Editor's Note: This article comes fromBlockVC(ID:blockvcfund)Editor's Note: This article comes from
, Author: BlockVC strategy research team, reprinted by Odaily with authorization.
Compared with the traditional financial market, although the richness of financial instruments in the encrypted asset market is lower, the overall scale and market value are smaller. However, thanks to the inefficiency of the market, there are more opportunities for mispricing and fewer arbitrage participants, the arbitrage strategy in the encrypted asset market can reach an annualized level of 15-35%, which is much higher than the annualized rate of 5%-15% in the traditional financial market. profit range.
secondary title
1. Financial market arbitrage
Below we will explain various arbitrage strategies in detail from the level of strategy type and strategy risk:
1. Futures arbitrage strategy
Futures arbitrage strategies can be further divided into futures and spot arbitrage, intertemporal arbitrage, cross-market arbitrage and cross-species arbitrage strategies;
Futures and spot arbitrage can be divided into positive futures and spot arbitrage and reverse futures and spot arbitrage according to different arbitrage directions. Positive futures and spot arbitrage refers to buying spot and shorting futures when the futures price is higher than the theoretical price of holding costs; Futures-to-spot arbitrage refers to buying futures and shorting the spot when the market price of the futures is lower than the theoretical price of the holding cost; obtaining income when the futures price and the spot price converge. For most spot markets, there is a lack of short-selling means, so the implementation conditions and costs of reverse arbitrage are relatively strict. Usually, the reasonable undervaluation range of futures prices is generally higher than its overvaluation range, and the probability of futures undervaluation is relatively high.
image description
Figure 1 Schematic diagram of spot arbitrage source BlockVC
1.2 Intertemporal arbitrage
In actual operation, spread arbitrage can be divided into bull market arbitrage, bear market arbitrage and butterfly arbitrage: Bull market arbitrage refers to buying the near-term delivery month contract and selling the forward delivery month contract at the same time, expecting the increase of the near-term contract to be greater than the increase of the forward contract ; bear market arbitrage is the opposite, buying the forward delivery month contract and selling the near delivery month contract, hoping that the price of the forward contract will fall less than the decline of the near-term contract.
image description
Figure 2 Schematic Diagram of Intertemporal Arbitrage Source: BlockVC
1.3 Cross-market arbitrage
1.4 Cross-variety arbitrage
2. Alpha arbitrage strategy
The return of the Alpha strategy comes from the excess return of the expected return higher than the β part in the portfolio theory:
E(Rp)=Rf+β×(Rm-Rf)
image description
Figure 3 Alpha Arbitrage Strategy Schematic Source: BlockVC
3. ETFs arbitrage strategy
ETFs arbitrage strategy is the arbitrage between the price difference between the primary market and the secondary market for products such as ETFs, mainly including discount arbitrage strategies and premium arbitrage strategies. When the unit net value of ETFs is higher than the secondary market price, ETFs are bought in the secondary market and then redeemed for a basket of stocks through the primary market and sold to achieve discount arbitrage. Conversely, when the net value of ETFs units is lower than the secondary market price, the ETFs are traded at a premium.
According to the different transaction targets, there are LOF arbitrage and graded fund arbitrage. Graded funds have two types of AB shares, which can be used to construct a synthetic fund of funds. If the price of the synthetic fund of funds deviates from the net value of the fund of funds, there will be an arbitrage opportunity to buy low and sell high. Realize profit.
4. Equity market neutral strategy
It mainly includes pairs trading (Pairs Trading) and statistical arbitrage (Statistical Arbitrage); pair trading is based on the principle of fundamental analysis, buying undervalued stocks while short selling overvalued stocks, also known as long-short combination; statistical arbitrage It is based on the volatility and correlation of stock prices to analyze stocks, looking for stock combinations that have a certain correlation in historical data, long low-priced stocks, short high-priced stocks, assuming that the price difference range between stocks returns and obtain arbitrage income.
This strategy generally imposes parameter restrictions on the construction of selected stocks and portfolios based on the model, including ensuring long-short consistent overall positions are neutral, the expected beta value of the portfolio is 0, and the portfolio sector and industry are neutral , there is no excessive net investment style exposure, etc. Through the neutral strategy, the volatility of the investment portfolio can be reduced, the Sharpe ratio can be increased, and the influence of the overall market environment on investment returns can be stripped away.
Option arbitrage strategies mainly include simple strategies, spread strategies and combination strategies.
