Editor's Note: This article comes fromEditor's Note: This article comes fromTencent Security Joint Laboratory
(ID: txaqlhsys), author: Tencent Security Joint Laboratory, reproduced with authorization.
In the first half of 2018, all kinds of industry information about blockchain, investment and financing entrepreneurship, technology and application exploration exploded, becoming a common pursuit of entrepreneurship and capital. However, with the continuous development of blockchain technology, the security issues in the blockchain field itself have gradually become prominent, and related problems continue to emerge.
Blockchain security incidents occur frequently, and it is not uncommon for cases involving cases worth over 100 million yuan;
Theft, ransomware, and mining Trojan horses have developed into three major security threats to digital cryptocurrencies;
The amount of money lost to blockchain security incidents worldwide is still climbing...
On August 2, Tencent Security and Zhichuang released the "Blockchain Security Report for the First Half of 2018", combining the big data provided by Zhichuang, Tencent Security Joint Laboratory, Tencent Cloud, Tencent Computer Manager, etc., to reveal the secrets of the blockchain. The three root causes of security issues, and put forward ideas on how to defend against blockchain security risks and establish a network security ecology.
Three Root Causes of Blockchain Security

The security issues caused by blockchain-based encrypted digital currency come from three aspects: blockchain's own mechanism security, ecological security and user security.
The theoretical 51% attack has become a reality, and smart contract security incidents, transaction malleability attacks, spam transaction attacks, etc. are becoming more and more serious; exchanges, mining pools, and websites face routine security risks such as being stolen and mined; personal Managed accounts and wallets are stolen, etc., which need to be resolved urgently.
Three Cybersecurity Threats Behind the “Hot” Blockchain Digital Currency
①Digital currency extortion incidents occur frequently, and infrastructure has become a key target of ransomware attacks

The ransomware virus is one of the most serious viruses that harm the Internet in the first half of 2018. The ransomware virus encrypts the computer system of the victim and requires the victim to transfer money to certain designated Bitcoin wallets. every industry.
②Mining Trojans "emerge suddenly" and become a "weather vane" of the value of the currency circle

Since the controller of the mining virus can directly sell the mined digital virtual currency for profit, the influence of the mining virus is unprecedentedly high, becoming the most widely spread network virus in 2018, and the popularity of mining is often directly proportional to the price of the currency.
It is worth noting that traditional mining methods, such as Bitcoin, generally use graphics card GPU mining, which is difficult for hackers to use, and more scenarios are encrypted for extortion; since the emergence of new currencies such as Monero that use the CryptoNight algorithm, The mining method has changed, no longer relying on GPU mining, and CPU mining has also become possible, so after hacking personal PCs and cloud hosts, hackers will choose to consume machine CPU resources for mining to directly obtain benefits.

According to the statistics of Tencent Security Cloud Ding Lab, machines with common security vulnerabilities such as Eternal Blue have become the main targets of intrusion. Hackers usually conduct malicious mining by scanning for common security issues in batches and invading and implanting mining programs. The phenomenon of machines being invaded and mined in some traditional enterprises, government agencies and other industries is particularly obvious. The main reason is that due to the lack of security awareness of some maintenance personnel in the cloud hosts of these industries, there are prone to loopholes. Long-term mining machines are provided. These cloud hosts with security problems are also a breeding ground for malicious behaviors such as cloud mining.
③Digital robbers "take risks" to attack the exchange, making a half-year profit of about 700 million U.S. dollars

Table of contents
Original address:https://slab.qq.com/news/authority/1754.html
Table of contents
preamble
preamble
1. Blockchain security incidents occur frequently, and cases worth over 100 million are not uncommon
1. Digital cryptocurrency supports a market value of 600 billion U.S. dollars
2. The outbreak rate of blockchain security incidents is increasing year by year, and the case value is increasing
2. Classification of blockchain security threats
1. Trigger three major security issues of blockchain digital encryption currency
2. Detailed explanation of blockchain digital encryption currency security incidents
2.1 Security incidents due to Bitcoin's own mechanism
2.2 Security incidents caused by the blockchain ecosystem
2.3 Risks faced by blockchain users
3. Three major network security threats behind the "hotness" of blockchain digital currency
1. Digital currency extortion incidents occur frequently, and infrastructure has become a key target of ransomware attacks
1.1 Characteristics of ransomware attacks in the first half of the year and the three major families of ransomware
1.2 The Spread Trend of Ransomware in the Second Half of the Year
2. Mining Trojan horses "emerge suddenly", and the value of the currency circle is "weather vane"
2.1 Analysis and propagation characteristics of mining Trojan horse samples in the first half of the year
2.2 The spread trend of mining Trojans in the second half of the year
3. Digital robbers "take risks" to attack the exchange, making a half-year profit of about 700 million U.S. dollars
3.1 Digital cryptocurrency trading platform was attacked
3.2 Personal account hacked
3.3 "Double Spending Attack"
4. Security Recommendations
preamble
preamble
2018 is recognized as a big year for blockchain. Discussions related to the blockchain not only exist in the entrepreneurial coffee in Zhongguancun, but also in the streets, subways, buses, Weibo and WeChat, almost everywhere. However, with the continuous development of blockchain technology, the security issues in the blockchain field have gradually become prominent, and social security issues such as fraud and pyramid schemes related to blockchain have become increasingly prominent.
As the economic value of the blockchain continues to increase, criminals are prompted to use various attack methods to obtain more sensitive data, such as "stealing", "blackmail", and "mining". The blockchain security landscape has become more complex. According to the survey data of the network security company Carbon Black, in the first half of 2018, digital cryptocurrencies worth about 1.1 billion U.S. dollars were stolen, and the amount of losses due to blockchain security incidents worldwide is still rising.
In order to escort the healthy development of the blockchain industry, at the "China Blockchain Security Summit Forum" on June 21, China Technology Market Association, Tencent Security, Zhichuangyu, China Blockchain Application Research Center and other government guidance units, network security More than 20 institutions and units, including enterprises, blockchain-related organizations and media, jointly launched the "China Blockchain Security Alliance". In the name of disguised pyramid schemes, fraud and other money-gathering activities.
Blockchain security is receiving more and more attention. In addition to the "air currency" that the majority of users are particularly concerned about, the Tencent Security Joint Laboratory also focuses on the security risks around the blockchain, and How can we avoid major losses in the face of risks. Based on this, the Tencent Security Joint Laboratory and Zhichuangyu sorted out the typical security incidents surrounding the blockchain in the first half of 2018, and gave defensive measures, hoping to help users avoid the "minefield" of the blockchain as much as possible .
1. Blockchain security incidents occur frequently, and cases worth over 100 million are not uncommon
1. Digital cryptocurrency supports a market value of 600 billion U.S. dollars
Digital encrypted currency is a string of symbols calculated according to a certain mathematical algorithm. Believers believe that this string of symbols represents a certain value and can be used like currency. Because it only exists in the computer, people often call it "digital cryptocurrency".
Different from the medium issued by the government and guaranteed by government credit, it is used as a medium for commodity circulation and exchange-legal currency. Digital encrypted currency is issued by a certain person or organization, finds a string of symbols through a certain algorithm, and then declares it to be "XX currency". The world's first digital cryptocurrency was discovered by the Japanese Satoshi Nakamoto and he called it Bitcoin. After Bitcoin successfully achieved the status of hard currency for black market transactions, it triggered a frenzy of digital cryptocurrency issuance. So far, there have been more than 1,600 digital cryptocurrencies that have appeared in the world, which is more than 8 times the total number of countries on the planet.
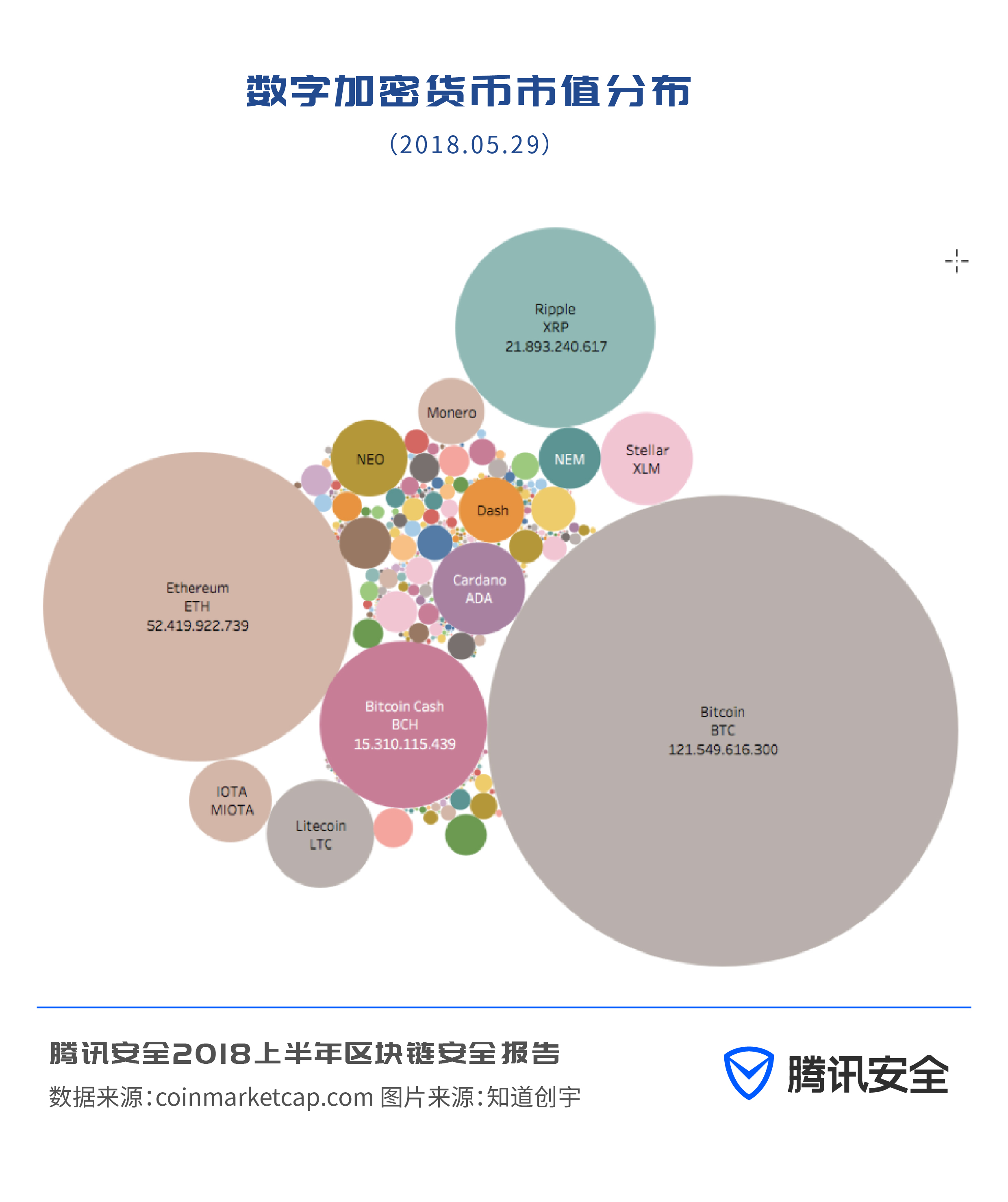
Among the more than 1,600 digital virtual currencies, there are a large number of air coins, which are considered worthless. However, these more than 1,600 digital virtual currencies supported a market value of 600 billion US dollars at their peak. The top ten encrypted digital currencies account for 90% of the total market, of which Bitcoin and Ethereum account for 46.66% and 20.12% of the total market value respectively.
About ICOs
When a listed company issues shares, it needs to submit an IPO application to the stock exchange. When a virtual digital currency needs to be listed and issued, it will seek a digital virtual currency exchange to apply for ICO. Unlike IPO institutions, ICO institutions are not established by government agencies of various countries according to law, and they are guaranteed by strong financial and political strength. ICO organizations are all organizations or alliances formed spontaneously by the people, similar to free markets. The actual performance of some ICO institutions is actually closer to transnational fraud organizations. Air coins are flying all over the world, and the ICO institutions that are everywhere have contributed a lot.
