abstract
secondary title
abstract
On June 24, 2022, Horizon, an asset cross-chain bridge between Ethereum and Harmony developed by the Layer 1 public chain Harmony, was attacked, with a loss of approximately US$100 million.
What exactly is going on?
Although the day the hacker attack occurred, it can be concluded that the "notary's private key was stolen", since the VIP clicks on it, you might as well come and have a chat. Don't worry, there are a few hard-core source codes, but the whole article is in vernacular and easy to understand!
Interpretation of Horizon contract audit report
Re-analysis and summary of the reasons for the theft
1. Technical principle of cross-chain bridge
Cross-chain, as the name implies, is the problem of how to transfer asset information between different blockchains, also known as interoperability. Currently, there are more than 50 cross-chain solutions with various definitions."From iosg-》
A list of cross-chain bridge solutions, who can gather multi-chain liquidity
secondary title
1.1. What are the cross-chain solutions?
In a nutshell, to achieve asset value being constant on another chain, there are two major paths: anchoring by "price" and anchoring by "physics"
At first glance, it sounds complicated, but in fact, anchoring by price is a stable currency such as USDT on various public chains. It is anchored 1:1 with the US dollar, so it is also a type of cross-chain asset.
Aside from all kinds of stable coins, a more intuitive cross-chain solution is physical anchoring, that is, the total amount of liquidity is constant, and there are many solutions (notary, side chain, relay chain, hash lock, etc.), we Focus on the notary model.
There are three distinctions in the notary model based on "who is the notary":
Guaranteed by the exchange: For example, Binance withdraws coins, all kinds of transactions are carried out on the centralized exchange, and the coins are cashed out
Liquidity pool bridging type: such as bridge.connext, o3swap
Contract locked casting type: various official bridge general solutions polygon/arbitrum/avax/celer, and today's protagonist harmony
All of the above have their own advantages and disadvantages, whether they are afraid of the exchange running away, or the liquidity is exhausted, or the private key of the notary is stolen. At present, there is no cross-chain solution that perfectly realizes the impossible triangle.
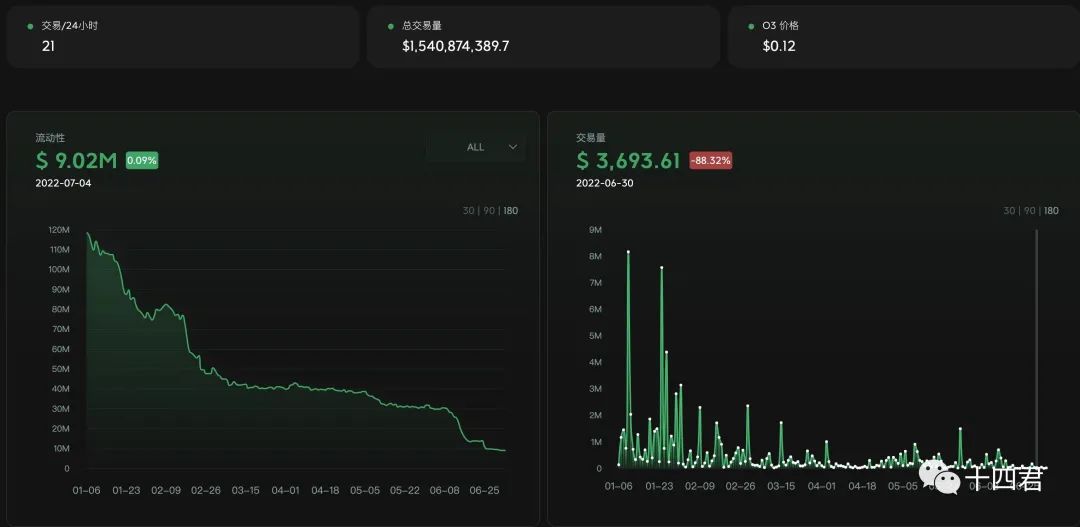
image description
"Total liquidity and trading volume, from o3swap official website"
secondary title
1.2. Cross-chain principle of Horizon Bridge
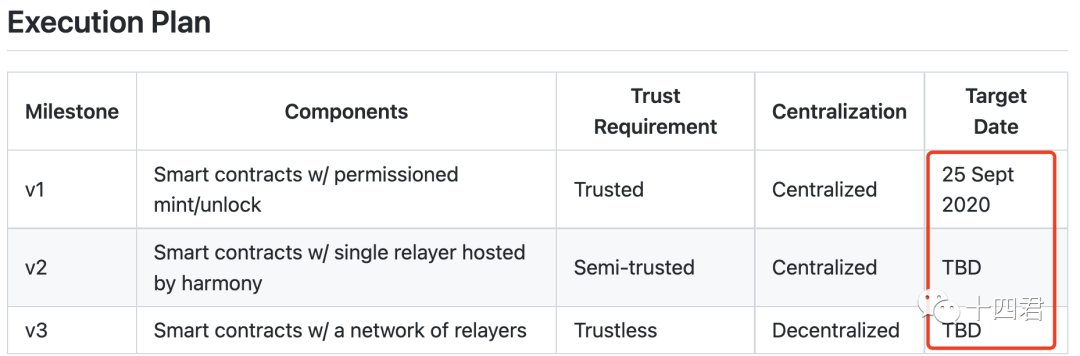
The Horizon bridge developed by Harmony is a pretty standard notary lock casting type.
