Author: Jessie, Edmond
Original Source: Overseas Unicorns
Original Source: Overseas Unicorns
Since Ethereum adopted the proof-of-work consensus algorithm, it has been looking for a better algorithm to make Ethereum a decentralized, scalable, secure, energy-saving and environmentally friendly network. Until 2017, Ethereum finally determined a hybrid PoW/PoS system - Casper the Friendly Finality Gadget.
In the following years, Ethereum Merge has been delayed repeatedly, and its slow work progress has gradually made many Ethereum supporters lose confidence. Until June 8 this year, Ethereum successfully completed the first Merge rehearsal on the Ropsten test network. Not surprisingly, Merge will be completed within this year.
Merge will have an impact on the Ethereum ecosystem and even the entire blockchain, this article attempts to explain the principles, advantages and disadvantages of Merge, and conduct an in-depth analysis of its impact, hoping to bring you more perspectives, so as to better grasp the investment opportunities in the new situation——
We believe that although Ethereum’s Merge has some controversies such as “wealth is more concentrated”, “MEV risks are more serious”, and “repeated delays”, in general, the PoS mechanism is more helpful than PoW to make Ethereum more stable. Safe, decentralized and energy efficient. Merge and subsequent sharding and Layer2 will make Ethereum more scalable and bring better user experience. In short, Ethereum will become a better ecology.
After Merge, the issuance of ETH will be reduced by 90%, and the inflation rate will be greatly reduced. With the cooperation of the EIP1559 agreement, ETH is likely to become a deflationary asset, which will help push up the value of ETH.Crypto quant trader Ryan Allis offers a novel perspective on the Bankless podcast: After converting to PoS, Ethereum adopts a pledge model, which means that ETH has fundamentals and cash flow. If DCF valuation method is used to value ETH, the value of ETH will reach at least 10,000 US dollars, which will attract more large funds. Institutional investors pay attention.In addition, the staking mechanism of PoS will also bring huge dividends to the staking track, which deserves attention and deployment.
The following is the table of contents of this article, and it is recommended to read it in combination with the main points.
The following is the table of contents of this article, and it is recommended to read it in combination with the main points.
01. What is The Merge?
02. How did The Merge happen?
03. Development progress of The Merge
04. The design concept of PoS
05. Advantages of PoS
06. Risks of PoS
07. Impact of Merge
first level title
01.
What is The Merge?
In 2013, Vitalik Buterin and Gavin Wood released a white paper, envisioning the "next generation smart contract and decentralized application platform" - Ethereum. After initially adopting the proof-of-work (PoW) consensus algorithm in 2015, becoming an energy-efficient proof-of-stake (PoS) network has always been the vision of Ethereum. In the first few years, the Ethereum community put a lot of effort into developing a PoS consensus mechanism with ideal security and efficiency; going through ideas such as "Slasher" and "Staking Consensus", until finally finalized in 2017.“Casper the Friendly Finality Gadget”, a hybrid PoW/PoS system.
The Ethereum main network is currently secured by the PoW mechanism. In order to smooth the transition, the beacon chain using the PoS mechanism is first introduced to run in parallel with the main chain. Merge is to merge the two systems together, and it replaces the current proof-of-work (PoW) consensus mechanism with a more environmentally friendly, efficient, and secure proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. When the merger occurs, the current PoW consensus mechanism will be completely abolished, and all blocks on Ethereum will be generated through PoS.
first level title
02.
secondary title
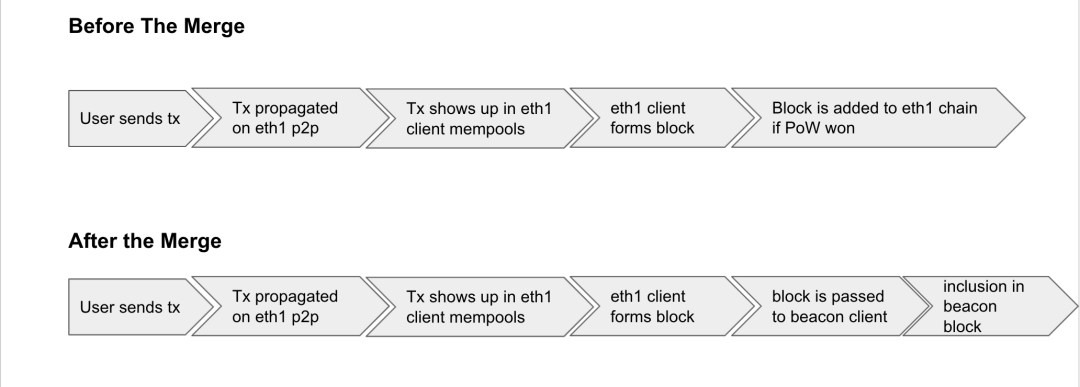
Parachain —> Merge —> Replacement
This merger is carried out on the principle of "minimum damage", which allows the originally running application clients to switch to PoS without any sense. The beacon chain first existed as an intermediate layer above PoW, similar to the second-layer consensus network. When it is "merged", this layer is directly used as the consensus layer, and the execution-related components in the PoW layer are combined into the new consensus layer. , PoW no longer exists.
The beacon chain block will contain the execution layer, which is the merged equivalent of the block on the current PoW chain. For end users and application developers, the execution layer is where they interact with Ethereum.
secondary title
Pledge mechanism
Pledge mechanism
In Ethereum’s PoS, anyone can stake 32 ETH to become a validator — a node that participates in the network’s consensus algorithm and is responsible for storing data, processing transactions, and adding new blocks to the blockchain. Finalizing a block requires signatures from 2/3 of the active validators, thus keeping Ethereum secure. During this process, stakers will receive staking rewards. Currently, the beacon chain only allows ETH to be deposited, at least until the Ethereum mainnet and the beacon chain are merged before you can get back your pledged ETH.
There is always risk when making large-scale changes to a protocol that secures hundreds of billions of dollars in assets, and thankfully the current PoS Ethereum chain, the Beacon Chain, has been running since December 2020 with no issues. any malfunction.
In order to ensure safe and smooth operation, there are currently 4 unique clients implementing PoS Ethereum nodes. This means that if PoS node operators experience issues with a particular implementation, they will have the ability to switch to a different client.
Forfeiture rules
If a malicious actor tries to tamper with the underlying protocol by using a large number of validators to recover a completed block (equivalent to a "51% attack" in PoW), their funds will be forfeited - meaning they Will lose part of the ETH they pledged. This makes attacks very expensive. It's like a PoW system, if you use mining hardware to attack the network, your hardware will be destroyed.
