In fact, there is no need to review the third quarter of DeFi. I believe everyone still has a deep impression. After all, who hasn’t dug up a few sweet potato pearls, but this kind of experimental assets are basically yellow now, and those who have earned two days are considered lucky. Hey, the Hotdog that returns to zero when it goes online really turns us into dogs, which shows that the soup is not so delicious. The high yield of YieldFarming (yield farming) has brought a large number of users and liquidity in a short period of time. The decline in yield in the later period is an inevitable event. However, after the correction in October, YFI, which has attracted much attention, performed well. The more friendly fork project YFII Second Uncle has not seen any obvious decline. We can still look forward to the future development direction of DeFi.
Next, we may turn our attention to another sector of DeFi-financial derivatives.
Andre Cronje, the founder of YFI, announced a new project Deriswap at the end of November. Deriswap is a new DeFi protocol. The project aims to provide transactions, options and loan products that improve capital utilization.
In a blog post on Medium, Cronje said: Deriswap (currently under audit), combines Swaps, Options, and Loans into a single contract that is highly capital efficient, allowing the two assets that make up the pair to interact ".
This is not the first time that options have appeared in the mouths of well-known founders. In fact, Huobi and Matrixport have already been laying out the options market for digital currencies. So far, Binance and OKEx have their own option products (BinanceFutures, OKEx Futures).
Although perpetual contracts and delivery contracts are still the absolute mainstream in the various derivatives exchanges we know, the views of major exchanges on options are generally neutral and optimistic. Options as financial derivatives We can also look forward to how options will develop in the DeFi field.
secondary title
Options: A good tool for risk hedging
Options (Options) is a right that can be exercised at a certain time in the future. After the buyer of the option pays a certain amount of option premium to the seller, he can obtain this right: buy or sell at a certain price in a certain time in the future Out of a certain amount of underlying assets, this is option trading. So, in other words, option trading is to buy and sell options as a commodity.
Compared with delivery contracts, options still have many differences, which are mainly reflected in three aspects:
1. The rights and obligations of buyers and sellers are different
The delivery contract that everyone is familiar with is a two-way contract, that is to say, the rights and obligations assumed by the buyer and the seller in the transaction are equal, and when the delivery date arrives, both parties must conduct the transaction according to the agreement.
The option is a one-way contract, the call (call) and put (put) of the option contract are not two directions of a contract, but two contracts. Each contract can be bought or sold. When predicting the direction of future price changes, buying a call option or selling a put option is bullish for the future market, but the two contracts are traded, and the income is different.
For the buyer of the option, after paying a certain option fee, he can obtain the right to buy or sell the asset as agreed in the contract. When the exercise date is reached, the buyer of the option can choose to execute or not to execute. Enjoy the rights, without any obligations. The option seller must bear corresponding obligations.
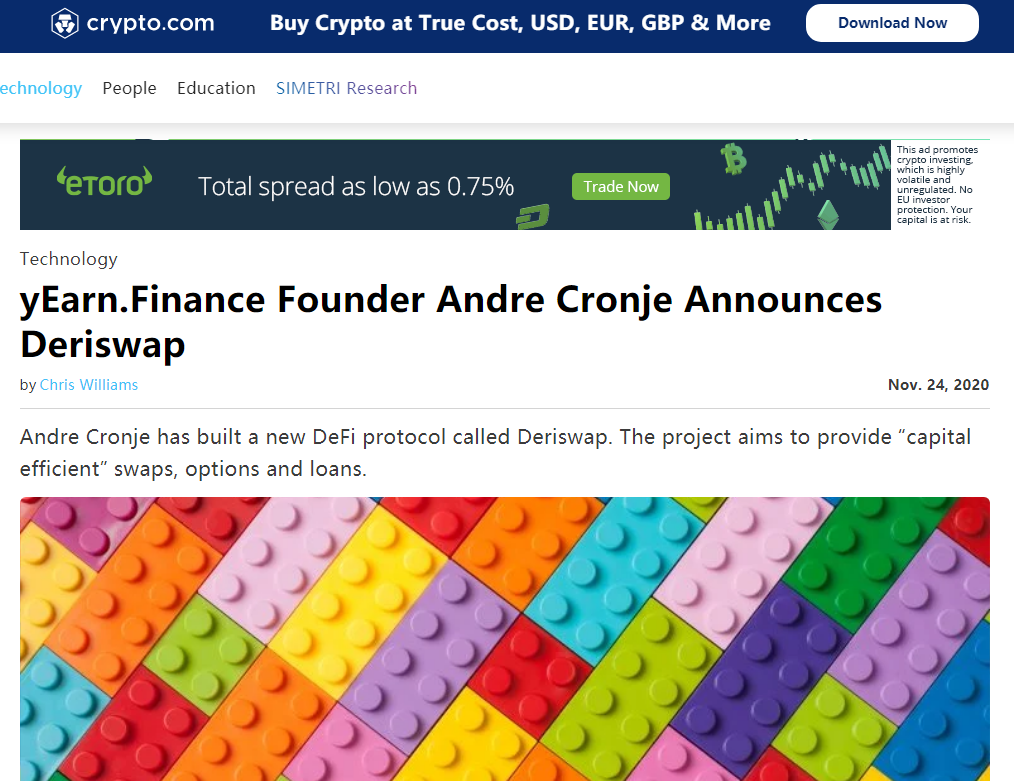
This feature gives options a unique advantage in the digital currency market, that is, it can avoid falling short of the market. For example, when BTC is hovering at 11,000 US dollars, everyone is worried that the top will fall, and they dare not enter the market, but they are also worried that BTC will suddenly rush to 12,000 and never look back, but they will be perfectly empty. Options are the solution. The problem. We can use a small amount of funds to buy BTC options. Once the market really rises sharply, we can use options to buy the corresponding amount of bitcoins at the price before the rise, so as to obtain a large amount of income; if the market continues to fall, we can also There is no loss if you forego exercising the option.