Why can locked casting be trusted?
It is because the contract on the blockchain is immutable. If there is no back door, even once it is deployed, there will be no way to affect its operation, just as the Boring Ape official transfers all permissions to address 0. After giving up ownership, no In any way, new monkeys can be further minted, and their total liquidity will be locked.
In the same way, although contracts are different between different public chains, if 10 ETH are locked with a contract on Ethereum, 10 wETH will be released with the same credible contract on another public chain. In fact, the overall liquidity is fixed. As long as wETH can be transferred back to Ethereum at any time and exchanged for ETH, then wETH can be considered to have the equivalent value of ETH.
Therefore, its core operation is
Burn-and-Release: Chain B destroys packaging tokens + Chain A unlocks the liquidity of an equal amount of basic tokens
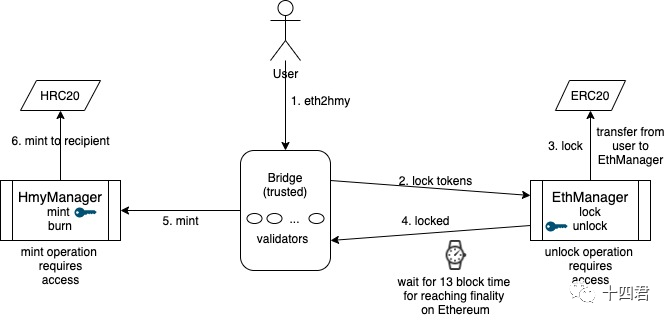
Notary: Responsible for discovering the A-chain Lock event, go to the B-chain Mint to mint anchor tokens, and transfer them to the target address.
Schematic diagram of the process of the Horizon bridge, from the official github
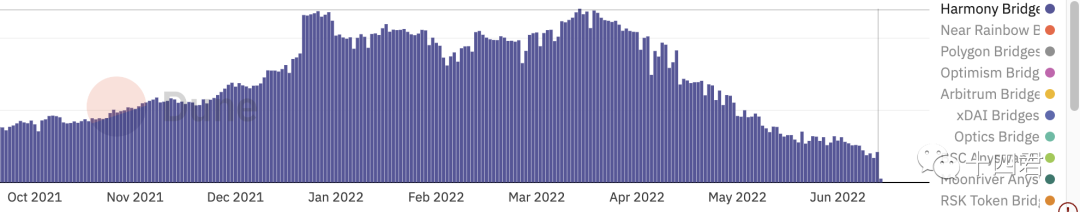
image description
Horizon chain bridge TVL diagram, from dune
first level title
2. Interpretation of Horizon bridge contract audit report
For many Web3 projects, if an accident is not 100% safe, it is basically equal to 0 value. Therefore, in order to check the security of the contract, it usually tests and simulates various attack scenarios, and conducts a security review through the checklist to ensure the security of the contract.
Development may only take a few days, but to be reliable enough, there are many processes and expensive (the general quotation starts at 10W based on time)

The core information of the audit report is: risk name, vulnerability description, risk level, security recommendations, repair status and audit results, etc.
The contract audit report of the Horizon Bridge was conducted by the established audit firm PeckShield, and five vulnerabilities were found
2.1. Low and medium risk point 1 - Insufficient compatibility

Is it hard to imagine that 3 lines of code can have bugs?
In fact, the logic of locking the token is very simple, that is, the user specifies the amount and the target address. After authorizing the withholding authority, the contract will transfer USDT to this contract to lock, and send a locked event, so that the notary under the chain can know that the asset has been locked. locked.