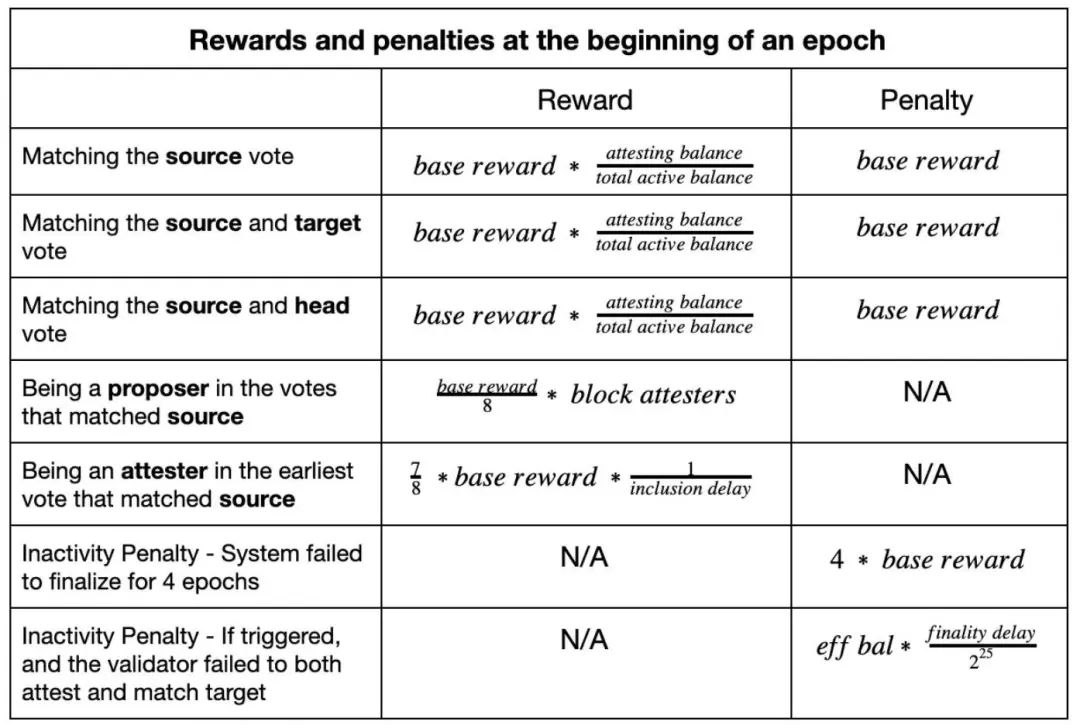
In a PoS network, a proposer mines a new block, and the prover votes whether the block becomes part of the blockchain. Slashing means that the validator violated the rules and was forced to withdraw. There are three slashing conditions:
As a proposer, the node signed more than one beacon block for a block
As a prover, a node signs more than one attestation on the same target
As provers, nodes sign proofs that conflict with history
difficulty bomb
difficulty bomb
The difficulty bomb is designed to greatly increase the difficulty for miners to verify transactions on the network, making mining significantly less profitable, and eventually, miners will be unable to verify blocks in order to dissuade miners before the long-awaited merger.
As EthHub explains: "Ethereum's 'difficulty bomb' is a mechanism that increases the difficulty of puzzles in the proof-of-work mining algorithm over a predetermined number of blocks, causing block times to be slower than normal." Long time (thereby reducing ETH rewards for miners). This mechanism increases the difficulty exponentially over time, eventually leading to the 'Ice Age' (Ice Age) - that is, mining on the chain becomes so difficult that Stop producing blocks."
first level title
03.
The development progress of The Merge
Speaking at the Shanghai web3.0 Developers Summit last month, Vitalik said that the merger of the Ethereum mainnet and the beacon chain is expected to be completed in August 2022.
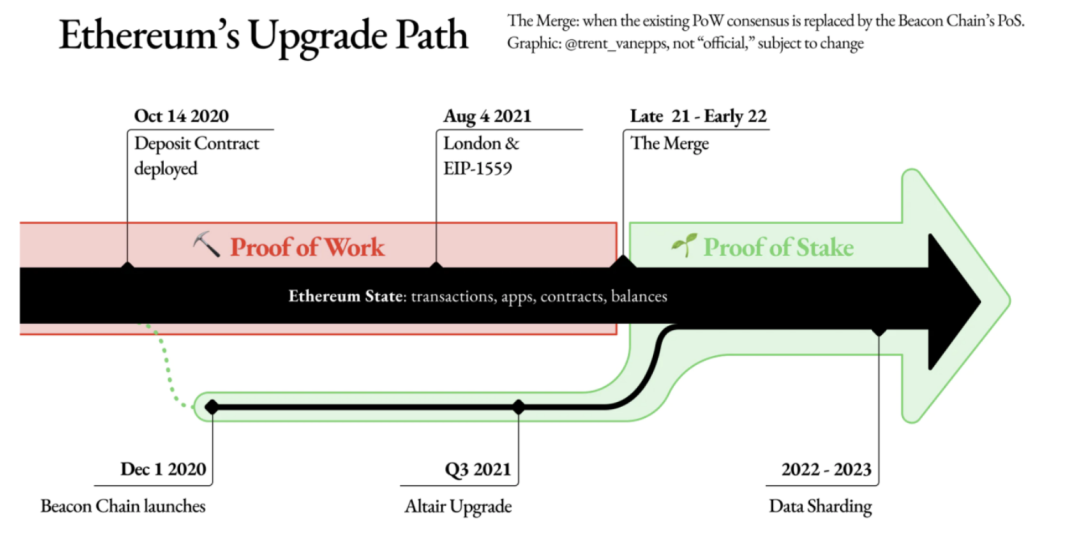
The merger process was difficult and tortuous. Beginning in 2017, Vitalik Buterin proposed to switch from PoW to PoS in 2019, but due to considerations of difficulty, security and other factors, the delay has not been completed so far.The main difficulties lie in the huge amount of funds and the tedious and complicated coordination and communication of the interests of all parties involved.
