
Staking usually refers to locking cryptocurrency as collateral to ensure the security of a certain blockchain network or smart contract agreement. Cryptocurrency assets pledged by equity are usually linked to DeFi liquidity, income rewards and governance rights. Use Cryptocurrency to pledge rights and interests, that is: lock the pass in a certain blockchain network or protocol to obtain returns; and these pass will be used to provide key services for users.
textThis article will discuss in depth the fundamental logic, operating mechanism and application scenarios in blockchain and DeFi ecology of cryptocurrency equity pledge. In addition, this paper will compareThe difference between the equity pledge mechanism and the existing blockchain network.
Blockchain equity pledge mechanism
textThe blockchain must ensure security and highlevel, it is necessary to establish an anti-Sybil attack mechanism to prevent a small group of nodes from attacking the network. If the anti-sybil attack capability of the blockchain is relatively weak, it may suffer from 51% attacks. A 51% attack refers to a small group of nodes conspiring to launch malicious attacks, such as rewriting blockchain history or manipulating users.
text
Proof of Stake (PoS) is an anti-Sybil attack mechanism on the blockchain. Verification nodes must pledge tokens in the network to have the opportunity to add new blocks to the chain. On the PoS blockchain, anyone who pledges a certain amount of native tokens can join the network to become a verification node (staker) and produce blocks. The amount of tokens staked by a validator or the number of validators run by a user usually determines its probability of being selected as a block producer. In other words, the more tokens you pledge, or the more verification nodes you control, the more likely you are to be selected as a block producer.
Validators typically receive staking rewards from the protocol, as well as a portion of user transaction fees, when they successfully create valid blocks. In order to reduce malicious behavior, the PoS blockchain often adopts a penalty mechanism. Under this mechanism, if the verification node violates the protocol rules, some or all of the pledged tokens will be confiscated. In some PoS blockchains, if the node goes offline or the block producing node fails to produce a block normally, the pledged pass will also be confiscated.
Three Types of Blockchain Staking: Proof of Work (PoW), Proof of Stake (PoS) and Delegated Proof of Stake (DPoS)
The anti-sybil attack mechanism of the PoW blockchain requires miners to compete with each other by solving computational problems, which is also the mechanism adopted by the Bitcoin blockchain. That is, the miner needs to generate a valid hash based on the information in a certain block. The first miner who solves the calculation problem, submits a valid block and obtains the consensus of the blockchain network will be rewarded. The Bitcoin blockchain automatically adjusts the difficulty of the calculation problem every 2016 blocks (note: about every two weeks), and its goal is to ensure that a block is generated every 10 minutes on average. The difficulty is usually adjusted based on the number of people participating in the miner (that is, computing power). If the number of miners increases, the difficulty will also increase accordingly to maintain the decentralization level of the network.
In the PoW mechanism, the probability of becoming a block node is proportional to the computing power consumed by the node. Therefore, although the PoW blockchain does not have an explicit pledge mechanism (note: the explicit pledge mechanism means that the user locks the cryptocurrency in the smart contract, and the money will be confiscated if the violation is violated), this type of blockchain does have an implicit pledge mechanism, because nodes will not only hold the network’s native certificates, but usually spend money on expensive hardware equipment to expand computing power in order to gain opportunities for block rewards, and usually these hardware cannot be used between chains. If miners cannot generate income through mining rewards, then the cost they spend on equipment and electricity is wasted. If network security cannot be guaranteed, the market value of mining equipment and native assets will also drop, which will indirectly lead to economic losses.