2. Margin collection rules are different from leverage rules
In the delivery contract, the buyer and the seller need a certain margin. In the option contract, the buyer only needs to pay the option fee, and does not need to pay a margin for the position, while the seller needs to pay a certain margin for the position, but can get the option fee from the buyer first.
Such rules enable option trading to increase the funds available to both buyers and sellers, making everyone's use of funds more flexible.
Unlike the rules of margin, the leverage and delivery contracts of options are also different. The leverage of the delivery contract is selected by the user and is fixed unless the user changes it manually. After selecting the leverage, decide how much margin you need to pledge to open a position. The leverage of option contracts is variable and determined by the market price, and users cannot choose by themselves. Therefore, the leverage of option contracts is only provided for users’ reference, and the degree of stimulation of the option contract can be roughly judged by the level of leverage.
3. The profit and loss characteristics are different from the liquidation rules
The trading modes of options and delivery contracts are different, and the profit and loss characteristics of the two are naturally different.
In the options market, risk has certain restrictions. For the option buyer, the loss must be limited, because no matter whether you make money after this option, you have to pay a certain option fee first. The biggest loss is the option fee, but if you make a profit, the profit will follow. Favorable changes in the underlying assets will increase, and if the direction is accurate, unlimited profits can be earned.
For the option seller, the profit is limited, because what you earn is only the option premium paid by the buyer, and if you lose money, you have to bear the risk of forced liquidation of the entire margin. Therefore, as far as the buyer is concerned, options are less risky than delivery contracts, but the profit margins are similar.
As for the seller, why should he unconditionally undertake the obligation of performance? Because although the seller unconditionally assumed the obligation, he also unconditionally obtained the option premium. For buyers to buy up, there are no more than three kinds of market conditions-rising, sideways and falling. Only when the market rises and the profit brought by the rise is greater than the option premium, the option will be executed and the profit will be obtained. On the contrary, it is the seller's profit (option premium). In other words, it is also a game. The buyer predicts the big market and chooses hedging, while the seller chooses high probability.
Because only the seller bears the risk of liquidation, the rules for liquidation are also quite different from delivery contracts. In a delivery contract, both buyers and sellers face unlimited profits and losses. If there is no margin call, the position will be forced to close at most and the margin will be lost.
If you are buying an option contract, you will not be forced to close the position before the expiration date, but if the market keeps moving in a direction that is not good for you, then the value of your option contract will approach zero infinitely. If the right cannot be exercised on the day of the right, it will be reset to zero. However, if the option contract is sold, there will be a possibility of forced liquidation. Because the seller of the option contract needs to undertake the obligation to perform the option contract when it expires, the trading platform needs to ensure that the assets in its account are sufficient to guarantee the performance of the obligation, and if it is not enough, a forced liquidation will occur.
secondary title
Analysis of DeFi option projects
Opyn
Opyn v1 can be said to be one of the earliest DeFi options protocols on the market. Through this protocol, anyone can create, buy and sell options on any ERC20 tokens. However, Opyn currently does not have a very large share of the decentralized options market. ideal.