2. The outbreak rate of blockchain security incidents is increasing year by year, and the case value is increasing
Once the encrypted digital currency was born, security was the focus of people's attention. Unfortunately, various major security incidents emerged one after another. Take the following surprising cases, for example:
In November 2013, the Australian Broadcasting Corporation reported that a local 18-year-old youth claimed that the bitcoin bank he operated was stolen and lost 4100 bitcoins;
In March 2014, the US digital currency exchange Poloniex was stolen, losing 12.3% of Bitcoin;
2014 Mt.gox coin theft case - 850,000 pieces, worth 12 billion US dollars;
In January 2015, Bitstamp exchange stolen money case - 19,000 bitcoins, worth 5.1 million US dollars at the time;
In February 2015, the hacker used Biter to fill the hot wallet from the cold wallet and stole all the bitcoins in the cold wallet of the Biter trading platform, a total of 7170 bitcoins, worth 100 million US dollars;
On January 1, 2016, 13,000 bitcoins, worth $190 million, were stolen from the Cryptsy trading platform;
On August 1, 2016, the world-renowned bitcoin trading platform Bitfinex stole coins—approximately 120,000 coins, worth $1.8 billion;
On March 1, 2017, 3,831 bitcoins were stolen from Yapizon, a South Korean bitcoin exchange, equivalent to 37% of the total assets of the platform, worth $57 million;
On June 1, 2017, the South Korean digital asset trading platform Bithumb was hacked, and the damaged account lost billions of won;
On July 1, 2017, the BTC-e exchange case of stealing coins - 66,000 pieces, worth 990 million US dollars;
On November 22, 2017, Tether announced that it had been hacked and $31 million worth of bitcoins had been stolen;
On November 23, 2017, 30,000 bitcoins were withdrawn instantly in a run on Bitfinex;
According to CNBC, a US financial website, survey data from the network security company Carbon Black showed that in the first half of 2018, digital cryptocurrencies worth about $1.1 billion were stolen.
2. Classification of blockchain security threats
1. Trigger three major security issues of blockchain digital encryption currency
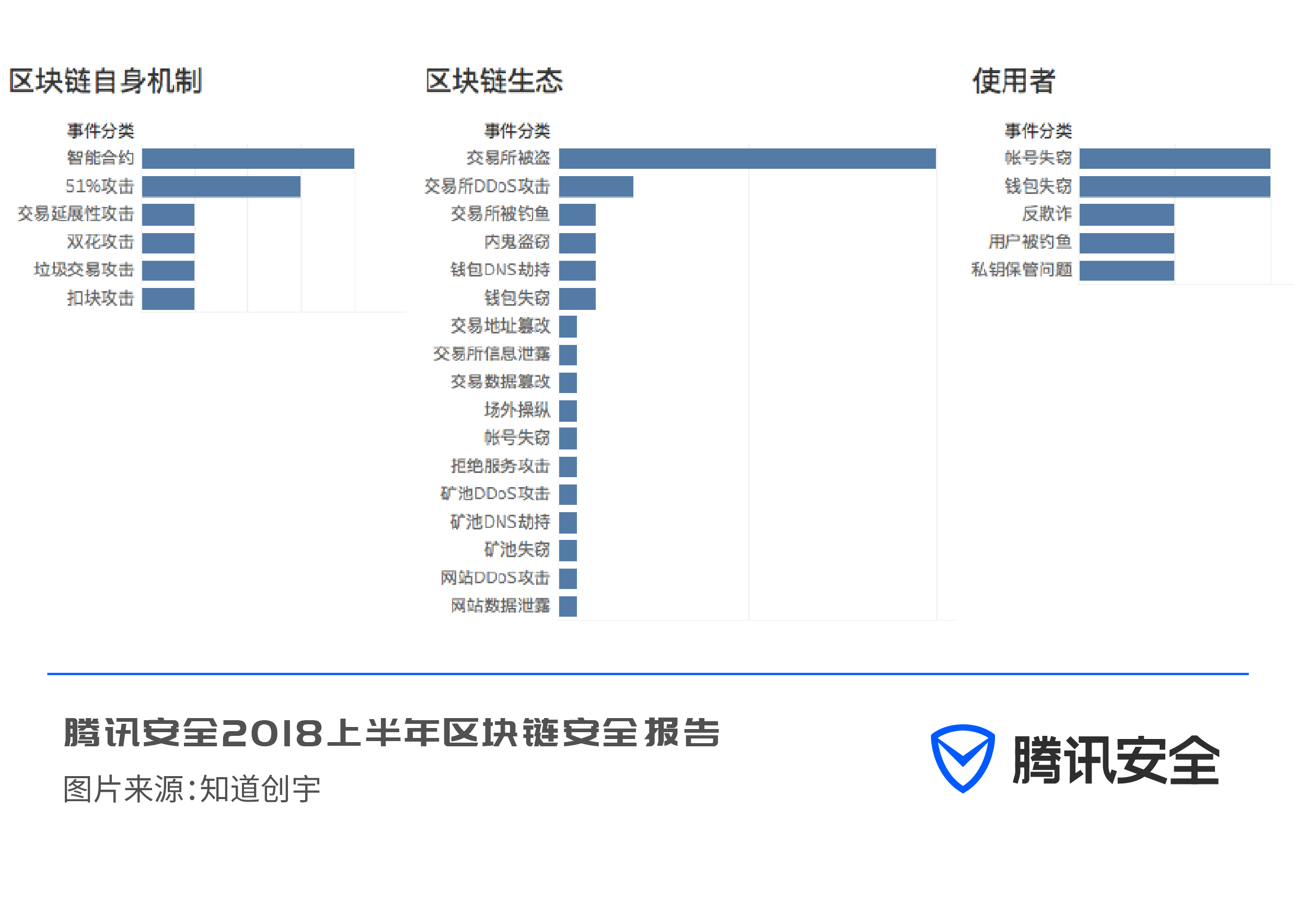
Why do security incidents related to digital cryptocurrencies have such a serious impact? Where is the reason for the security risk? Tencent’s joint security laboratory and Zhichuangyu Company believe that the security problems caused by blockchain-based encrypted digital currency come from three aspects: blockchain’s own mechanism security, ecological security and user security.
The economic losses caused by the above three reasons were 1.25 billion, 1.42 billion and 56 million US dollars respectively.
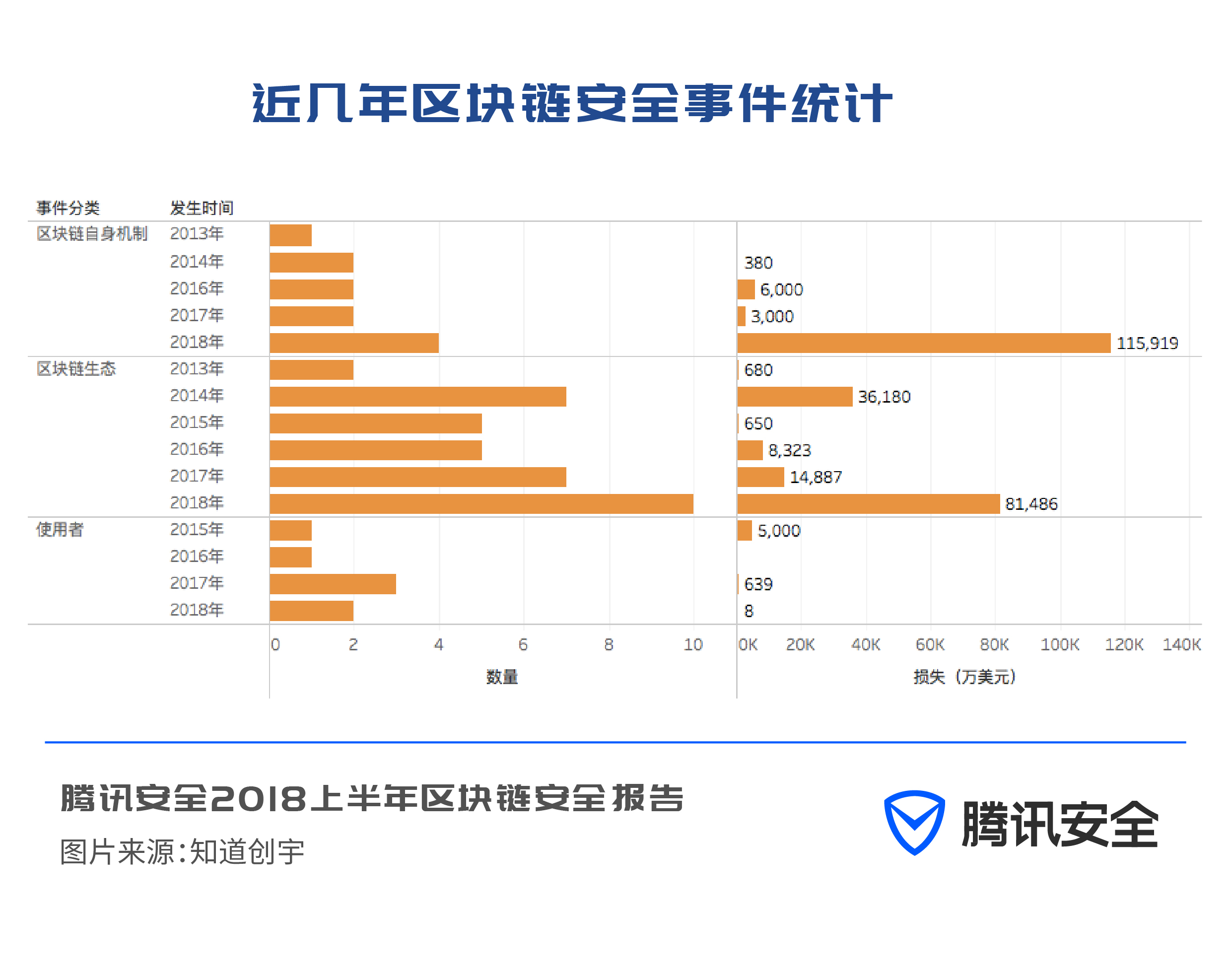
The general trend is that with the increase of digital virtual currency participants, security incidents caused by various reasons have also increased significantly.
Segment to observe:
Blockchain's own mechanism security issues
——— Problems with smart contracts
——The theoretical 51% attack has become a reality
Blockchain Ecological Security Issues
— The exchange was stolen (shocking as mentioned earlier)
——Exchanges, mining pools, websites were DDoS
——Wallets and mining pools face the risk of DNS hijacking (viruses that hijack digital virtual currency transaction wallet addresses have emerged in endlessly)
——Exchanges were phished, insiders, wallets were stolen, various information leaks, accounts were stolen, etc.
User Safety Issues
——Personally managed accounts and wallets were stolen
——Being cheated, phished, poorly managed private keys, encountering viruses and Trojan horses, etc.
2. Detailed explanation of blockchain digital encryption currency security incidents
2.1 Security incidents due to Bitcoin's own mechanism
In May 2018, Bitcoin Gold (BTG) suffered a 51% double-spend attack and lost $18.6 million.
In October 2017, the Bitcoin network encountered a spam transaction attack, causing more than 10% of Bitcoin nodes to go offline.
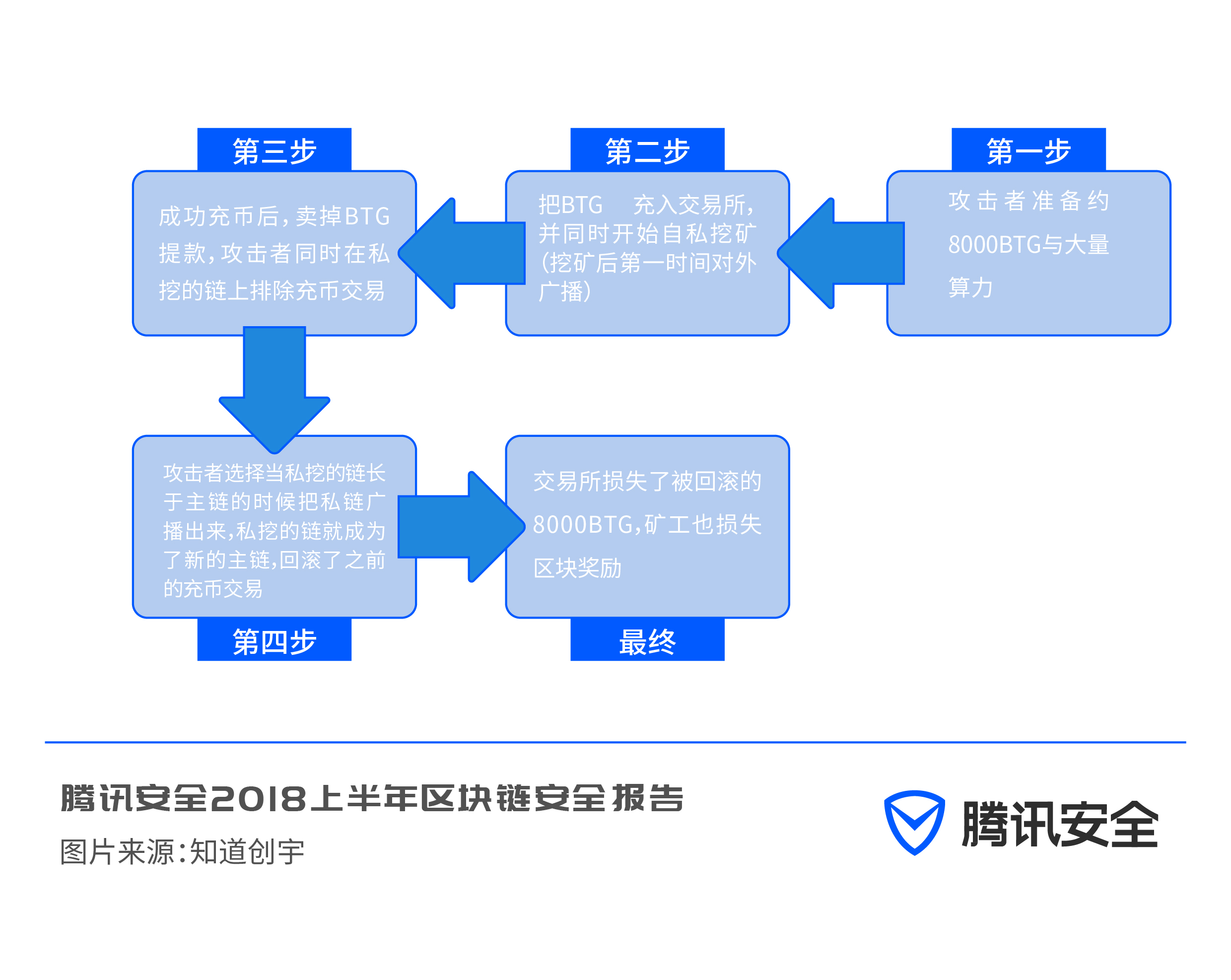
The 51% double-spending attack is the most typical. The so-called 51% attack means that after someone has mastered more than 51% of the computing power of the entire network, they can complete a longer chain of forged transactions first, like a race. Bitcoin only recognizes the longest chain. Therefore, the forged transaction will also be recognized by all nodes, and the fake one will become true; "Double Spending" literally means that a sum of money is spent twice. Taking the BTG incident as an example, after the hacker temporarily controlled the blockchain, he continuously initiated and revoked transactions on the exchange, transferred a certain amount of BTG between multiple wallet addresses, and how much money was spent. Times, the hacker's address thus gets extra bitcoins.
