It is not too much to say that this year is the first year of DeFi. During the year, DeFi has set off countless climaxes. Although by the end of the year, Bitcoin has taken over strongly, DeFi seems to have fallen into a state of decline. Counting money with a smile, watching YFI surpassing Bitcoin to become the most expensive digital asset, who can say that he does not feel regretful. So at the end of the year, I am going to make a summary, review this year's DeFi boom, and predict where DeFi will explode again next year.
The basic concept of DeFi
In fact, when it comes to DeFi, in the eyes of most people, it is just an abstract synonym. DeFi is actually not a complicated thing. It comes from decentralized finance in English. The literal translation into "decentralized finance" is actually not accurate. We It will be easier to understand the composition of open finance.
I have always suggested that everyone should at least have a general understanding of DeFi, rather than rushing without thinking, so as to avoid some risks, because it does not mean that there is no risk if I just speculate and withdraw after drinking the soup. A clear understanding can not only Let you smell the scam, and also allow you to ambush in the best position in some long-term investments. Usually, the value of a project in DeFi is directly proportional to the price of the currency it reflects, and there are exceptions. For example, Chainlink, which has done a very good job in the community, far exceeds the essence of its oracle machine. Take the top spot in DeFi market value, but this is just an example, and Chainlink itself is also a very good project.
DeFi is roughly composed of several industries: asset management, infrastructure, stable coins, DEXs, mortgages, lending, data services and derivatives, and this year's protagonists are basically in infrastructure (Chainlink, Band and other oracle machines), DEXs ( Uniswap, etc.) and lending.
These industries constitute the so-called Lego kingdom of DeFi, and the principle is that the logic is self-consistent. If we explain the entire system one by one, the length may reach tens of thousands of words, so the article will use some projects that everyone is more familiar with and are more interested in as the entry point and extension.
Keywords: Compound, AAVE, MakerDAO, liquidity mining
Different from traditional lending, DeFi lending has the characteristics of trustless, distributed, transparent and open source. The currently applied scenarios are similar to the traditional financial banking business model. In the digital asset lending market, the supply and demand subjects of products and services are mainly divided into three categories: Three levels: technology layer, application layer and transaction layer, respectively corresponding to projects that provide lending agreements based on blockchain platforms, lending platforms, and liquidity suppliers and demanders.
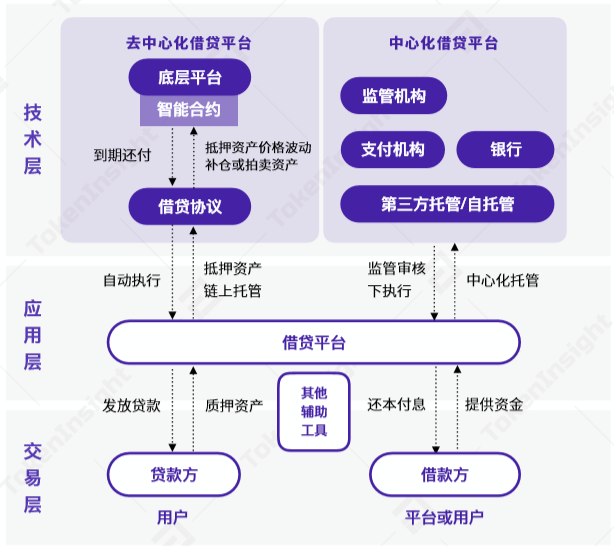
According to the loan matching method, it can be divided into peer-to-peer matching lending and lending by aggregating borrowers’ funds to lenders. The leading projects that have caused a boom this year are all aggregated.
Although the original intention of the lending part is to provide long-tail people with access channels that do not require centralized credit certification, it is obvious that the current participants have little relationship with retail investors. The borrowers are mainly quantitative teams, hedge funds and active traders, while the lenders Mainly for asset managers, family business-level high-net-worth individual investors. This is why when it comes to DeFi, very few participants have experience in arbitrage on lending platforms, and most of them still stay in the trading of platform tokens.