In this regard, the Opyn project developed the v2 version of the protocol, aiming to lay the foundation for a more efficient and highly liquid options protocol. Currently, the Opyn v2 contract is being audited, and we can still analyze the v2 version a little bit.
Consistent with the mainstream of the current options market, Opyn is also an executed European option, that is, the option holder can only exercise the option when it expires.
At the same time, Opyn implements cash settlement, that is, option holders do not need to provide underlying assets to exercise options. Instead, options are settled in collateralized assets, with the option holder receiving the difference between the underlying asset's expiration price and the strike price from the option seller.

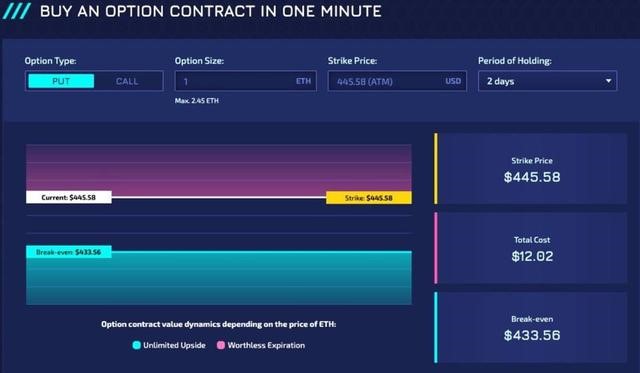
Opyn v2 starts from the point difference (the change range of the target financial transaction object, based on the opening price, and a trading method that uses margin amplification to place bets on the unilateral change range, that is, the spread change) to improve the capital use efficiency of options . That is, long oTokens can be mortgaged to short oTokens, thereby improving capital efficiency.
The protocol now allows farming yield assets (such as cTokens, aTokens, yTokens, etc.) to be used as collateral for options and allows participants to harvest earned and airdropped oTokens. The first batch of options launched in v2 will be collateralized by USDC, but shortly after the initial release, yield-collateralized options will be released.
Regarding the spread and allowing farming income assets to be used as collateral for options, it can be seen from these two points that Opyn v2 has achieved a very comprehensive mining usage scenario. Perhaps it can indeed be expected to develop in DeFi Lehigh, but there should be no such thing in the short term. Too much liquidity, because it also depends on the value of DeFi in the later stage.
Opium
The positioning of Opium is that you can launch the decentralized derivatives you want, you can also conduct option transactions on DeFi gas prices, and you can also transfer token mortgage positions (ERC721). In terms of leverage, it is conservative to 100 times rich and thrifty. It sounds like the degree of freedom is very high, and the platform has indeed launched a lot of derivatives tools, but because it is in a very early stage, the liquidity is poor, and the security of the contracts has yet to be confirmed.
Currently, the contracts that have been launched on the exchange include:
1. ETH/DAI futures weekly contract;
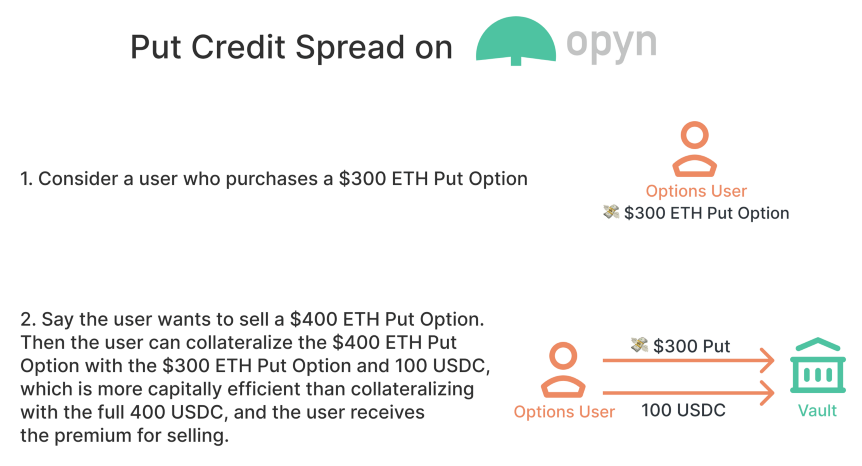
2. Weekly call option contract for ETH Gas price;
3. Weekly put option contract on ETH Gas price;
The call and put option contract on Gas price still sounds interesting, but as mentioned earlier, this is still a too small market, especially in the case of poor liquidity.