2.2 Security incidents caused by the blockchain ecosystem
For example, the risks faced by exchanges, such as being attacked by DDoS, often occur. There are also exchange accounts controlled by hackers, the attackers control the trading market, and arbitrage.
In March 2018, "Binance", known as the world's second largest exchange, was hacked, and a large number of users found that their accounts had been stolen. The hacker sold all the bitcoins held in the stolen account and bought VIA (Vircoin) at a high price, causing bitcoin to plummet and VIA soaring 110 times.
2.3 Risks faced by blockchain users
For digital virtual currency wallets, there is a high threshold for understanding or fully mastering the use of these trading tools. Users are required to have a high understanding of computers, encryption principles, and network security. However, many digital virtual currency transaction participants do not have these capabilities, which are very prone to security problems.
On July 1, 2017, 188.31 bitcoins were stolen from a residential area in Zhongyuan Oilfield. A few months later, the oil field police captured Dai, a thief in Shanghai, worth $2.8 million;
In October 2017, an imToken user in Dongguan discovered that more than 100 ETH (Ethereum currency) had been stolen, and finally confirmed that it was a friend around him who stole his digital cryptocurrency.
3. Three major network security threats behind the "hotness" of blockchain digital currency
1. Digital currency extortion incidents occur frequently, and infrastructure has become a key target of ransomware attacks
Ransomware is one of the most serious viruses that harm the Internet in the first half of 2018. The ransomware virus encrypts the victim's computer system and requires the victim to transfer funds to certain designated bitcoin wallets. The scope of its damage is expanding day by day, affecting various industries related to the national economy and people's livelihood.
1.1 Ransomware attack characteristics and three major ransomware families in the first half of the year
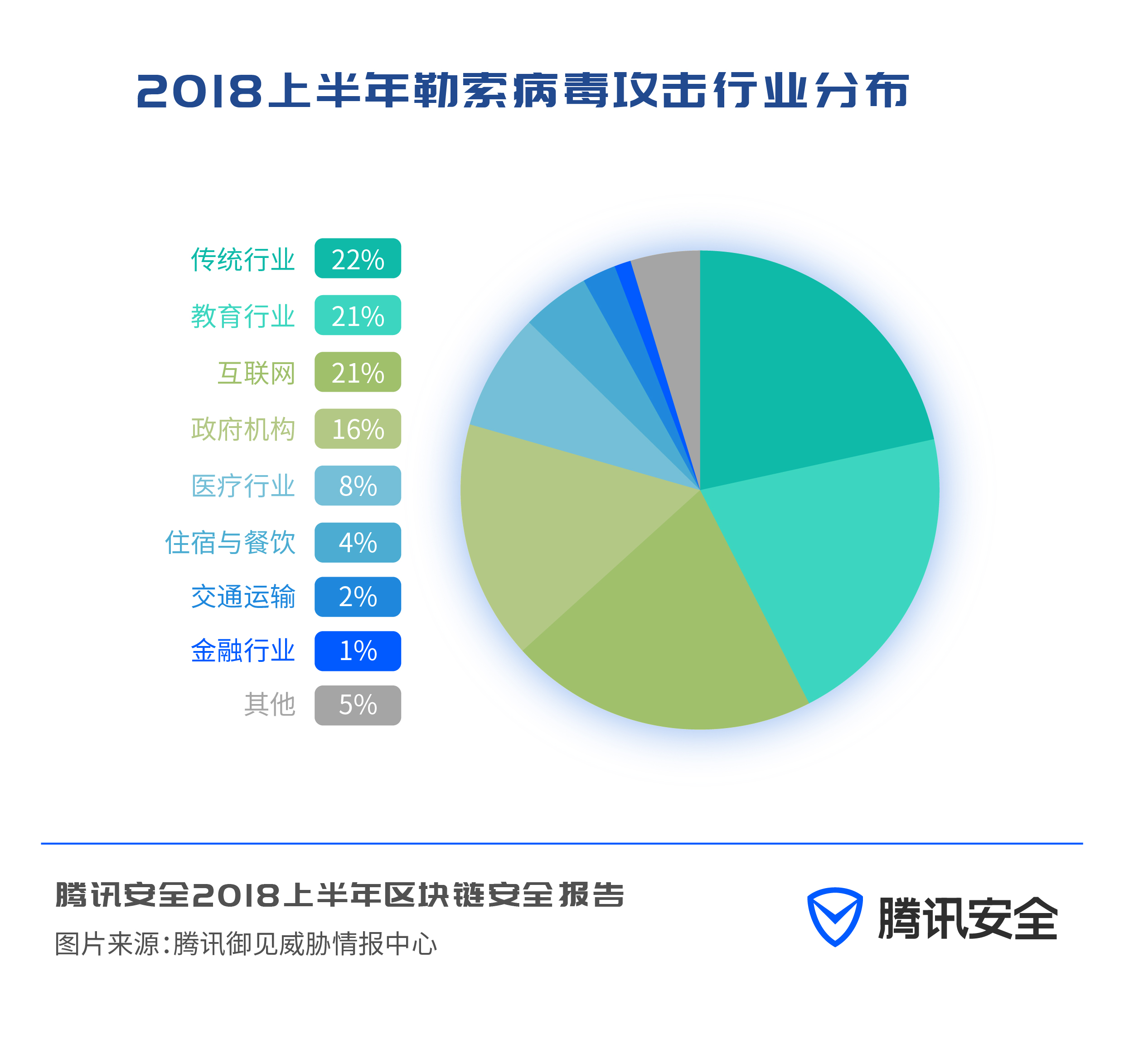
From the perspective of the distribution of attacked industries, traditional industries, the Internet industry, the education industry, and government agencies are the hardest-hit areas attacked by ransomware, followed by the medical industry. Due to the particularity of the medical industry, once the business is shut down due to a virus attack, the consequences will be disastrous.
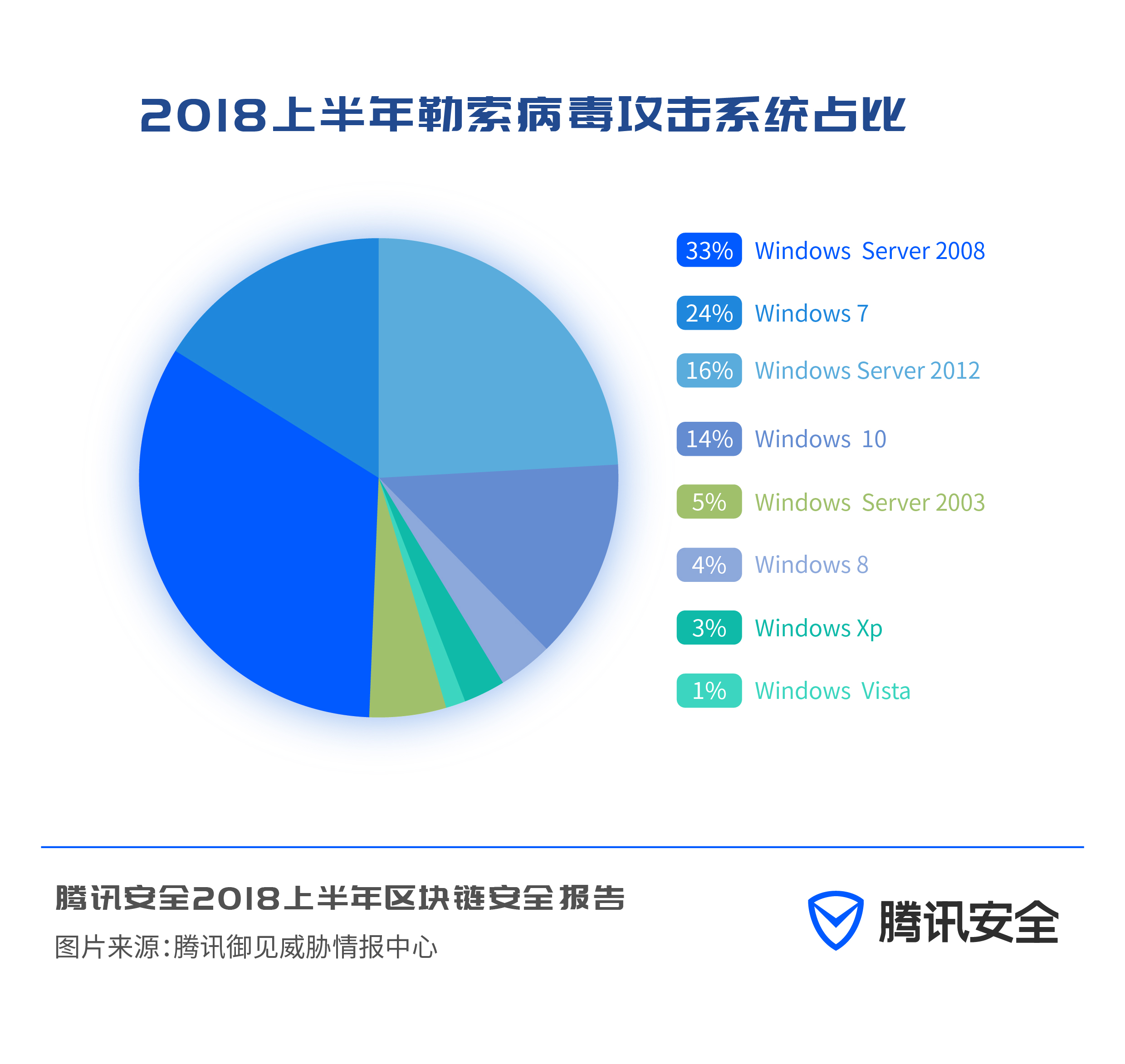
Observing the proportion of systems attacked by ransomware in the first half of 2018, it can be seen that the proportion of Windows Server version systems attacked is greater than that of ordinary home and office systems. Among Windows Server versions, Windows Server 2008 accounts for the largest proportion of ransomware attacks. The main reason for this phenomenon is that the data value of enterprise servers is generally much higher than that of ordinary users. This feature further stimulates attackers to carry out targeted attacks on server system devices.
