Author: OP Research
It is human nature to try to change the status quo. When this driving force is combined with technology, capital, information, and data, human society will inevitably change and develop towards new social forms and production relations.
Web 3.0, the next phase of the Internet, is the best example of this process. Based on the development of blockchain and related technologies, Web3.0 is gradually approaching. Concepts and applications such as Metaverse, GameFi, SocialFi, X-to-Earn, and DID have entered the public's field of vision, setting off an upsurge. What this upsurge brings is not only a variety of new applications and new ways of playing, but also a feast of investment (speculation) driven by capital. More importantly, when the tide recedes, what is left after the big wave washes away the sand.
Projects may die, applications may be replaced, and capital may move to different tracks, but the underlying logic and values of Web3.0 will have a profound impact on human society under the current Web2.0 paradigm. Change doesn't happen overnight, it happens gradually, but eventually we have entered a new era.
It is undeniable that human beings have gained great convenience under the life and economic model shaped by the Web2.0 paradigm, and Web2.0 has also promoted the continuous progress and development of human society. But perhaps because people are too familiar with the lifestyle shaped by Web2.0 and too accustomed to the various phenomena that occur under this paradigm, it is difficult for people to perceive the "mystery" in it. Under the Web2.0 paradigm, everyone is essentially a "consumer product" of this model. Compared with the earlier traditional era, Web2.0 has given people more choices and channels for realization, but people are still in this way. The "accessory" of the first mode is a screw in this mode, and has no real control ability.
At the same time, not only individuals, but also enterprises, companies, and institutions are subject to various rules and regulations formulated by Web2.0, and products need to be designed and operated according to an inherent set of rules. Although enterprises, companies, and institutions have more powerful power and funds to optimize some settings than individuals, they cannot completely break through the Web2.0 paradigm to which they belong, and sometimes need to sacrifice the user experience of products and applications or abandon the original concept of design to achieve profitability.
Fortunately, we have not lost the ability to reflect and think. Fortunately, technology is always developing. Just like in real life, everyone will control their own destiny at important life intersections. In the virtual world of the Internet, we also have the same Ability.
secondary title
1. Changes in business models
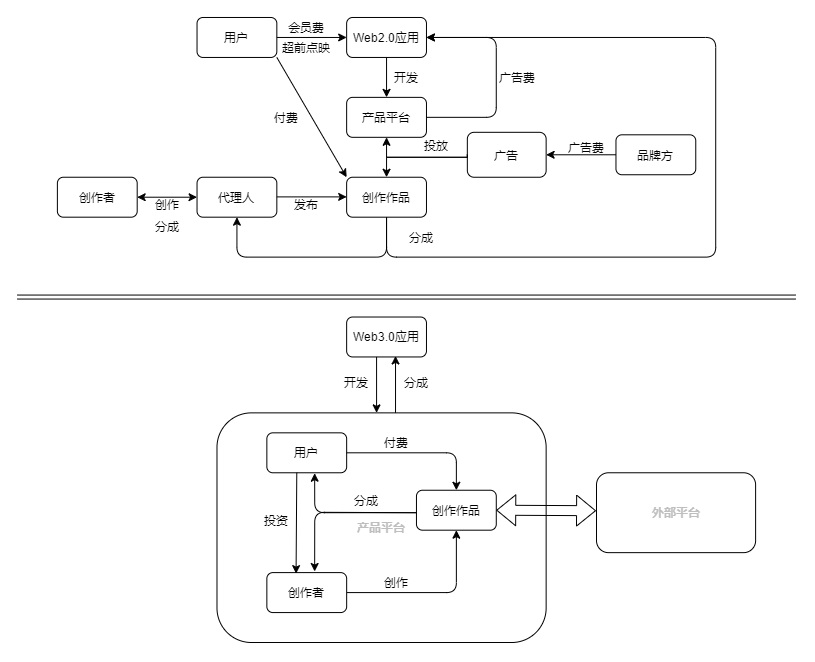
Web3.0 brings a new business model to traditional Web2.0 applications, and solves the problem of a single profit method for Web2.0 application companies from the root. The most important thing is to revolutionize social media and transfer payment applications.
