in the just released"In-depth Research Report on Web 3 Security Situation in the First Half of 2022"In , we have shown and analyzed the overall situation in the blockchain security field from various dimensions, including the total loss amount, the type of attacked projects, the loss amount of each chain platform, attack methods, capital flow, project audit status, etc.
first level title
1. How much was the total loss caused by loopholes in the first half of the year?
According to the monitoring of Chengdu Lianan Hawkeye Blockchain Situational Awareness Platform, in the first half of 2022, a total of 42 major attack cases caused by contract loopholes were detected, and about 53% of the attacks were exploited by contract loopholes.
By statistics,In the first half of 2022, a total of 42 major attack cases caused by contract loopholes were detected, with a total loss of US$644.04 million.
Among all exploited vulnerabilities,first level title

2. What types of vulnerabilities have caused significant losses?
February 3, 2022Wormhole, the Solana cross-chain bridge project, was attacked, and the cumulative loss was about 326 million US dollars.Hackers exploited a signature verification vulnerability in the Wormhole contract that allowed hackers to forge sysvar accounts to mint wETH.
On April 30, 2022, the official Fei ProtocolRari Fuse PoolSuffered from flash loan plus reentry attack, causing a total loss of 80.34 million US dollars.secondary title
Review of Fei Protocol events:
Since the vulnerability appeared in the basic protocol of the project, the attacker attacked more than one contract, and only one case is analyzed below.
attack transaction
0xab486012f21be741c9e674ffda227e30518e8a1e37a5f1d58d0b0d41f6e76530
attacker address
0x6162759edad730152f0df8115c698a42e666157f
attack contract
0x32075bad9050d4767018084f0cb87b3182d36c45
text
0x26267e41CeCa7C8E0f143554Af707336f27Fa051
#Attack process
1. The attacker first makes a flash loan from Balancer: Vault.

2. The flash loan funds are used in Rari Capital for mortgage lending, because Rari Capital's cEther implementation contract has re-entry.
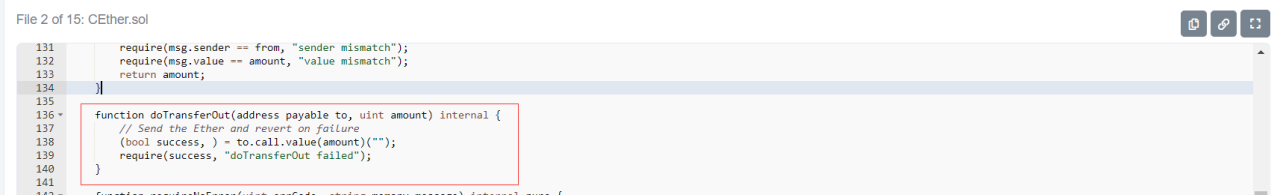
The attacker extracts all tokens in the pool affected by the protocol through the attack function callback constructed in the attack contract.

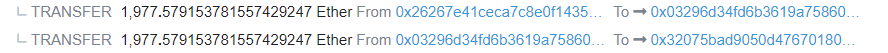

3. Return the flash loan and send the proceeds from the attack to the 0xe39f contract
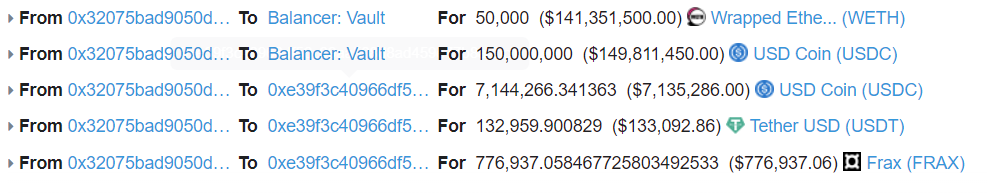

This attack mainlyFurther reading:
Further reading:first level title
3. What are the most common loopholes in the audit process?
secondary title
1. ERC721/ERC1155 re-entry attack
secondary title
2. Logic loopholes
1) Missing considerations for special scenarios:
Special scenarios are often the place where the audit needs to pay the most attention. For example, the design of the transfer function does not consider the transfer of money to oneself, resulting in nothing.
2) The design function is not perfect:
secondary title
3. Lack of authentication
secondary title
4. Price manipulation
Oracle price oracles do not use time-weighted average prices;
first level title
according to
according toChengdu Lianan Eagle Eye Blockchain Security Situational Awareness PlatformAccording to the perceived security incident statistics, almost all the loopholes that appeared during the audit process have been exploited by hackers in actual scenarios, and the exploitation of contract logic loopholes is still the main part.
passChengdu Lian'an Chain Must Check-Smart Contract Formal Verification Platformimage description
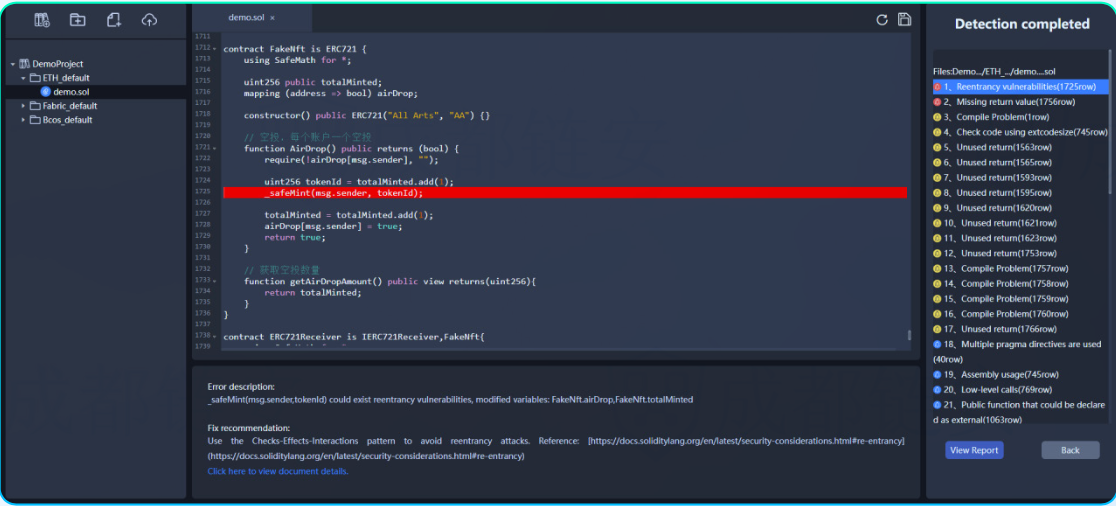
Scanned by the ChainBitCheck tool, there is a reentrancy vulnerability in a contract