But what if it is a "deflationary" token? What should I do if the amount decreases during safeTransferFrom? This will lead to the risk that the lock-up amount is lower than the release amount of the B-chain[Source Code Interpretation] What exactly is the NFT you bought?
You can read the previous article:
[Source Code Interpretation] What exactly is the NFT you bought?
In the standard protocol, the virtual function is used as a hook method to add logic before and after the transfer. Some tokens may increase the transaction loss here _beforeTokenTransfer, so as to control the circulation and achieve deflation.
Of course, harmony must have been modified and optimized in the end, and the method of reading balance twice before and after the transfer is used to calculate the actual locked amount.
Still this code, is it hard to imagine that there are not only BUGs in the 3 lines of code, but also 2![Source Code Interpretation] What exactly is the NFT you bought?
[Source Code Interpretation] What exactly is the NFT you bought?
For safe Mint, in fact, the standard protocol prohibits mint to address 0. If the destination transfer address recipient is filled with address 0 when lockingToken, the casting on the B chain will fail, resulting in locking into this contract but no cross-chain effect. This treasury contract does not reserve a suitable transfer method and it will be permanently locked.
secondary title
2.3. High risk points
In the original procedure, the unlocking and release of mint minted assets can only be carried out by designated notaries.

This is exactly the reason for this trick. Harmony finally changed the notary to a multi-signature wallet, but only changed it to 3, and if 2 of the private keys are stolen, they can run amok.
image description
PeckShield's Audit Report on the Horizon Bridge
How should I put it, you said he changed it, I always feel a little perfunctory, even when the hacker stole the assets, the harmony bridge was still in operation, which means that his private key was even saved in plain text and was copied by the hacker
For the blockchain browser usage guide, see:What are we looking at when we look at Etherscan?
What are we looking at when we look at Etherscan?
secondary title
wallet1:0x0d043128146654C7683Fbf30ac98D7B2285DeD00
wallet2:0x9E91ae672E7f7330Fc6B9bAb9C259BD94Cd08715
wallet3:0x58f4baccb411acef70a5f6dd174af7854fc48fa9
3.1. Key information
MultiSigWallet:0x715cdda5e9ad30a0ced14940f9997ee611496de6
attacker wallet
Cross-chain bridge related addresses
ETH vault address: 0xF9Fb1c508Ff49F78b60d3A96dea99Fa5d7F3A8A6
ERC20 vault address: 0x2dccdb493827e15a5dc8f8b72147e6c4a5620857
Stolen notary address: 0x812d8622c6f3c45959439e7ede3c580da06f8f25

3.2. Analysis of the theft process
Steal 13100 Ether, see the transaction Link for details (quoted in the appendix)
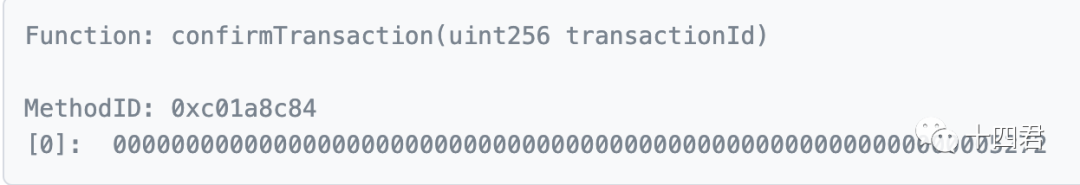
The execution is to confirm a certain transaction ID (a part of multi-signature voting)
Confirmation by the notary -> The number of notaries waiting for confirmation reaches the standard -> Unlock the treasury assets and transfer them to the target address
It can be seen from the logic in the multi-sign contract contract code that this function will make a notConfirmed judgment, so only the notary address set by the system before can be called
The executeTransaction method will be executed later, and then the isConfirmed method will be called to make a judgment. If the number of administrators who authenticate the transaction reaches 2, the unlockEth method of the EthManager contract will be called internally, and finally the ETH will be sent to the attacker’s wallet.