(1) Social media
Social media Web2.0 applications are limited by their own single source of income and have to sacrifice user experience, add blunt membership mechanisms, and introduce advertisements. In order to obtain more advertisements, social media applications gradually deviated from their own product positioning, began to chase traffic, and monetized traffic to maintain their livelihoods. However, due to the platform nature of social media applications, they can advertise based on the impact of user works and draw a profit from them. This system is now becoming more and more mature in Web2.0. For example, Twitter and Weibo’s advertising posts, YouTube’s video advertising share, TikTok’s advertising placement, etc. In fact, the system already has the shadow of Web3.0 in it, but most platforms rely on their own platform advantages to squeeze the distribution ratio of platform creators. Web3.0 applications have also adopted the membership system, which is a method of paying in advance to obtain services, but Web2.0 chooses to sacrifice user experience and launch so-called member-only advertisements and member advance screenings, which violates the original commitment of the membership mechanism. It is very ugly to eat.
Web3.0, on the other hand, is based on the open source of the smart contract code and the introduction of the economic model in the white paper, and charges users the corresponding fees and provides corresponding services in a completely transparent manner. For example, Mirror confirms the rights of each article by generating NFT, and users can create without worrying about plagiarism, manuscript washing and deletion. At the same time, creators can initiate crowdfunding under the article, and distribute dividends to investors for each transaction by issuing share tokens—"article NFT"—to participating crowdfunding users. The proportion of dividends is clear, and the final amount that can be obtained can also be calculated from the transaction volume of the article. Everything is transparent and credible. Although Mirror's economic model is relatively light and there are no exaggerated profit opportunities, due to its comfortable user experience and encryption-native attributes, many creators have switched from Medium to Mirror.
Another case is Monaco. As a phenomenon-level SocialFi application, although its survival time is relatively short, its appearance has opened up the hot spot of SocialFi, and also inspired the enthusiasm of project parties to revolutionize Twitter and Weibo. After that, SocialFi projects are all innovations based on their "ownership and governance rights are determined by users" and "content is mining". In Monaco, users can get benefits from publishing content and receiving interactive behaviors (such as likes and comments). The same benefits are transparent and predictable, which makes users happy to share and participate in interactions, and project parties can also Extract from it openly and aboveboard.
The recently popular Lens Protocol, as SocialFi developed by the Aave team and deployed on Polygon, has attracted a lot of attention. Lens Protocol defines itself as "an open, composable Web3.0 social media protocol that allows anyone to create unmanaged social media profiles and build new social media applications". Specifically, any application can be inserted into Lens' open social graph, and users own their own data through NFT, which can be deployed to any application built on the Lens protocol. NFT determines the user's voting weight and revenue distribution. However, Lens Protocol has just been launched, and whether its business model is sustainable is still a bit of a test of time.
In addition to Mirror, Monaco and Lens Protocol, other media Web3.0 projects have also broken through the valuation bottleneck, such as Audius. As a decentralized music streaming protocol, Audius solves the problems that creators have too weak control over copyright and it is difficult to trace the source, creators get too little revenue and the distribution channels of works are monopolized on traditional music platforms. In the current royalty distribution of Web2.0 music applications, musicians can earn less income. Usually 42% of the royalties of a song are distributed to record companies (such as Sony, Universal, etc.), about 30% are distributed to operating systems (such as Android, iOS, etc.), and about 20% are distributed to Internet playback platforms (such as Spotify, QQ Music) , Lyricists and songwriters can share a total of 8%, and singers are mostly settled by record companies. If the lyrics and music are represented by multiple layers, the royalties will also be divided layer by layer, and there will be less in the hands of the creators. And this is when the copyright is clear and the assignment is timely and transparent.
In contrast, Audius directly connects creators and fans in different dimensions such as music listening, song sharing, work collection, royalty sharing, and free creation, breaking the monopoly and inefficiency problems in the original industry, and not only increasing the number of creators. Incentives to stimulate their creation, and also improve the audience's user interaction experience and collection needs, while the follow-up NFT derivative market can give creators and projects more benefits. This allows it to obtain a circulating market value of $311.7m and a fully released market value of $478.5m with 6m monthly active users and 26k wallet addresses, or 13% of Crypto users. And Spotify, the world's largest music platform, has 428m monthly active users, and its market value is only $21.9b.
It can be seen that the changes in the industry's business model brought about by Web3.0 social media applications not only provide project parties with more diverse sources of income and more durable and stable cash flow, but also give users, including creators, unprecedented fairness and freedom. and a smooth interactive experience. The high composability of Web3.0 applications also gives them greater room for imagination for future development.