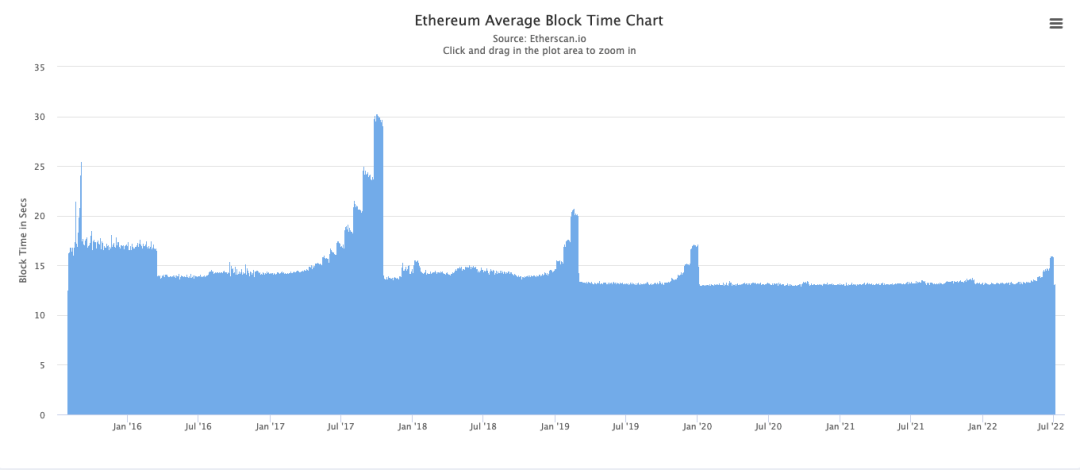
On March 15, 2022, Ethereum merged with the public test network Kiln to go online, which means that it has successfully transitioned and upgraded to a complete PoS mechanism. On June 8, 2022, Ethereum completed the first rehearsal of Merge-the testnet Ropsten successfully completed the merger. Launched in 2016, Ropsten is the longest-running Ethereum testnet to date. According to the core developer of Ethereum, about 14% of validators experienced downtime during the merger process of Ropsten, but most of them were caused by wrong node configuration, and these problems were quickly resolved. Additionally, the merger on Ropsten is considered near-perfect and serves as an important milestone in Ethereum's migration to PoS. In the future, the merger will be executed successively on the Sepoli and Goerli testnets. If all goes well, the ethereum mainnet is expected to be merged between late August and November.
What is the line of work after the "merge"? Based on disclosures from the Ethereum Foundation and its core developers, we conclude as follows:
2023, The Surge (take off)
The merger will not reduce the gas fee of Ethereum, but The Surge is committed to solving the problem of Ethereum traffic congestion and high gas. Ethereum will be divided into 64 shards, combined with Layer2 rollups technology, the theoretical upper limit of tps may be 100,000 transactions per second (the current Ethereum tps is about 13 transactions per second).
Note:
Note:
Sharding is a computer term that refers to horizontally splitting the database in order to spread the load. Ethereum sharding refers to the creation of new chains/shards, and multiple shards process data at the same time, thereby reducing network congestion, increasing tps, and reducing The Verge (Border)
The Verge (Border)
Technology update, plan to transition from merkle tree to verkle tree, they can be regarded as the database of Ethereum, at this stage due to the increase of block data, it will in turn verify the expansion and decentralization of the network.
ThePurge (purge work)
Clear, meaning that not all nodes have to permanently store all history blocks. Instead, the client will stop storing history older than one year. This means that Ethereum’s hardware requirements for nodes will be reduced, and the bandwidth of the network will also be reduced.
The Splurge
first level title
04.
The design concept of PoS
Vitalik, the founder of Ethereum, once explained the design concept of Casper PoS:
Cryptography is a rare technology that is easy to defend and difficult to attack (the defender has an advantage over the attacker in the face of an attack). It is like attacking a castle is much easier than building a castle. The island is more defensive, but it is still inevitable to be attacked. In contrast, an ordinary person's key is secure enough to even resist state-level attacks. Fundamentally, the cypherpunk philosophy is to take advantage of this preciousasymmetryTo better protect personal sovereignty, encryption economy is an extension of this idea, but it is to protect the security and effectiveness of coordinated complex systems, not just the integrity and confidentiality of simple private information. The ideological successors of the cypherpunk spirit should maintain this basic attribute, so that the cost of destruction is much higher than the cost of use or maintenance.
The spirit of cypherpunk is not only an idealism, but also the most basic engineering to create a system that is easier to defend than attack.
Note:
Note:
The ability to calculate a hash value is a computer's ability to run and solve different hashing algorithms. These algorithms are used to generate new blocks on the blockchain. This process is also known as mining.
However, blockchains secured only by social consensus are too inefficient and slow, and too prone to allow disagreements to persist endlessly; therefore, byConsensus on economic means plays an extremely important role in the short-term in terms of protection effectiveness and safety.
Because the security of PoW can only come from block rewards, and the incentives for miners can only come from the risk of them losing future block rewards, PoW is a system that is motivated by a large number of rewards. It is very difficult for PoW to recover from an attack, Vitalik is not optimistic about this logic, because(i) Its energy consumption is huge (ii) It does not realize the spirit of cypherpunk, the ratio of attack cost and defense cost is 1:1, so there is no defender advantage.
PoS breaks this symmetry by not relying on rewards but punishments for security. Validators stake their money, get a small reward to compensate them for locking capital and maintaining nodes, and take extra precautions to keep their private keys safe, butrevert transactionMost of the costs of spoofs come from penalties that are hundreds or even thousands of times greater than the rewards they received during this period. Therefore, to sum it up in one sentence, PoS is notNote:
Note:
first level title
05.
Advantages of PoS
When asked by Fortune magazine why PoS is a better mechanism, Vitalik replied:
I think there are many benefits for Ethereum switching to Proof of Stake. In terms of environmental issues, the Ethereum ecosystem can be made to consume less resources. In addition, the proof-of-stake mechanism can improve the security of the system. It makes attacks more expensive and makes it easier to recover the network from an attack than people thought possible. Additionally, proof-of-stake is more censorship-resistant, and the computers running validators make it easier for miners to detect and shut down the program. Therefore, the proof-of-stake mechanism has a series of different advantages.
secondary title
1. PoS provides more security at the same cost
Note:
Note:
Due to the special mining mechanism of ETH, the Ethereum network has not developed ASIC mining machines with a large computing power similar to BTC. Currently, Ethereum mining is mainly GPU mining, and the ASIC mining machines account for a very small share. Therefore, this Only GPU mining is considered here.
