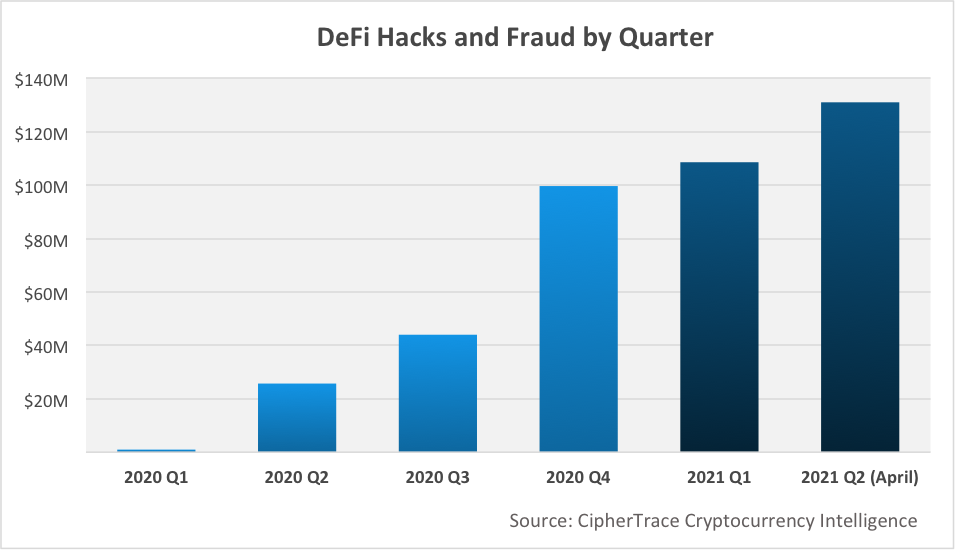
According to the CipherTrace report in May 2021, as of the end of April 2021, the amount of theft, hacking and fraud in the encryption field reached 432 million US dollars, and Defi hacking cases accounted for more than 60% of all hacking attacks, which is higher than 25% in 2020. From the figure below, it can be clearly seen that the cases of DeFi hacking attacks are increasing year by year, and the stolen amount in Q2 of 2021 is about 130 million US dollars.
Among the many cases of DeFi hacking attacks, Flashloan is undoubtedly the most common type of hacking attacks. Flashloan is an unsecured, unsecured loan that can provide a large amount of funds in a short period of time. The smart contract for the loan must be completed in the same transaction as the loan, so the borrower must use other smart contracts to help him at the end of the transaction. Execute instant transactions with loan funds. This has led to hackers exploiting loopholes in the code to manipulate pricing and profit from it.
We have counted the cases of Flash Loan hacking in the past two weeks:
1. PancakeBunny BSC ecology
On May 19th, PancakeBunny was attacked by a flash loan from an external developer. The hacker used PancakeSwap to borrow a large amount of BNB, and then continued to manipulate the prices of USDT/BNB and BUNNY/BNB to obtain a large amount of BUNNY and sell them, causing the price of BUNNY to crash. Finally, the hacker exchanged BNB back through PancakeSwap. In this flash loan attack, the estimated loss is 114,631.5421WBNB and 697,245.5699BUNNY, totaling about 45 million US dollars. The price of the token BUNNY once fell below $2, with the highest drop exceeding 99%.
2. Bogged Finance BSC ecology
On May 22, hackers carried out a flash loan attack on the vulnerability of the pledge function of the BOG token contract. The loophole is designed to be deflationary by charging 5% of the transfer amount. Specifically, of the 5% fee, 1% is burned and 4% is used as a fee for staking profits. However, the implementation of the token contract only charges 1% of the transfer amount, but still inflates 4% as staking profit. As a result, attackers can use borrowing to significantly increase the amount of staking, and repeatedly perform automatic transfers to claim inflated staking profits. Immediately afterwards, the attacker sold the inflated BOG for approximately $3.6 million in WBNB.
