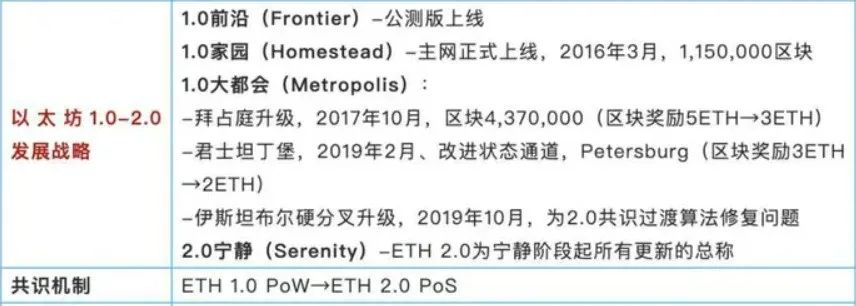
The positioning of Ethereum is the world computer. In order to achieve this goal, developers have planned an upgrade path for it at the beginning of its birth, namely Frontier (frontier), Homestead (homestead), Metropolis (metropolis), Serenity (tranquility) four stages.
At present, the entire network has reached the third stage. The first three stages belong to Ethereum 1.0, and the last stage, Senerity, is also the Ethereum 2.0 we often hear (in order to avoid misleading, Ethereum officials have abandoned Ethereum. Workshop 2.0, but we will continue this idiom in this article).
The Ethereum 2.0 upgrade is mainly to solve some problems that limit the development of the entire network during the development of Ethereum. There are three main issues:
The first is the high energy consumption brought by mining. Due to the adoption of the PoW (Proof of work) mechanism as the consensus mechanism, Ethereum needs nodes to provide computing power for mining. The calculation process of various mining machines consumes a lot of power, so it is often blamed on the network. Not green enough to run.
Another performance issue. At present, the block generation speed of the Ethereum chain is about one block every 12-15 seconds, and the TPS (Transaction per second, the number of transactions processed per second) is about 15. This processing speed is not even enough to support an ordinary commercial application. The congestion of the Ethereum network from time to time also limits its development.
The third is the issue of usage costs. To use the Ethereum network, you need to pay gas fees to the miners who maintain the network, usually ranging from a few dollars to tens of dollars, depending on the congestion of the network, and even hundreds of dollars at most. The high gas fee has caused some protocols to turn to competitors of Ethereum, such as public chains such as Solana and Near.
secondary title
Ethereum 2.0 Roadmap
The Roadmap of Ethereum 2.0 mainly includes 3 steps of parachain-beacon chain, merging and sharding. The purpose of the first two steps is to change the consensus mechanism of the entire network from PoW to PoS (Proof of Stake, Proof of Stake), and the last step is to improve the performance and scalability of the entire Ethereum network.
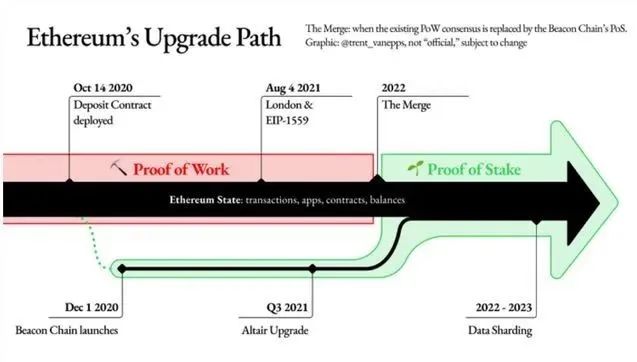
1. Parallel chain--beacon chain
In order to achieve a smooth transition of the consensus mechanism, on December 1, 2020, while the current PoW main network is running, Ethereum first enabled a parallel chain called the Beacon Chain. The beacon chain uses PoS as the consensus mechanism and operates independently of the main network. Participants need to pledge 32 ETH to a smart contract on the chain as a proof of rights and interests. After review, they will enter the validator list and become validators of the beacon chain. In this chain, verifiers replace the role of miners and become the builders of the chain.
Under the PoW mechanism, nodes generate the next block through calculation and mining, while in the beacon chain of the PoS mechanism, the generation of the next block is selected by the verifiers. This choice is random and not determined by a verifier, which reflects the characteristics of decentralization. If the verifiers perform well, they can get rewards. On the contrary, if they do evil, the system will deduct part of the 32 ETH they pledged. When the pledged ETH is less than 16, they will be removed from the validator list.
Before the merger, which is the current stage, Ethereum is in the stage of parallel operation of PoW+PoS. The early activation of the PoS parachain chain is mainly due to two considerations. The first is to minimize the impact on the currently running PoW chain and reduce the impact of consensus conversion on the network. The second is to give the new PoS network enough time to collect Pledged ETH to ensure the safe operation of the network.