(2) Transfer payment
As far as transfer payment applications are concerned, electronic transfer payment has become an important way of life for people. In real life, people hardly carry cash, but a mobile phone, and download Web 2.0 applications such as third-party payment apps (Alipay, Paypal, etc.) Daily transfer and payment needs can be completed. However, as the demand for electronic transfer payment becomes more frequent and the amount is larger, people are increasingly concerned about the centralized institution's ability to handle transfer payments.
The main business model of the centralized organization is to collect service fees such as transfer payment and cash withdrawal; to obtain rebates for the sale of wealth management products; to place advertisements; to earn interest spreads based on user deposits for loans, etc. In addition, due to inter-bank isolation and international foreign exchange control, the procedures for inter-bank transfers and cross-border transfers are very cumbersome and complicated. Banks or transfer payment applications will charge high fees for them, and limit the single amount and total amount of transfers. In fact, these profit points will not bring about the improvement of its products and services, but will affect the user experience.
However, payment methods such as face-scanning payment launched by Alipay, Paypal and other applications have indeed optimized the user's payment experience, but they have not used this as a profit point. Most centralized institutions use the difference between deposit interest and loan interest as their main source of income. For example, the bank deposit interest rate is about 1-2% annualized, while the loan interest rate is about 3-4% annualized; for other installment services, In other words, the loan interest rate can be as high as 10% per annum. It can be seen that the centralized organization extracts a large amount of income from it, but the user has to accept it, because there is no second choice.
Payment applications based on blockchain decentralized services, such as MetaMask (little fox wallet), TP wallet, etc., although in essence they also earn rebates or spreads by accessing centralized financial management services and decentralized mining protocols. Advertise or sell derivative products such as hardware wallets, and collect Swap fees as profit points, but the transfer process is simpler and more convenient than traditional Web 2.0 methods, and the fees are lower, and there are no restrictions, especially when dealing with cross-border When paying for transactions, it is more time-sensitive and operable.
From this point of view, it seems that the Web3.0 payment application is similar to the centralized organization in the Web2.0 transfer payment field. They are all based on the services they provide beyond the functions of the product itself to maintain profitability, and the Web3.0 wallet cannot even host users. Assets, interest-bearing investments, etc. However, the smart contract wallet based on the multi-signature wallet can break this deadlock. It can get rid of the problem of private key leakage through NFT gated, allowing users to transfer their own wallets without trust, such as selling, leasing, and operating on behalf of others. . This will bring about a qualitative change in the business model of transfer payment. On the basis of smart contract wallets, a series of functions that optimize user experience and even subvert traditional payment and transfer models can be developed, such as privacy payment, binding payment, payment i.e. signing and so on. The profit point of this type of smart contract wallet can be based on these innovative functions provided by it. In addition, it can also openly and transparently add value to user assets based on smart contracts, and distribute income according to the agreed ratio, instead of simply Aspects of earned spreads.