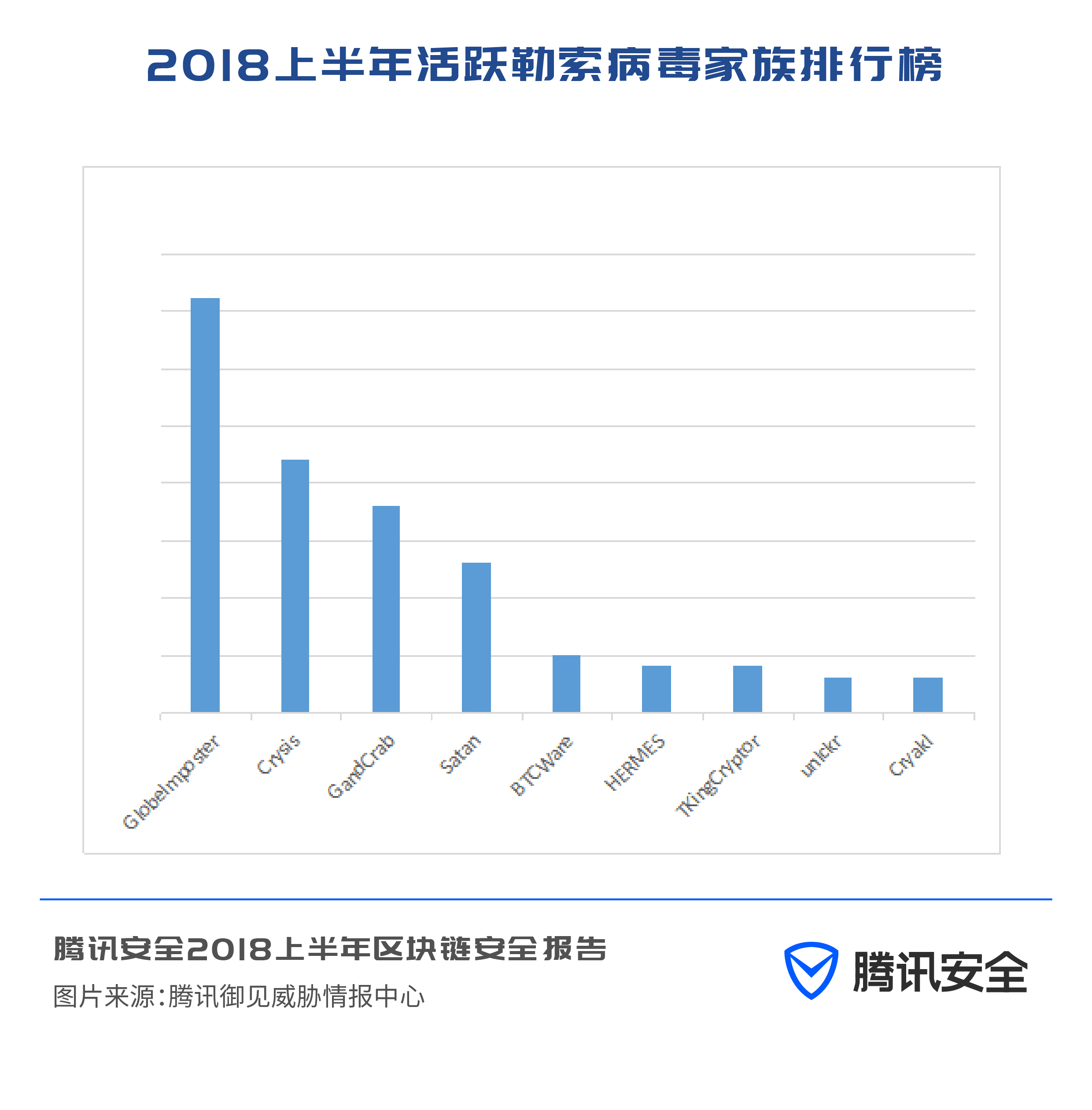
In the first half of 2018, the attacks carried out by the three major extortion families led by GlobeImposter, Crysis, and GandCrab accounted for the vast majority of cyber extortion incidents. In addition, the attacks launched by the Satan family in the first half of 2018 have also increased significantly, and other established families are still active to varying degrees.
Top1: GlobeImposter ransomware family
In February 2018, shortly after the Spring Festival, the servers of many domestic public institutions, including the medical industry, were attacked by the latest variant of the GlobeImposter family ransomware virus. Hackers released and ran the ransomware virus after breaking through the corporate protection boundary, and the encryption was destroyed. The database file will eventually cause the system to be destroyed and the normal working order will be affected.

This ransomware variant renames the encrypted files to .GOTHAM, .Techno, .DOC, .CHAK, .FREEMAN, .TRUE, .TECHNO and other extensions, and informs the victim of the payment method by email to make them profit Easier and more convenient.
Top2: Crysis ransomware family
The Crysis family can be traced back to March 2016, and since 2017, it has launched continuous attacks on Windows servers. The attack mode of the Crysis ransomware family is mainly for hackers to manually spread and execute the ransomware after remote login through blasting.
Crysis ransomware disappeared for a while after the master key was announced in May 2017, but new variants were still relatively active in the first half of 2018. There are also many variants of the Crysis family. The more popular encrypted suffixes are mostly .arena, .arrow, etc., and the additional suffixes will also contain the victim id and the email address of the blackmailer, such as 1.txt.id-EE5106A8.[ decrypthelp@qq.com].arrow. The ransom amount needs to be known by the victim by contacting the hacker himself.
Top3: GandCrab ransomware family
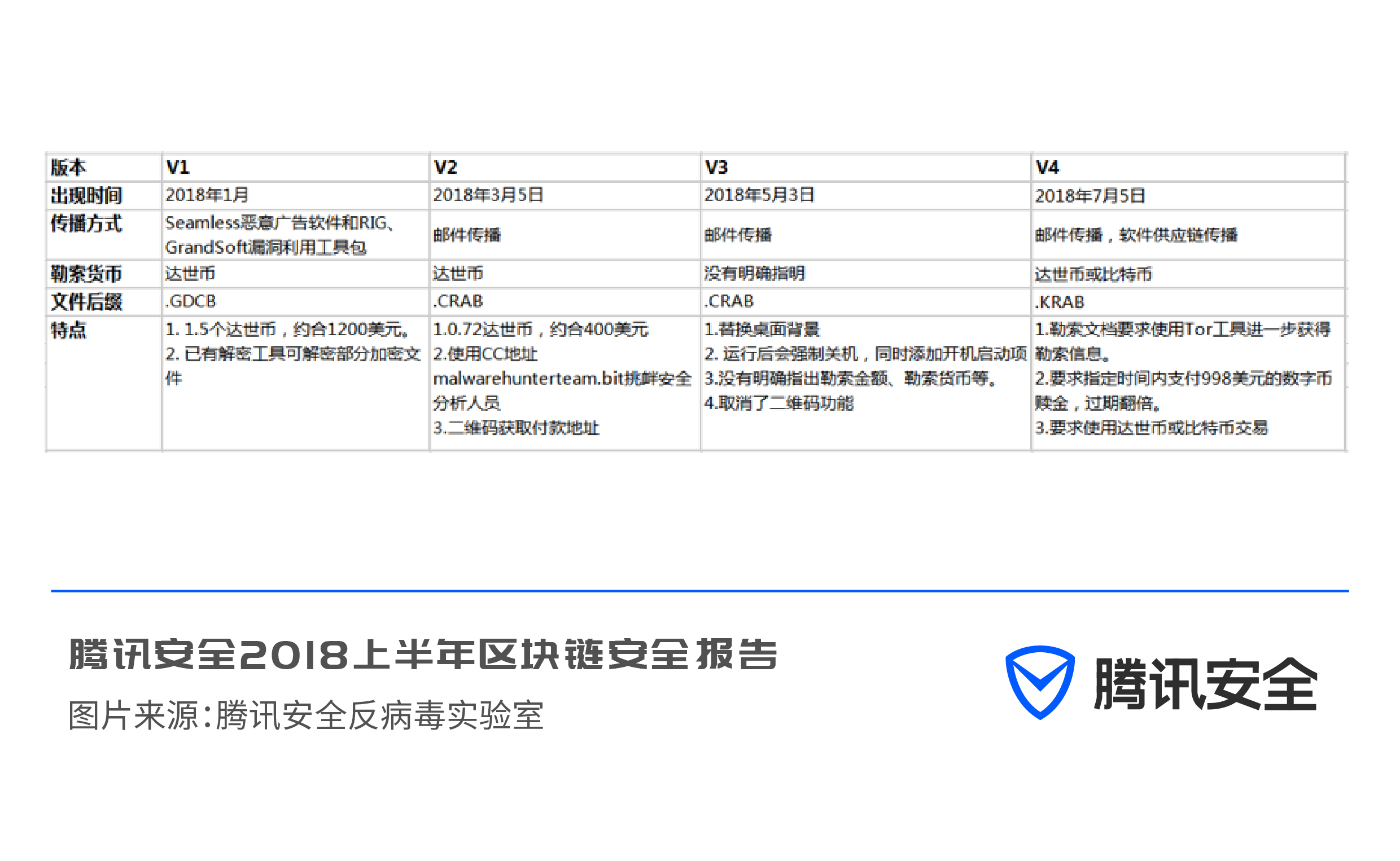
The GandCrab ransomware family can be called the "new star" in the ransomware world in 2018. Since Tencent Yujian Threat Intelligence Center captured the first ransomware GrandCrab targeting Dash in January, in just a few months, GrandCrab has gone through four Major version changes.
The first version of the GandCrab ransomware hit the headlines of major technology media because the C&C was controlled by an overseas security company and the police. Two months later, the GandCrab V2 ransomware appeared. The ransomware author took revenge on the security company and the police to control it The V1 version of the C&C server directly uses the characters related to the security company and the police as its V2 version of the C&C server in the V2 version, so it once again appeared on the technology news page.
Two months later, the GandCrab V3 version combined the code hiding technology of the V1 version and the V2 version, making it even more covert. The GandCrab V3 ransomware uses the CVE-2017-8570 vulnerability to spread. When the vulnerability is triggered, it will release a decoy document containing the words "안녕하세요" ("Hello" in Korean). Compared with previous versions of this family of ransomware, this version does not directly specify the ransom amount, but requires users to use the Tor network or Jabber instant messaging software to contact the extortionist.
GandCrab V4 is the latest iterative version of this family of viruses. Compared with previous versions, the file encryption suffix of the V4 version has been further changed (.KRAB), and the transmission channel has also been further expanded. The virus is hijacked through the software supply chain. The cracked software packs virus files, and further spreads to the victim's machine to carry out ransom attacks.
In addition, on April 3rd, it was discovered that the "Satan" ransomware virus made a comeback with the "Eternal Blue" vulnerability, and variants continued to appear, posing a great threat to corporate users. The virus will encrypt the database files, backup files and compressed files of the poisoned computer, and then extort 0.3 bitcoins from the company in Chinese, English and Korean. It will also use multiple new vulnerabilities to attack, including JBoss deserialization vulnerability (CVE-2017-12149), JBoss default configuration vulnerability (CVE-2010-0738), Tomcat vulnerability (CVE-2017-12615), Tomcat web management background weak Password blasting, Weblogic WLS component vulnerability (CVE-2017-10271), etc.
1.2 The Spread Trend of Ransomware in the Second Half of the Year
(1) The confrontation between ransomware and security software has intensified
As security software's solutions to ransomware mature and improve, it becomes more difficult for ransomware to successfully invade users' computers, and virus spreaders will continue to upgrade their countermeasures.
(2) Diversification of ransomware transmission scenarios
The traditional spread of ransomware is mainly based on phishing emails, and ransomware uses more high-risk vulnerabilities (such as EternalBlue), harpoon game attacks, or watering hole attacks to spread, which greatly improves the success rate of intrusion. Taking GandCrab as an example, this family of ransomware spreads using four methods: phishing emails, watering hole attacks, web page trojans, and exploits.
(3) The target of ransomware attacks has shifted to corporate users
Most personal computers can use security software to complete vulnerability patching. When encountering ransomware attacks, individual users often give up data and restore the system. And enterprise users will tend to pay ransom to restore data if there is no timely backup. Therefore, it has been found that more and more attack targets are government agencies, enterprises, hospitals, schools.
(4) The ransomware update iteration speeds up
Take GandCrab as an example. After the backend of the first generation was hacked by a security company, GandCrab2 was released within a week, and it has now been upgraded to version 3.0. Vulnerabilities in the early releases of the virus allowed security companies to decrypt encrypted files, but later versions cannot be decrypted.
(5) Increased ransom
With the improvement of user security awareness and the improvement of security software defense capabilities, the cost of ransomware virus invasion is getting higher and higher, and the ransom may also increase accordingly. In the first half of the year, after a company was invaded by a ransomware virus, it was blackmailed for 9.5 bitcoins. Now the attack target of the ransomware is more clear, perhaps the next extortionist will take advantage of the fire and increase the ransom.
(6) Ransomware encryption object upgrade
Traditional ransomware encryption targets are basically files and documents. Now more and more ransomware attempts to encrypt database files, disk backup files, and even disk boot sectors. Once encrypted, users will not be able to access the system, which is more harmful than encryption, and may force users to pay ransom.