2. Merge
The merger (Merge) often mentioned when talking about Ethereum 2.0 is to merge the PoW main network (Ethereum is called the execution layer for processing transactions) with the PoS beacon chain (Ethereum is officially called the consensus layer). The merger of Ethereum needs to be tested on the test network first. Once any problems are found during the test, the nodes will be repaired according to the situation.
At present, Ropsten and Sepolia, the testnets of Ethereum, have been merged on June 9 and July 6 respectively. The remaining Goerli testnet will also be merged in the near future. If all goes well, the official Ethereum network will end the merger in mid-to-late September. After that, the PoW mechanism will be abandoned, and the entire network will generate new blocks through PoS.
In order to ensure the success of the consensus mechanism switch, Ethereum developers proposed to implement a difficulty bomb to increase the mining difficulty of PoW. The difficulty bomb was added to the Ethereum code in 2015. It is described as: increasing the difficulty of the puzzle in the PoW algorithm based on the predetermined number of blocks, making the calculation time to generate blocks longer and mining difficult , so as to reduce the mining rewards of miners and dispel their enthusiasm. After the difficulty bomb is implemented, the miners will become unprofitable, and the original PoW network will not be able to continue to operate.
3. Fragmentation
The transformation of the consensus mechanism cannot improve the performance of Ethereum, and the performance improvement needs to be achieved through fragmentation.
Sharding is a concept of database partitioning, which is used to optimize storage and fast processing. By dividing the organization's network into smaller partitions, the database is divided horizontally, and the load is distributed. Each shard has its own independent data. Multiple shards Slices can be processed in parallel, thereby reducing network congestion, increasing TPS, and achieving network scalability.
The early sharding plan of Ethereum is to divide the main network into 64 shards, each shard has an independent block proposer and committee, and the block proposer and committee are randomly selected and assigned. The proposer selects the transaction to be included in the block from the transaction pool, and the block can be included in the chain after obtaining a two-thirds approval vote from the committee.
This early sharding scheme was designed to scale the performance of the Ethereum main chain. However, it is very complicated to implement. In addition, after several years, layer2 has developed rapidly, and Rollup has flourished. Therefore, developers of Ethereum centered on Vitalik gradually abandoned this original solution and turned to new technology selection. That is, instead of directly sharding on the Ethereum mainnet in order to carry more transactions, it is transformed into a road map of the underlying chain centered on Rollup, with Rollup expanding at the transaction level, and the main chain only providing data availability for Rollup.
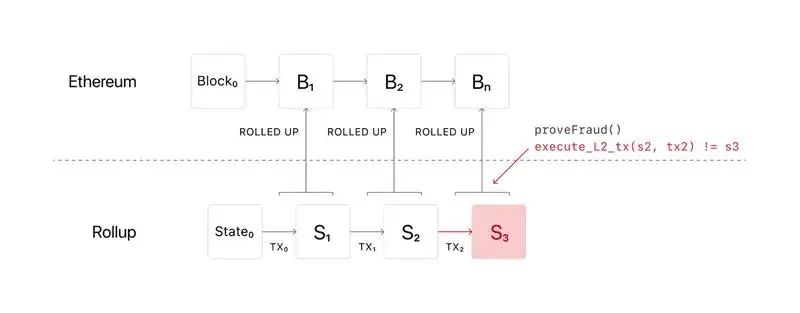
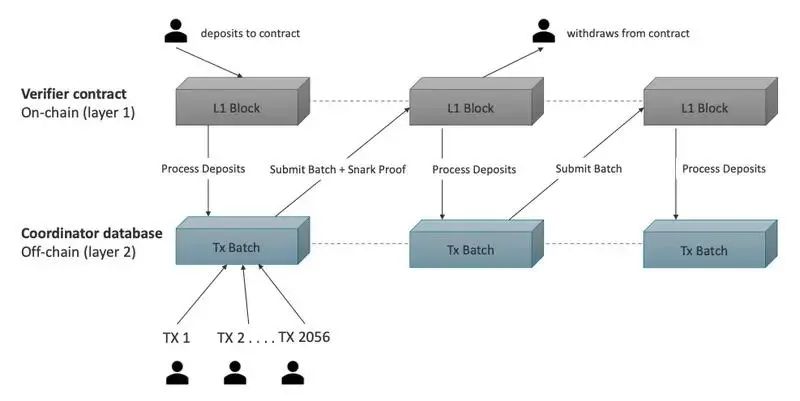
In the new scheme, the goal of Ethereum is to serve as a scalable data availability layer, which can be simply understood as the final settlement and bookkeeping. The expansion of the main chain will focus on expanding the data capacity of the block, rather than improving the computing efficiency on the chain, that is: Ethereum sharding aims to provide more data blob (binary large object) space to support Rollup, and Ethereum does not need to For explanation, only the calculation and proof results of Rollup are collected to ensure that the data is available, while more calculation execution and transaction validity are realized by Layer2 Rollup. More specifically, the calculation and verification of transactions is performed by Rollup, and multiple transactions and proof results after verification are included in a package, while the blocks on the main chain only record these packages.