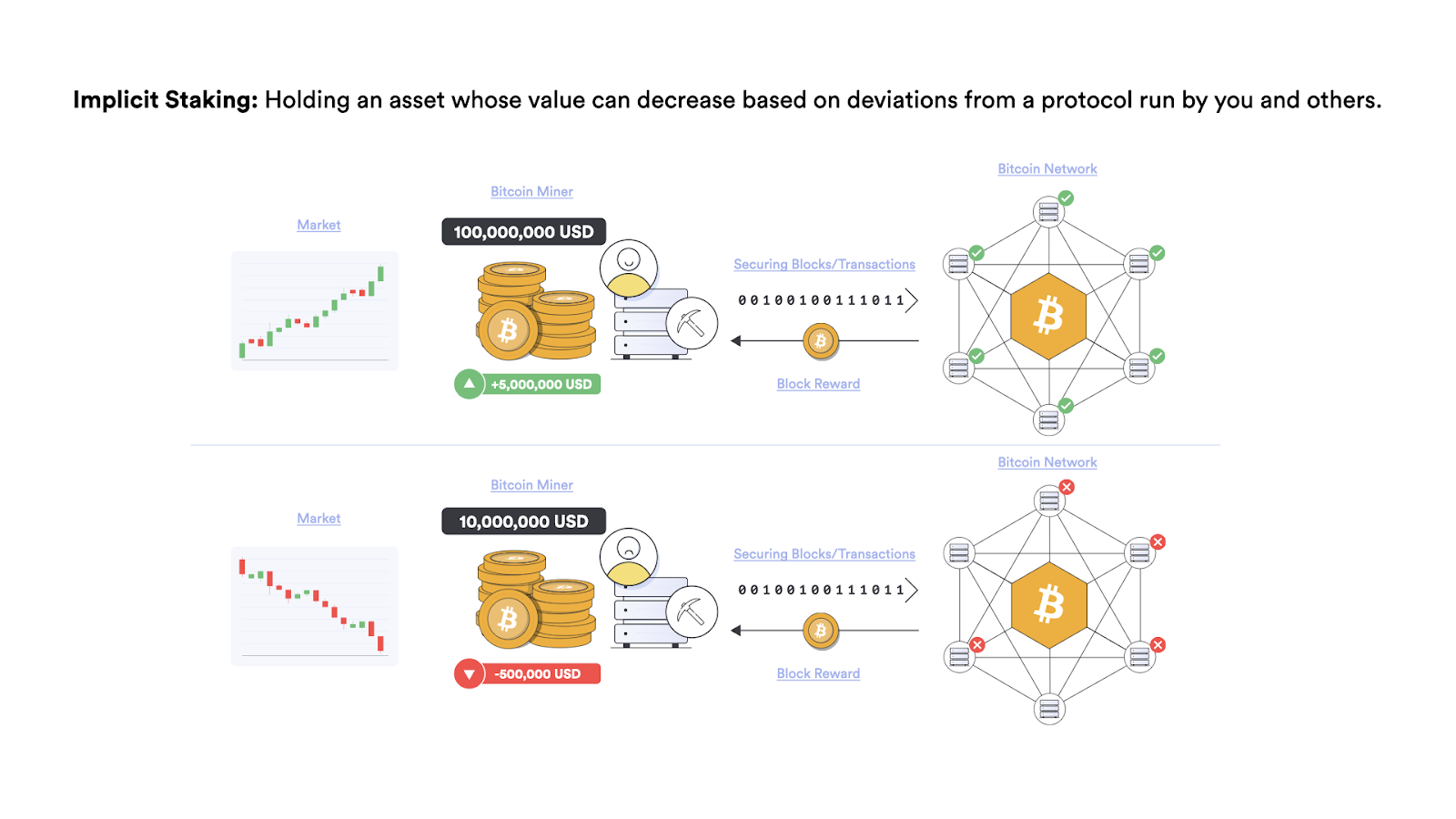
Although Bitcoin does not have a traditional pledge mechanism, it uses some kind of implicit pledge mechanism. Miners must work hard to maintain network security so that Bitcoin can maintain a high value and achieve profitability.
textThe Merge), transforming from PoW to PoS.
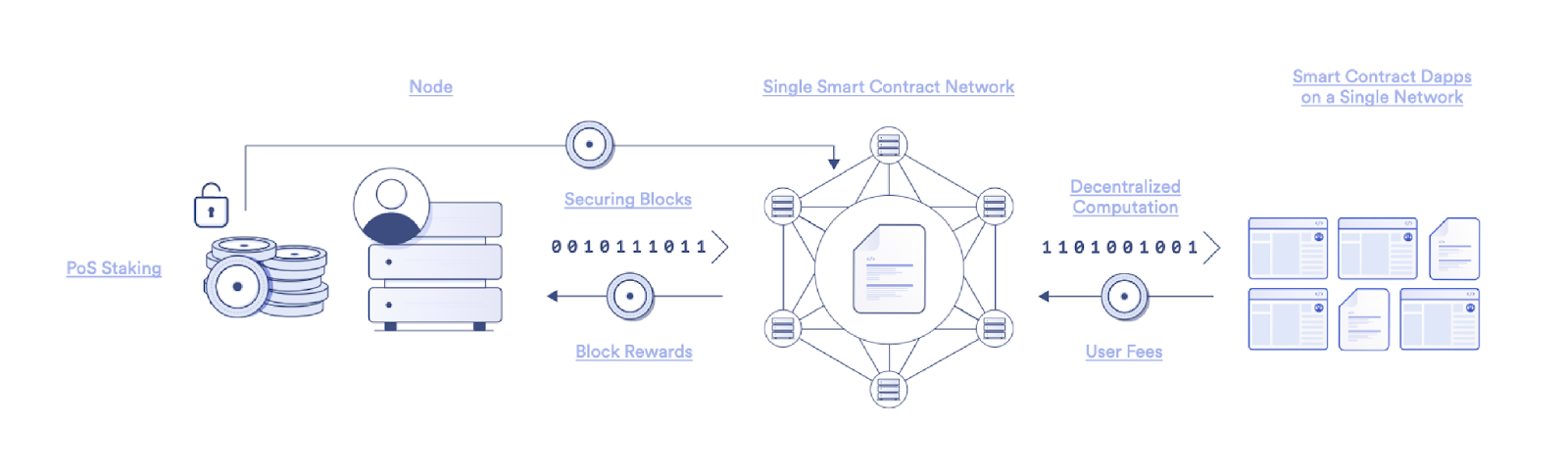
The PoS blockchain uses an explicit pledge mechanism, and the verification node pledges a certain amount of tokens as a deposit. If the node violates the protocol rules, the deposit will be confiscated.