secondary title
2. Economic model incentives for users
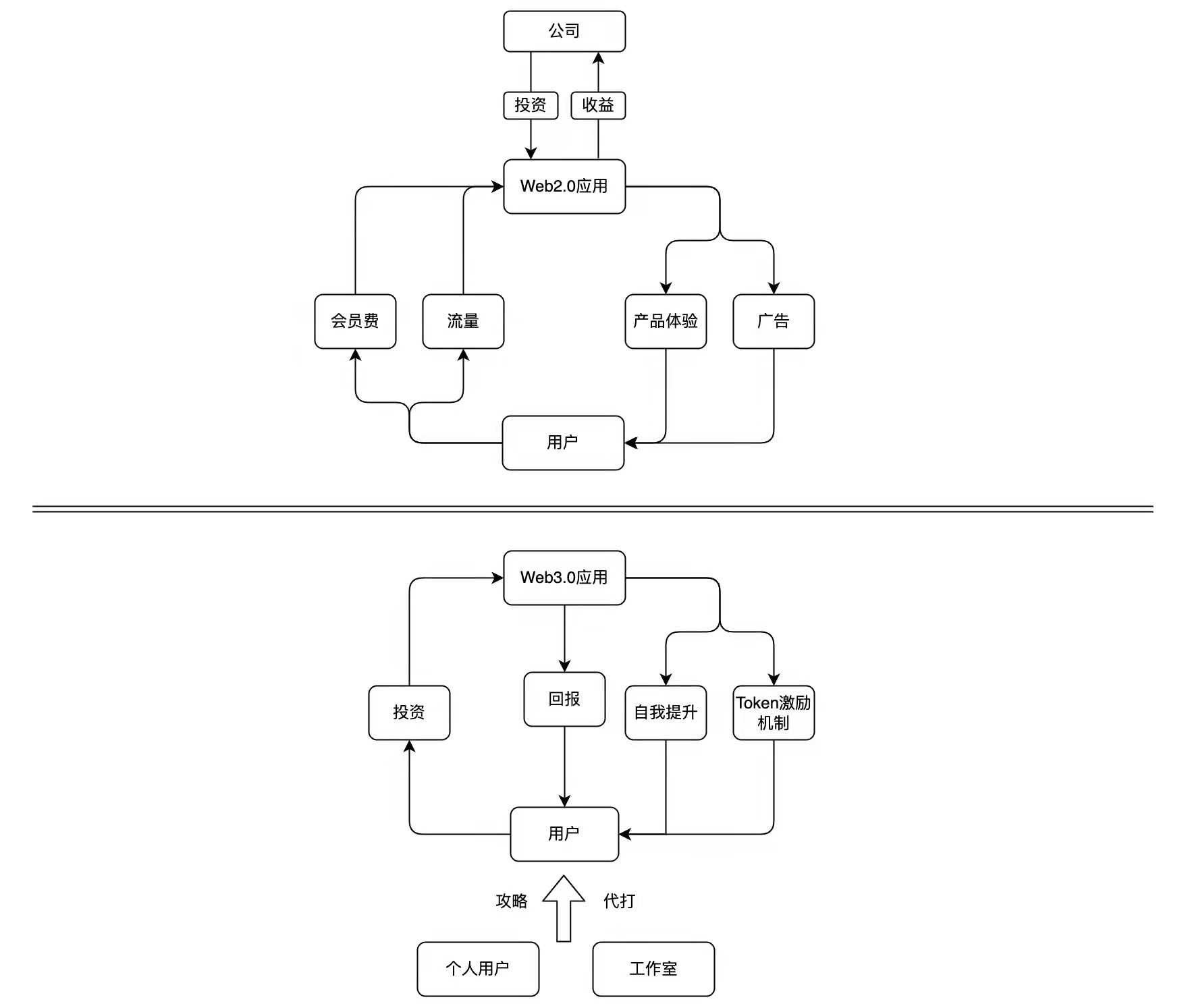
Another big leap in the application of the Web3.0 era compared to the Web2.0 era is that on the basis of determining the ownership of information and assets, a complete incentive model can often be formed within the project, which can also be seen as a Web3.0 The inner manifestation of the business model. Through the incentive system for all ecological participants in the system, Web3.0 will have more sufficient driving force and more vigorous vitality than Web2.0, which will also change the life of every participating user. The following will take Web3.0 applications in different fields as examples, focusing on the incentive model to compare the main differences between Web2.0 and Web3.0.
(1) Learning and sports
For most people, learning and exercising is something that accompanies their lives. For example, many people like to turn on their mobile phones to recite words, read novels, watch news, or exercise in the gym during commuting. Everyone often uses personal self-motivation, such as "I think memorizing vocabulary will be beneficial to my study abroad", "I want to lose weight through exercise", or external pressure, such as "If you want to pass the exam, you have to memorize vocabulary" "School makes it hard every day. Requiring inter-class exercises" and so on to achieve "delayed gratification". (The so-called delayed gratification refers to a choice orientation that is willing to give up immediate gratification for more valuable long-term results, as well as the self-control ability displayed during the waiting period). In the learning/sports applications in the Web 2.0 era, how to let users use "anti-human" applications and maintain constant incentives to achieve delayed gratification is a difficult problem faced by all application developers. However, this difficulty may now be in The world of Web3.0 is solved.
In the current Web2.0 applications, there are very few that can achieve economic incentives. On the contrary, most applications require payment for learning or knowledge services, or set membership thresholds to obtain membership fee income, or Adding advertisements to monetize traffic, obviously, not only has nothing to do with the incentive mechanism, but also prevents people's enthusiasm for learning and exercising. Numerous news apps require payment to watch key news, and the reciting word app requires members to unlock key functions, as well as advertisements that lie in front of you at various moments... such examples abound. As the main knowledge sharing platform, Zhihu has been widely acclaimed from the initial sharing of cognition by the industry giants, to the ghosts and snakes in the column, and the advertisements in every corner, although this allows platform users to have a certain degree of profitability. , but its ultimate goal has also become to expand traffic to attract more readers in order to obtain higher advertising quotations, which has greatly changed the entire business logic of Zhihu and seriously damaged the user experience.
