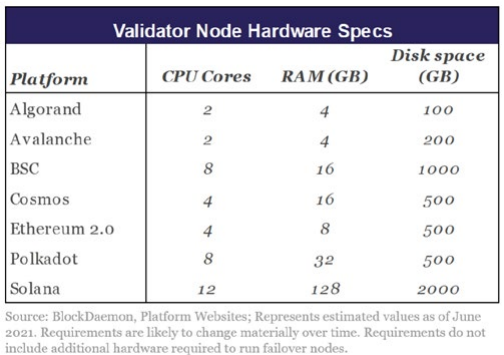
l Minimal hardware: CPU with four cores, 8GB RAM and 300GB storage space
l Lower hardware requirements than most competitors
Now, you might ask a question.
secondary title
Aptos Vs Sui
Sui's Mysten Labs, like AptosLabs, was founded by Meta's former Novi research team. It is a high-performance L1 PoS chain whose core is to expand composable and dynamic NFTs for a wide range of metaverse applications (such as games, social, business, etc.).
Like Aptos, Sui's tech stack has made significant progress on top of Diem, which was originally designed to handle light payment scenarios with a small number of custodial wallets (between 10 and 100). Diem's original architecture will not be able to support mass adoption.
Aptos and Sui have many of the same investors. Both have been heavily bet by VCs, achieving valuations of over $2 billion.
However, there are many basic and superficial similarities between Sui and Aptos. Here are some of the differences.
l Programming languages: While they both use their respective variants of the Move programming language for parallel execution, Sui's object model is slightly different from Aptos'. Sui's Move language clearly states ownership/shareability or mutability/immutability of an object, whereas Aptos does not. Sui’s ownership API is also cleaner than Aptos’ because it more clearly exposes the blockchain’s design.
l Architecture: Sui adopts a DAG-based mempool (Narwhal) and Tusk consensus algorithm. The DAG is then used to execute layer parallelization. Meanwhile, Aptos achieves parallelization by dynamically detecting dependencies and scheduling execution tasks using BlockSTM, an evolution of the high-performance HotStuff algorithm (inspired by software transactional memory).
l total scalability. It is worth noting that neither chain is optimized for the home validator situation or for large-scale decentralization, but for"Maximize network capacity"Optimized (i.e. like Solana). It is very likely to encounter a bottleneck of state growth.
Aptos treats technological development with a user-centric approach. This stems from a belief that to achieve democratization, the user experience needs to improve significantly in terms of security and scalability. When done correctly, it has the potential to provide a significant competitive advantage.
Development is an important consideration as it affects the quality of on-chain applications (which affects user acquisition). According to popular models, the flow of funds goes like this. Capital -> Developers -> Users -> Transactions -> TVL -> Price. Investing early in the cycle means reaping the greatest benefits.
To that end, Aptos has a Devnet where developers can contribute open source code. There is already an impressive list of developers, including Coinbase, Binance, Anchorage, Blockorus, Livepeer, Moonclave, Paxos, Paymagic, and Rarible, to name a few.
Currently, 8,000 developers are on Aptos' Discord server, which has 63,000 members. Also, although Aptos does not yet have a white paper, the fact is that it already has 4,000 node operators from 40 countries.
Aptos also announced a grant program to encourage development. The team’s main areas of focus are DeFi, NFTs, and gaming, and they will pay developers who successfully apply for their grant program (amounts that have not been disclosed).
final thoughts

final thoughts
Aptos has a well-funded team with the continuity and organizational maturity to execute on its vision. With the modernity of its technology stack and the efficiency of Move's language, it has the ability to become a leading L1 chain.
References:
References:
2.https://medium.com/aptoslabs/welcome-to-aptos-incentivized-testnet-2-af26e2fd69a7
5.https://pontem.network/posts/the-future-of-pontem-with-aptos
6.https://members.delphidigital.io/reports/the-hitchhikers-guide-to-ethereum/
7.https://medium.com/aptoslabs/aptos-incentivized-testnet-roadmap-209be695c77c