According to the Opium project team, the Opium protocol has been audited by Smart Dec, you can find the relevant audit report here, and you can also view all its smart contracts on Github.
Hegic
HegicHegic provides buyers with the opportunity to buy up and down with WBTC or ETH. Relaunched in October with a new innovative design: a two-way option liquidity pool. The two pools (ETH and WBTC) have attracted over $80 million in funding since launching less than two months ago, giving traders considerable depth in options liquidity.
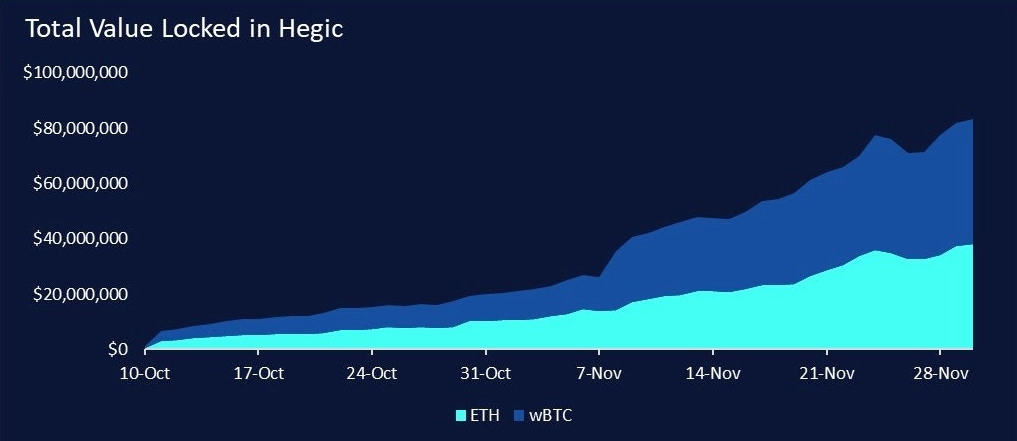
Probably the most innovative and experimental aspect of Hegic is its bidirectional liquidity pool for ETH and WBTC. Both the ETH pool and the WBTC pool act as liquidity, buyers can buy BOTH call/put options of any size (as long as there is liquidity) at any strike price for five periods (1 day, 7 days, 14 days, 21 days, 28 days) .
This design overcomes the liquidity fragmentation problem encountered by order-thin options protocols when allocating liquidity across multiple strike prices, put and call contracts, and expiration dates.
For example, an order book options platform might allow you to sell a 10-day ETH put option with a $500 strike price on a 7-day period, but want to buy a 5 ETH call option with a $650 strike price on a 14-day period. No one can buy based on my position/liquidity.
This allows traders and hedgers to fine-tune their trading strategies. In traditional finance, customized deadlines and exercise prices are privileges only available to over-the-counter transactions and large amounts of funds.
For users who want to use ETH or WBTC stablecoin pairs for mining on Uniswap or Sushiswap, but are worried about impermanent losses, they can use Hegic for hedging and straddle arbitrage:
Buy put options to protect you from impermanent losses if the price of ETH/WBTC falls. Or buy a call option to protect against a decrease in non-stablecoin assets due to price increases. You can even buy both at the same time, in case both happen.
Hegic's strengths are flexibility and simplicity.
Each strike price on Opyn has no liquidity, and only a few strike prices close to the market price have enough liquidity to close positions. This is very fatal. And Hegic reduces the flexibility of the option seller and increases the flexibility of the option buyer. This increases the purchase cost of the buyer, and the seller then obtains a higher marginal profit, which also brings higher liquidity.
Smart contracts are a risk that has come up on Hegic. The protocol was deployed on Ethereum, and the mainnet was launched within a few days, but an error occurred in the code, which made the option impossible to execute. A month later, another vulnerability in the core design of the Hegic protocol was exploited.
In this case, the Hegic team paid 100% compensation to the damaged users. Various aspects of the protocol have been strengthened after the redeployment, but there is no guarantee that the problem will not recur.
Taken together, Hegic seems to be the most used among several DeFi options platforms at present, because it is also the closest to the current demand, and the liquidity is also considerable. Whether the follow-up liquidity can grow steadily is the key to development.