Another example to the contrary is Wikipedia, which neither charges users for membership nor refuses to include advertisements. This has led to Wikipedia being a product with a high demand for use, but it is difficult to make a profit. Allowing users to participate in sharing information with enthusiasm is not long-term and unstable. So Wikipedia is a good service, but not a good commercial product.
The Token economy of Web3.0 can just solve this problem. In fact, traditional Web2.0 applications have also tried to use the concept of Token economy. The best example is the point system: applications reward users with points for their contribution behavior, and Points can be used to redeem some products and services, or perform other value exchanges. However, the limitations of Web2.0 have greatly restricted the points system, and the usage scenarios of points have not been opened, and there is also a lack of guarantee for users to confirm their rights. This makes the emergence of Web3.0 applications more revolutionary.
The introduction of Token economy makes the self-driving force produce economic benefits, thus forming a certain externality. Just like the recently popular APP - StepN allows users to get Token rewards by running outdoors, which gives users motivation other than self-drive, and the user's mentality is different from the traditional GameFi, because even if there is no Earn money, exercise your body and gain health. In fact, this is basically the same mechanism as the current "VAM Learning Group". Users pay a certain fee in the early stage based on their own learning expectations, and obtain continuous benefits through learning actions. And this reward mechanism is settled in real time according to the user's sports behavior. Users can clearly see different dimensions such as their running speed/duration/route and get corresponding rewards. The establishment of this instant feedback economic system is in line with human nature. Many users have the same addiction-like feeling after using StepN, and this mechanism is at work.
Finally, the Token economy also introduces certain externalities, such as proxy running, proxy reading, quick task completion strategy, etc., to attract more users to enter related industries, put pressure on traditional Web2.0 applications, and promote more applications based on certain The economic model focuses on product quality to provide a better user experience, rather than simply thinking about how to attract traffic, incorporate advertising, or find ways to collect money.
(2) Games
In this era of ever-accelerating pace, games have become a very important part of modern life. Different from learning and sports applications, game applications are for entertainment purposes and use shorter positive feedback, so in The setting of the incentive model is slightly different from the previous category. In game applications, the self-driving force of users is mainly realized by gameplay and entertainment, while the incentive model focuses more on the allocation of resources and the confirmation of asset rights.
In the games of the Web 2.0 era, game developers generally adopt the model of centralized investment-centralized development-player consumption. Traditional games almost control 100% of the return of game profits, and players are pure consumers: for example, Tencent controls its King of Glory Almost all direct profits. But just like the previous learning and sports applications, game applications are also optimizing the incentive model, and have made many similar attempts to use the Token economic concept: Dota2 TI series prizes are drawn from the profits of players buying game products Convergence, players can get bonuses through competitions. Players can also contribute to the ecology of Dota 2 while obtaining game equipment. In this mode, TI's bonuses can reach as high as several million U.S. dollars.
All props, items, spaceship vehicles, etc. in the EVE game are produced by the players themselves, and the players complete the complete industrial chain from mining raw materials-processing-market sales, and form the economic system in the game.
The economic model of Fantasy Westward Journey has been repeatedly studied as an excellent example of Gamefi. As an old game nearly 20 years old, the economic system is still mature and vibrant, and the equipment is still appreciating... It is undeniable that a considerable part of the Web2.0 era The game has achieved some success in these aspects, but based on the limitations of Web2.0, these advancements are still not enough. For example, although Dota 2 adopts this mode to obtain super high bonuses, it also allows players and professional players to participate Ecological contribution and a sense of achievement in participation, but in fact, it does not bring cash profits to real users who have invested real money. Users are still consumers in essence; although EVE and Fantasy Westward Journey ecology are complete and have a mature economic system and free market, However, in order to avoid the collapse of the game economic system, the project party has repeatedly adjusted and intervened in the economic model, pursued the long-term development of the game, suppressed studios and businessmen, and harmed the interests of some players. Without the support of blockchain technology, it is difficult for the game to guarantee user game assets and Information and core interests.
While these games have achieved good results in new mechanisms and economic models in the Web 2.0 era, these attempts should trigger some thinking about the application of Web 3.0 games: Different from traditional Web 2.0 games, In the games of the Web3.0 era, the game developer’s take rate is extremely low (take rate), and most of the profits will be returned to the player group itself: for example, the former Play to Earn game leader Axie Infinity protocol generates revenue in the following ways: : When players buy and sell Axie NFTs on the market in the game, the Axie protocol will charge a fee of 4.25%. Compared with the 100% rake rate of traditional games, most of the revenue generated by the game will be returned to the players themselves.