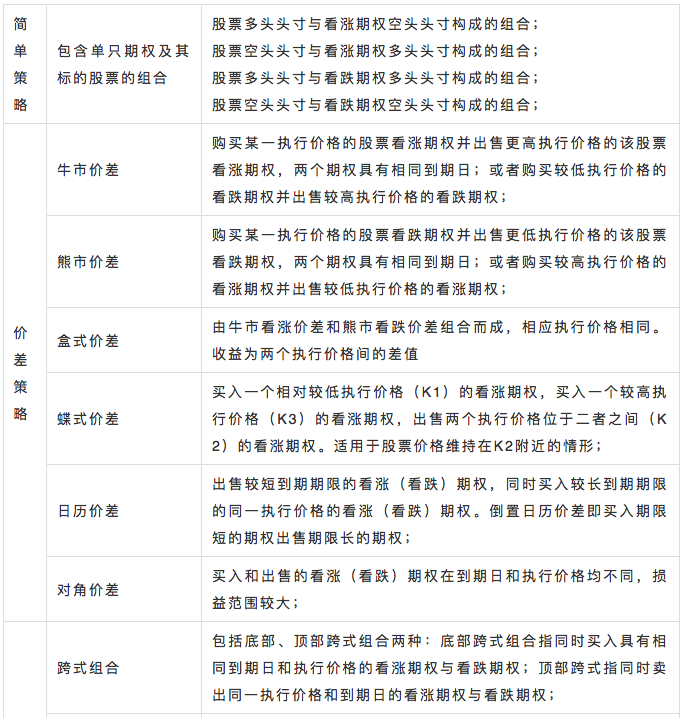

image description
Figure 4 Classification and Explanation of Option Strategies Source: Guodu SecuritiesFor specific strategy descriptions and profit methods, please refer to the previous article of BlockVC"New Blue Ocean of Encrypted Asset Derivatives, Detailed Explanation of Options Trading"
From the perspective of strategic logic, the arbitrage strategy is opposite to the trend strategy, and has the characteristics of high winning rate and low profit-loss ratio. Because the profit source of the arbitrage strategy mainly comes from the small changes in the price difference between various assets, this also determines that the profit space of the arbitrage strategy is limited, and the strategy capacity is limited. When the market tends to be efficient or the number of traders with the same strategy increases, it will cause a crowding effect and reduce the rate of return of the strategy.
Figure 5 Global Hedge Fund Strategy Size Index Source: Eurekahedge
image description
From the hedge fund scale index compiled by Eurekahedge, it can be found that the development scale of arbitrage strategies has remained unchanged in the past few years, and the proportion of management scale of other strategies has a tendency to shrink. The main reason is that with the development of programmatic trading and the improvement of the effectiveness of various trading markets, the arbitrage space has been squeezed, and the management scale and profitability have declined year by year.
image description
However, the arbitrage strategy also has its own advantages. There are two main points. One is that it has a low correlation with the returns of stock strategies, CTA strategies, etc. The overall market is neutral, and there is no directional transaction. The arbitrage strategy has a greater impact, so it can form a complementary effect with other trend strategies to optimize the investment portfolio; second, the strategy has stable returns, low volatility, small retracement, and high Sharpe ratio.
Figure 8 Global hedge fund strategy income analysis Source: Eurekahedge
image description
Figure 9 Analysis of the yield rate of domestic CTA products Source: Wind
With the development of financial engineering and the increase of various financial products, arbitrage opportunities among various financial assets are also emerging, and the increase of arbitrage participants will inevitably lead to the enhancement of market efficiency, so arbitrage opportunities and arbitrage profits will also increase. Then decrease. For the encrypted asset market with relatively limited market participants and low market efficiency, arbitrage trading strategies still have a large space, and it has become the first step for most program traders to enter the encrypted asset market.
secondary title
2. Crypto asset market arbitrage
Since the trading varieties and trading environment in the encrypted asset market are quite different from those in the traditional financial market, and the types of financial derivatives are not as rich as in the traditional financial market, only some arbitrage strategies can be practiced in the encrypted asset market. Below we will analyze the specific arbitrage strategies in the encrypted asset market:
1. Futures arbitrage
Here we take the BTCUSD futures delivery quarterly contract launched by the OKEx platform as an example. The contract uses the BTC USD index set by the platform as the underlying price, and the delivery and settlement will be carried out at 4:00 pm on the last Friday of each quarter. The difference between its transaction price and the spot index reflects traders' expectations for future bitcoin prices and the comprehensive added value of futures liquidity and transaction costs.
image description
Figure 10. OKEx Quarterly Delivery Contract Basis Source: OKEx
From the historical data of quarterly delivery contracts, it can be seen that during the period from September 2017 to February 2018, the volatility of the Bitcoin market was extremely active on a monthly basis. The peak of the bull market in the middle of the month reached a peak of 1515. The positive basis spread continued to widen during the rise, and the negative basis spread continued to accumulate during the fall.
2. Intertemporal arbitrage
At present, exchanges that launch delivery contracts generally launch three types of contracts, namely, weekly delivery contracts, next-week delivery contracts, and quarterly delivery contracts, which correspond to delivery on the Friday of the current week, Friday of the next week, and Friday of the last week of each quarter. There are three types of contracts with different expiry dates. Weekly contracts automatically switch to weekly contracts on the Friday before expiration, while quarterly contracts switch to next-week contracts on the Friday two weeks before expiration.
There is a certain correlation between the three types of futures, so statistical arbitrage can be used to achieve intertemporal arbitrage among these three types of futures. There are also some arbitrage strategies that build arbitrage combinations between delivery contracts and perpetual contracts, and at the same time adjust the funding rate in perpetual contracts at the hedging level. Spread arbitrage does not close the position with the delivery of the futures contract, so the position is generally opened when the basis spread expands, and the position is closed when the basis spread decreases. Some arbitrage traders will also adopt high-frequency trading techniques to frequently trade during basis changes to capture fluctuating returns.