(7) Formation of a black industry chain of ransomware
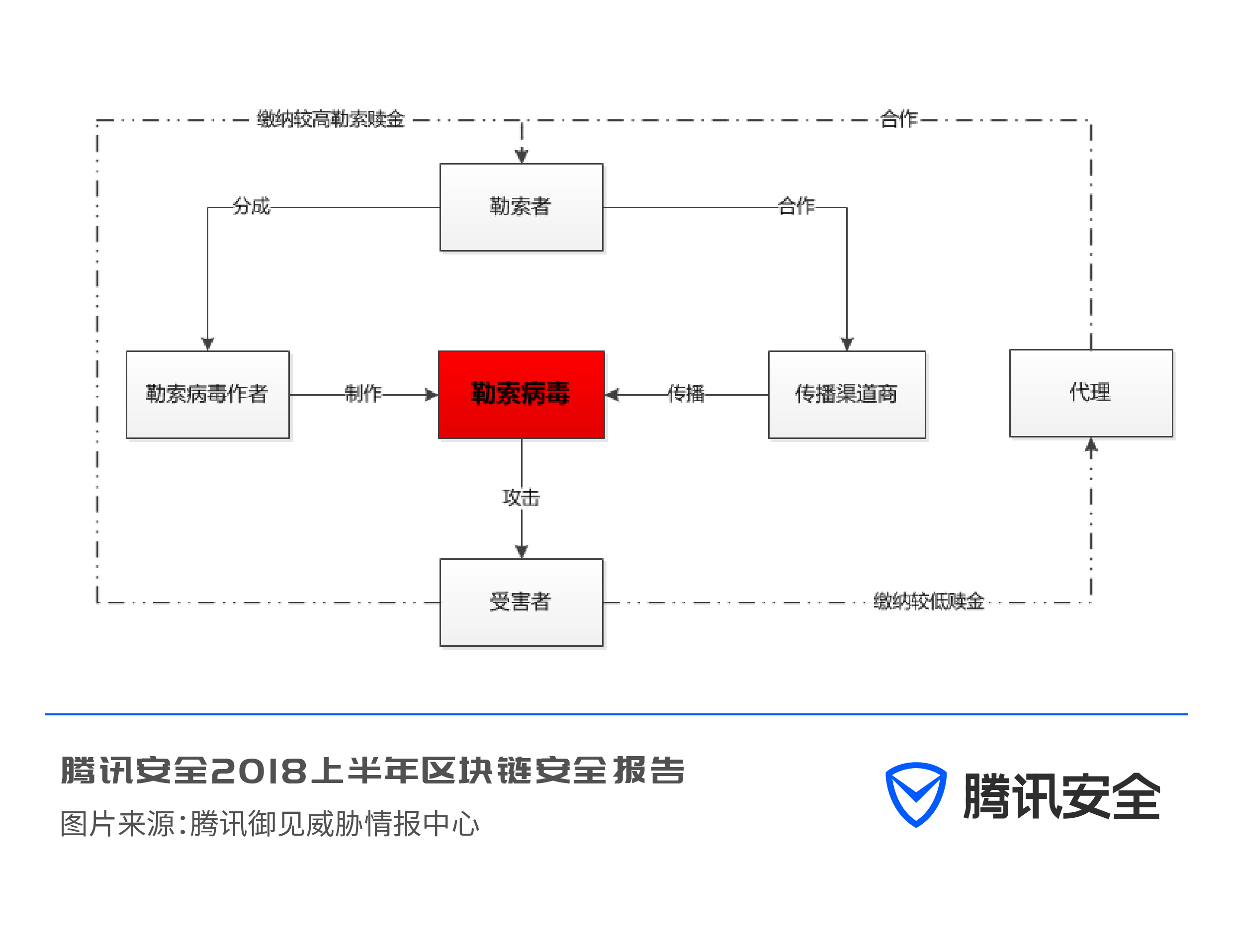
With the continuous emergence of ransomware, Tencent Yujian Threat Intelligence Center even observed the birth of a special industry: the ransomware agency business. When an enterprise is attacked by a ransomware virus, key business data is encrypted, but theoretically it cannot be decrypted at all, and the ransomware agency undertakes the business of negotiating transactions between the victim and the attacker to restore the data.
2. Mining Trojan horses "emerge suddenly", and the value of the currency circle is "weather vane"
The mining virus has developed into the most widely spread network virus in 2018, and the popularity of mining is often directly proportional to the currency price. Since the controller of the mining virus can directly sell the mined digital virtual currency for profit, the influence of the mining virus is unprecedentedly high, and it has completely replaced the account hacking Trojan for gamers, the transaction hijacking Trojan for online shoppers, and even It is a remote control Trojan used to spy on the victim's home camera.
When the victim’s computer is running a mining virus, the CPU and GPU resource usage of the computer will increase, and the computer will become slow. increase, and the computer runs slower. Mining occurs every year, but since 2018, PC-side mining Trojan horses have grown at an unprecedented rate. In the first half of the year alone, there were 45 mining Trojan horse incidents, more than the number of mining Trojan horse incidents that broke out in 2017. .
2.1 Analysis and propagation characteristics of mining Trojan horse samples in the first half of the year
Tencent Yujian Threat Intelligence Center classified hundreds of thousands of mining virus samples, and summarized the port numbers, process names, and mining pool addresses used by mining Trojans.
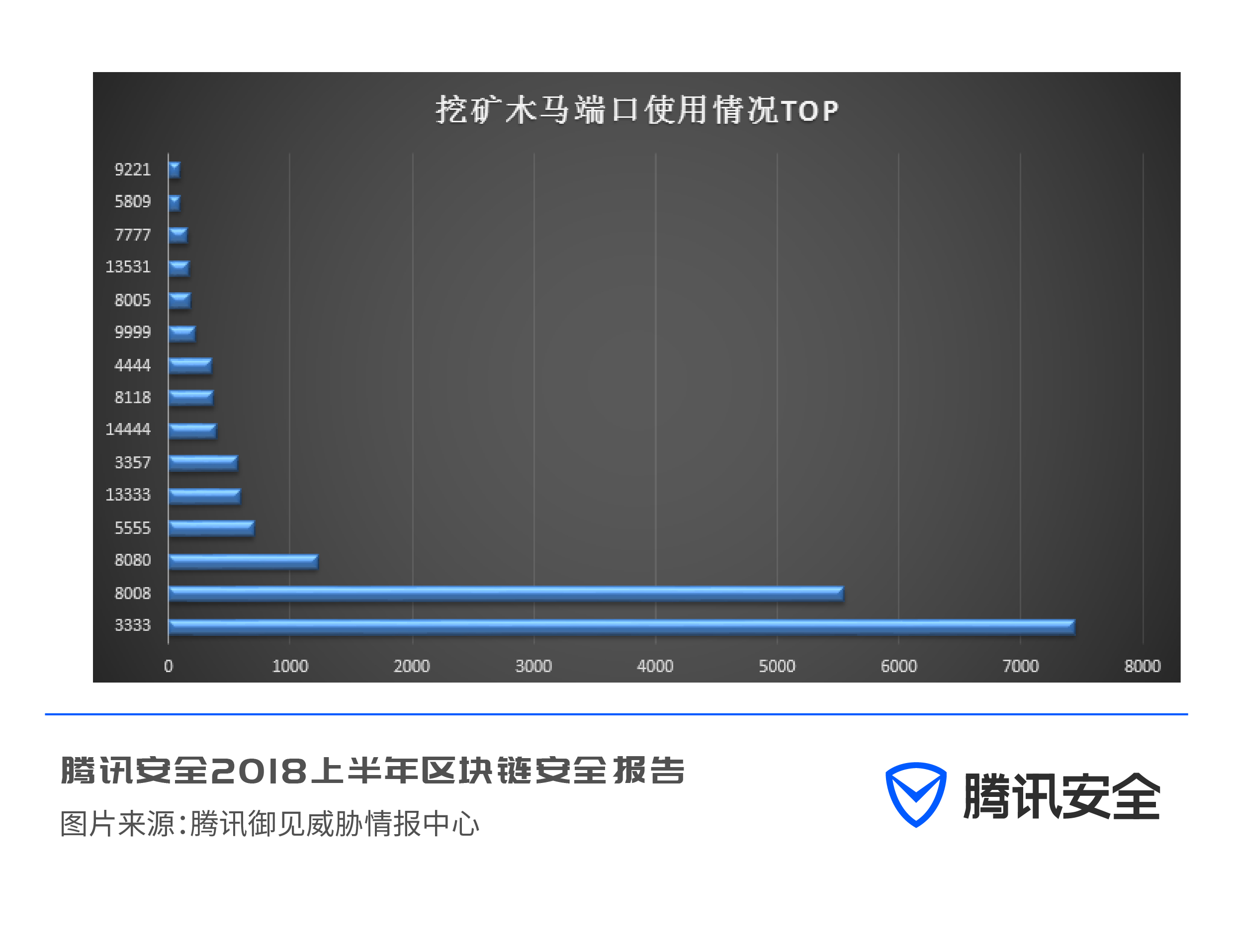
The port number most preferred by mining trojans is 3333, followed by ports 8008, 8080, and 5555.
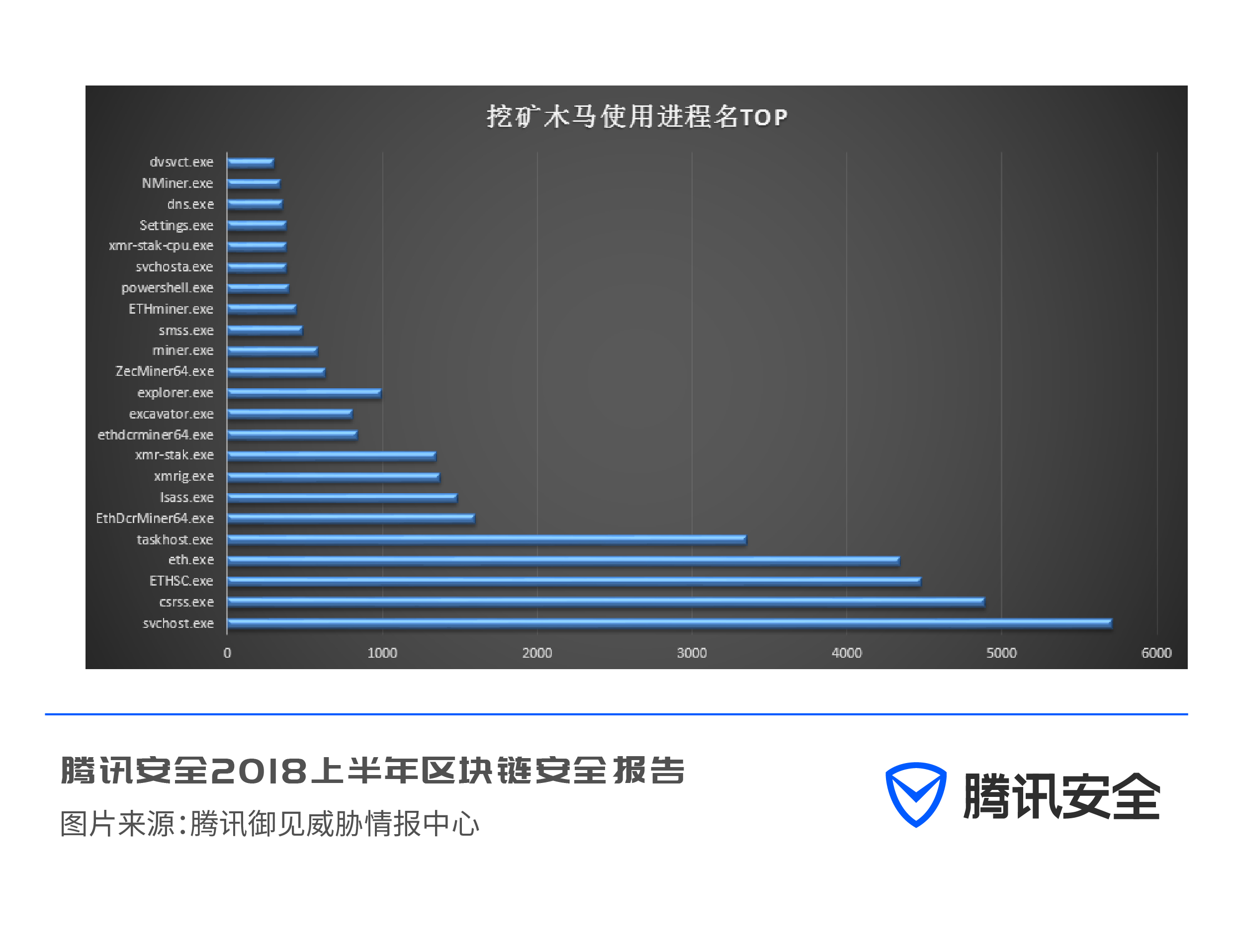
The Trojan horse’s favorite borrowed process names are svchost.exe and csrss.exe. These two names originally belonged to the Windows system process, but are now used by the mining Trojan horse to confuse users.