secondary title
Impact of Ethereum 2.0 Upgrade
energy consumption reduction
After switching to the PoS mechanism, the entire network no longer relies on miner nodes that consume a lot of power, and thus becomes more environmentally friendly. The energy efficiency of nodes under the PoS mechanism is more than 99% higher than that of PoW, so the energy efficiency of the PoS network will be greatly improved. When the PoW mechanism is adopted, miner nodes need powerful and energy-intensive hardware devices to perform complex mathematical calculations. Whoever completes the calculation first will be eligible to build blocks and receive block rewards. In this case, miners can only run their mining equipment at full capacity 24 hours a day to obtain the maximum profit. These high-energy-consuming equipment have a huge demand for electricity.
In the PoS network, the proposer of the block is randomly selected, and there is no longer a need for a large number of mining hardware to compete for the right to produce blocks, and there is no need for huge power consumption.
ETH production
After the Ethereum shifted from the PoW consensus to the PoS, it no longer generates miner rewards, but instead, pledge rewards. So the issuance rate of ETH will be reduced by 90%. Everyone calls this situation "Triple Halvening", because it is equivalent to 3 Bitcoin halvings at the same time, and Ethereum will experience an instant decrease in circulation. At the same time, because the pledged ETH cannot flow into the market, ETH will enter deflation stage.
ETH pledge
After the merger is completed, more users will choose to pledge their ETH, because they can obtain an almost risk-free pledge income. According to calculations, the annual rate of return for staking ETH is about 4%. Kraken predicted in the report "Staking Status in the First Quarter of 2022" that after the merger of Ethereum is completed, the annual rate of return of staking users can reach 8.5%-11.5%.
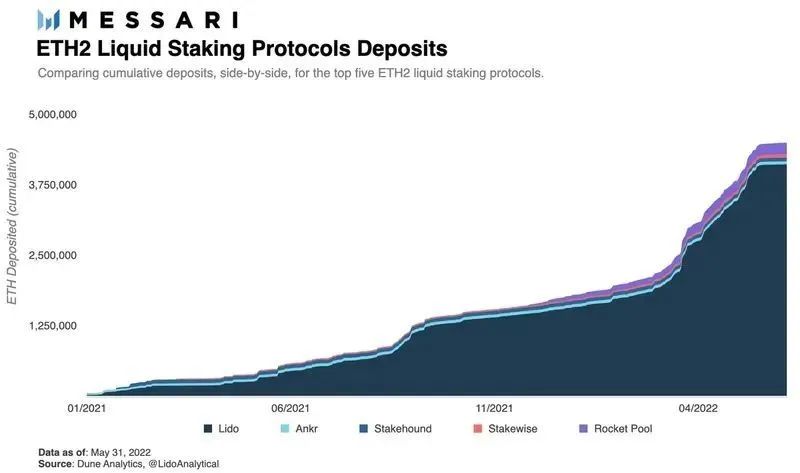
In addition, due to the increase in the need for pledges, the pledge service track is expected to have a wave of outbreaks. At present, more than 13 million ETH are pledged on the beacon chain, which exceeds 10% of the total amount of Ethereum, and a total of 410,000 validators participated in the pledge.

Since the network requires at least 32 ETH to be pledged, and there are certain technical and financial thresholds for running node equipment at the same time, it is much more attractive to choose a pledge service provider than to pledge by yourself. Lido, the current leader in the staking track (see aboveLet’s talk about the discount of stETH-stETH’s pricing, liquidity and riskminer
miner
epilogue
epilogue
An Ethereum merger is within reach. Although the upgrade plan has been changed several times, so far, the progress has been basically smooth. As the most influential public chain with the most developers in the blockchain world, the upgrade of Ethereum will undoubtedly have a huge impact. With the arrival of Ethereum 2.0, the development of the public chain has also entered a new chapter. The problems of low performance, high cost, and high energy consumption that have plagued Ethereum users for a long time are expected to be resolved through a series of upgrades. We are looking forward to everything that is about to happen.