Foreword:
Accounting is an important part (essence) of economic management activity. It is an economic management activity aimed at improving economic efficiency, using currency as the main unit of measurement, and using special methods to conduct accounting and supervision (basic functions) of the economic activities of entities, enterprises, and institutions.
Among them, accounting is the comprehensive, continuous and systematic recording and reflection of the economic business that occurs or is completed by enterprises and institutions. Supervision is to review and inspect the legality, compliance and effectiveness of the economic business that is accounted for.
Similarly, we will analyze PlatON's economic model from the perspective of accounting, and record and reflect the relevant economic businesses in the system comprehensively, continuously and systematically. This is the first article in the series, and the follow-up will modularly interpret the accounting subjects in PlatON on the basis of an overview, so stay tuned!
secondary title
In PlatON's economic plan, from an accounting point of view, the economic activities included mainly include: initial issuance, additional issuance, rewards, penalties, handling fees, miners' fees and other major economic activities. The generation of every economic activity involves the transfer of Token (in the public chain, Token is the main currency unit of measurement).
In PlatON's economic plan, from an accounting point of view, the economic activities included mainly include: initial issuance, additional issuance, rewards, penalties, handling fees, miners' fees and other major economic activities. The generation of every economic activity involves the transfer of Token (in the public chain, Token is the main currency unit of measurement).
Similarly, from the perspective of accounting identity rules, in the PlatON network, any economic business will not change the balance of accounting equations. By using accounting identities combined with accounting bookkeeping methods (double-entry bookkeeping), the Various economic and business activities in PlatON are intuitively reflected.
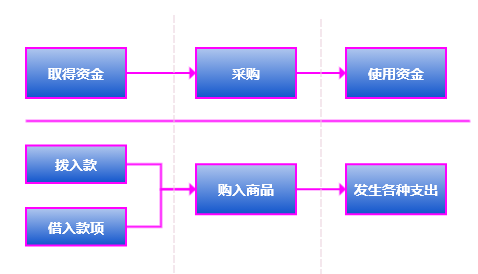
From the comparison of the above pictures, we can find that if the entire system of PlatON is regarded as a large-scale commercial company, its economic model dominates various economic businesses, and all subjects participating in the system will be accompanied by Token changes, that is, corresponding economic activities have occurred.
Economic activity on PlatON:
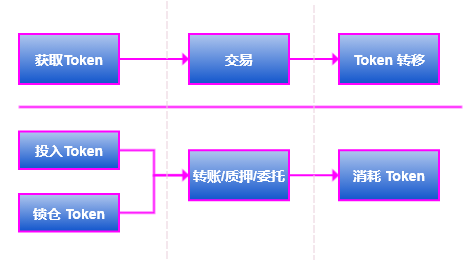
From the comparison of the above pictures, we can find that if the entire system of PlatON is regarded as a large-scale commercial company, its economic model dominates various economic businesses, and all subjects participating in the system will be accompanied by Token changes, that is, corresponding economic activities have occurred.
Income: The total inflow of economic benefits formed by an enterprise in its daily activities such as selling goods and providing services. In PlatON, the block rewards obtained by the daily activities of miner nodes are part of the main income of miners.
In accounting and bookkeeping, it is necessary to set up corresponding accounts before bookkeeping. Account setting needs to be defined in combination with accounting elements. In accounting, accounting elements are a simple classification of accounting objects, mainly including six accounting elements: assets, liabilities, owner's equity, income, expenses and profits. in:
Assets: Refers to the resources formed by past transactions or events, owned or controlled by the enterprise, and expected to bring economic benefits to the enterprise. In PlatON, assets mainly refer to Tokens held by various entities.
Liabilities: Refers to the debts undertaken by an enterprise that can be measured in currency and need to be repaid with assets or labor. In PlatON, we define Tokens to be issued as liabilities.
Owner's equity: refers to the remaining equity enjoyed by the owner after deducting liabilities from the assets of the enterprise, or the investor's right to claim the net assets of the enterprise.
Income: The total inflow of economic benefits formed by an enterprise in its daily activities such as selling goods and providing services. In PlatON, the block rewards obtained by the daily activities of miner nodes are part of the main income of miners.
Expenses: It is the outflow of economic benefits from daily economic activities such as sales of products and provision of labor services. In PlatON, the transaction fee for the subject to send the transaction loss is the fee.
A rule that every accountant knows, the accounting equation:
A rule that every accountant knows, the accounting equation:
Expenses + Assets = Liabilities + Owner's Equity + Revenue
Expenses + Assets = Liabilities + Owner's Equity + Revenue
In order to clearly record the economic activities of each subject in PlatON, track and verify the correctness of the economic model, ensure system stability, data correctness, etc., and improve economic benefits. Combining the double-entry bookkeeping theory of accounting, starting from different subjects and setting up accounting subjects, we introduce the principle of accounting identity into the PlatON economic model.
Here is the flexible use of the basic functions of accounting: accounting and supervision. The occurrence of any economic business will not change the balance relationship of the accounting identity. Based on this principle, the entire economic model system of PlatON can be monitored and verified. By combining accounting-related knowledge points, the PlatON system can be well verified and the economic model of the entire system is further strengthened.