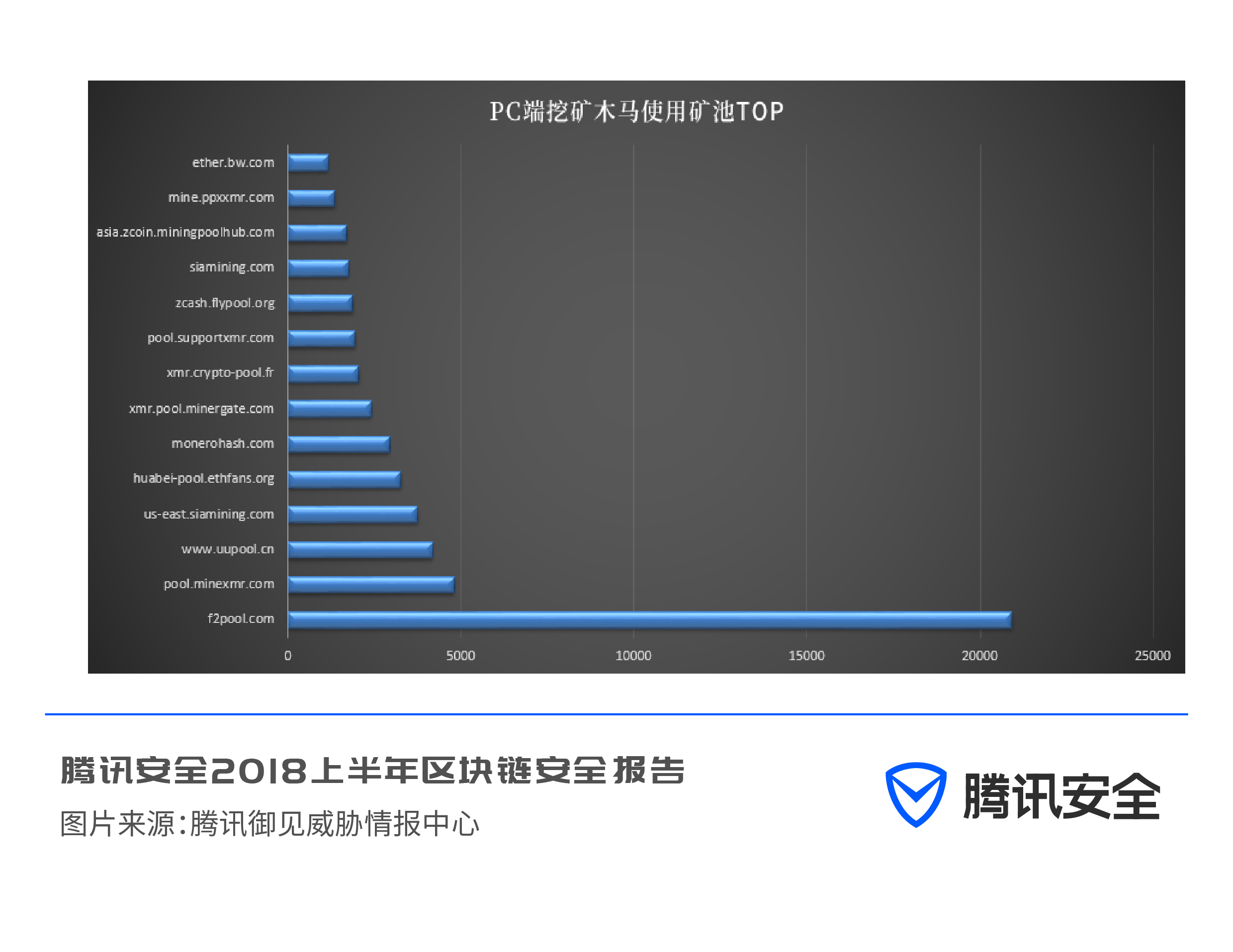
The mining pool is an open and fully automatic mining platform. At present, the mining trojan mainly connects to the mining pool for mining. The miners connect their mining machines to the mining pool, contribute their computing power to mine together, and share the benefits. In the first half of the year, f2pool was the most widely used mining pool for PC-side botnet mining.
Compared with the previous mining Trojans, in the first half of 2018, mining Trojans showed new spreading characteristics:
(1) Aiming at high-end gaming machines, high-efficiency mining
Auxiliary cheating is one of the favorite hiding software for mining Trojans in the first half of 2018. Since game users have high requirements for computer performance, criminals aiming at game player computers is equivalent to finding a mining machine with "excellent" performance.
In January 2018, Tencent Computer Manager revealed that the tlMiner mining Trojan was hidden in the auxiliary program of "PUBG Mobile" and spread, affecting up to 200,000 machines in a single day. Then in March, he cooperated with the security team of Tencent Guardian Project to assist the Shandong police to quickly crack down on the Trojan horse author, and in early April, he knocked down the black company at the top of the chain. According to statistics, the gang has mined more than 20 million digital cryptocurrencies such as DGB (Great Bitcoin), HSR (Braised Meat Coin), XMR (Monero Coin), SHR (Super Cash), BCD (Bitcoin Diamond) and so on. , Illegally made more than ten million yuan.
In February 2018, Tencent Computer Manager found a Monero mining Trojan hidden in hundreds of "Wild Action" auxiliary secondary packaging programs, and spread through social groups, online disks and other channels in the middle and late February. There is a clear upward trend.
In May 2018, Tencent Yujian Threat Intelligence Center sensed that a mining trojan named "520Miner" spread through game plug-ins, controlled thousands of machines to mine mines for several days, and finally harvested 67 VIT coins. Worth less than a dime of RMB, it can be said to be the most troublesome mining Trojan in history.
(2) Use web pages to hang horses and spread them on a large scale
The dissemination channels of mining Trojans are not limited to disguising themselves as computer software downloads, but the most efficient method of dissemination, which is the most efficient way of disseminating Trojans on web pages.
On April 12, 2018, Tencent Yujian Threat Intelligence Center detected a large-scale domestic webpage hanging incident. On that day, more than 50 types of computer software with tens of millions of users, including a variety of well-known player software, video website clients, and common tool software, encountered a large-scale web page Trojan attack.
The attacker actively distributes the attack code through the system of an advertising alliance, and this poisonous page is embedded in more than 50 commonly used software with tens of millions of users. These users' computers will automatically connect to the Internet to download Advertising resources, the computer will download several viruses, including mining viruses. Tencent Computer Manager intercepted more than 200,000 virus downloads that day.
In addition, Tencent Yujian Threat Intelligence Center also detected an abnormally high infection rate of a mining virus. After virus traceability analysis, it was found that the mining Trojans on the victim's computer came from certain pornographic websites under the banner of "body art".
When netizens browse these websites, due to high-risk Flash security vulnerabilities in some systems, they will be poisoned immediately after opening the webpage. After that, the victim's computer will run the mining code, and the computer becomes a miner. Attackers will control a large number of miners' computers to concentrate their computing power on mining, and use this to make profits.
(3) Invasion and control of corporate servers to form a botnet for mining on the cloud
With the increasing difficulty of mining various digital cryptocurrencies, it is difficult to maximize the benefits through the personal computers of ordinary users. To carry out large-scale mining in a short period of time, in addition to hanging horses on the webpage, the most common method is to control bot computers to form botnet mining. The strong server performance and 24-hour online feature attract more unscrupulous miners to turn their attack targets to the servers of enterprises, government agencies, and public institutions to realize cloud mining.
Tencent Yujian Threat Intelligence Center once discovered a "PhotoMiner Trojan" with an astonishing number of infections, which expanded its spread by invading and infecting FTP servers and SMB servers for brute force cracking. Query the address of the Monero wallet controlled by the Trojan horse, and found that the Trojan horse controlled the broiler computer to mine 80,000 Monero coins, and the cumulative mining income reached an astonishing 89 million yuan. He is a veritable "gold miner".
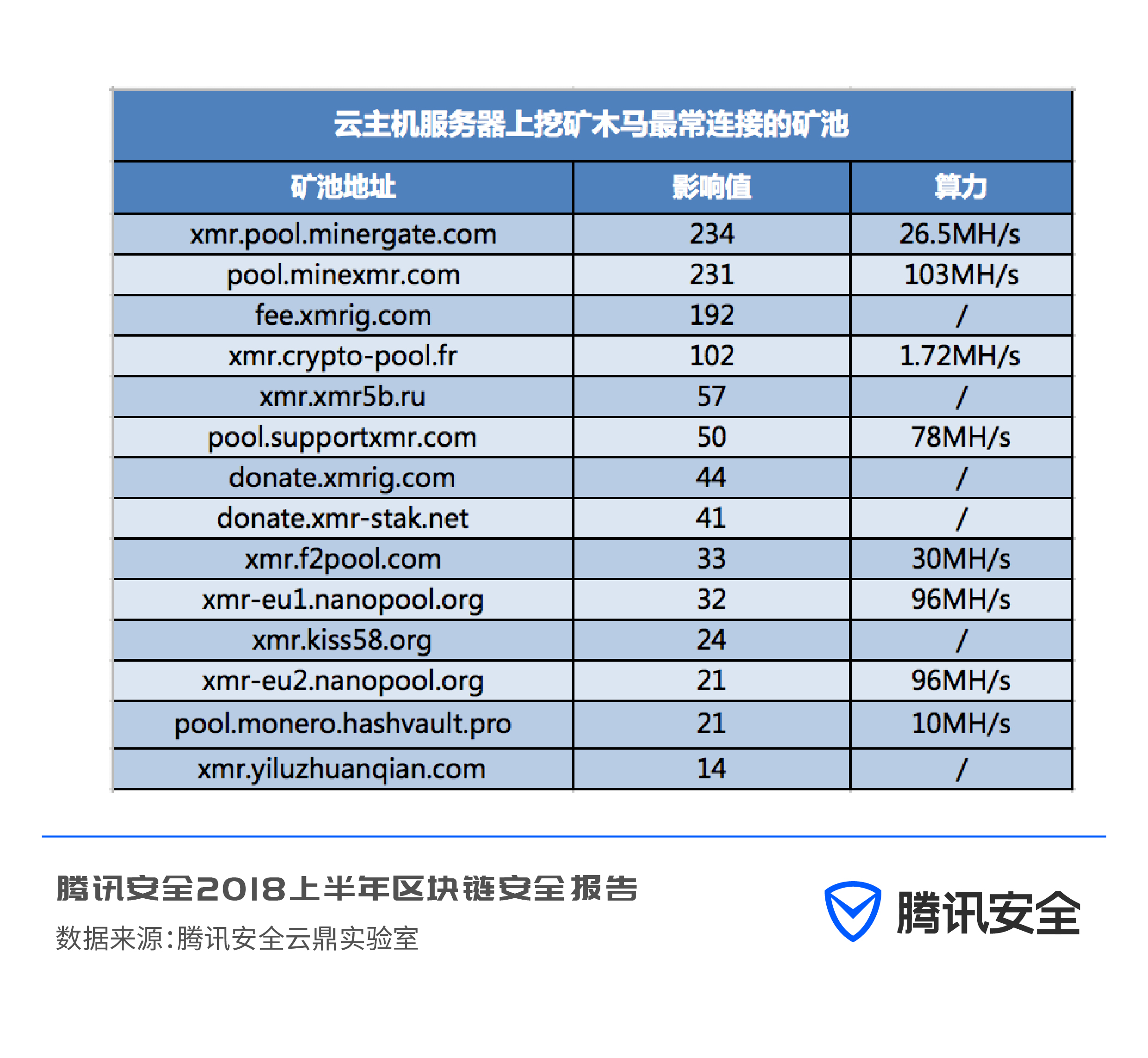
Through statistics and classification of mining pool addresses requested by DNS, Tencent Security Yunding Lab found that the main currencies for mining on the cloud are XMR (Monero), Ethereum (ETH) and ETN (Elito). Statistics were made on the addresses of the mining pools most commonly connected by mining Trojan horses on cloud host servers, and it was found that xmr.pool.minergate.com was used most frequently.
Some of the mining trojans that are popular in China use self-built mining pools for mining. This is mainly due to the use of third-party mining pools. Ways to reduce these unnecessary expenses.
