What is digital currency spot trading?
Digital currency spot trading refers to the trading of digital currency in the form of instant delivery. In short, it means paying the money and delivering the goods, and the transaction is completed immediately.
What are the methods of digital currency spot trading?
1. Exchange trading
2. OTC transactions
2. OTC transactions
Over-the-counter transactions refer to transactions conducted outside digital currency exchanges, also known as over-the-counter trading markets or OTC trading markets. Unlike order-matching transactions in the open market, over-the-counter transactions are one-to-one transactions in non-public markets, which generally do not have unified trading rules and related systems. For example, traders can choose corresponding sellers to conduct transactions directly according to the price on the platform that provides OTC transactions, or post transaction requirements, and wait for buyers to contact and complete the transaction.
Digital currency spot trading rules
1. Trading hours
Digital currencies are traded 24 hours a day, 7* around the world. All transactions follow the T+0 (Trade+0 trading day transaction) system, which can be bought and sold at any time, and the transaction can be completed immediately.
2. Transaction direction
Digital currency spot trading has only one transaction direction of buying and selling - buying assets, selling them after the price rises, and earning the difference. Compared with leverage, the contract can be shorted, which belongs to two trading directions, by buying up and then selling, or selling down and then buying to earn profit from the price difference.
3. Trading pairs
In digital currency transactions, a target currency and a quote currency together form a transaction pair. For example, the BTC/USDT trading pair is composed of BTC and USDT. This trading pair shows that if you hold USDT, you can trade BTC with USDT, and vice versa, if you hold BTC, you can trade USDT with BTC.
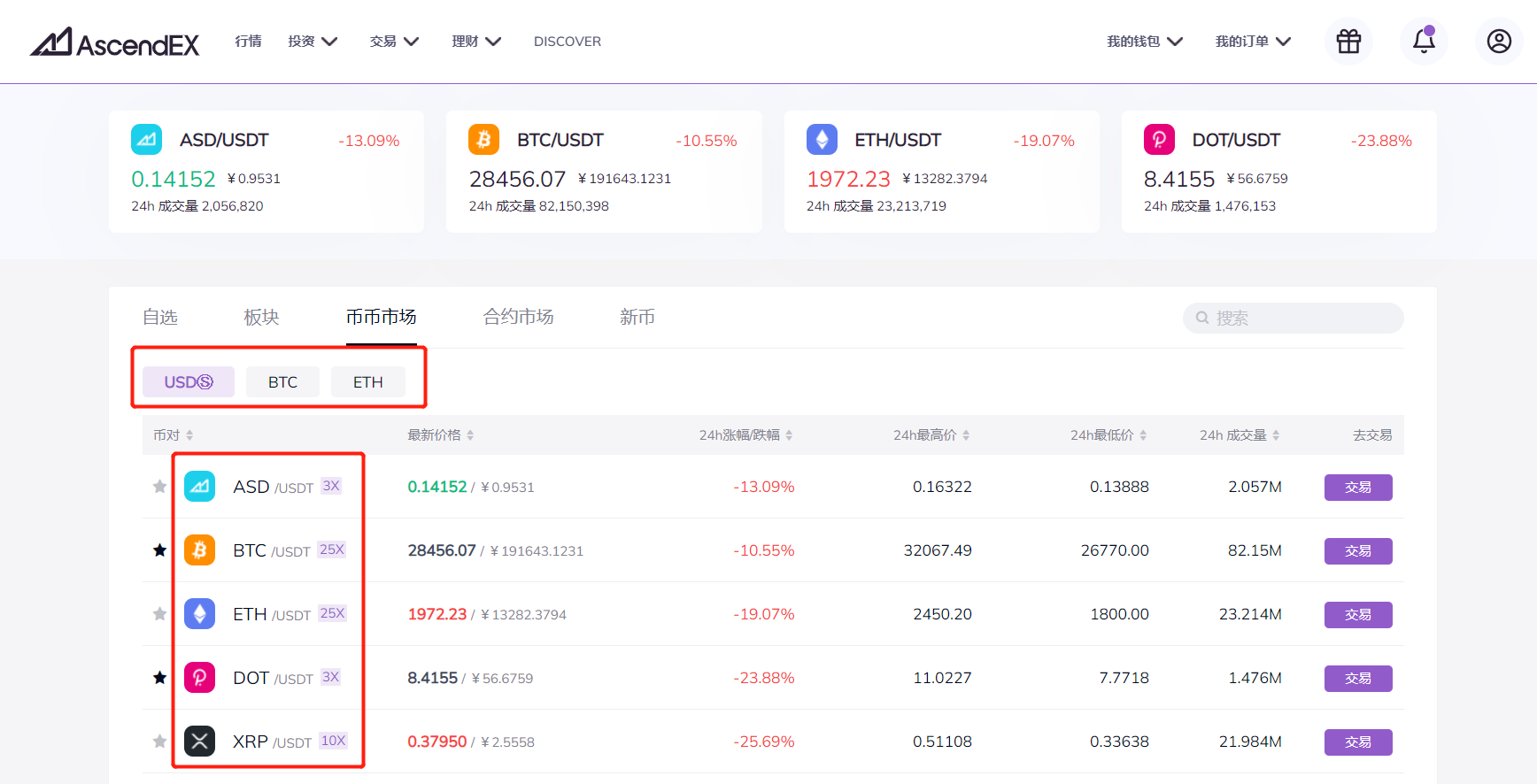
Generally, in a transaction pair, the currency in front is the target currency, and the currency in the back is the pricing currency. At the same time, the currencies that can usually be used as pricing currencies are mostly stable coins (USDT, etc.) and mainstream currencies (BTC, ETH, etc.).
4. Trading market
Digital currency spot transactions can generally be carried out in the currency market and the legal currency market. The so-called currency market refers to the exchange of currency for currency. In the currency market, usually more subdivided trading markets are divided by pricing currency, such as the USDT market, BTC market, and ETH market. The legal currency market refers to the direct exchange of digital currencies with legal currencies (such as US dollars, Japanese yen, etc.).
5. Price limit
Unlike traditional stock market trading with a price limit system, digital currency trading has no price limit. Therefore, digital currency transactions are generally volatile, and it is possible for a currency to rise several times a day or fall to zero.
6. K line
In digital currency trading, most trading platforms follow the K-line chart design of "green represents the positive line, and red represents the negative line". This is different from the "red sun and green yin" in the traditional stock market, but it is just a practice and not mandatory. Users can adjust and change the K-line display design according to their own trading habits.
7. Order entrustment type
Depending on the settings of the specific trading platform, the types of orders it provides may vary. But in general, mainstream digital currency trading platforms will provide several common types of order entrustment, such as market order, limit order and stop loss order.
(Note: The above rules specifically refer to on-site trading rules, and some of the rules are general rules for digital currency transactions, and also apply to digital currency leverage and contract transactions.)
What are the characteristics of digital currency spot trading?
1. Uninterrupted trading around the clock, real-time settlement of entering and exiting the market at any time, to meet the trading needs of traders.
2. All transactions are bid in the open market, and the system is uniformly matched, the information is relatively clear, and the price is more transparent.
3. The trading rules are simple and easy to understand, and the trading is flexible, and investors who are new to the market can also quickly participate.
4. After the order is placed, there is no need to operate frequently, and there is no need to worry about details such as margins for contract transactions, and the transaction risk is small.