Stake rewards
Stake rewards
Stakers in a blockchain network are economically incentivized to create valid blocks, and nodes receive transaction fees for each transaction as well as block rewards. That is, validators who successfully create blocks or validate blocks receive newly issued cryptocurrencies.
Different protocols will calculate equity pledge rewards in different ways, usually considering factors including the number of tokens pledged by each verification node, the duration of the verification node pledge, the total number of tokens pledged in the network, and the circulation of tokens in the total supply ratio etc. The PoS blockchain will use different methods to determine the reward distribution ratio, but generally speaking, the rate of return will be determined according to the total amount of tokens pledged in the network.
In some PoS systems, token holders can pool their resources (i.e. staking assets) together to increase the odds of being selected and winning staking rewards. If the equity pledge threshold is set in the network, even if the number of tokens in the hands of users does not reach the minimum threshold, they can still participate in the PoS blockchain through the equity pledge fund pool. Rewards will be distributed proportionally to stakers and the operation team of the fund pool.
Staking stakes in DeFi
Equity is pledged inDecentralized Finance (DeFi)Also common in protocols. The pledge of rights and interests in DeFi is not to ensure the safety of block chain generation, but to lock the token in the DeFi protocol to achieve a specific goal. Although the term "equity pledge" deviates from its original meaning in this case, it has become a common saying because it is commonly used in the industry.
The following are some examples of equity pledge in DeFi:
textAaveDecentralized lending agreements use equity pledge mechanism to stimulate liquidity, AAVE token holders can pledge their tokens in the security module of the agreement, providing additional security for depositors when black swan events occur and insurance. Users who pledge tokens can get rewards from the agreement.
textGovernance - goCurveThe equity pledge mechanism is adopted to coordinate the long-term economic incentives of liquidity providers and governance participants. CRV token holders can "vote-lock" the CRV in their hands and obtain voting entrusted CRV (ie: veCRV). The longer the user locks up, the more veCRV they will get. Token holders can vote on the protocol proposal through voting lock, determine the CRV rate of return in a certain liquidity pool, and share part of the transaction fee income of the protocol.
textProvide liquidity——SynthetixThe equity pledge mechanism is adopted to provide collateral for synthetic assets. Synthetic assets anchor the price of an off-chain asset and are mortgaged by pledged SNX. Users who pledge SNX will receive economic incentives, provide liquidity for the protocol, and receive equity pledge rewards and transaction fees generated by dApps using the Synthetix protocol such as Kwenta.
textAlchemixDeFi protocols such as DeFi use the equity pledge mechanism to issue tokens to the community and stimulate liquidity in the decentralized ecosystem. Users can obtain LCX tokens by staking tokens in the Staking Pools contract.
Comparison of equity pledge mechanism between blockchain network and oracle network
The role of the equity pledge mechanism in the decentralized oracle network is fundamentally different from that in the blockchain network. asChainlink 2.0 White PaperChainlink 2.0 White Paper"Understanding the similarities and differences between blockchain and oracle machines and their synergistic effects in one article"。
In general, the blockchain provides a service (ie: block verification) that follows a set of predefined and widely recognized rules. Therefore, the blockchain adopts this equity pledge mechanism to ensure the security of the entire network. In contrast, Chainlink’s decentralized oracle network provides a range of different services, including external data, off-chain computation, cross-chain interoperability, and data output to legacy systems, each of which can be flexibly Customized to meet the specific needs of users in terms of performance, budget and trust assumptions. Therefore, the oracle machine needs to establish a very flexible equity pledge mechanism to meet the specific needs of different users to verify external data and events.