In Radio Caca, the game where Elon Musk’s mother Mayer Musk is the manager, Binance MVBIII’s No. All will be used for token and NFT buybacks. Also, Radio Caca earned over 60,000 BNB from selling RACA NFTs. And Radio Caca will use part of the proceeds to buy billions of RACA to burn, reducing market circulation, and at the same time put most of the proceeds into the liquidity pool. According to statistics, in the past two years, Axie Infinity has driven more than 200,000 people to participate in employment in the Philippines, Venezuela, Vietnam and other places. The peak DAU exceeded 1 million, and the income was even higher than the level before the epidemic spread.
From this point of view, the player group is the most important part of the game economic model in the Web3.0 era, which means that the economic model of the entire game is peer-to-peer. In most cases, players provide players with funds, transactions and liquidity. Not these game developers in the Web2.0 era. In this mode, game players will also change from mere consumers to game co-developers, ecological builders and marketers. The position of game developers will be more similar to providing platform services rather than management and controllers, and players can deeply participate in the game in various ways, such as producing game props, building game facilities, casting NFT required by the game and even shaping World view, making game history and more. For example, the famous Sandbox built a metaverse on the Ethereum blockchain, on which players can freely create their own virtual world, use their creativity and imagination, and customize it as they wish. Backed by blockchain technology, Sandbox allows players to own everything they create in the game: every in-game asset on Sandbox is automatically converted to NFT (Non-Fungible Token). It will allow players to verify the uniqueness and ownership of assets.
secondary title
3. Ownership of information and assets returns to users
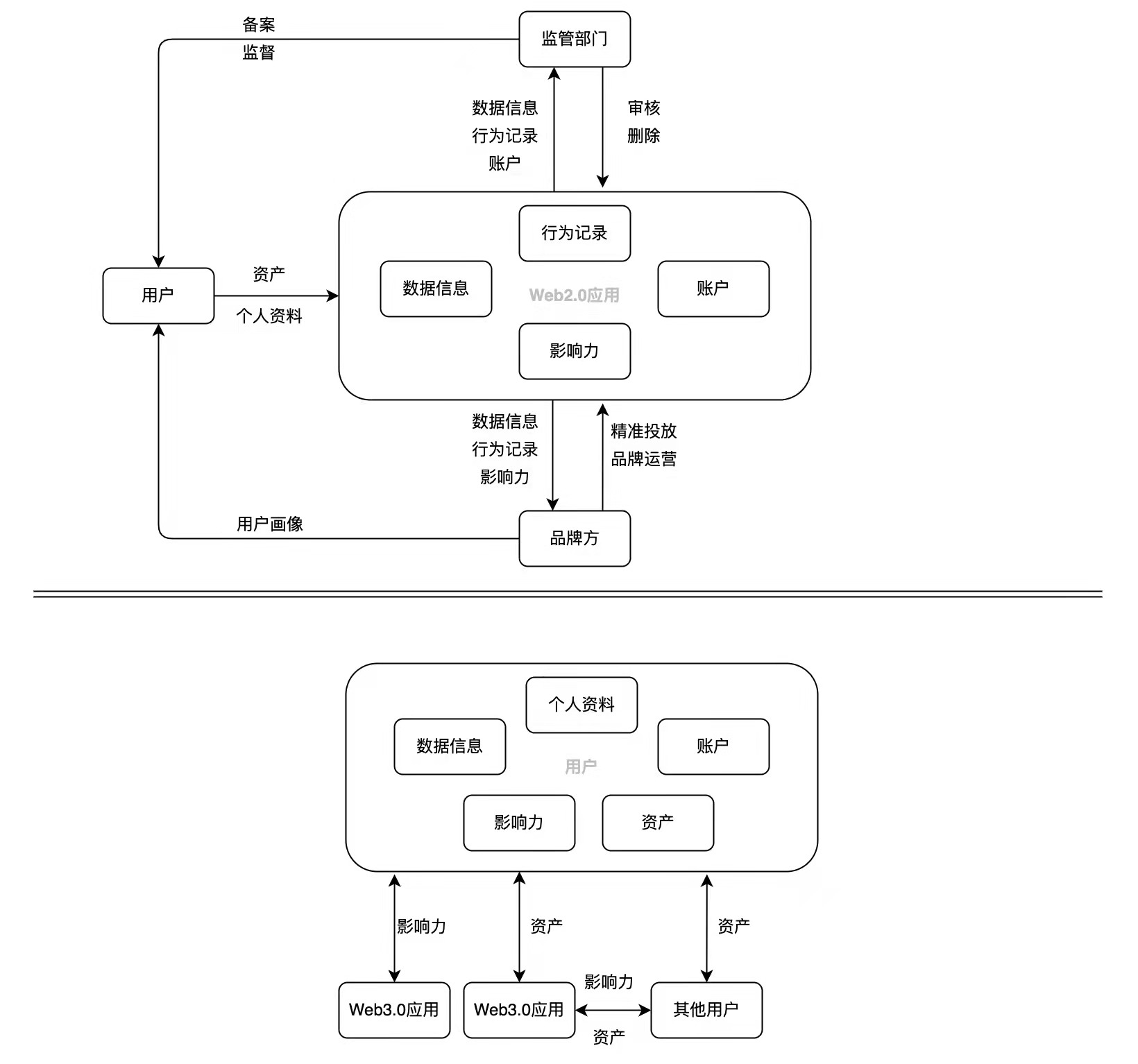
A very important proposition of Web3.0 is to allow users to truly own information and data ownership. For the change of business model, or the change of economic model and profit model, this change can be said to be a change of underlying values. People play games on Web 2.0, register and operate their own self-media accounts, and even transfer and pay. It seems that the game equipment, platform accounts, and funds in bank cards belong to themselves, but in fact, they do not really own them. Under the centralized operation mode of Web2.0, assets that seem to belong to people are actually under "danger" all the time: equipment, account numbers, and funds are kept in the centralized server of the platform. If the platform destroys these assets and data one day , the user will have "nothing". Web3.0 wants to change this situation. Since users have invested time, energy, and money, the assets obtained by users will naturally belong to them, and users can use, control, and manage them at will.
(1) Games