GPU-based PoW
The cost an attacker needs to pay to attack a network is to rent enough GPU power to surpass existing miners. For every $1 in block rewards, existing miners spend close to $1 in cost (if they spend more, miners quit as unprofitable, if they spend less, new miners can join and get high profits). Therefore, attacking the network only costs a little over $1 a day, and only takes a few hours.
Assuming an attack for 6 hours and renting a GPU for 6 hours, the rental cost is about $0.26.As the attacker earns the block reward, its cost could be reduced to zero.
PoS
The cost of PoS is mainly the capital investment (that is, the coins deposited) and the operating costs of operating nodes. The deposited coins will not depreciate, and when participants complete the pledge, they will get back their deposited coins after a period of time. Therefore, participants are willing to pay a much higher cost of capital for the same amount of rewards.
Assuming a ~15% return rate is enough to incentivize people to stake, a reward of $1 per day would attract $2,433 in deposits over a period of 6.667 years. The cost of hardware and electricity to operate a node is very small, only 100 US dollars per month in electricity and network fees, but a thousand-yuan computer can pledge hundreds of thousands of dollars in deposits. We can conservatively assume that these ongoing costs are 10% of the total cost of staking, with a reward of $0.90 per day for invested capital.
Note:
Note:
6.667 years = $1/(15% return); $2433 = $1/day x365x6.667
1/0.15=6.667 (return/IRR)
In the long run, this cost is expected to be higher as staking becomes more efficient and people become accustomed to lower rates of return. Vitalik expects that figure to eventually rise to around $10,000.
secondary title
2. Attacks are easier to recover in PoS
In a PoW network, what would you do if your chain suffered a 51% attack? In historical practice so far, the only response has been "wait until the attacker gets tired". But this ignores the possibility of a more dangerous attack, a spawn camping attack - where an attacker attacks a chain over and over again with the explicit goal of making the chain useless.
In a PoW network, a persistent attacker can easily disable a chain permanently.For the first few days, the cost to the attacker can become so low that honest miners will quit because they have no way to get rewarded while the attack is going on.
In a PoS network, the situation is much better.For certain types of 51% attacks (notably restoring completed blocks), there is a built-in slashing mechanism in the PoS consensus whereby a majority of the attacker's stake is automatically destroyed without affecting other human rights. Attacking the chain for the first time will cost the attacker millions of dollars, and the community will return to normal within a few days. Attacking the chain a second time would still cost the attacker millions of dollars as they would need to buy new coins to replace the old ones that were burned. And the third time will... cost many more millions of dollars.secondary title
3. More energy efficient
PoS nodes are estimated to be 99% (or more) more energy efficient than PoW nodes, so PoS represents a quantum leap in energy efficiency for blockchain technology. The PoW mechanism is very energy-intensive. In order to generate each block on the network, participants need to use powerful and energy-consuming GPUs to solve a complex mathematical problem. Whoever solves the block first will be rewarded. Simply put, PoW is an arms race, and if you have more hashrate than your competitors, you are more likely to win. The end result of this arms race is that PoW miners run as many GPUs as possible at 100% load, 24 hours a day. The more block rewards they want to earn, the higher the demand for electricity.
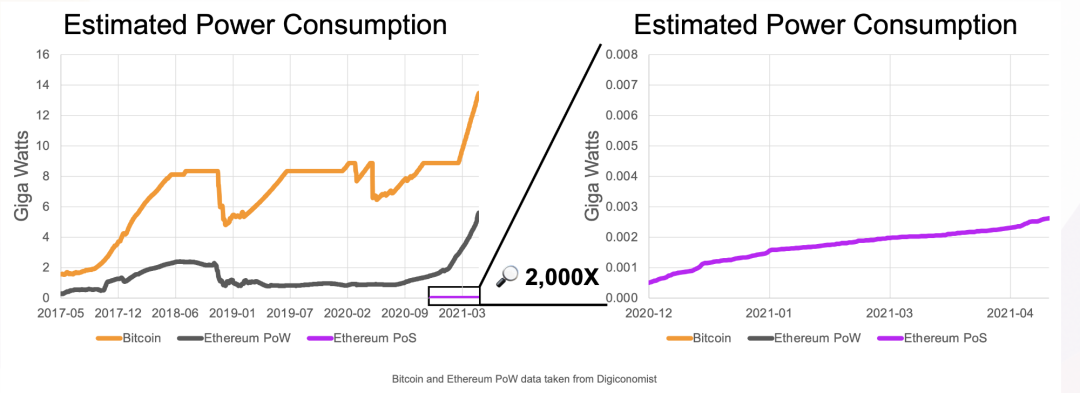
In PoS, the block proposer is randomly selected, the arms race will no longer exist, there is no need to consume more energy to improve the competitive advantage, so there is no need for energy-intensive hardware like PoW, any relatively new consumption Class hardware is capable of running the software required to operate 32 ETH staking nodes. If you deposit more than 32 ETH, you will be allocated multiple "validator slots" by the protocol, but you will still be able to run them from a single computer, although the more staked, the higher the hardware requirements.
