
Author | Chenglin Pua (Malaysia) editor | Yu Baicheng typesetting | Wang Jilongyan
2021 is called the first year of the metaverse. Since the outbreak of the new crown epidemic, more and more people's activities have been shifted online, which has also attracted unprecedented attention to the Metaverse.
Many companies are announcing their forays into the Metaverse in 2021. Meta's "All In" metaverse, and Microsoft, the world's top two market capitalization, also has a presence in the metaverse. Chip giants such as Nvidia, AMD, and Qualcomm have successively deployed metaverse-related businesses.
first level title
Seoul to create a metaverse city
On November 3, 2021, Seoul Mayor Oh Se-hoon proposed the Seoul Vision 2030 (The Seoul Vision 2030) plan, which aims to make Seoul a city of coexistence, a global leader, a safe city and a future emotional city. The five-year Metaverse Seoul Basic Plan is part of a future city vision that aims to improve social mobility among citizens and enhance the city's global competitiveness. Currently, Seoul plans to invest 3.9 billion won (about 21 million yuan) in the project.
According to the plan, the metaverse ecosystem in Seoul is mainly carried out in three stages, namely introduction (2022), expansion (2023-2024), and settlement (2025-2026).
Seoul plans to establish a high-performance platform called Metaverse Seoul in the first phase of 2022, and provide services in the fields of economy, education, and tourism, and complete the creation of the platform before the end of the year and present it to the public. In the future, the Seoul Metropolitan Government will also expand the application of the Metaverse platform to all areas of municipal management to improve the work efficiency of government officials.
Mayor Oh Se-hoon has said in an interview that if the project becomes a reality, Seoul citizens will soon be able to don their VR devices and meet with city officials for virtual consultations. Likewise, municipalities can participate in mass events.
According to the five-year "Basic Plan for Metaverse Seoul", the Metaverse platform is tentatively named "Metaverse Seoul" and will be completed by the end of next year. Globally, the Seoul Metropolitan Government is the first local government to formulate a comprehensive mid- to long-term metaverse policy plan. According to the plan, the Seoul Metropolitan Government will successively provide various business support facilities and services on the Metaverse platform, including the virtual mayor's office, Seoul Fintech Lab, Seoul Investment, and Seoul Campus City.
In this plan, the services provided by the built metaverse will cover seven basic areas including economy, education, tourism, communication, city, administration and infrastructure. The Seoul Metropolitan Government has also specifically formulated policies to provide public services to overcome problems such as time and space constraints and language barriers in the real world through the metaverse platform developed using advanced technology.
In the economic field, Seoul will set up the Seoul Fintech Lab in the Metaverse. Its purpose is to provide relevant services in the economic field in the virtual world. The Seoul Fintech Lab will help companies attract foreign investment in the metaverse, and virtual characters will provide consulting and one-stop services for foreign investors.
In addition, the startup incubation business in Campus Town, a Seoul startup camp set up by Google for entrepreneurs, will be carried out on the Metaverse platform, including digital content creation training and social activities.
In terms of education, the most active field in the Metaverse, the Seoul Metropolitan Government will host the virtual campus of Seoul Open City University. Seoul Learn, an online education platform operated by the Seoul Metropolitan Government, will provide teenagers with various immersive content such as lectures, mentorship programs and job fairs.
In terms of tourism, Seoul will build tourist attractions, such as Gwanghwamun Square, Deoksugung Palace, and Namdaemun Market, which will become special areas for virtual tours of Metaverse Seoul. According to the Seoul Metropolitan Government, tourists can take a city tour bus to tour the Metaverse. Seoul's representative festivals and exhibitions, such as the Seoul Drum Festival and the Seoul Lantern Festival, cannot be held due to the epidemic. In the future, they can be held as 3D immersive content on the Metaverse platform.
Then there are public services, such as civil complaints, consultation, and reservation of public facilities. The above services will also be provided in Metaverse to provide citizens with more convenient services, which will also improve the overall digital city level of Seoul. The Seoul Metropolitan Government will also create a metaverse version of the mayor's office at City Hall in the future, and use it as an open communication channel between the government and residents.
Seoul also plans to upgrade city management using a combination of virtual reality, augmented reality, and extended reality. Numerous services are provided to ensure the safety and convenience of vulnerable groups, including the use of extended reality devices to provide safety and convenience services for people with disabilities.
Finally, Seoul will introduce the Metaverse Conference to hold different events and use it as a communication channel. Seoul will also develop a metaverse-based remote work environment using state-of-the-art technology. The Seoul Metropolitan Government said it will launch a smart office in a virtual space. Avatars of public officials offering counseling services will become a reality.
In the announcement, Seoul Metropolitan Government officials stated that the Metaverse ecosystem was built to expand access to public city services. But the Seoul government also said that current professional equipment for VR/AR and extended reality may be expensive for many people and not as popular as smartphones and computers.
image description

image description
first level title
text
In May 2021, the South Korean government launched the Metaverse Alliance to support the development of Metaverse technologies and ecosystems. The Metaverse Alliance initially consisted of 17 companies, including major wireless carrier SK Telecom and auto giant Hyundai Motor Co, as well as eight industry groups including the Korea Mobile Internet Business Association. With the South Korean government vigorously promoting Metaverse-related projects, the alliance now includes more than 500 companies and institutions, including Samsung and KT (Korean telecom giant).