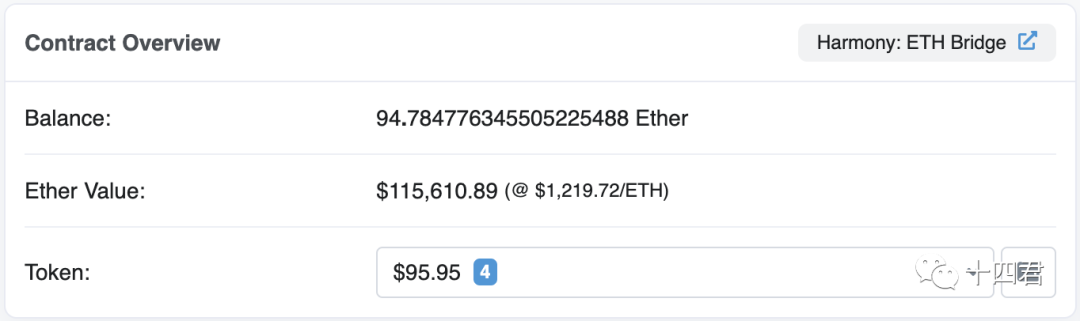
By now it is clear that there is no particular possibility of error in such a simple and straightforward contract, other than the theft of the private key.
By the way, I took a look at the balance of the ETH vault of the cross-chain bridge and there are still 94 Eth, and the ERC20 vault still has 300,000 dollars of various tokens
4. Thinking summary
4.1 What will happen to the thief?
Although Harmony immediately offered 1 million US dollars, proposing that the hacker return the assets and promise not to pursue the responsibility, but even if the hacker returns and the official does not pursue it, other social teams will prosecute. Therefore, the best route for the hacker is to do everything possible to cover the stolen assets. Asset desensitization.
As of June 29, the attackers had transferred approximately 35,000 ETH (approximately $39 million) to Tornado Cash, a common coin mixer, although the blockchain is a public ledger and any transaction can be hacked. Tracking, but the currency mixer is like a collection of transactions for 100 people, and it cannot accurately determine which funds will eventually fall into which person's hands.
4.2. How to be more secure?
To optimize, the method of distributed hosting can be adopted, and it is hosted to the MPC (Multi-Party Computation) notary network, and no more than a certain percentage of nodes do evil at the same time to ensure security
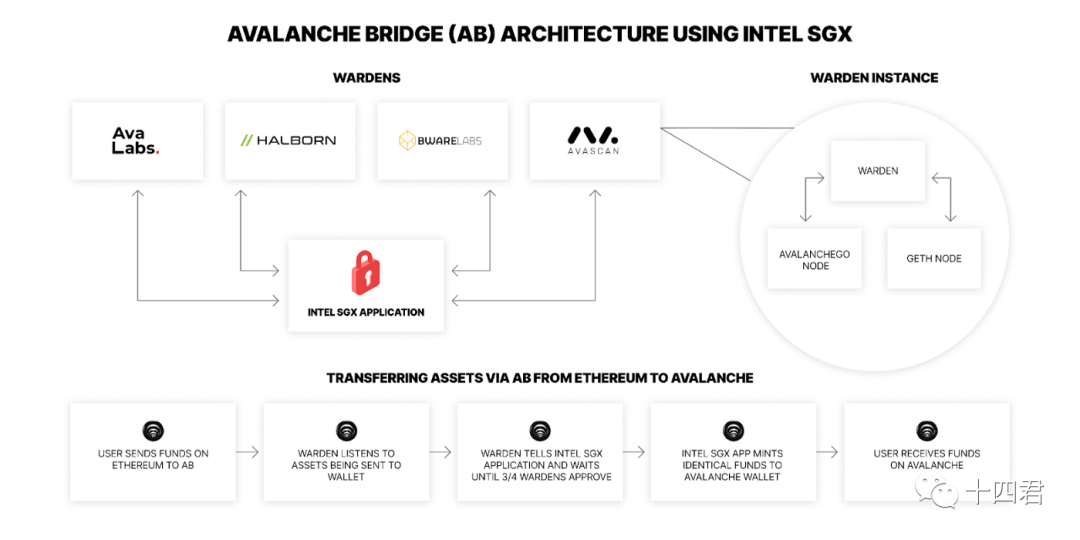
Even if the notary is scarce, you can refer to the SGX trusted computing technology adopted by the avalanche bridge
Avalanche Bridge: Secure cross-chain assets with Intel SGX
Quote:
Quote:
A list of cross-chain bridge solutions, who can gather multi-chain liquidity
Horizon bridge official GIT: https://github.com/harmony-one/ethhmy-bridge
https://etherscan.io/tx/0x27981c7289c372e601c9475e5b5466310be18ed10b59d1ac840145f6e7804c97
Horizon chain bridge TVL diagram: https://dune.com/queries/118245
https://docs.harmony.one/home/general/bridges/horizon-bridge/audit
Stealing Transaction Link:
https://medium.com/avalancheavax/avalanche-bridge-secure-cross-chain-asset-transfers-using-intel-sgx-b04f5a4c7ad1