The PoS blockchain uses an equity pledge mechanism to motivate honest nodes to reach a consensus on the validity of the block and pass a series of transactions. Penalty mechanisms for verification nodes include but are not limited to:
textA verification node generates two different blocks at the same block height, and re-signs (for example: re-signs multiple blocks).
textThe generated block contains invalid transactions, and the transaction amount does not exist in the account (such as double-spend transactions).
textThe block created by the verification node violates the protocol rules (for example: the number of tokens minted exceeds the upper limit of block rewards).
In the decentralized oracle network, the significance of the equity pledge mechanism is not to ensure the creation of valid blocks, but to ensure that reliable and tamper-proof oracle reports can be generated, and the reports can accurately reflect the state of the external world. Since the off-chain world itself is full of variables and uncertainties, different users may have different punishment mechanisms for oracle nodes, and in addition to the encryption technology, internal state, and internal rules mentioned above, it is necessary to establish other penalty mechanism. An on-chain service level agreement (SLA) will be signed between the oracle machine user and the oracle network, which stipulates the penalty conditions, reward and punishment mechanism, and which verification scheme to use to trigger the penalty mechanism.
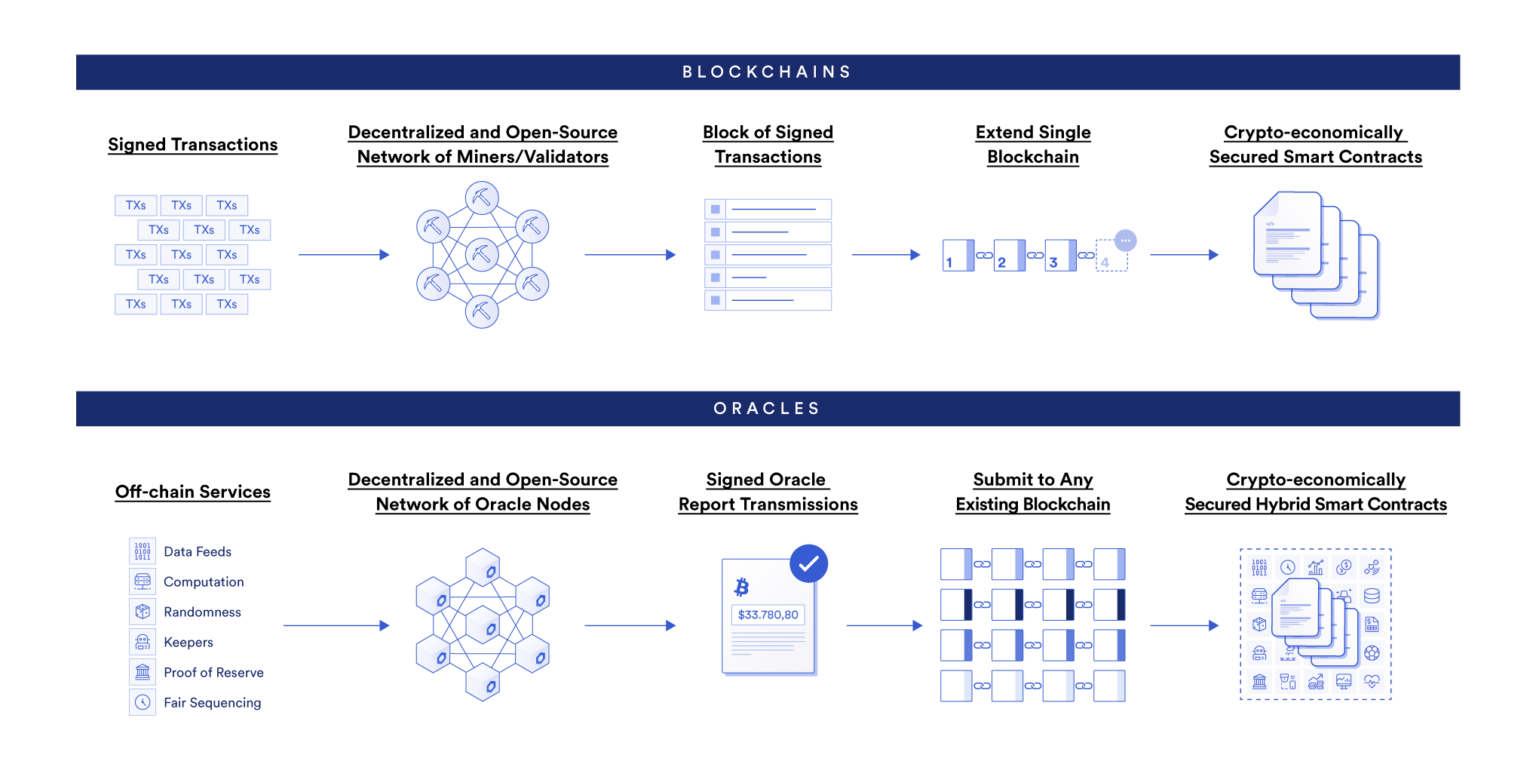
The blockchain verifies and reaches a consensus on the block where the transaction is located, while the oracle network reaches a consensus on external data and off-chain calculations.