In the development process of traditional games in the Web2.0 era, game developers and agents have always had almost all control rights and final interpretation rights of game assets, which means that no matter how much players pay for this game, players are still just For pure consumers, game developers can modify games and even player personal data if conditions permit. But in the games of the Web3.0 era, players will truly own their own game assets, and the ownership of game assets will be guaranteed by the underlying blockchain technology. And the real ownership of game assets will greatly endow the financial and narrative attributes of game assets.
Please imagine, assuming that you own a certain weapon from the first copy of World of Warcraft, or a certain skin from a certain professional player’s highlight moment in Dota2, these game assets are permanently preserved in the form of NFT (currently NFT is becoming or has become one of the underlying elements of the Web3.0 era), which is undoubtedly very tempting. You can choose to collect them as a gaming enthusiast, or choose to sell them at a high price to generate a profit.
According to the survey, 71% of players who have spent money in the game said that if they can really own the game assets and sell them, they are willing to spend more money on the assets. This will also greatly promote the development of the game industry-you know, the paying users of traditional games account for less than 2%, which promotes a market worth 40 billion US dollars.
(2)DID
"Identity" is extremely important to each of us, because only when "I am myself" is proved and there is a credit foundation, can relevant activities be carried out with an independent identity. In real life, the authoritative way to prove yourself is to have your own ID card. The photo on the ID card and your own digital number are the passports to participate in various activities in real life. When individuals continue to interact in society, such as making bank loans, participating in work, paying social security, and traveling by means of transportation, all kinds of information and data are constantly attached to individuals marked with ID cards, forming a person's identity in society. identity.
In the Internet world, "identity" is still very important, and has even gradually become an important personal asset. Under the current Internet framework of Web 2.0, since there is a special identity layer to provide authentication for users, people usually use various APPs to register account passwords on the APP or use mobile phone numbers, ID numbers, etc. for identity verification. On the one hand, this method increases the difficulty of user identity management. Although there is currently a "one-click login" method, not all apps support this login method.
On the other hand, personal digital information, data, and "traces" left by online activities are all stored on the centralized platform. The platform can use and disclose personal information without the user's permission, but the information originally belonging to the individual cannot be controlled. owned by the user. Furthermore, when an individual becomes an influential person such as a KOL, "Internet celebrity", or a big V on a certain platform, the precious "identity asset" of the user is actually in the hands of the platform, and the platform can control the user account at will. Using, deleting, blocking, and limiting traffic, users are always at risk of being exploited or losing this asset.