Adopting the PoS mechanism will be more environmentally friendly and greatly reduce power consumption.secondary title
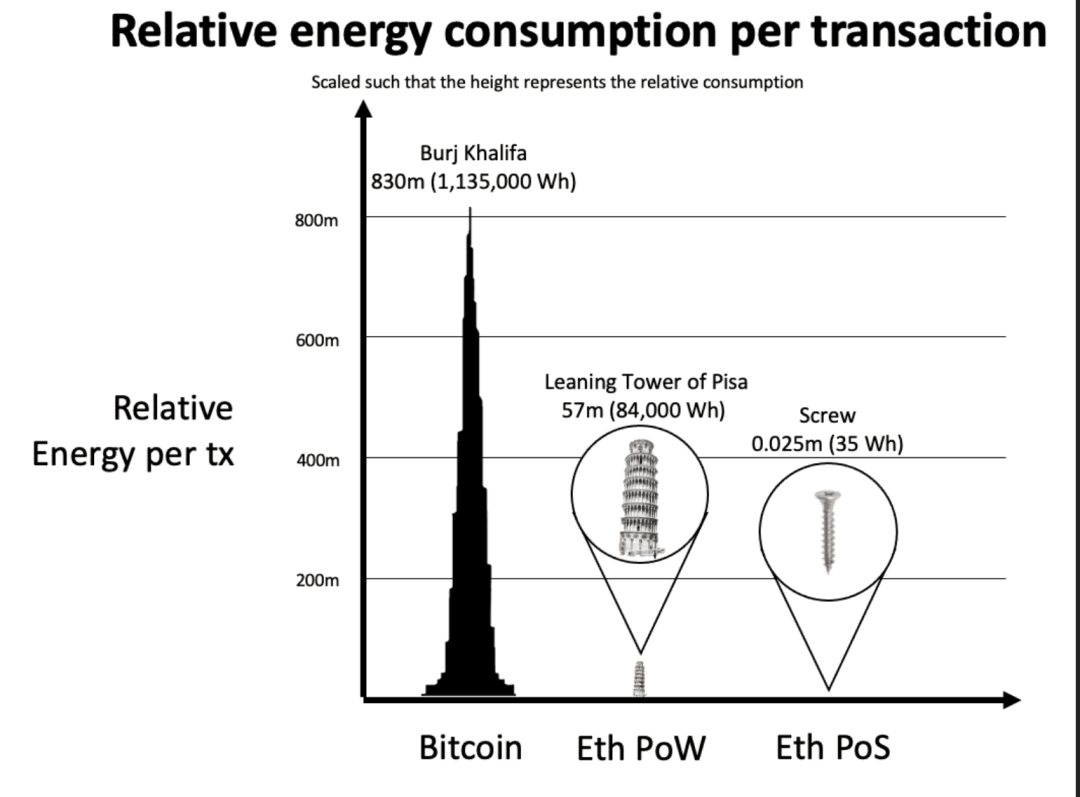
4. Higher censorship resistance
first level title
06.
secondary title
1. PoS is more of a "closed system" that may lead to higher wealth concentration in the long run
In PoS, you can get more coins by staking your coins. In PoW, you can always get more coins, but some external resources are needed to support it. Therefore, in the long run, there are concerns that the PoS currency distribution may become more and more centralized.
Regarding such doubts, Vitalik responded like this:secondary title
2. PoS requires "weakly subjective", while PoW does not
Although nodes that already exist in the network will not be deceived by attackers, for nodes that join the network for the first time, they do not have enough information to determine which chain was created first, so new nodes will tend to choose the chain created by the attacker. longer chain. To avoid this situation, new nodes need to somehow learn about the main chain off the chain, which essentially requires them to choose to trust a certain subject in the network. This third party can be their friend, it can be An exchange or a blockchain explorer, or a client developer. PoW has no such requirement.
first level title
07.
secondary title
Impact on ETH
ETH Issuance Drops 90%, Inflation Falls
Bitcoin halves its issuance rate every 4 years, and when Ethereum merges, its issuance rate will be reduced by about 90% because it no longer needs to reward miners for mining. The community refers to this situation as "Triple Halvening" because it is equivalent to *3 Bitcoin's "halving" happening at the same time. Ethereum would experience a reduction in issuance in an instant, whereas on Bitcoin's network it would take an additional 12 years to match.
Under the current PoW mode, Ethereum issues about 13,500 ETH per day (the annual issuance is about 4.3% of the total supply of ETH). However,The PoS issuance model is determined by the amount of active ETH on the network.Current projections are that when the merger occurs, the issuance rate will drop to between 0.3% and 0.4%.
For comparison, Bitcoin currently issues about 900 BTC per day — an annual issuance of about 1.7% of the total BTC supply. The next two "Halvenings" (halving) will reduce Bitcoin's issuance to approximately 0.8% in 2024 and 0.4% in 2028. With Ethereum’s expected circulation dropping to between 0.3% and 0.4% post-merger, Bitcoin’s circulation won’t match Ethereum’s until 2028.
Note:
Note:
EIP-1559 is the first step in turning ETH into a deflationary asset, and since its launch in August 2021, it has caused about 1.8% of the total ETH supply to be burned. However, its destruction rate is not certain, more will be destroyed when the network is busy, and less will be destroyed when the network is not busy.

After Merge, more and more people will choose to pledge ETH, but it is also easier to withdraw
Currently, about 9.7% of the ETH supply is staked. All pledged ETH will cease to circulate until the Merge is completed. According to the amount of ETH pledged after The Merge, network fees and MEV, the ETH pledge yield may be between 8.7-10.3%.
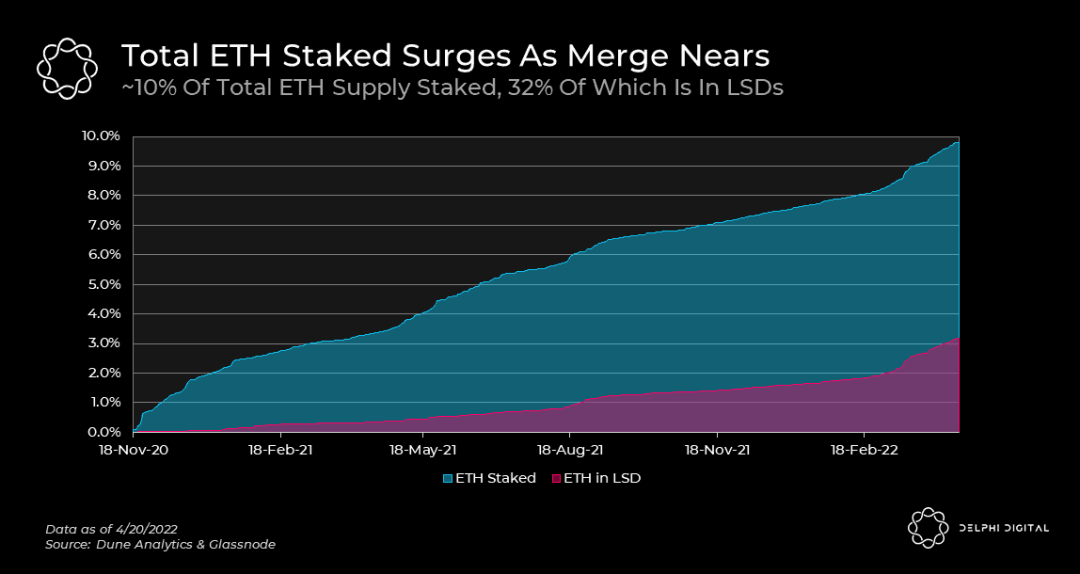
As of June 12, about 13.46 million ETH has been pledged, about 400,000 validators, and the APR is about 4.2%. Stakers will also receive gas fees that currently belong to the miner, which will increase the APR by 2x or more. An APR of 4.2% can be considered a near-risk-free return on Ethereum. When it rises, more ETH will be attracted to be staked.