Chainlink currently supports more than 800 oracle networks distributed across various services and blockchains. Chainlink is working hard to develop an explicit pledge mechanism, which covers various customized fine mechanisms, reward and punishment mechanisms, and verification schemes, and is compatible with various blockchains. Therefore, Chainlink's explicit staking mechanism can incentivize honest oracle node operators and flexibly customize various Chainlink oracle networks and services.
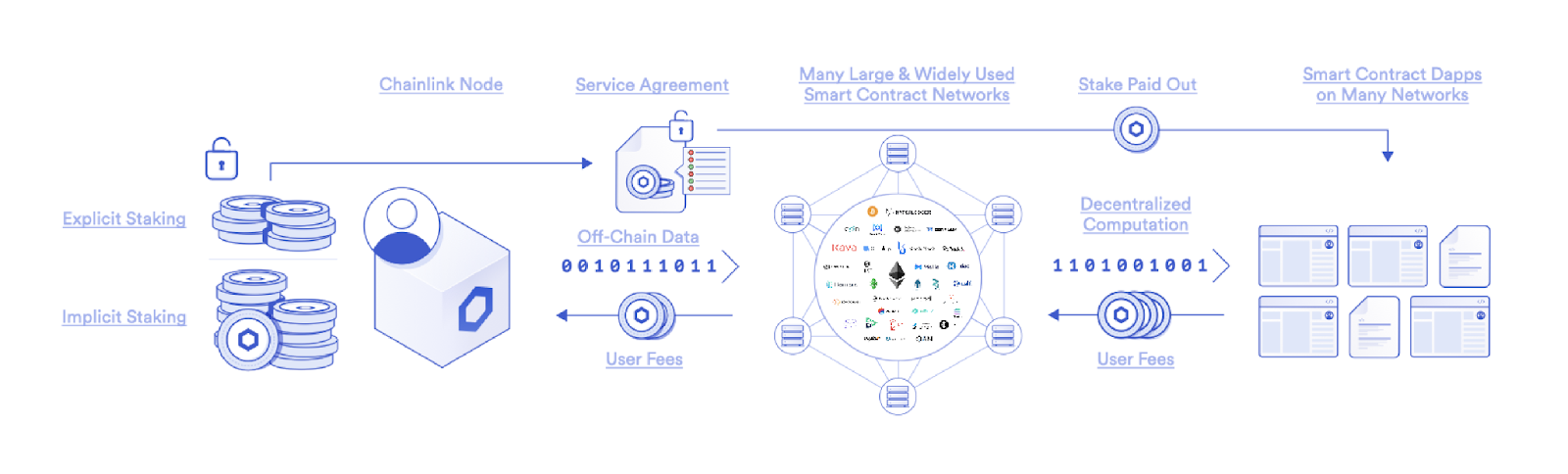
image description
It is worth noting that the equity pledge mechanisms of blockchain, DeFi, and oracle networks have one thing in common, that is, users who pledge tokens to ensure the normal development of services can share a portion of user transaction fees. As the number of protocol users continues to grow, stakers can share more and more transaction fees.
The future development prospect of equity pledge
The encrypted economic model of equity pledge is becoming more and more mainstream in the smart contract ecosystem, and can be directly applied to the oracle network. The original purpose of equity pledge is to ensure the security and economic sustainability of the blockchain, and it is now widely used in DeFi protocols to manage liquidity and protocol governance. In addition, the Chainlink oracle network will also further enhance security by adopting a stake pledge mechanism.
textTo learn how staking will improve the security of the Chainlink oracle network, read"Chainlink Equity Pledge Mechanism Overview", or watch Chainlink co-founder Sergey Nazarov talk about,subscription
To learn more, please visitchain.link,subscriptionChainlink newsMore articles on this topic@chainlink。
More articles on this topic