In this alliance, companies and industry groups will share Metaverse trends and technologies, and form an advisory group on ethical and cultural issues related to the Metaverse market. The alliance will also undertake joint metaverse development projects. South Korea's Ministry of Science and ICT said it would provide support to the consortium, especially in helping companies build open Metaverse platforms.
first level title
The widening gap between the rich and the poor indirectly gave birth to the metaverse boom
In South Korea, more and more young people of the MZ generation are throwing themselves into the metaverse world. The MZ generation generally refers to young people born in the 80s and 00s in South Korea. Young people in South Korea are very welcome to Metaverse. According to expert analysis, the reasons behind this phenomenon are the soaring housing prices and the huge income gap between the rich and the poor.
Kim Sang-kyun, a professor of industrial engineering at Kangwon National University in South Korea, has published two best-selling books on the Metaverse. He commented on this: The fandom for the metaverse reflects the sadness and anger of the polarized MZ generation. Unlike the older generation, the MZ generation is a generation that communicates with the world through devices from birth. The MZ generation generally doesn't see the metaverse as an alternate reality, instead it's just another part of their lives.
image description
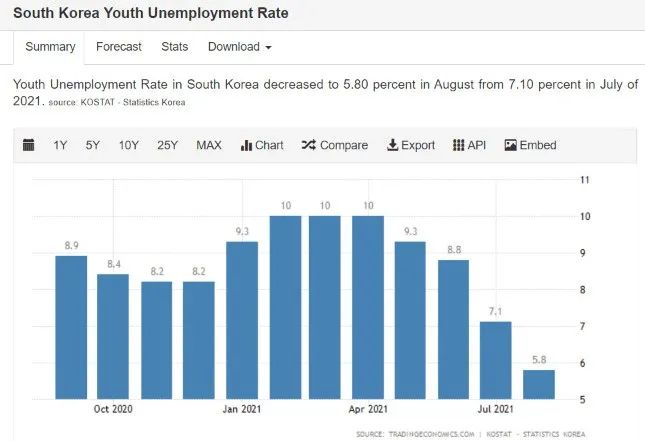
image description
Source: Trading Economics
Many Korean college students are facing the state of unemployment upon graduation. Under such a predicament, the madness of blockchain products such as Crypto and NFT has attracted the attention of young Koreans. "The Verge" published an article saying: "For young Koreans, Crypto seems to be a rare opportunity to turn around."
Many young people were interviewed by "Seoul Shimbun" and said that they could not buy a house in Seoul anyway with the money they have worked for a lifetime. It is better to invest in Crypto or NFT. This may be "the last chance to change your life." Many young Koreans are unwilling to succumb to the current social status quo, and hope to gain hope to change their situation.
The "Korea Times" recently released some survey data: Nearly a quarter of college students in South Korea are speculating in Crypto, and one-third of investors are young people in their 20s. The proportion of boys investing in Crypto is 34.4%, while that of girls is slightly lower at 14.4%.
IGA Works, a South Korean mobile big data platform, conducted a survey on why it entered the Crypto industry. 33% said it was because of the high return on investment, and 31% said it was because the investment threshold was low and there was no need to have a lot of money. And 15.1% of people pointed out that this is the last way to overcome class solidification and achieve class advancement.
In the virtual world, people can buy virtual real estate, hold parties, shop, and even work, and the impact of these actions is very similar to the real world. For example, in Decentraland, a virtual world based on the Ethereum blockchain, users can buy, sell and build blockchain assets. After users purchase virtual real estate in Decentraland, they can build and operate real businesses on this land, such as nightclubs that charge other users access fees, stores that sell virtual goods, and so on.
In Decentraland, land near popular areas is usually more valuable than other land, and if a good supporting store or facility is built around a certain land, the price of the land can also increase. The real estate hype in Decentraland is even more exaggerated than in the real world: when Decentraland held its first land auction in 2017, some plots sold for about $20, and now, just four years later, they are changing hands for hundreds of thousands of dollars.
Decentraland once issued a statement that the number of users in South Korea reached 7,067, second only to the United States in the platform. Another metaverse land platform "Earth 2" stated that Koreans on its platform are the most active users, and have spent about 9.1 million US dollars (about 58.08 million yuan) on its platform.
A 37-year-old user of "Earth 2" said in a survey that he chose to buy the virtual land of "Earth 2" because he couldn't afford the Gangnam area (a rich area in Seoul, South Korea) in reality. In addition, the construction of the metaverse will not be affected by the epidemic, there will be no labor shortages or soaring construction costs.
The metaverse platforms mentioned above are not regulated by the governments of various countries and are easy to get hyped. Recently, South Korea has resorted to heavy blows to restrict the development of Crypto, and the development of its own metaverse is bound to supervise this field. Although there are still fewer Korean citizens participating in the "investment" related to the Metaverse than Crypto, there will inevitably be regulatory issues with the development of the decentralized Metaverse in the future.