Web 3.0 tries to break this situation, make "identity" management more convenient, and truly return the value attached to "identity" to users. DID (Decentralized Identity) - the identity construction system for Web 3.0 users. In the DID system, based on the blockchain technology, the individual's identity exists on the chain, which naturally has the attributes of decentralization, non-tampering, interoperability, and truly owned by users. For example, Litentry, as a decentralized identity aggregator, can link user identities across multiple networks. Users can manage their own identities through it, and DApps can obtain real-time DID data of identity owners across different blockchains. The user's personal information, behavior, digital assets, credit, etc. on the blockchain will be aggregated to become the user's comprehensive identity information. For example, through all the on-chain activity data collected by Litentry on each address, users can generate certificates in a decentralized manner by submitting the addresses of IDO/airdrop whitelist and other activities.
Another example is that Spruce is trying to build a cross-platform and cross-public chain identity authentication system to realize the intercommunication and integration of Web 3.0 public chain addresses and Web 2.0 platform accounts. A KOL with millions of followers may be able to obtain more Favorable mortgage rates and interest rates. In projects such as ENS and .bit domain names, blockchain addresses, social accounts, and email addresses can be bound, and personal data, other information, and all digital resources can be stored, and individual identities can be marked in the form of human-readable domain names. The shaping of the individual body of Web 3.0 is also a constantly enriching and three-dimensional process, such as the on-chain behavior authentication project Project Galaxy, which dynamically updates the user's identity status. This type of project does not give the user a DID, but more like Constant replenishment of user DIDs.
Updating and supplementing user identities is also an important part of Web 3.0. Since users are constantly interacting, and individual identities and data are constantly changing, real-time updates to user behaviors also create a more "accurate" "identity" necessary steps. The DID application builds its own comprehensive and rich identity certificates for Web 3.0 users. Users can manage, control and use their own identity information independently, and use DID to better carry out activities in the Web 3.0 and blockchain fields to obtain benefits. Avoid centralized platforms using user identity information to squeeze user value.
(3) Transfer payment
People often encounter these situations when transferring funds to the other party. After transferring money to the other party, the APP shows how many hours it will take to arrive at the account; when withdrawing cash, it shows that it will take a while before the funds can be withdrawn; It takes several working days for the amount to be returned; the number of daily transfers and the transfer amount of the user will also be strictly limited. These signs actually indicate that the funds in the user account are just a series of numbers, and the real assets may have been centralized. Institutional usage is out, so Web 2.0 payment facilitators are sometimes unable to respond immediately to customers' needs to move funds.
secondary title
Challenges and opportunities of Web3.0
Web3.0 applications have fundamental advantages over Web2.0 era applications, but new things often advance in twists and turns, and new trends always go through the pains of growth: at present, Web3.0 applications are not mature enough, The resources required for application development are huge. For Web3.0 developers and even entrepreneurs, they still face certain difficulties, such as lack of infrastructure, lack of experience in Web3.0 application development, and so on. For traditional entrepreneurs, they are more faced with problems such as difficult transformation and high transformation costs. And the application in the Web 3.0 era often means that entrepreneurs have to change from a model in which 100% of APP sales profits flow to developers to a model in which a larger proportion is shared and symbiotic with users, which may reduce return expectations and lengthen the return cycle . Considering this series of difficulties, both current Web3.0 developers and entrepreneurs and traditional Web2.0 entrepreneurs and developers still face challenges when entering the Web3.0 field.
In addition, the high threshold of blockchain applications in the Web3.0 era is also an urgent problem to be solved: at the current stage, compared with traditional Web2.0 era APPs, Web3.0 applications still have higher user entry thresholds, for example, at least Need a wallet address, be familiar with wallet operation, or purchase public chain tokens and require basic operating knowledge, etc. This undoubtedly creates difficulties for a large number of ordinary user groups to enter. At the same time, most of the current public chains have a relatively large computing speed limit, which has not kept up with the rapid increase in the number of products built on their chains and the rapid influx of traffic, which means that this will lead to very high interaction costs on the chain. High, which will lead to a great increase in the use cost of the user group, directly affect the APP experience, and even bring difficulties to the normal operation of the entire project.
However, in the long run, Web3.0 applications will have a wider user base, because of the protection and confirmation of personal information and assets, coupled with a more excellent and regular business model, and the blessing of incentives from the internal economic model, can Make more users join the Web3.0 ecological economy, and make users and developers form a deep alliance. It is believed that these will become the core driving force for the long-term development of Web3.0 applications, and after experiencing the initial pains, the future will definitely belong to Web3.0.