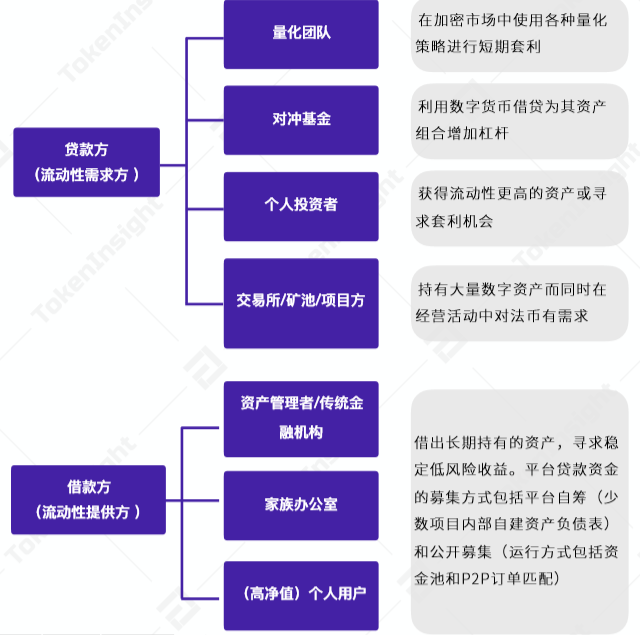
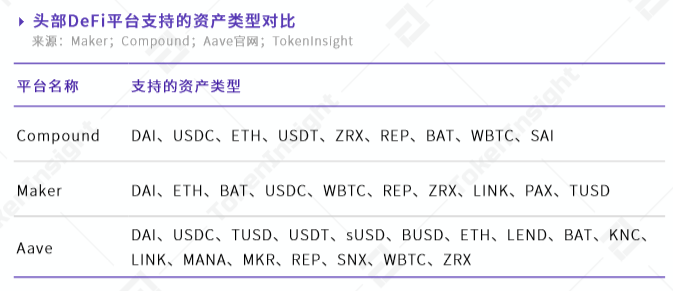
At present, the top representatives of lending projects are Compound, AAVE, and MakerDAO, all of which were established in 2017 and 2018 and only broke out this year (the predecessor of AAVE is ETHlend).
Judging from the Total Value Locked in Lending data from January 18 to June 20, DeFi lending projects generally maintained a lock-up amount of US$500 million in the second half of 2019. In the first half of 2020, DeFi exploded, and Total Value Locked in Lending continued to rise, increasing from US$465 million to US$1.287 billion, an increase of 176.77%. Since Compound launched liquidity mining in late June, the borrowing volume and capital supply of the lending platform have grown rapidly. It can be said that this is the beginning of this round of DeFi boom.
Affected by Compound, the loan share of MakerDAO and AAVE has been largely squeezed out, and liquidity mining has also become a hot element of DeFi.
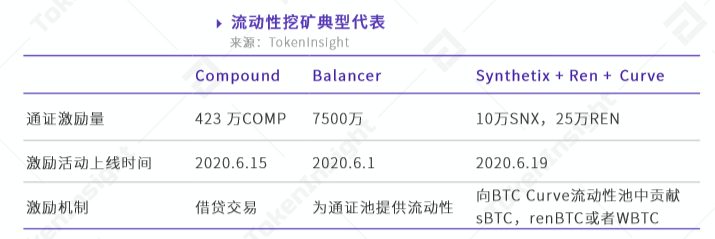
Liquidity mining, generally speaking, is to obtain income by providing liquidity for DeFi products on Ethereum, that is, depositing certain token assets can be used for mining, such as liquidity mining on Compound, which mainly refers to Perform operations such as depositing tokens or lending tokens on it to obtain COMP governance token rewards.
Different from the liquidity mining of the lending platform, the liquidity mining on Balancer is to provide liquidity for the token pool of the transaction, such as providing liquidity for the BAL-WETH pool, and the liquidity provider can follow a certain The ratio (such as 80:20) is deposited into BAL and WETH tokens, and then according to certain rules, BAL tokens and related transaction fees are obtained.
All in all, liquidity mining is mainly to obtain income by providing token assets.
Keywords: Chainlink, oracle
To understand oracles, we also need to understand smart contracts first. A smart contract is a preset agreement on the blockchain. The contract evaluates the data and automatically executes when certain conditions are met. In the traditional contract behavior, the rules are formulated by people and executed by people. When encountering boundary problems or abnormalities, it is also up to people to define them. The smart contract is that the developer formulates a set of rules through the smart contract, and then publishes it online. People interact directly with the smart contract, and the machine completes the part of the business, which avoids possible problems caused by human execution. of cheating.