3. Cross-market arbitrage
Cross-market arbitrage is the earliest arbitrage strategy that appeared in the encrypted asset market, also known as "moving bricks". Its main principle is to use the price difference of the same currency in different markets to buy low and sell high to obtain income.
According to Coinmarketcap statistics, the current number of digital currencies has reached 5,154, and digital currency exchanges have reached 20,636, and most of them are traded 7*24 hours, so there are many arbitrage opportunities for the same currency in various markets. However, due to the serious liquidity problems in most small-cap currencies and small exchanges, most of the current cross-market arbitrage is mainly concentrated in the mainstream currencies of mainstream exchanges. In addition to spot trading, futures contracts launched by exchanges such as OKEx and Huobi have basically similar contract mechanisms and pricing principles, so arbitrageurs can also achieve cross-market arbitrage by moving bricks on futures trading platforms.
4. Triangular Arbitrage
5. Rate arbitrage
Rate arbitrage mainly refers to the arbitrage of the perpetual contract funding rates of various digital currency futures exchanges. The encrypted asset market perpetual contract is pioneered by BitMEX, which is a swap contract that anchors the spot price index through the adjustment of the funding rate. Funding fees are incurred every eight hours and are paid by one party in the opposite direction of the trade to the other. Longs pay shorts when the funding rate is positive, and shorts pay longs when the funding rate is negative.
Since the main function of the funding rate is to stabilize the consistency between the price of the perpetual contract and the spot index, the size of the funding rate is also related to the discount or premium of the contract. For the convenience of understanding, we use the XBTUSD contract as an example to explain:
The funding rate is composed of interest rate and discount/premium, and the interest rate is the difference between the pricing currency interest rate (USD) and the base currency interest rate (XBT):
Interest rate (I) = (pricing interest rate index - base interest rate index) / funding rate interval
* Where funding rate interval = 3 (generated every 8 hours)
The discount/premium refers to the discount and premium of the price of the perpetual swap contract on the BitMEX platform compared to the mark price: premium index (P) = ( Max ( 0 , depth-weighted bid price - mark price) - Max ( 0 , mark price - Depth-weighted selling price)) / spot price + reasonable basis of mark price;
BitMEX calculates the premium index P and the interest rate (I) every minute, and then calculates its minute time-weighted average every 8 hours. The funding rate is calculated based on the interest rate and premium/discount components every 8 hours, adding +/- 0.05% buffer.
Funding rate (F) = premium index (P) + clamp (interest rate (I) - premium index (P), 0.05%, -0.05%)
By observing the figure below, it can be found that due to the rise of digital currencies some time ago, the funding rates of perpetual contracts on major exchanges have reached a relatively high level, so a large number of arbitrage traders obtain profits by opening short positions.
Figure 11 Perpetual contract funding rate source: SKEW
image description
Figure 12 Bitmex Perpetual Contract Funding Rate Source: SKEW
The main risk of funding rate arbitrage is that the funding rate is not stable as the market environment changes, so short-term transactions can only be carried out under specific market conditions.
The arbitrage strategies in the traditional options market can basically be applied in the encrypted asset market, and the arbitrage strategies are mainly spread strategies and combination strategies. Deribit and LedgerX were the main trading platforms that launched options in the early stage. The trading volume and open interest of options launched by OKEx have also grown rapidly. At present, more than 89% of Bitcoin options transactions in the market are conducted on Deribit, and OKEx accounts for 10%.
Figure 13 Bitcoin options open interest and trading volume Source: SKEW
image description
secondary title
epilogue
epilogue
Currently limited by the overall market value of encrypted assets, the number of teams engaged in quantitative trading of encrypted assets is still small, and the management scale of a single quantitative team is mainly between millions to tens of millions of dollars. The management scale of the asset quantification team can reach hundreds of millions of dollars in market value. There are hundreds of encrypted asset quantification teams with stable asset management capabilities in the world. According to the average management scale of tens of millions of dollars, the overall management market of global encrypted asset quantification is about 1 billion US dollars. The strategies of the encrypted asset quantification team mainly focus on two types of trend tracking and neutral arbitrage strategies. Among them, the proportion of quantitative teams focusing on different types of arbitrage strategies is relatively high, accounting for about 60-70% of the overall market size.
Although the overall management scale of encrypted digital asset quantification is very small compared to the management scale of traditional quantitative markets, due to the characteristics of encrypted assets that can be traded 7*24 hours, high volatility, and poor effectiveness, the arbitrage strategy focused on the encrypted asset field The annualized rate of return is significantly higher than that of traditional market-neutral strategies. Judging from the data of the most common futures and cash arbitrage strategy in the field of encrypted assets, according to the results of due diligence on dozens of arbitrage strategy funds in the encrypted market by BlockVC, the annualized return rate of the futures and cash arbitrage strategy of encrypted assets is distributed between 15-35% The average annualized rate of return can reach about 24%, which is much higher than the average annualized rate of return of 10% in traditional market arbitrage strategies.