But under PoS, it is easier for a node to withdraw. The difference with the mining machine is that although the mining machine has financial attributes, it is not a completely financial product like ETH. Ethereum is not allowed to withdraw before the merger is completed, so it will only increase in one direction, but after the merger is allowed, there will be no physical asset support after ETH is transferred to PoS. It is difficult to determine the number of withdrawals. It is indeed not as stable as before, and volatility may bigger.
image description
Users who stake on Ethereum will earn about 4.2% APR, before deducting server costs. Kraken predicted in the report "The State of Staking Q1 2022" that after the Ethereum Merge is completed, the annual interest rate for staking users will increase to 8.5%-11.5%.
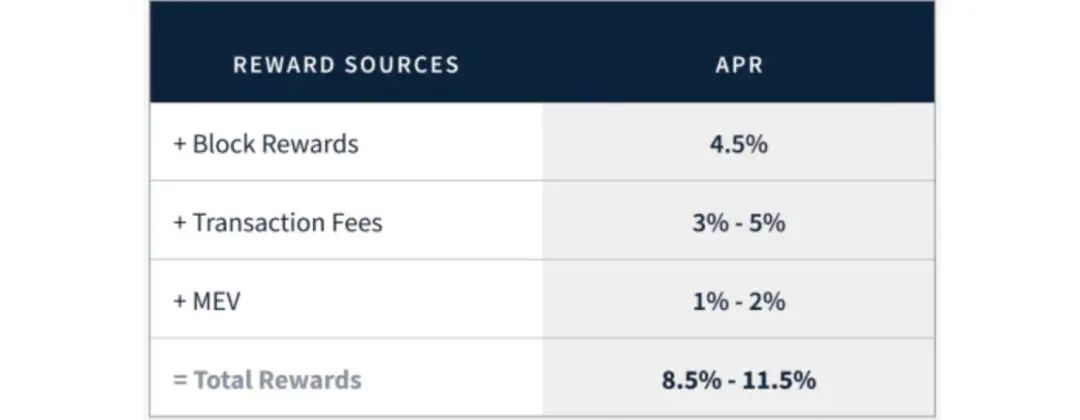
The State of Staking in Q1 2022
After the merger, a large number of users withdrew ETH, causing serious damage to ETH?
We have reservations about this view for the following reasons:
We have reservations about this view for the following reasons:
1. Only 30k Ethereum can be withdrawn per day
2. The unlocked ETH will be released slowly
secondary title
Impact on Ethereum ecology
4. Sell the mining machine and pledge the mined ETH to participate in PoS
Before the merger, EIP 1559 had been activated on Ethereum, and by the time the merger occurred, most of Ethereum’s transaction fees had been burned for almost a year. The remaining fees that are not burned after EIP-1559 (called "tips" or "priority fees") will be paid to the block proposer of the PoS block, not to the PoW miner.
If any nodes continued to mine on the PoW version of Ethereum, they would be a forked minority whose economic value of block rewards would be far less than their operating costs. Since miners are driven by interests, it is expected that the miner group after Merge may:
1. Mining other PoW tokens
2. Provide high-performance computing data center
3. Provide computing for Web3 protocol
4. Sell the mining machine and pledge the mined ETH to participate in PoS
Collusion Arbitrage in MEV
MEV stands for Maximal Extractable Value, the maximum extractable value.A simple explanation of MEV is:Miners or verifiers of a blockchain network can determine the ordering of transactions in a block, and the maximum value that can be determined by this ordering is called MEV. Similar to front-running transactions in traditional securities trading.
The current miner sorting scheme does not change in PoW and PoS, but after PoS, the negative impact of MEV will be magnified:Under PoW, block proposers are randomly generated based on the computing power they have, and a mining pool with more computing power will have a higher chance of proposing the next block. But this is still random, and the block proposer cannot predict it in advance, so it is difficult to implement a multi-block MEV strategy. But under the PoS scheme, block proposers are pre-selected every 12 minutes, which meansBlock proposers adjacent to each other can not only extract MEV from their own blocks, but can also collude to implement multi-block MEV strategies.
This has two very important effects:
1. The multi-block MEV strategy screens and sorts more transactions within a larger block space, thereby "stealing" a greater MEV value.
2. To make matters worse, it is very centralized.
a. Higher percentage of validators under your control -> greater chance to control two or more adjacent block proposers -> more MEV mined
b. This means that centralized staking pools can not only provide more stable economic returns (as an individual staker, the chances of proposing a block are rather small), but the economic returns will be higher due to the generation of more MEV. Therefore, people will probably give up going it alone and join a centralized staking service or pool instead.
If Ethereum fails to mitigate this risk, this will likely destroy the entire Ethereum protocol. For this,The Flashbots team proposed the MEV-Geth proposalNote:
Note:
Mempool — short for Memory and Pool, is used to store unconfirmed transaction information, it acts as a waiting area for transactions that have not yet been included in a block, and is also where MEV robot searches can be used to capture certain MEV transactions.
It is worth noting that after the merger is completed, the process of ordering transactions has not changed much. Likewise, we have reason to believe that MEV will continue to exist. The difference is that the person who decides the transaction order is changed from a miner to a verifier, and the verifier will be randomly selected to participate in the execution of the beacon chain.
Upgrade of technology platform
To help improve this system and make it easier for newcomers to the platform, the Ethereum upgrade will replace the EVM with a new system called Ethereum WebAssembly (ewasm). The system will allow developers to write code creatively and freely without having to learn Solidity, the native Ethereum-specific language.
To help improve this system and make it easier for newcomers to the platform, the Ethereum upgrade will replace the EVM with a new system called Ethereum WebAssembly (ewasm). The system will allow developers to write code creatively and freely without having to learn Solidity, the native Ethereum-specific language.
PoS converts ETH into Internet bonds, which is more regulatory-friendly
The recently enacted Responsible Financial Innovation Act (Responsible Financial Innovation Act) aims to encourage 'responsible innovation' by integrating digital assets into existing laws and provides a clearer framework for the crypto industry.The SEC (U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission) will supervise digital assets classified as securities, while the CFTC (U.S. Commodity Futures Trading Commission) will be responsible for supervising digital assets that are recognized as commodities.secondary title
Optimistic expectations:
Optimistic expectations:
Pessimistic expectations:
Pessimistic expectations:
Merge has been postponed again and again, everyone has lost confidence in the execution of Ethereum, and other public chains have risen, and Merge has become a "waiting for Godot" game.
secondary title
Merge follow-up: expansion
The Merge is not an expansion plan of Ethereum, its scope is limited to upgrading the consensus mechanism of Ethereum. In practice, it will not have any impact on the current Ethereum user experience. The gas fee is a function of the block space requirement and is not affected by the consensus mechanism
first level title
08.
secondary title
Is the substantial reduction in the cost of Ethereum a good thing?