If the smart contract is to be connected to an environment other than the blockchain, it is necessary to convert the off-chain data into a compatible format on the chain. However, the incompatibility between on-chain smart contracts and off-chain data is the biggest bottleneck that prevents smart contracts from being widely used.
At this time, the oracle machine is needed. The oracle machine is more like a repeater. It serves as a bridge for communication between off-chain data and on-chain smart contracts, and acts like a translator, allowing each other to understand each other's language. As an important infrastructure in the DeFi field, oracle machines have also received widespread attention. Among them, Chainlink is the leader and is used by many projects in the ecosystem, including AAVE, Synthetlx, Loopring, and Set Protocol. Other oracle projects, such as Band Protocol, Tellor, Coinbase Oracle, etc. have their own focus.
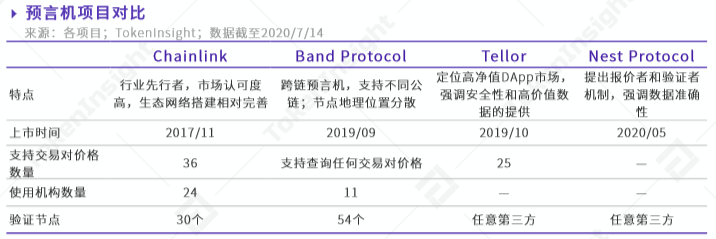
Keywords: Uniswap, Sushi, YFI, AMM
In the second half of 2020, DeFi hotspots continued to emerge, each time pushing the transaction fee of Ethereum to a historical peak. The four most typical events are:
1. The income aggregator project Yearn.Finance is launched;
2. The DeFi experimental asset YAM using the Rebase mechanism is launched;
3. Sushiswap, a fork of Uniswap, is launched;
4. Uniswap goes online and airdrops the governance token UNI to users who have provided liquidity in the past.
Whether it is the revenue aggregation channel Balancer embedded in the revenue aggregation project Yearn.Finance, or the DEXs project Uniswap and the forked Sushiswap, they all have an interaction point, which is the automatic market maker (AMM).
AMM is a non-order book model in DEX, which generates transaction prices through certain algorithms; any participant can become a liquidity provider. Different from the traditional order book transaction mode, both parties of the AMM transaction are only interacting with the liquid asset pool on the chain rather than peer-to-peer. Liquidity pools allow users to seamlessly switch between tokens on-chain in a fully decentralized and non-custodial manner. Liquidity providers, on the other hand, earn passive income through transaction fees, which depend on the percentage of their contribution to the asset pool.
Constant function market makers can be divided into four types from the mechanism (formula) behind them:Constant product market makers, constant volume market makers, constant average return market makers, and hybrid constant function market makers. The only difference lies in the mechanism:
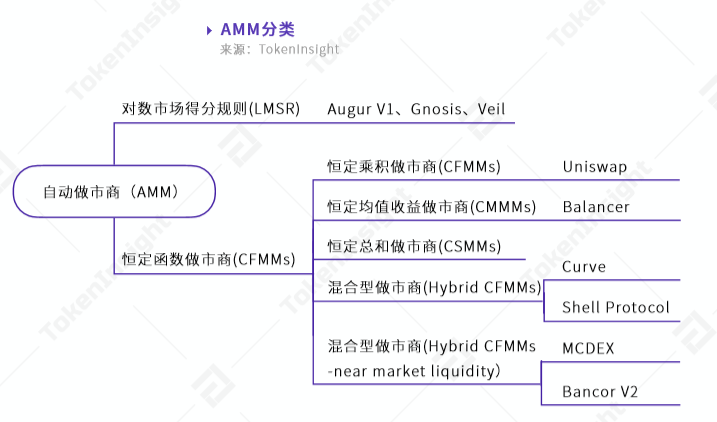
In the next article we will focus on the currentThe situation of DeFi makes a prediction of future hot spots - financial derivatives, and a list and analysis of some key financial derivatives projects, so stay tuned