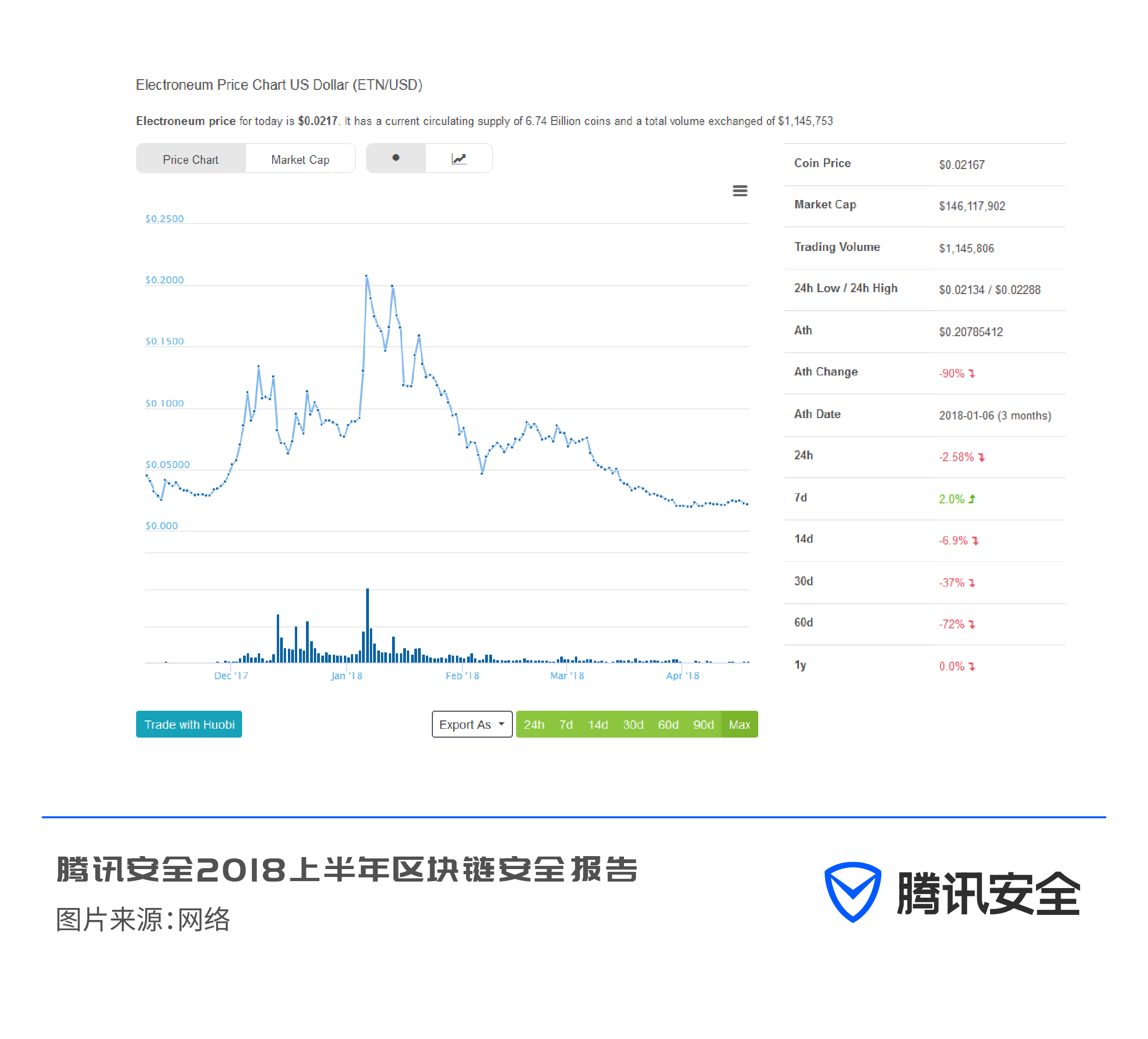
Through the correlation analysis of the price trend of the digital currency and the mining heat, it is found that the mining heat is directly proportional to the price of the currency. This also proves once again that the goal of online black production is to maximize profits. Observing the price trend of ETN (Elito), we can find that it has been in a downward trend since mid-January:
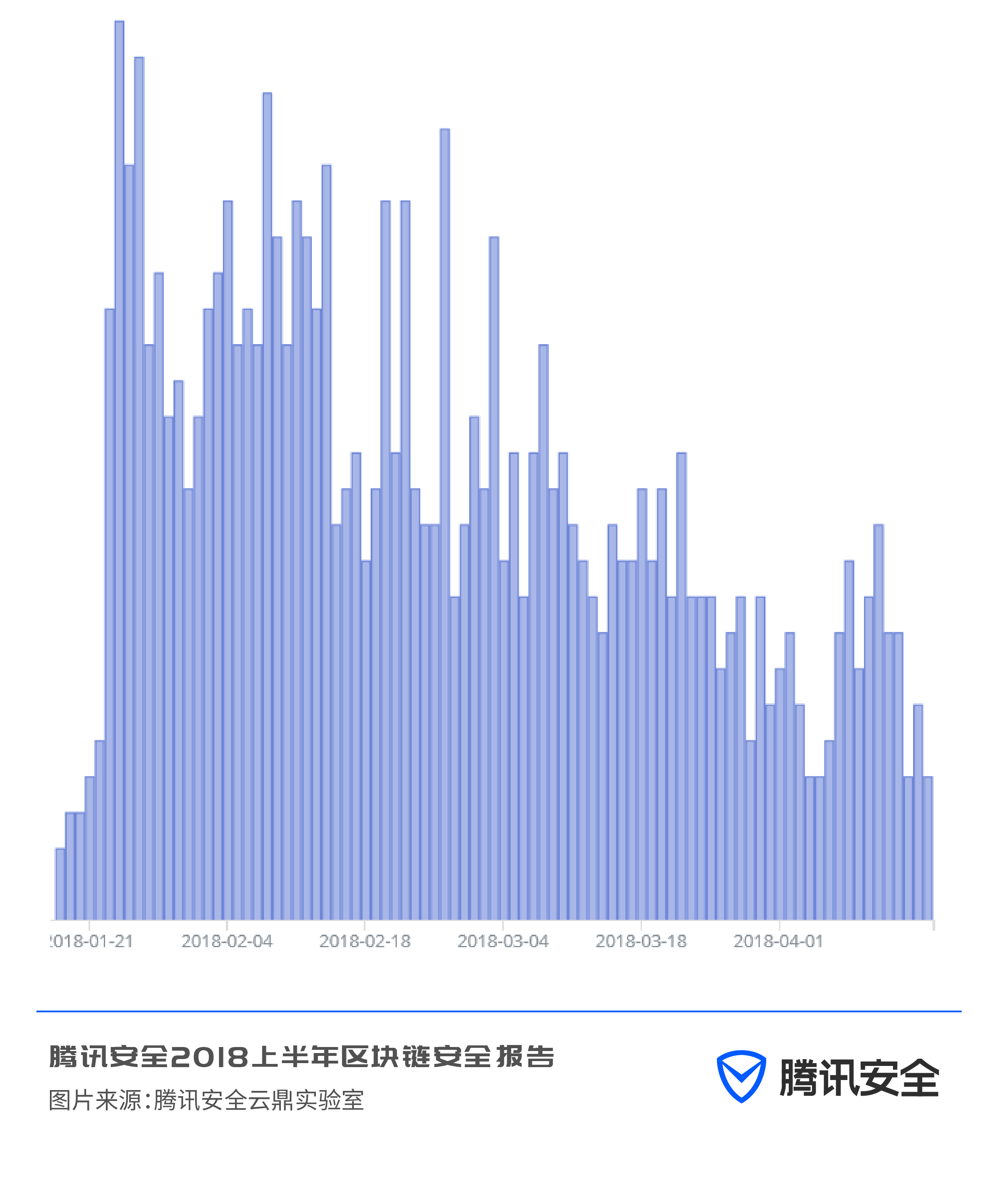
And observing the access to its corresponding mining pool, it is found that it is also a downward trend:
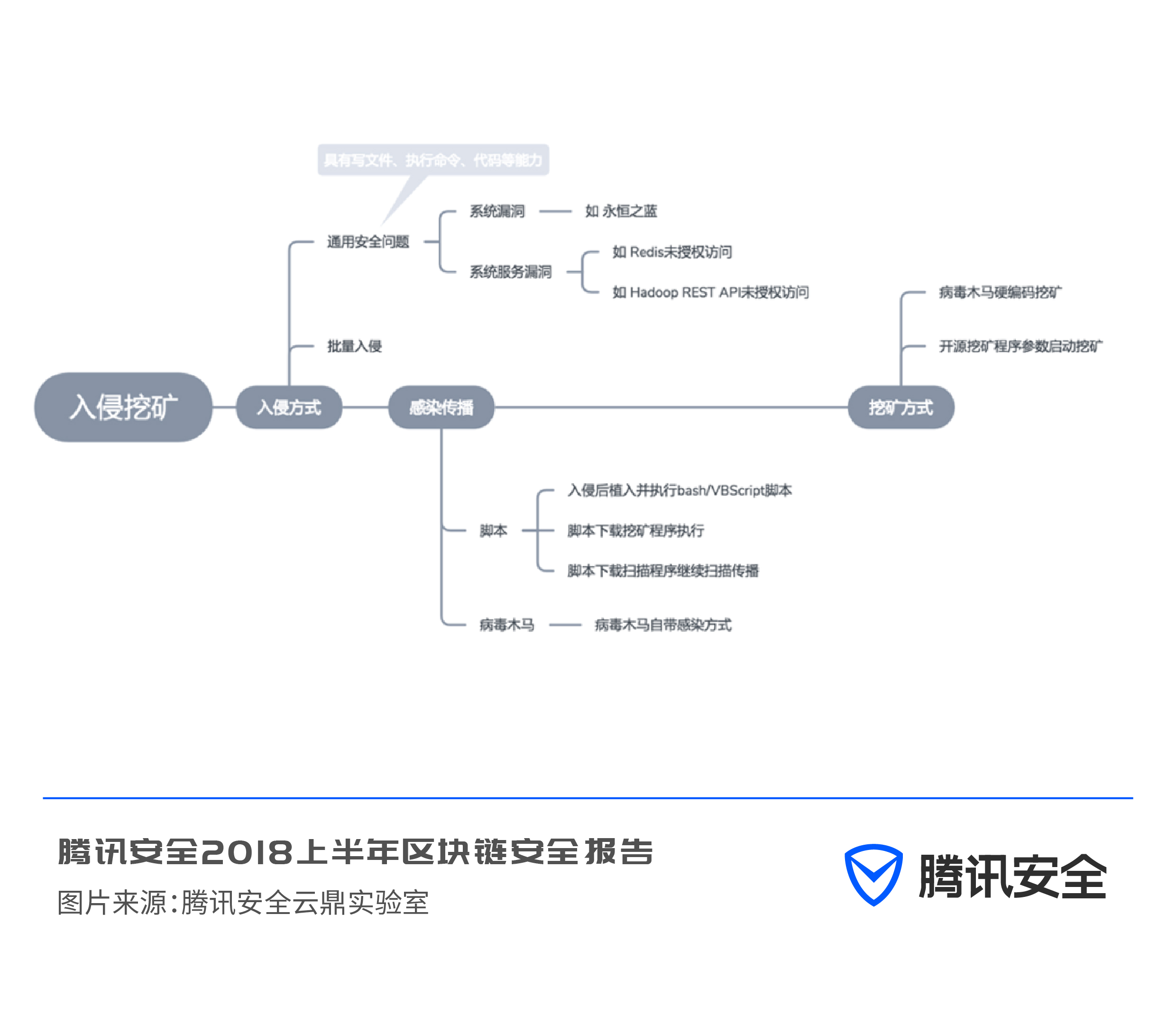
Through the analysis of historical capture mining cases, mining on the cloud is usually a method of batch intrusion, and due to its characteristics of batch intrusion, it can only use general security issues, such as system vulnerabilities and service vulnerabilities, and the last The common ones are Eternal Blue, Redis unauthorized access problems, and Apache Struts 2 vulnerabilities that lead to mass invasion of corporate web servers.
Attackers are also good at using mining Trojan generators, weak password attack dictionaries and other attack tools to invade servers, and then spread mining Trojans in large quantities.
(4) Webpage mining: insert mining codes in normal URLs
Due to the existence of anti-virus software, many mining Trojan horse files may be blocked as soon as they land on the user's computer, which is not conducive to expanding the scale of mining. More attackers tend to implement web mining: by invading websites with security vulnerabilities, planting Enter the mining code. As long as the visitor's computer visits this webpage with a browser, it will become a miner.