The Ethereum Foundation holds approximately $1.6 billion, broken down into $1.3 billion in cryptocurrencies and $300 million in non-cryptocurrency investments and assets. The vast majority (99.1%) of cryptocurrencies held are held in the form of ETH, accounting for 0.297% of the total ETH supply.
The ETH paid in the gas fee does not benefit any centralized entity, no company takes a cut of the fee you pay, the gas fee is paid to the miners because they contribute the necessary resources to keep Ethereum running. Therefore, you can think of gas Fee as the basic "materials" required for network operation.
income:When you use any Layer1, you pay native tokens for the services they provide (that is, block space), and the income you pay will be owned by asset holders in the form of staking rewards, which is Ethereum income (Example: Developers must pay fees to the Ethereum network in order to create new tokens or dapps on the network).
expenditure:Hal Press, founder of crypto hedge fund North Rock Digital, offers a novel perspective——For PoW, the circulation is a fee, because the circulation is not owned by the token holders, but owned by the miners, so now Ethereum issues 4 million coins per year, which is a huge fee. However, after Merge, the issuance of ETH is no longer considered an expense, because under the PoW mechanism, miners tend to sell ETH in order to compensate their hardware costs such as mining machines, but under the PoS mechanism, pledgers usually choose long-term Staking and holding, the staking rewards are still in the Ethereum ecosystem and have not left the system, so this part of the issuance cannot be counted as cost.
In addition to this, most of the costs of PoW are electricity costs.This is an actual expense of the network, because for the people running the network, it costs money, and while PoS still needs to run nodes and pay for electricity, the cost is much lower than before.
In 2021, the total expenditure of the Ethereum Foundation is about 48 million US dollars. Approximately $20 million of this was in the form of external expenditures, including grants, commissioned field assignments, third-party funding, bounties, and sponsorships.
Although the cost of Ethereum has been greatly reduced, is this necessarily a good thing?
Analogous to commodities or traditional currencies, its value is the sum of the production materials and other costs that need to be input. So, if the way ether is minted changes, people's consideration of its intrinsic value will change.The pledged ETH becomes the new Ethereum, and Ethereum no longer needs to be withdrawn, users can have the convenience of liquidity, and the book assets have been rising. Just like an algorithmic stablecoin that obtains future potential returns through staking, this method is likely to be a preview of future risks: once an extreme risk event occurs and external liquidity is impacted, then the relationship between the two currencies will The value of will be unanchored.
We all know the law of "energy conservation", the reduction of external energy input is likely to bring greater risks to the stability of the system. The expected management of the liquidity of Ethereum and the future value of assets is based on the existing PoW mining mechanism, which makes everyone think that "casting out of thin air" assets are valuable.secondary title
Ethereum can be viewed with the valuation method of traditional finance
Encrypted quantitative trader Ryan Allis proposed in a Bankless podcast that PoS gave ETH the fundamentals for the first timeNote:
Note:
DCF, Discounted Cash Flow, is a method of valuing today's assets based on an asset's expected future cash flow (a forecast of how much money it will earn in the future). To model a DCF for a company, you need to know its current net profit (income - expenses), which is the annual cash flow. Then you need to assume the growth rate of these cash flows and evaluate them over a longer period of time (say 15-20 years).
The cost of the Ethereum network is primarily the security cost of maintaining consensus. It is issued to block producers in the form of ETH (block rewards), which are currently miners, but in PoS they are pledgers in the Ethereum network. There are no other costs for the network, and hardware, electricity, etc. are all borne by third-party suppliers .
Therefore, we have two types of cash flows:
Burned fees (equivalent to indirectly distributing profits to ETH holders through "repurchase")
Tips and block rewards for stakers
Based on them and the expected growth rate of Ethereum revenue, it is possible to build a DCF model to evaluate the fair value of ETH.
DCF model input:
Annualized income = income in January 2022 × 12
Growth rate: 25% per year (conservative compared to last year's 400% growth)
Staking rewards: $1.1 million in ETH per year
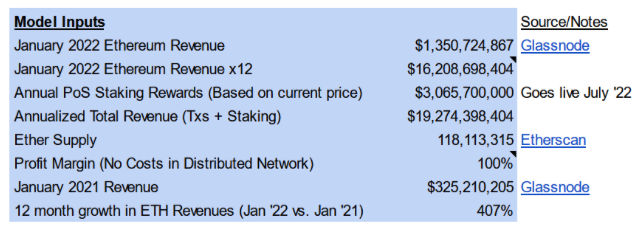 DCF model output:
DCF model output:
DCF value per ETH: $10,600
DCF value per staked ETH: $12,600
These numbers are calculated by dividing the net present value of future cash flows by the current supply of ETH. However, they ignore the deflation of ETH after the merger.

If we assume that the supply of ETH will drop from the current 118 million to 100 million in 20 years (to 71 million based on the current projected annual supply decline of 2.5%), the above price will rise to $12,500 (without pledge ) and $15,000 (staking).
Using valuations based on price-to-earnings (P/E) ratios turns out to be more bullish. Ethereum currently trades at a P/E ratio of 20, while the average company in the S&P 500 has a P/E ratio of 35, with an average growth rate of 8-10% per year. Ethereum’s growth rate last year was 400%.
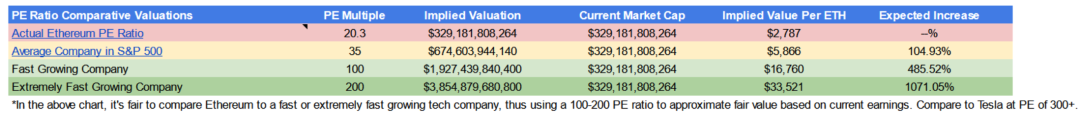
If we compare Ethereum to a high growth tech company, we can assume a P/E ratio of 100-200 (Tesla is above 300), which would give an implied value of $17,000-33,000 per dollar of ETH, which is the current price Moderate growth of 5-10 times.