3. AutoShark BSC ecology
On May 24, AutoShark was attacked by flash loans. According to the analysis of SlowMist:
1). The attacker lent a large amount of WBNB from Pancake's WBNB/BUSD trading pair;
2). Exchange half of all WBNB lent in the first step to a large amount of SHARK through Panther's SHARK/WBNB trading pair, and at the same time, the number of WBNB in the pool increases;
3). Enter the WBNB and SHARK in Step 1 and Step 2 into SharkMinter to prepare for subsequent attacks;
4). Call the getReward function in the WBNB/SHARK strategy pool in the AutoShark project. This function will draw a part of the service fee from the user's profitable funds and reward the user with SHARK tokens as a contribution value. This part of the operation is in the SharkMinter contract operate;
5). After the SharkMinter contract receives the LP handling fee earned by the user, it will re-split the LP into corresponding WBNB and SHARK, and re-add it to Panther's WBNB/SHARK trading pool;
6). Since the attacker has entered the corresponding tokens into the SharkMinter contract in advance in step 3, when the SharkMinter contract removes liquidity and then adds liquidity, it uses the WBNB and SHARK balance of the SharkMinter contract itself Add, this part of the balance includes the balance that the attacker entered into SharkMinter in step 3, resulting in the wrong balance of added liquidity obtained by the final contract, that is to say, the SharkMinter contract mistakenly believes that the attacker has entered a huge amount of handling fees into in contract;
7). After the SharkMinter contract obtains the amount of the handling fee, it will calculate the value of the handling fee through the tvlInWBNB function, and then mint SHARK tokens to the user according to the value of the handling fee. However, when calculating the value of LP, the real-time number of WBNB in the Panther WBNB/SHARK pool is divided by the total amount of LP to calculate how much WBNB LP can exchange. However, since in the second step, the number of WBNB in the Panther pool is already very large, the value of the calculated LP is very high;
8). In the case of the wrong LP value and the wrong amount of handling fees, the SharkMinter contract finally calculated a very large value when calculating the attacker's contribution, which caused the SharkMinter contract to mint a large number of SHARK tokens for the attacker. currency;
9). The attacker subsequently sells SHARK tokens to exchange for WBNB and repay the flash loan. Then take a profit and leave.
This incident caused the price of AutoShark to crash, falling to $0.01, a drop of more than 99%.
4. MerlinLabs BSC ecology
On May 26, MerlinLabs, a DeFi revenue aggregator, was attacked. The attack method was similar to that of PancakeBunny, with a loss of 200ETH.
5. JulSwap BSC ecology
On May 27, the DEX protocol and the automated liquidity protocol JulSwap were attacked by flash loans, and $JULB fell by more than 95% in a short period of time.
6. BurgerSwap BSC ecology
The automatic market maker BurgerSwap was suspected of being attacked by a flash loan, and more than 432,874 Burgers were stolen, worth about $3.3 million. The attackers have realized profits through 1inch. Some investors lost nearly 97%.
7.Belt Finance BSC ecology
On May 29, Belt Finance suffered a flash loan attack. The attackers used flash loans to obtain more than $6.2 million in funds from the Belt Finance protocol through 8 transactions, and converted most of the funds into anyETH and extracted them to Ethereum. The loss was $6.2 million.
The above hacked projects all have one thing in common, that is, they all belong to the BSC ecosystem. Since May, the BSC ecological project has been attacked by lightning loans, and the total loss has exceeded 157 million US dollars. The huge amount of losses also sounded the alarm for developers: flash loans are something developers must consider when creating smart contracts.
DeFi has always been considered as a new paradigm of future finance, and its emergence also allows us to participate in brand new financial transactions. However, due to the complexity of the technology stack, certain functions may be misused in completely unrelated parts of the system, causing huge losses, which not only harms the interests of investors, but also casts a stain on the project and the industry , so that outsiders flinch.