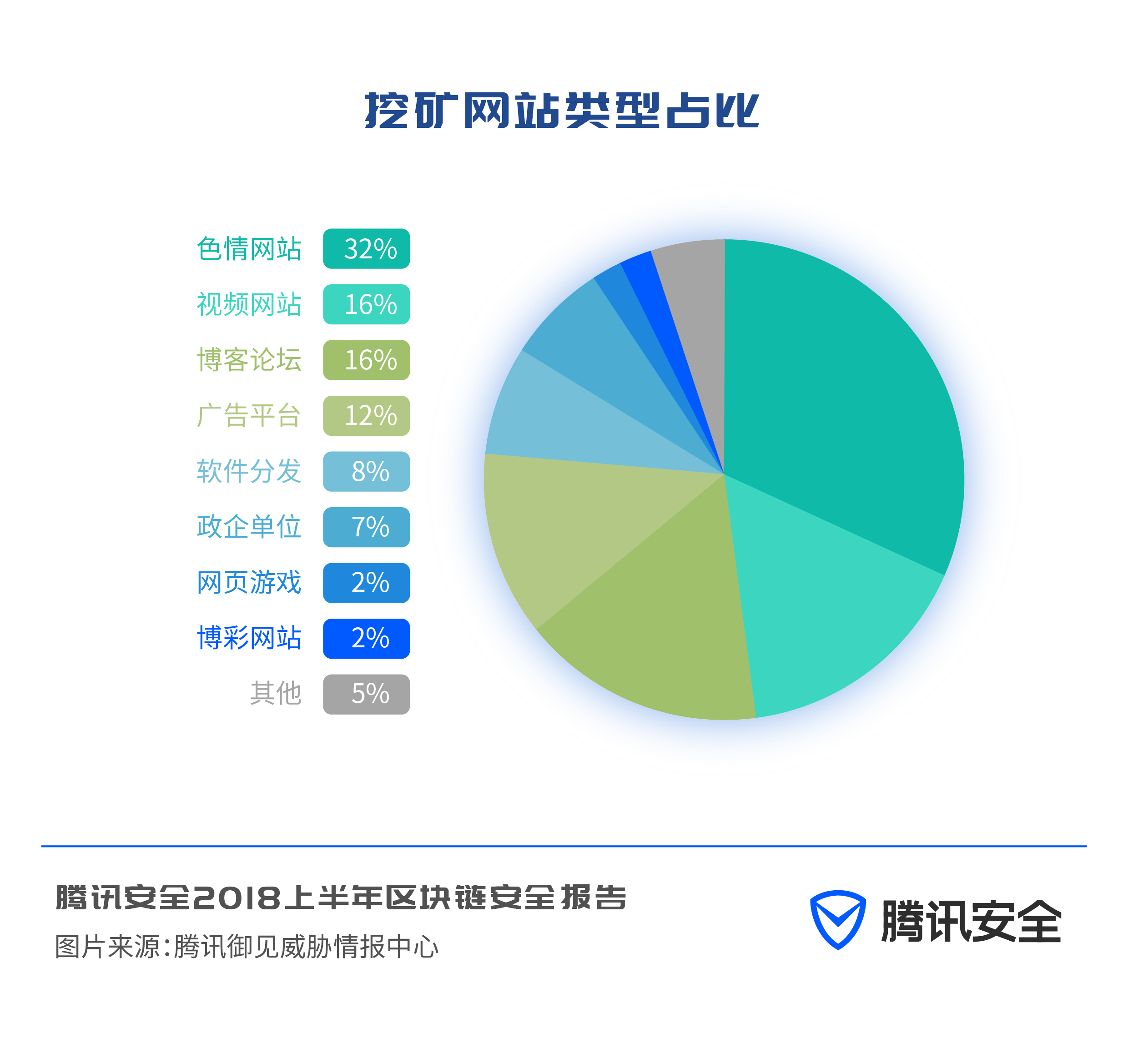
Among the types of websites that are mined, pornographic websites account for the highest proportion, followed by video websites, blogs, and forums. Users watch videos and read articles on such websites and stay for a long time. Hackers use these websites for mining to obtain higher profits.
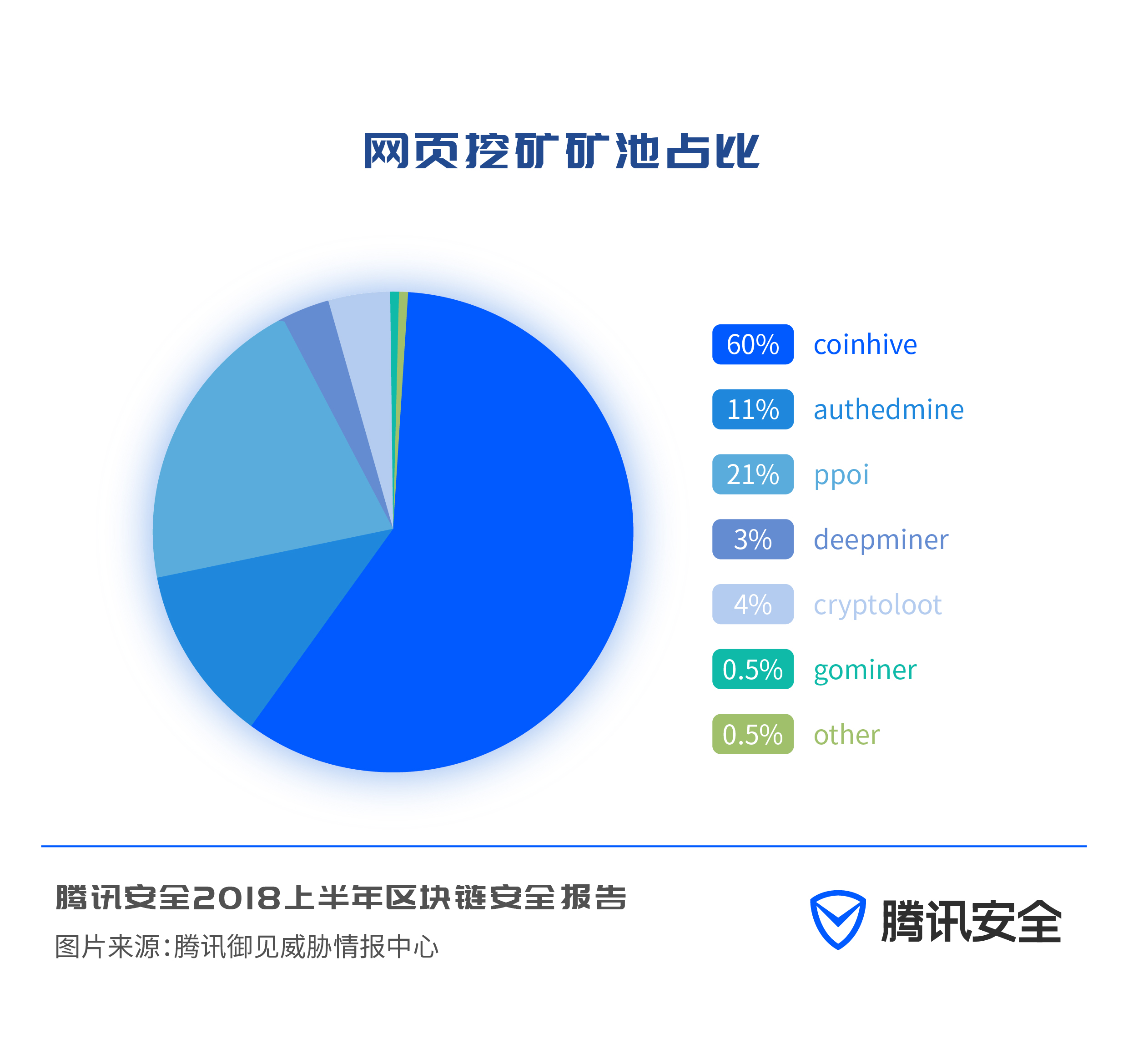
In terms of mining pools, the coinhive mining pool that appeared first occupies the largest proportion of web mining, and the authemine mining pool on the same platform as coinhive accounts for 11%; the ppoi mining pool and cryptoloot mining pool based on coinhive account for 21% and 4% respectively .
2.2 The spread trend of mining Trojans in the second half of the year
Digital cryptocurrencies continued to plummet in the first half of 2018. Bitcoin has fallen from $20,000 at the end of last year to less than $7,000 now. The "coin speculation" fever seems to be cooling down, but this has not affected the progress of mining Trojans. After all, mining Trojan horses rely on broiler mining to make money, and there is no need to invest in physical equipment. However, from the recent incidents of mining Trojan horses, it has been found that mining Trojan horses can choose more and more currencies, and the design is becoming more and more complicated. It is also getting deeper and deeper, mining will continue to be active in the second half of the year, and the confrontation with anti-virus software will intensify.
(1) Almighty mining Trojan horses are produced, bringing multiple hazards at the same time
The name of a PC virus usually includes information such as the source of the virus, its transmission path, and its purpose. For example, "Trojan.StartPage" means that this is a type of homepage locking Trojan horse, and "Backdoor.GrayBird" belongs to the gray pigeon backdoor virus. Under the attack, the "habitat" of virus Trojan horses is getting less and less, and expanding "business" has become the primary task of many virus Trojan horses, and mining Trojan horses are no exception.
The "Arkei Stealer" Trojan horse that appeared in the first half of the year integrates secret stealing, remote control, DDoS, mining, and coin theft, and can be described as an "omnipotent" trojan horse. In the second half of the year, mining Trojans may integrate more "businesses" and invade user machines through various channels.
(2) The hidden technology is stronger, and the confrontation with security software is becoming more intense
Since the development of viruses, the most powerful hidden technology on PCs is undoubtedly the B/Rootkit virus. This type of Trojan horse is complicated to write, and each module is designed with precision. It can directly infect the disk boot area or the system kernel. A type of virus that is difficult to remove.
Such viruses are often used to lock homepages and extort money. Recently, it was found that R/Bookit technology was also used in mining Trojan horses, which improved the hidden skills of mining Trojan horses to several levels. In the second half of the year, the security situation of digital cryptocurrency is still severe, and the hidden confrontation of mining Trojan horses may become more intense.
3. Digital robbers "take risks" to attack the exchange, making a half-year profit of about 700 million U.S. dollars
In addition to the losses caused by ransomware, theft can also cause a lot of losses to holders of digital cryptocurrencies. From the early days of digital cryptocurrencies, there have been endless news about digital cryptocurrencies being stolen. At present, there are roughly four ways to steal digital cryptocurrencies: hacking into exchanges, hacking into individual users, "double spend attacks", and vulnerability attacks.
3.1 Digital cryptocurrency trading platform was attacked
Cryptocurrency exchanges were attacked and lost about $700 million in the first half of 2018 alone.
(1) In January 2018, Coincheck, the largest digital cryptocurrency exchange in Japan, was stolen from NEM (new economic currency) worth 534 million US dollars;
(2) On March 7, 2018, the Binance transaction lock was invaded. This time, it was a big rule to obtain user accounts through phishing and try to steal coins;
(3) On April 13, 2018, CoinSecure, an Indian digital cryptocurrency exchange, was deprived of 438 bitcoins, suspected of being stolen by insiders;
(4) On June 10, 2018, Coinrail, a South Korean digital cryptocurrency exchange, was attacked and lost more than $50 million;
(5) On June 20, 2018, the South Korean digital cryptocurrency exchange Bithumb was hacked, and digital cryptocurrency worth 30 million US dollars was stolen. This is the third time Bithumb has been hacked.
3.2 Personal account hacked
(1) Steal wallet files by implanting virus Trojans
In February 2018, Tencent Computer Manager discovered a large number of attack samples that exploited the vulnerability of the Office formula editor component (CVE-2017-11882), and stole sensitive information such as user bitcoin wallet files by downloading and running the Pony Trojan horse whose source code has been made public.
In March 2018, a money-stealing Trojan horse based on clipboard hijacking appeared in China. The Trojan horse was written in easy language and reached the user's machine through activation tools and download stations. The Trojan horse will monitor the user's clipboard. Once a wallet address is found , then replace it with the wallet address of the Trojan horse. There are more than 30 wallet addresses built into the Trojan horse, and some wallets have already been stolen.
In addition, the analysis of Tencent Yujian Threat Intelligence Center found that more and more viruses will try to hijack the wallet address of digital cryptocurrency transactions. Replace the address specified by the virus, and the virus behaves like a robber in reality. Similar viruses also appeared when computer online shopping was popularized. The virus transferred the victim's funds to the transaction account designated by itself at the moment the transaction was completed.
(2) Internal theft of cryptocurrency
In March 2018, an Internet attack employee in Beijing took advantage of his position to deploy malicious code on the company's server and stole 100 bitcoins from the company. He has been arrested according to law. This is the first case of bitcoin theft in Beijing.
3.3 "Double Spending Attack"
"Double-spend attack" is to attack the digital encrypted currency blockchain after controlling 51% of the computing power of a certain digital encrypted currency network, which can destroy the data that has been completed and re-pay, so that double service can be obtained .
In May 2018, the BTG (Bit Gold) trading chain was attacked by hackers. The hacker quickly withdrew coins after recharging to the exchange and destroyed the withdrawal records. A total of 388,000 BTGs were transferred away, making a profit of 120 million yuan.
3.4 Vulnerability Attack
In April 2018, a data overflow vulnerability was exposed in the BEC smart contract, and the attackers stole a total of 57.9 billion BEC coins, and then SMT coins were also exposed to similar vulnerabilities.
4. Security Recommendations
Blockchain technology is still a key research field for many Internet companies and even state-owned banking systems. The application of blockchain is not equivalent to digital virtual currency. Security experts do not encourage people to speculate in coins, so we will not repeat the behavior of speculating in coins here.
For blockchain security, from the perspective of system architecture, it is recommended that relevant companies cooperate with professional blockchain security research organizations to discover and repair system vulnerabilities in a timely manner to avoid serious large-scale fund theft incidents;
For netizens involved in digital virtual currency transactions, they should fully understand the possible risks, use security software on their computers and mobile phones, avoid falling into phishing traps, and avoid theft of digital virtual currency wallets;
For ordinary netizens, they should prevent computer poisoning from becoming a "miner" controlled by others, and use game plug-ins, cracking software, and video website client cracking tools with caution. The probability of these software being artificially implanted with malicious programs is high. At the same time, install regular anti-virus software and update it in time. When the computer freezes or the temperature is overheated, use Tencent Computer Manager to check to prevent the computer from being illegally controlled and causing unnecessary losses;