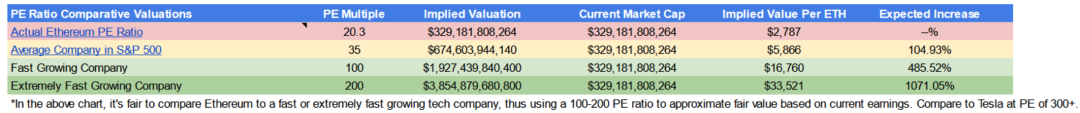 Not only do we have an asset where 100% of revenue is profit, but its growth rate is more than 10 times the average growth rate of a company, but ETH's trading price-earnings ratio is still lower than that of an ordinary company, and there is still a lot of room for growth.
Not only do we have an asset where 100% of revenue is profit, but its growth rate is more than 10 times the average growth rate of a company, but ETH's trading price-earnings ratio is still lower than that of an ordinary company, and there is still a lot of room for growth.
secondary title
Good for staking track service providers (staking as a service)
Pledge classification
Solo home staking
Staking alone means that users pledge at least 32 ETH on Ethereum and operate their own validator nodes. There are many restrictions on self-staking: 1) The pledged funds cannot flow, and the ETH pledge cannot be released before the upgrade of Ethereum is completed; 2) Many tasks of operating nodes 24*7
Exchange staking
Pledging through the centralized exchange allows users to pledge or cancel the pledge at any time, and the exchange will charge a certain service fee. Since users cannot get back the money pledged on Ethereum at the beginning, there is a certain pressure on the exchange's capital turnover-the exchange can only pledge up to about 60% of the deposited ETH. Therefore, the return rate of exchange staking is much lower than that of staking alone or liquid staking.
In addition, exchange staking poses a centralization risk to the Ethereum network.Exchanges represent some of the largest ETH holders, and staking on exchanges will make their ETH holdings larger, which will cause great damage to the Ethereum ecosystem. The three largest custodial staking solutions (Kraken, Coinbase, and Binance) collectively deposited nearly 2.7 million ETH.
Liquid staking
Liquid staking allows users to stake any amount of Ethereum and unstake them at any time by issuing a tokenized version of the pledged funds, similar to a derivative that can be transferred, stored, spent, or traded like ordinary tokens.
For example, Lido allows users to stake any amount of Ethereum in return for issuing stETH, which can be used for lending, staking, etc., while still earning daily staking rewards. Since the ETH staked by users generates staking rewards, the user's balance will increase daily, allowing them to earn the value of the staking rewards.
Liquid staking services like Lido are suitable for all types of ETH holders. Holders of small funds can stake any amount of Ethereum and can unstake at any time; holders of large funds can use the Liquid Staking Service to hedge their funds against ETH volatility; basically, it allows parties to Staking without maintaining complex staking infrastructure.
Staking track market analysis
The pledge rate of Ethereum has reached 10%, and it will continue to increase by more than 3 times in the future. The promotion and completion of Merge will benefit the pledge track service providers.At present, about 370,000 validators have pledged 12 million ETH on the Ethereum beacon chain, more than 10% of the total amount of Ethereum, with a total value of 35 billion US dollars. Referring to the long-term pledge rate of existing PoS main chains such as Binance and Solana, which are between 40% and 70%, the pledge rate of Ethereum still has room for growth of at least 3 times.
Running your own staking node involves a lot of risk and requires a lot of capital to get started. It is very difficult for an individual to maintain a 24/7 online server and not get slashed for doing so. In order to facilitate individuals to stake and earn rewards,"Staking-as-a-service" node providers have emerged in the market.The node provider will be responsible for managing the infrastructure, and users only need to pledge their funds on the platform provided by the node provider, and the node provider will charge a node operation fee or commission fee every month.
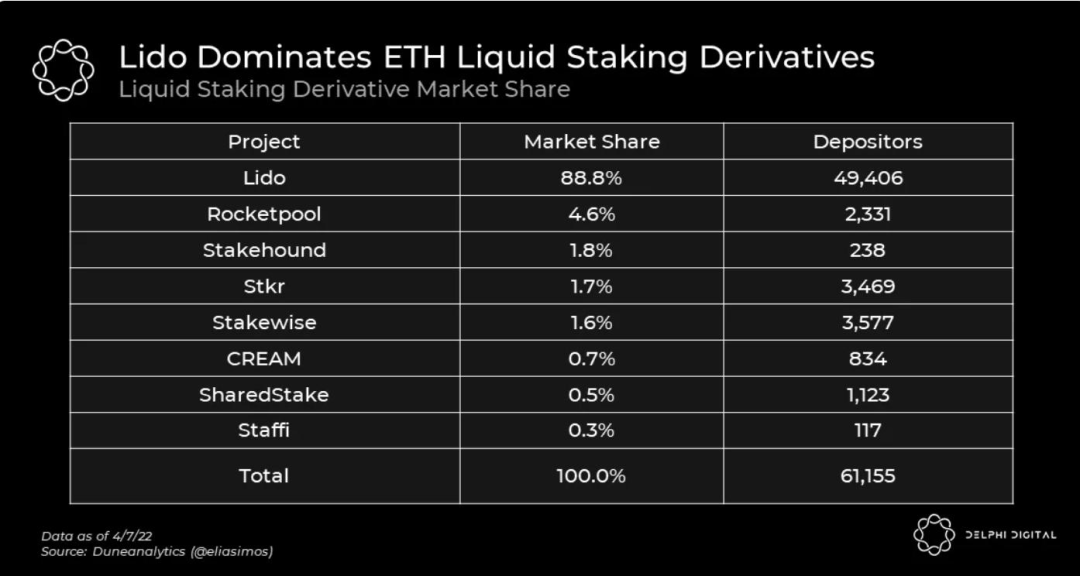
Among them, Lido, which has already occupied 90% of the market share in the liquidity staking track, established an ETH exchange liquidity pool with Curve, allowing users to still obtain ETH liquidity during the period when the pledge funds are locked; Rocket stepped out with an ultra-low pledge threshold of 0.001 ETH. A differentiated route suitable for small retail investors; and SSVNetwork, as the underlying technology provider, took the lead in launching the testnet, using distributed verification (DVT) technology to provide upper-level customers with more decentralized technical solutions.
Special thanks to:
Thanks to Frank, Junchen, and the web3 navigator community for their inspiration and contributions to this article